吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1112-1121.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210794
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
干湿循环与交变荷载作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀损伤
关博文1,2( ),邸文锦1,2,王发平3,吴佳育1,2,张硕文1,2,贾治勋3
),邸文锦1,2,王发平3,吴佳育1,2,张硕文1,2,贾治勋3
- 1.长安大学 材料科学与工程学院,西安 710061
2.长安大学 交通铺面材料教育部工程研究中心,西安 710061
3.青海省交通控股集团有限公司,西宁 810003
Damage of concrete subjected to sulfate corrosion under dry⁃wet cycles and alternating loads
Bo-wen GUAN1,2( ),Wen-jin DI1,2,Fa-ping WANG3,Jia-yu WU1,2,Shuo-wen ZHANG1,2,Zhi-xun JIA3
),Wen-jin DI1,2,Fa-ping WANG3,Jia-yu WU1,2,Shuo-wen ZHANG1,2,Zhi-xun JIA3
- 1.School of Materials Science and Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi′an 710061,China
2.Engineering Research Center of Transportation Pavement Materials,Ministry of Education,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710061,China
3.Qinghai Transportation Holding Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Xining 810003,China
摘要:
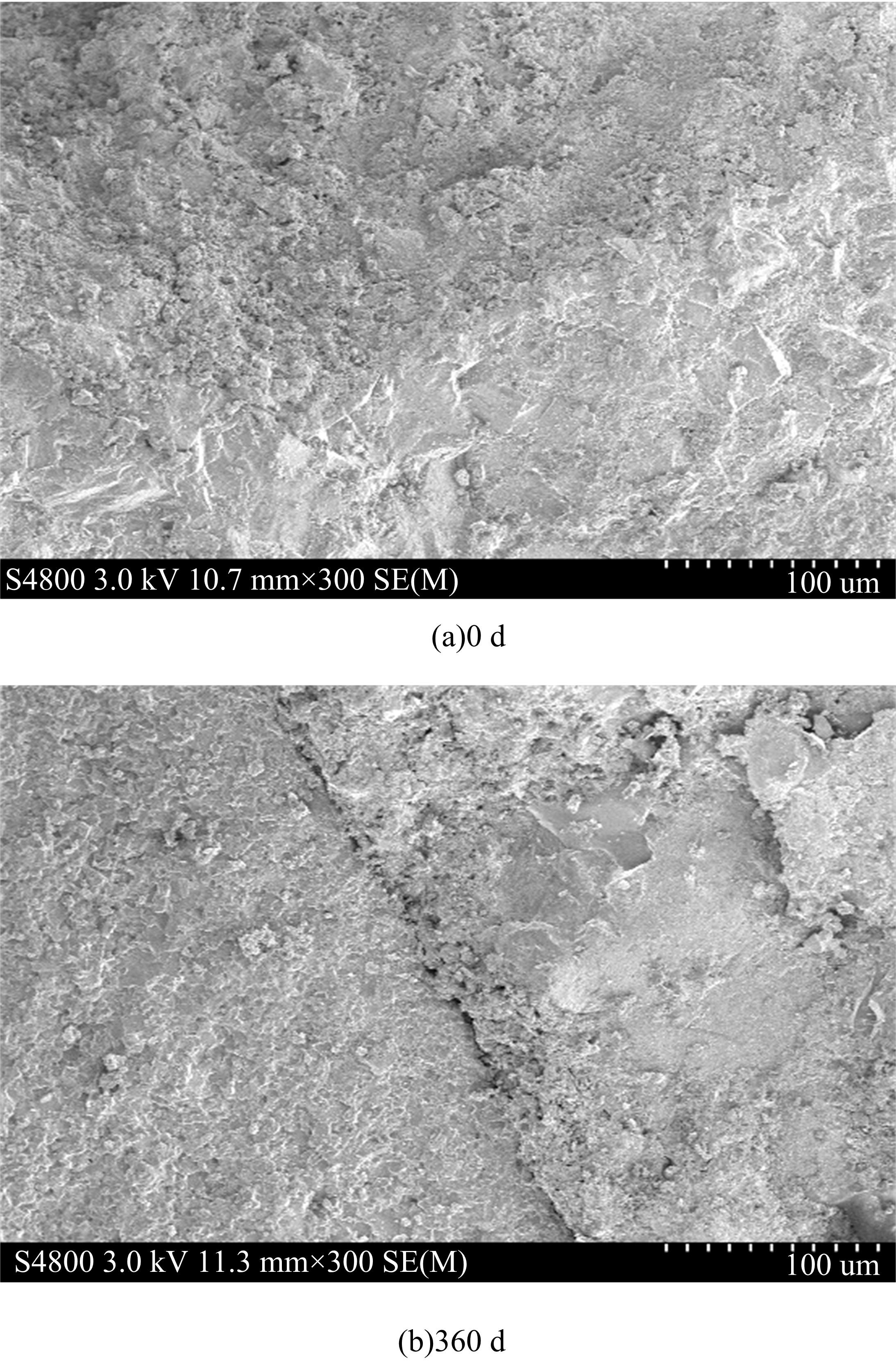
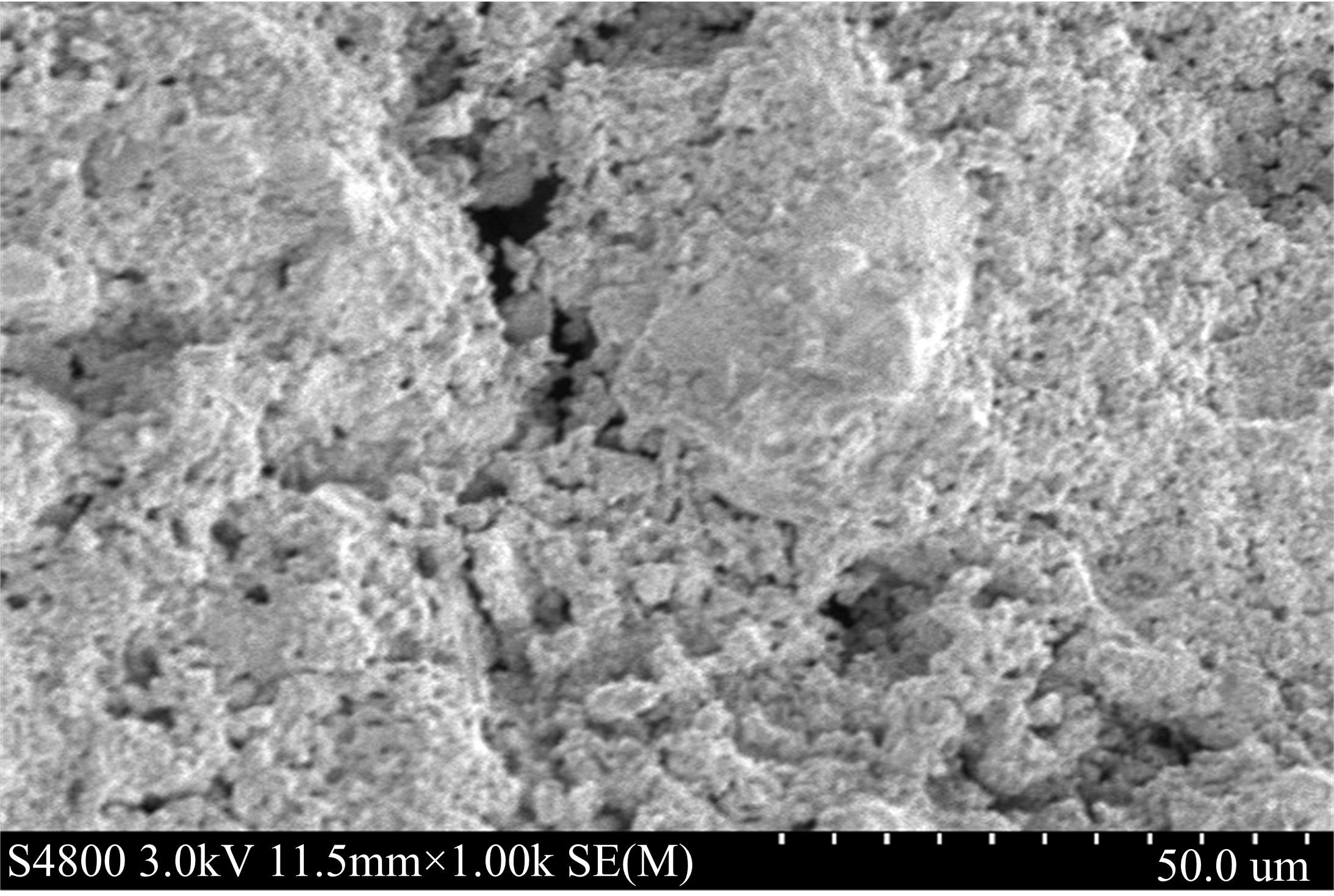
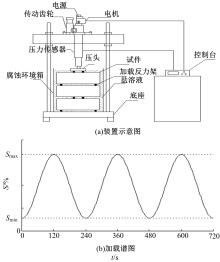
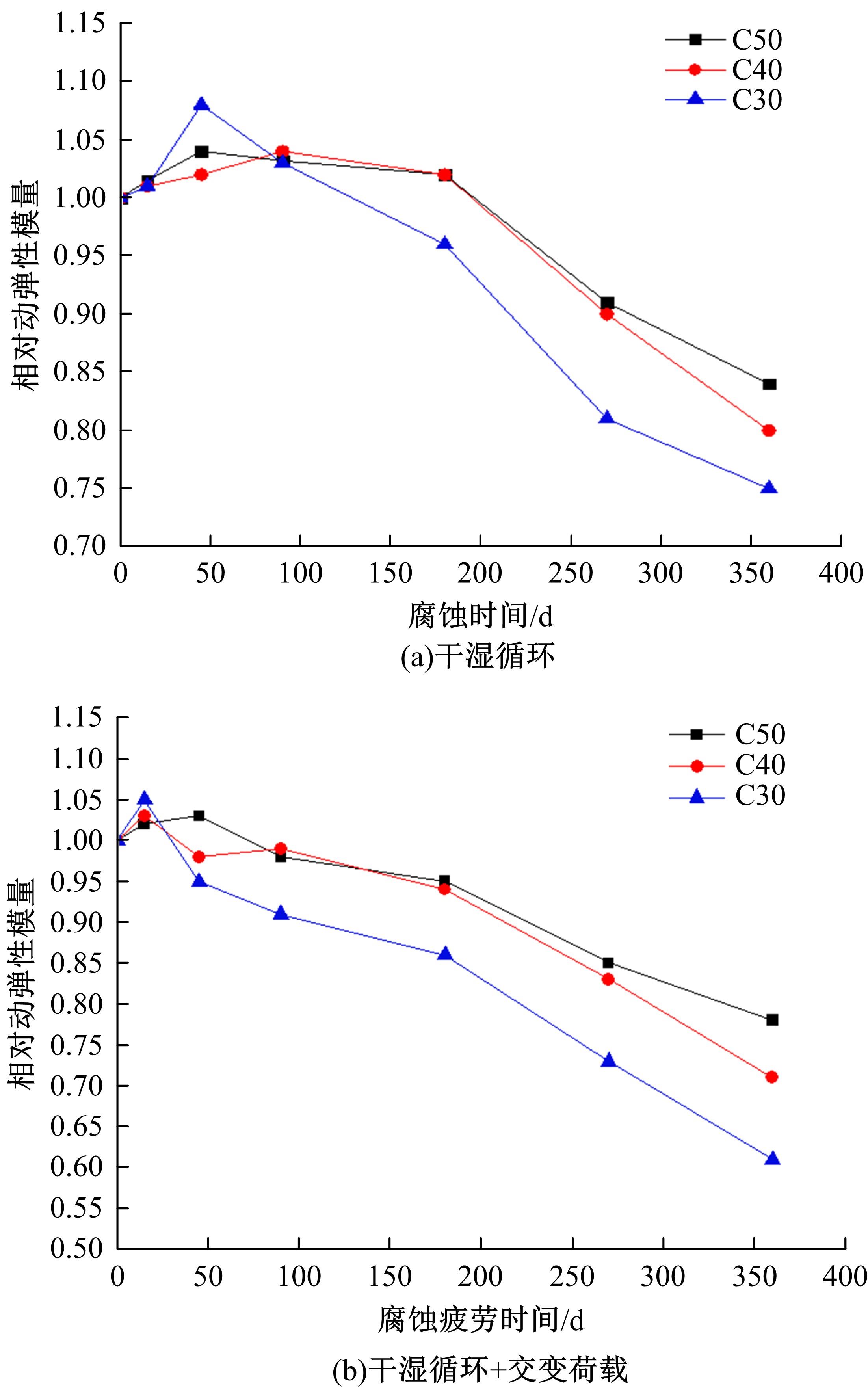
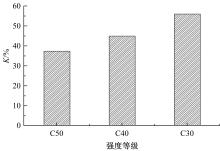
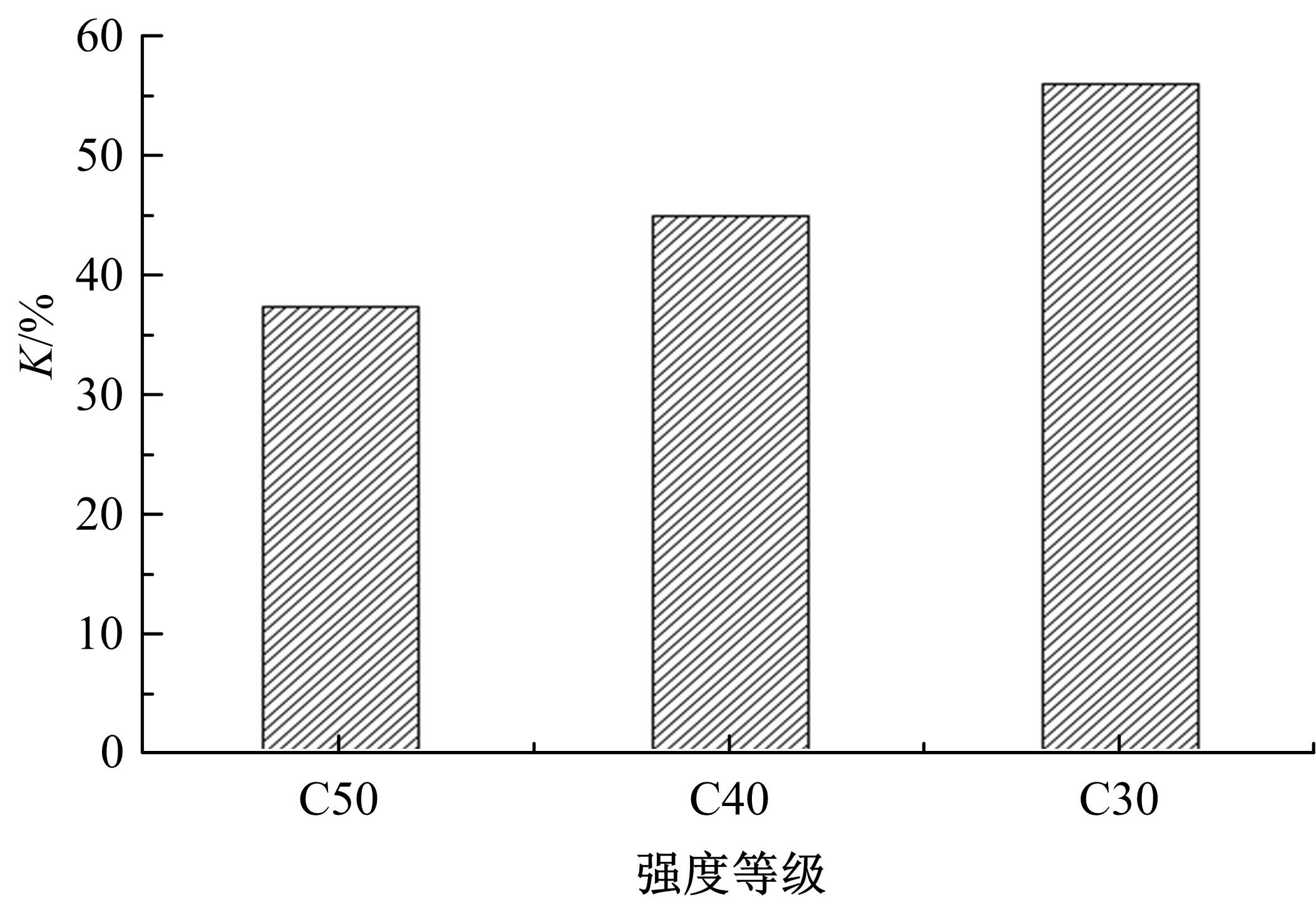
