吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1746-1755.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221353
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
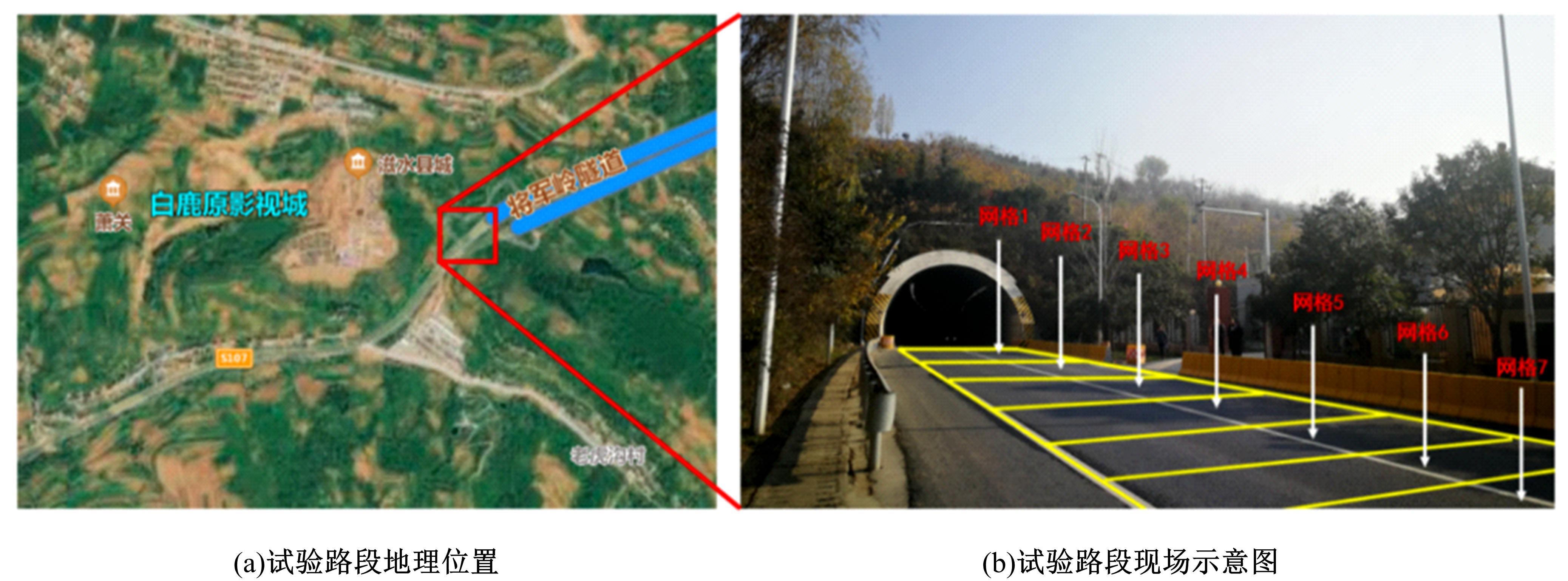
基于网格化的路表温度感知技术
刘状壮1,2( ),郑文清1,郑健1,3,李轶峥1,季鹏宇1,沙爱民1,2