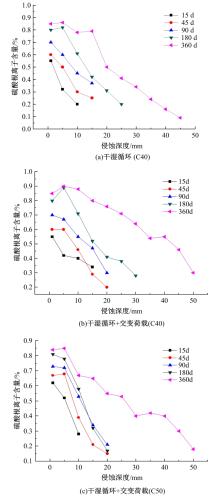
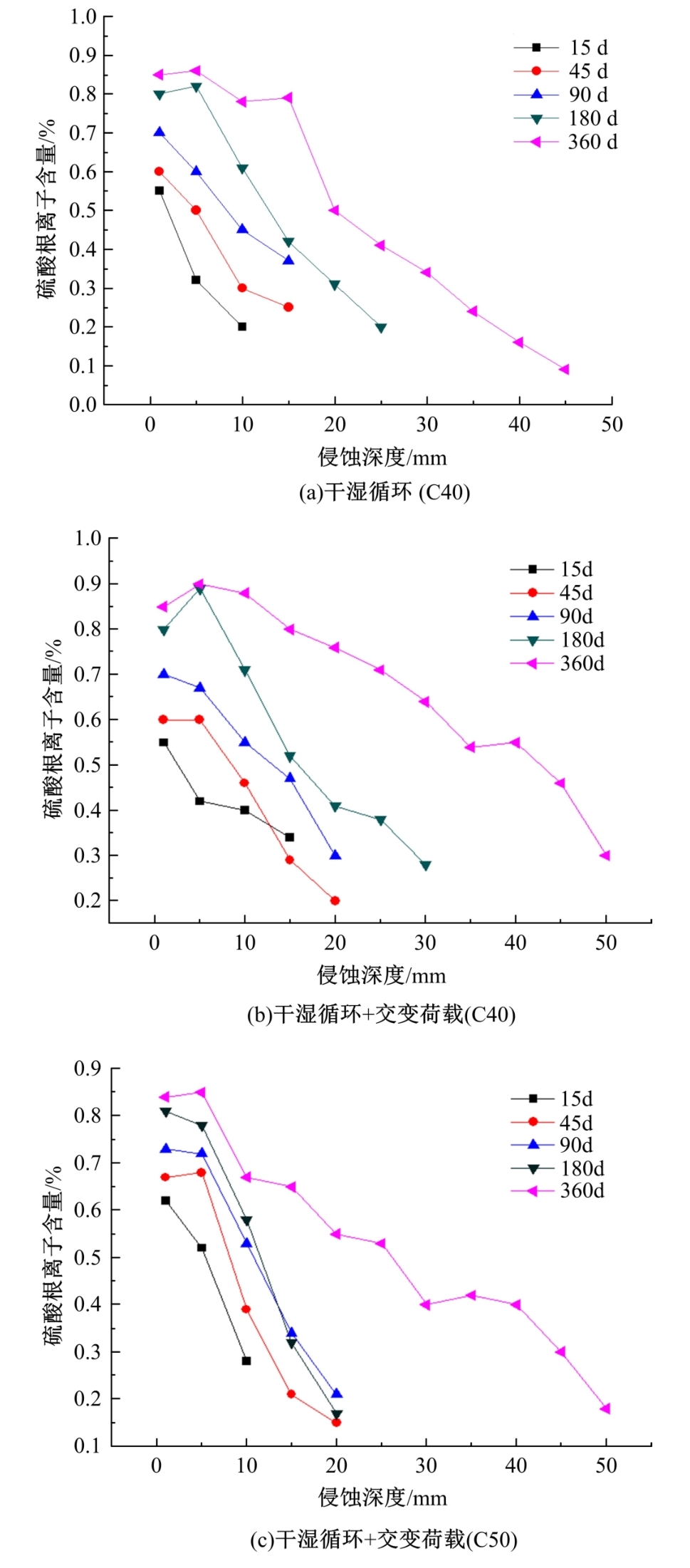
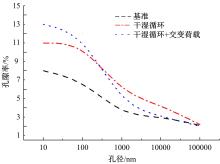
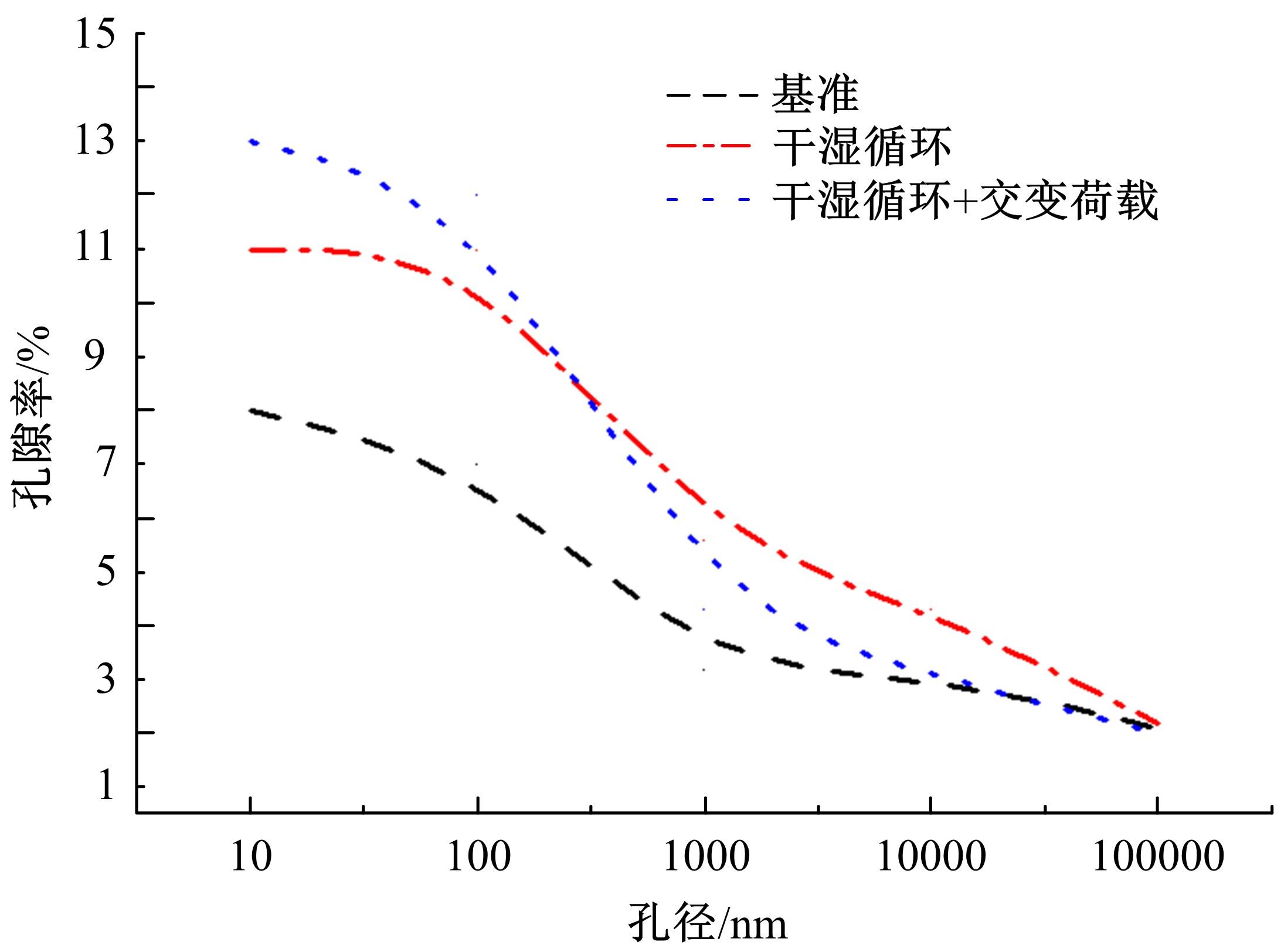
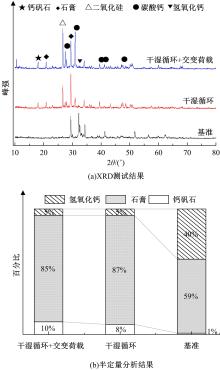
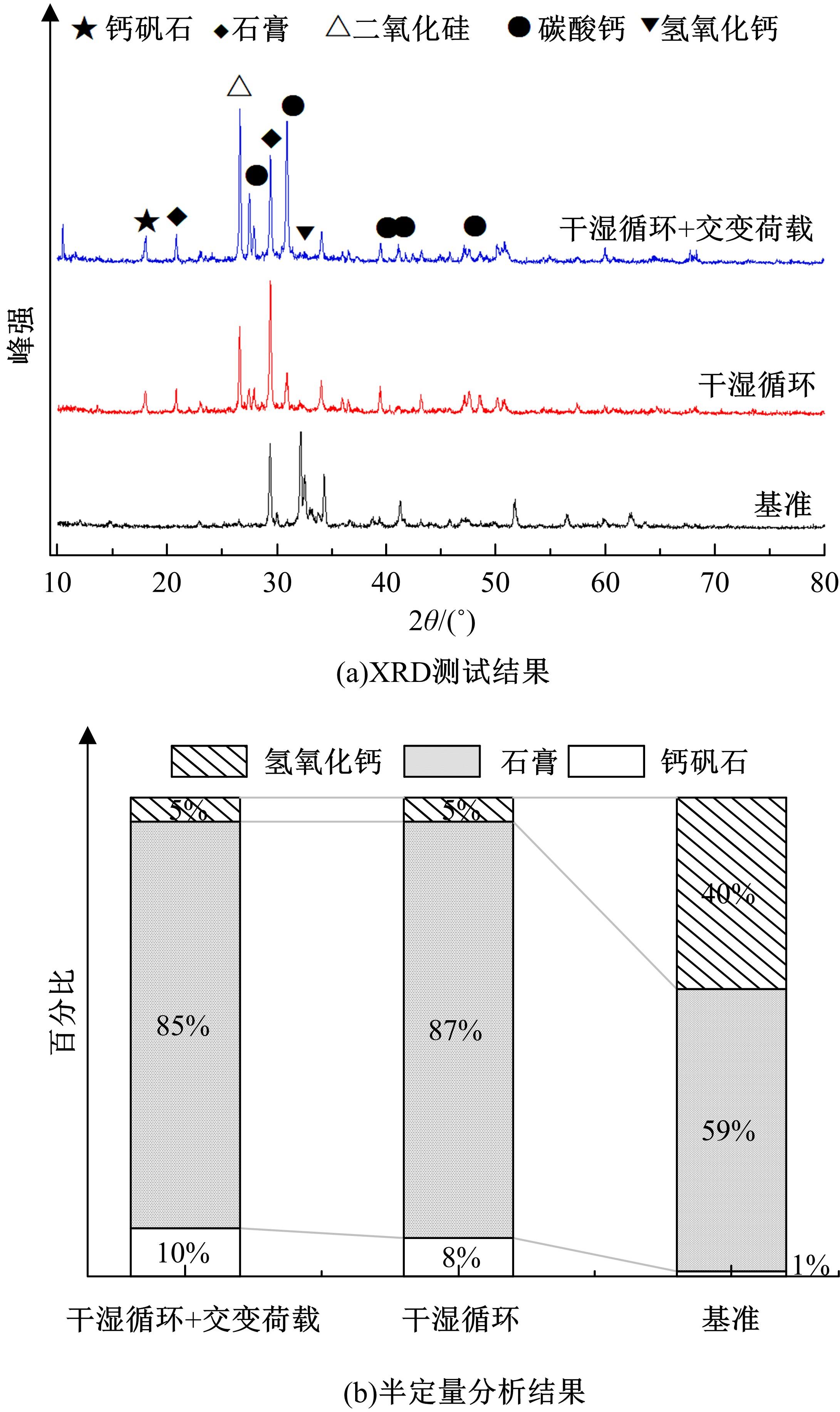
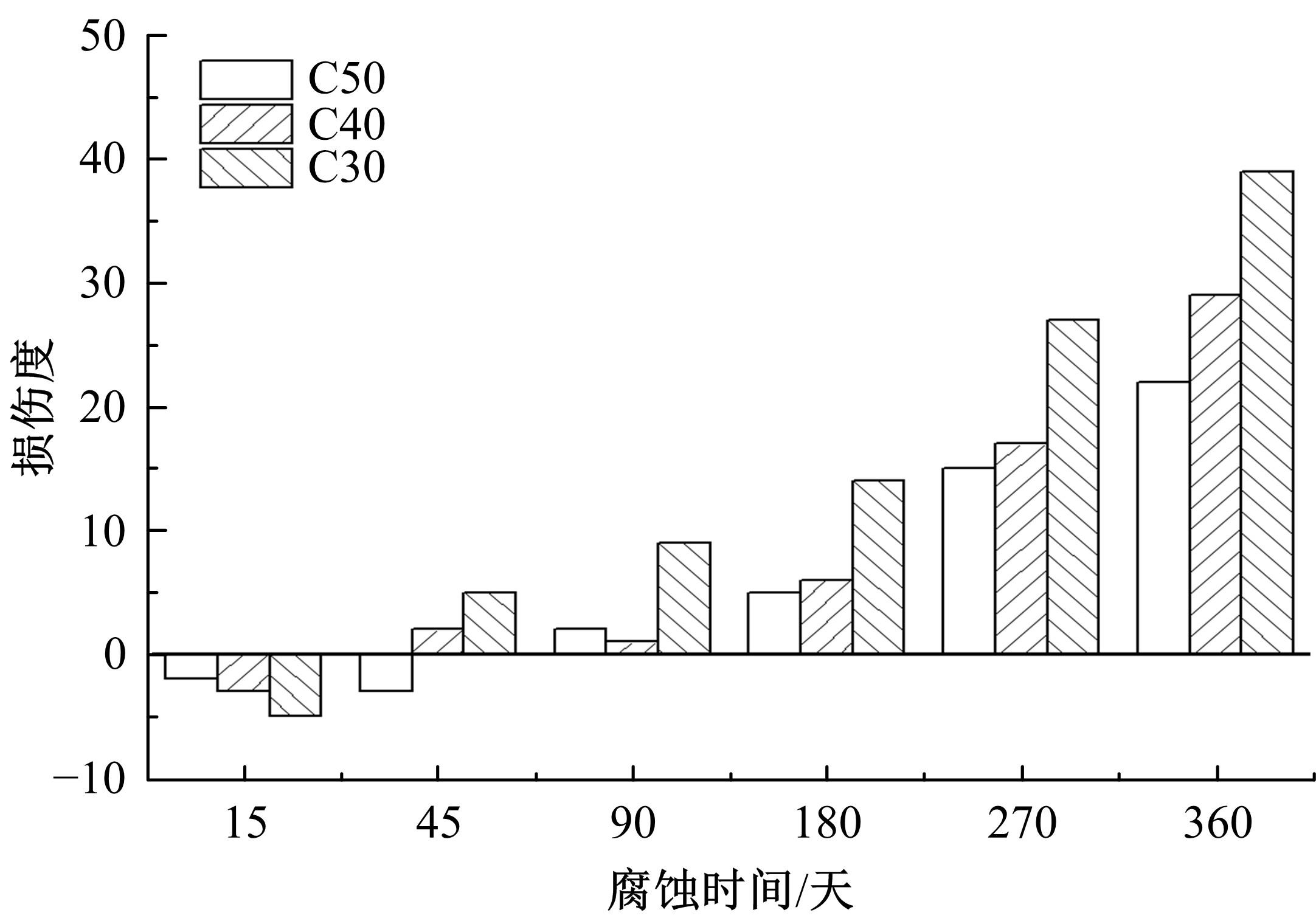
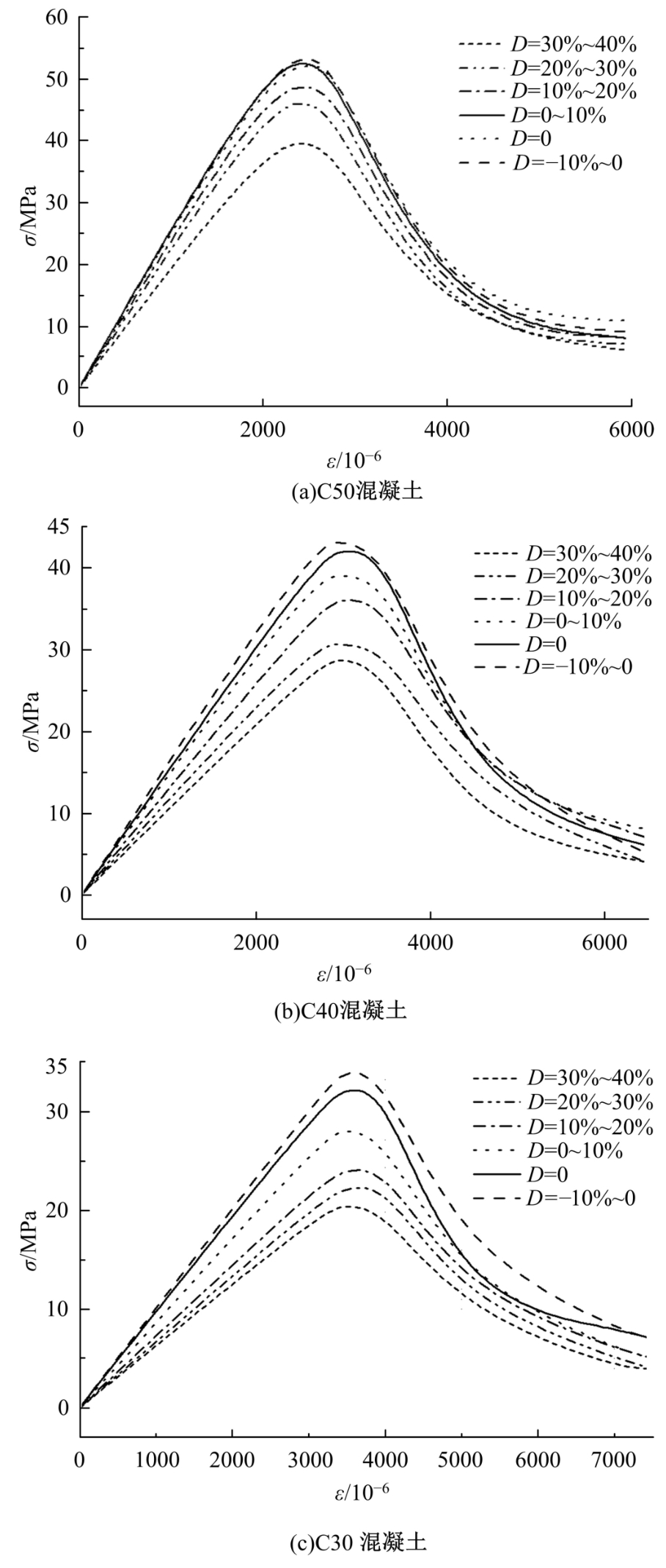
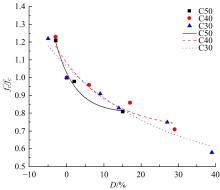
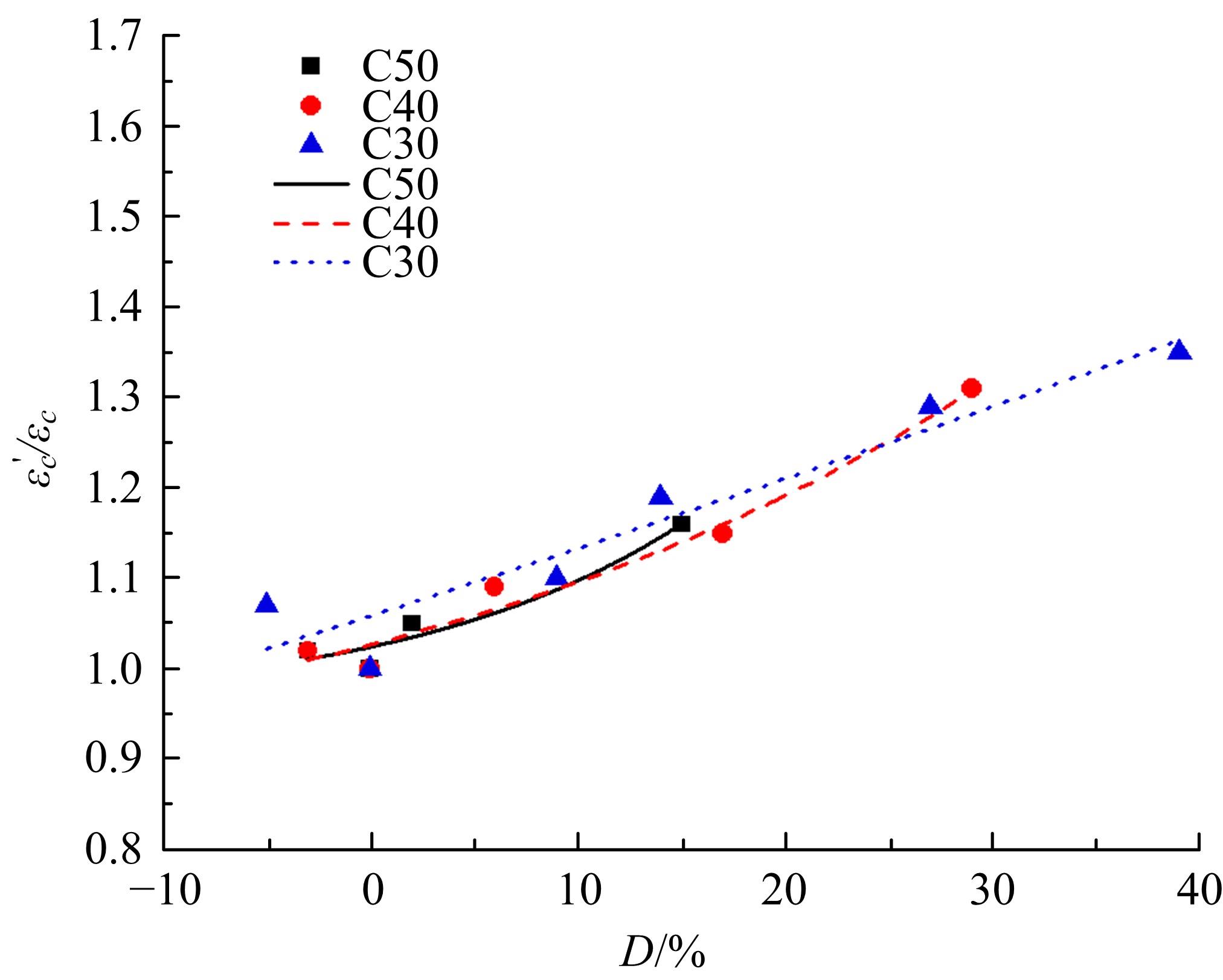
针对盐富集地区混凝土性能损伤问题,通过自主研发试验装置模拟干湿循环与交变荷载作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀,采用超声无损检测、孔结构分析、化学分析法、应力-应变测试分析混凝土受硫酸盐侵蚀宏微观性能劣化规律。研究结果表明:交变荷载对低强度等级混凝土的侵蚀作用更为严重。交变荷载增加混凝土中有害孔含量,加速了微裂纹的扩展,促进了硫酸根离子传输,加重了受蚀混凝土损伤。基于干湿循环与交变荷载作用下受硫酸盐侵蚀混凝土应力-应变曲线,以损伤度为变量,提出了受硫酸盐侵蚀混凝土相对峰值应力以及应变随损伤度变化的拟合方程。
中图分类号:
- U414
| 1 | Zhao G W, Guo M Z, Cui J F, et al. Partially-exposed cast-in-situ concrete degradation induced by internal-external sulfate and magnesium multiple coupled attack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 294(3): No.123560. |
| 2 | Zou D J, Qin S S, Liu T J, et al. Experimental and numerical study of the effects of solution concentration and temperature on concrete under external sulfate attack[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 139: No.106284. |
| 3 | 关博文, 吴佳育, 陈华鑫, 等. 再生骨料残余砂浆覆盖率测试及其对混凝土渗透性的影响[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(10): 155-165. |
| Guan Bo-wen, Wu Jia-yu, Chen Hua-xin,et al. Test of coverage rate of residual mortar om recycled aggregate and its influence on permeability of conrete[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(10): 155-165. | |
| 4 | Liao K X, Zhang Y P, Zhang W P, et al. Modeling constitutive relationship of sulfate-attacked concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 260: No. 1191902. |
| 5 | 关博文. 交变荷载与硫酸盐腐蚀作用下水泥混凝土疲劳损伤机制[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2012. |
| Guan Bo-wen. Study on the fatigue damage of cement concrete subjected to sulfate corrosion and alternating stresses[D]. Xi′an: College of Highway Engineering of Chang'an University, 2012. | |
| 6 | Chang H L, Jin Z Q, Wang P G, et al. Comprehensive resistance of fair-faced concrete suffering from sulfate attack under marine environments[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 277: No. 122312. |
| 7 | Wei Y M, Chai J R, Qin Y, et al. Effect of fly ash on mechanical properties and microstructure of cellulose fiber-reinforced concrete under sulfate dry⁃wet cycle attack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 302: No.124207. |
| 8 | Xu F, Wang S L, Li T, et al. The mechanical properties of tailing recycled aggregate concrete and its resistance to the coupled deterioration of sulfate attack and wetting-drying cycles[J]. Structures, 2020, 27: 2208-2216. |
| 9 | Wang K, Guo J J, Wu H, et al. Influence of dry-wet ratio on properties and microstructure of concrete under sulfate attack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 263: No.120635. |
| 10 | 关博文, 杨涛, 吴佳育, 等. 交变荷载作用下损伤混凝土中氯离子传输行为[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2018, 21(2): 304-308. |
| Guan Bo-wen, Yang Tao, Wu Jia-yu, et al. Chloride transport behavior of damaged concrete under alternating load[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2018, 21(2): 304-308. | |
| 11 | Ren J G, Lai Y M, Bai R Q, et al. The damage mechanism and failure prediction of concrete under wetting⁃drying cycles with sodium sulfate solution[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 264: No.120525. |
| 12 | Li J P, Xie F, Zhao G W, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of cast-in-situ concrete under external sulfate attack and drying-wetting cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 249: No.118789. |
| 13 | Zhang J R, Sun M, Hou D S, et al. External sulfate attack to reinforced concrete under drying-wetting cycles and loading condition: numerical simulation and experimental validation by ultrasonic array method[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 139: 365-373. |
| 14 | Yu D M, Guan B W, He R, et al. Sulfate attack of Portland cement concrete under dynamic flexural loading: a coupling function[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 115: 478-485. |
| 15 | Yin G J, Zuo X B, Tang Y J, et al. Numerical simulation on time-dependent mechanical behavior of concrete under coupled axial loading and sulfate attack[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2017, 142: 115-124. |
| 16 | Gao J M, Yu Z X, Song L G, et al. Durability of concrete exposed to sulfate attack under flexural loading and drying-wetting cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 39: 33-38. |
| 17 | Liu F, You Z, Diab A, et al. External sulfate attack on concrete under combined effects of flexural fatigue loading and drying-wetting cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 249: No.118224. |
| 18 | Swamy R N, Tanikawa S. An external surface coating to protect concrete and steel from aggressive environments[J]. Materials and Structures, 1993, 26(162): 465-478. |
| 19 | 常艳婷, 田丰, 张震. 动态疲劳荷载对路面砼不同部位抗渗性影响[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2014, 36(11): 53-57. |
| Chang Yan-ting, Tian Feng, Zhang Zhen. Dynamic fatigue loading effects on the impermeability of different parts of concrete pavement[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2014, 36(11): 53-57. | |
| 20 | Sahoo S, Mahapatra T R. ANN modeling to study strength loss of fly ash concrete against long term sulphate attack[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(11): 24595-24604. |
| 21 | Ikumi T, Cavalaro S H P, Segura I, et al. Alternative methodology to consider damage and expansions in external sulfate attack modeling[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2014, 63: 105-116. |
| 22 | 吴中伟,廉慧珍.高性能混凝土[M].北京:中国铁道出版社,1999:38-43. |
| 23 | Li T, Wang S S. Modeling diffusion coefficient of sulfate ion in concrete using probabilistic approach[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 215: 435-446. |
| 24 | Cao T, Zhang L, Sun G, et al. Simulation of chloride ion transport in concrete under the coupled effects of a bending load and drying⁃wetting cycles[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 241: No.118045. |
| 25 | Xiao Q H, Li Q, Cao Z Y, et al. The deterioration law of recycled concrete under the combined effects of freeze-thaw and sulfate attack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 200: 344-355. |
| 26 | 关博文, 刘佳楠, 吴佳育, 等. 基于侵蚀损伤的混凝土硫酸根离子传输行为[J].硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(10): 3169-3174, 3183. |
| Guan Bo-wen, Liu Jia-nan, Wu Jia-yu, et al. Transport behavior of sulfate ions in concrete with attack damage[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 39(10): 3169-3174, 3183. | |
| 27 | Chen Y, Liu P, Yu Z. Study on degradation of macro performances and micro structure of concrete attacked by sulfate under artificial simulated environment[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 260: No.119951. |
| 28 | Nie L X, Xu J Y, Bai E, et al. Dynamic stress-strain relationship of concrete subjected to chloride and sulfate attack[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 165: 232-240. |
| 29 | Liao K X, Zhang Y P, Zhang W P, et al. Modeling constitutive relationship of sulfate-attacked concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 260: No. 119902. |
| [1] | 熊二刚,巩忠文,罗佳明,范团结. 基于数字图像相关技术的钢筋混凝土梁裂缝试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1094-1104. |
| [2] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [3] | 王晓东,李宁静,李强. 高压脉冲放电破碎混凝土梁试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 496-504. |
| [4] | 匡亚川,陈立斌,李超举,贺宇豪. 栓钉剪力连接件力学性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 538-546. |
| [5] | 魏海斌,马子鹏,毕海鹏,刘汉涛,韩栓业. 基于力学响应分析方法的导电橡胶复合路面铺装技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 531-537. |
| [6] | 叶华文,段智超,刘吉林,周渝,韩冰. 正交异性钢⁃混组合桥面的轮载扩散效应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1808-1816. |
| [7] | 顾章义,张治成,李辉. 基于能量法的超高韧性纤维混凝土疲劳损伤特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1598-1606. |
| [8] | 郭庆林,刘强,吴春利,李黎丽,李懿明,刘富春. 导电沥青及混合料裂缝局部温度场及愈合效果[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1386-1393. |
| [9] | 时成林,王勇,吴春利,宋文祝. 路堤挡土墙主动土压力计算方法修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1394-1403. |
| [10] | 姚玉权,仰建岗,高杰,宋亮. 基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
| [11] | 夏全平,高江平,罗浩原,张其功,李志杰,杨飞. 用于高模量沥青砼的复合改性硬质沥青低温性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [12] | 叶奋,胡诗园. 考虑旧水泥路面接缝传荷能力的超薄罩面力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2636-2643. |
| [13] | 王毅红,田桥罗,兰官奇,姚圣法,张建雄,刘喜. 630 MPa高强钢筋混凝土大偏压柱受力性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2626-2635. |
| [14] | 于晓贺,罗蓉,柳子尧,黄婷婷,束裕. 沥青路面典型裂缝湿度场数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2343-2351. |
| [15] | 许博,李传习. 基于灰色理论的大跨度钢管混凝土拱桥承载能力检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2360-2366. |
|
||