),郑文清1,郑健1,3,李轶峥1,季鹏宇1,沙爱民1,2
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.长安大学 特殊地区公路工程教育部重点实验室,西安 710064
3.中冶南方工程技术有限公司 深圳分公司,广东 深圳 518028
Pavement surface temperature monitoring method based on gridding approach
Zhuang-zhuang LIU1,2( ),Wen-qing ZHENG1,Jian ZHENG1,3,Yi-zheng LI1,Peng-yu JI1,Ai-min SHA1,2
),Wen-qing ZHENG1,Jian ZHENG1,3,Yi-zheng LI1,Peng-yu JI1,Ai-min SHA1,2
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.Key Laboratory of Highway Engineering in Special Region,Ministry of Education,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
3.Shenzhen Branch,Wuhan Iron & Steel Design & Research Institute,Shenzhen 518028,China
摘要:
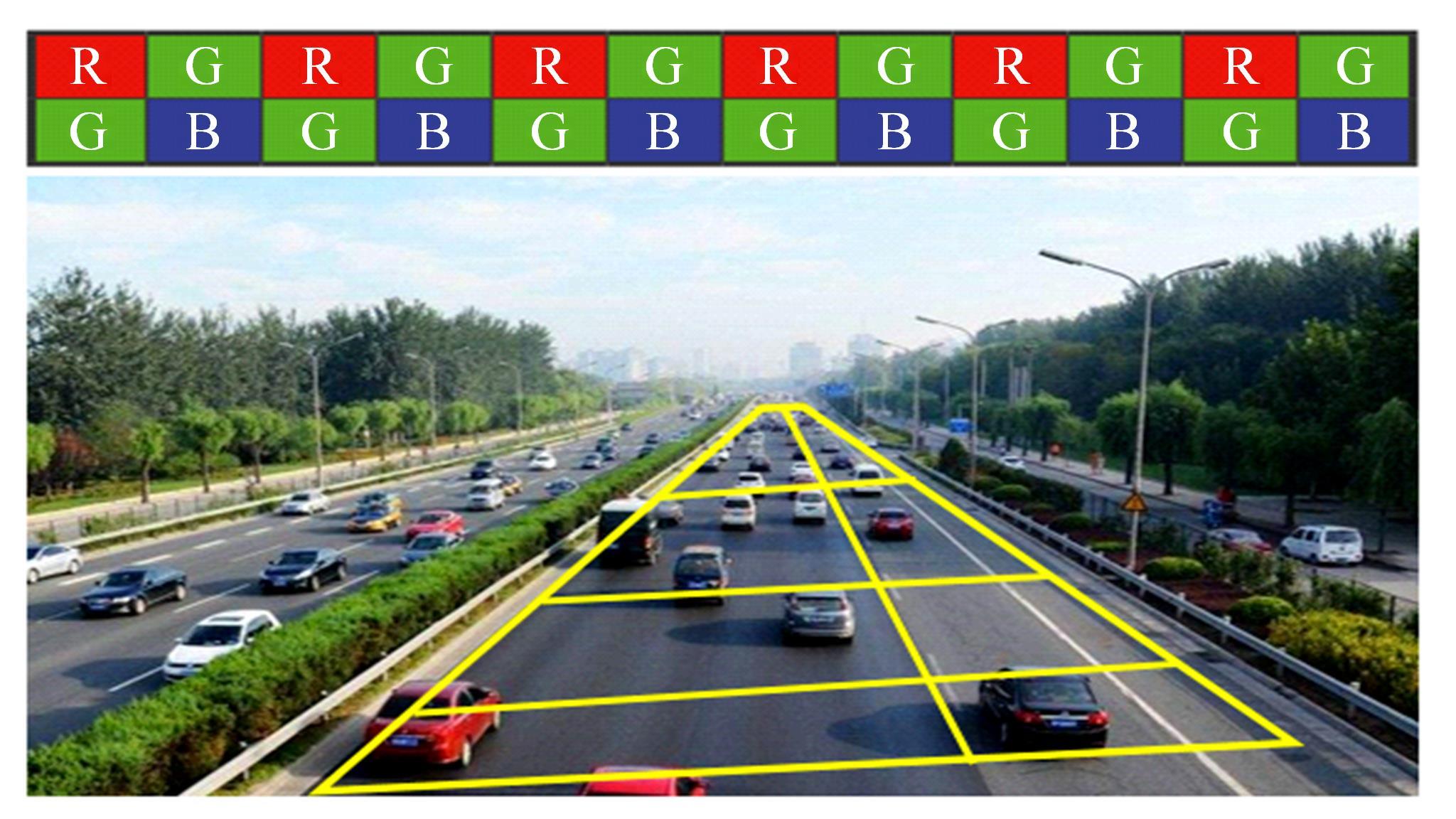
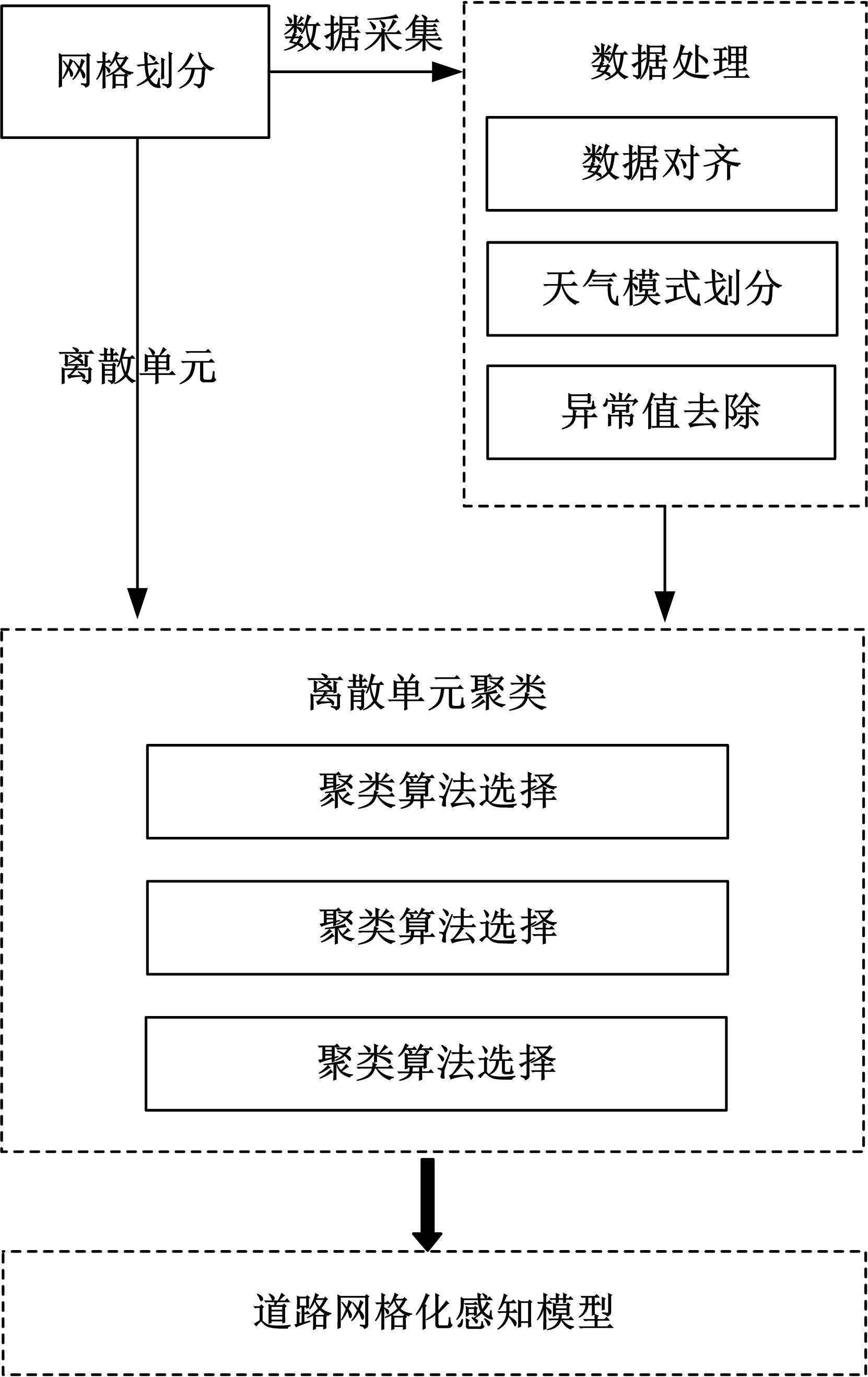
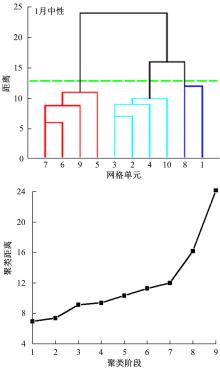
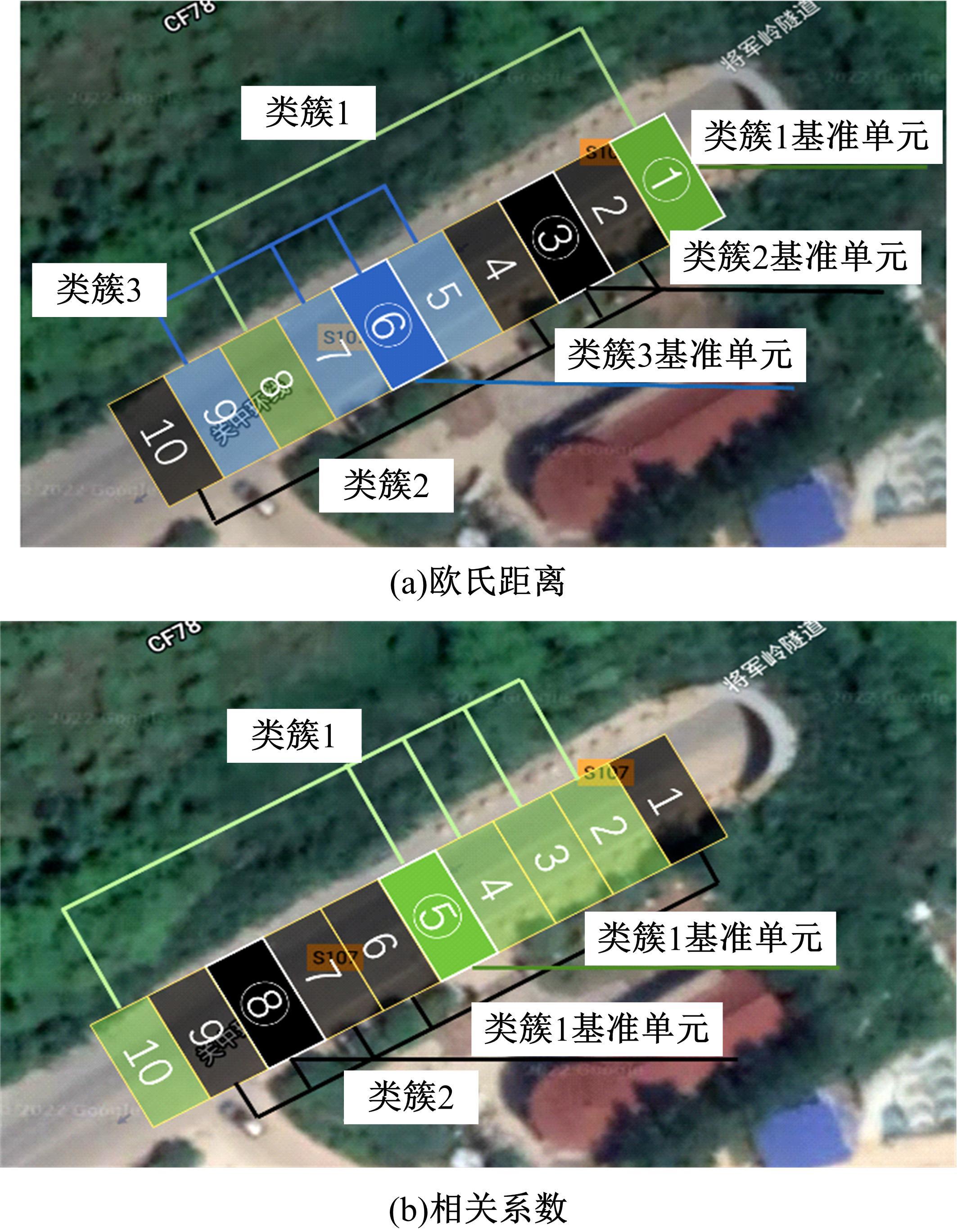
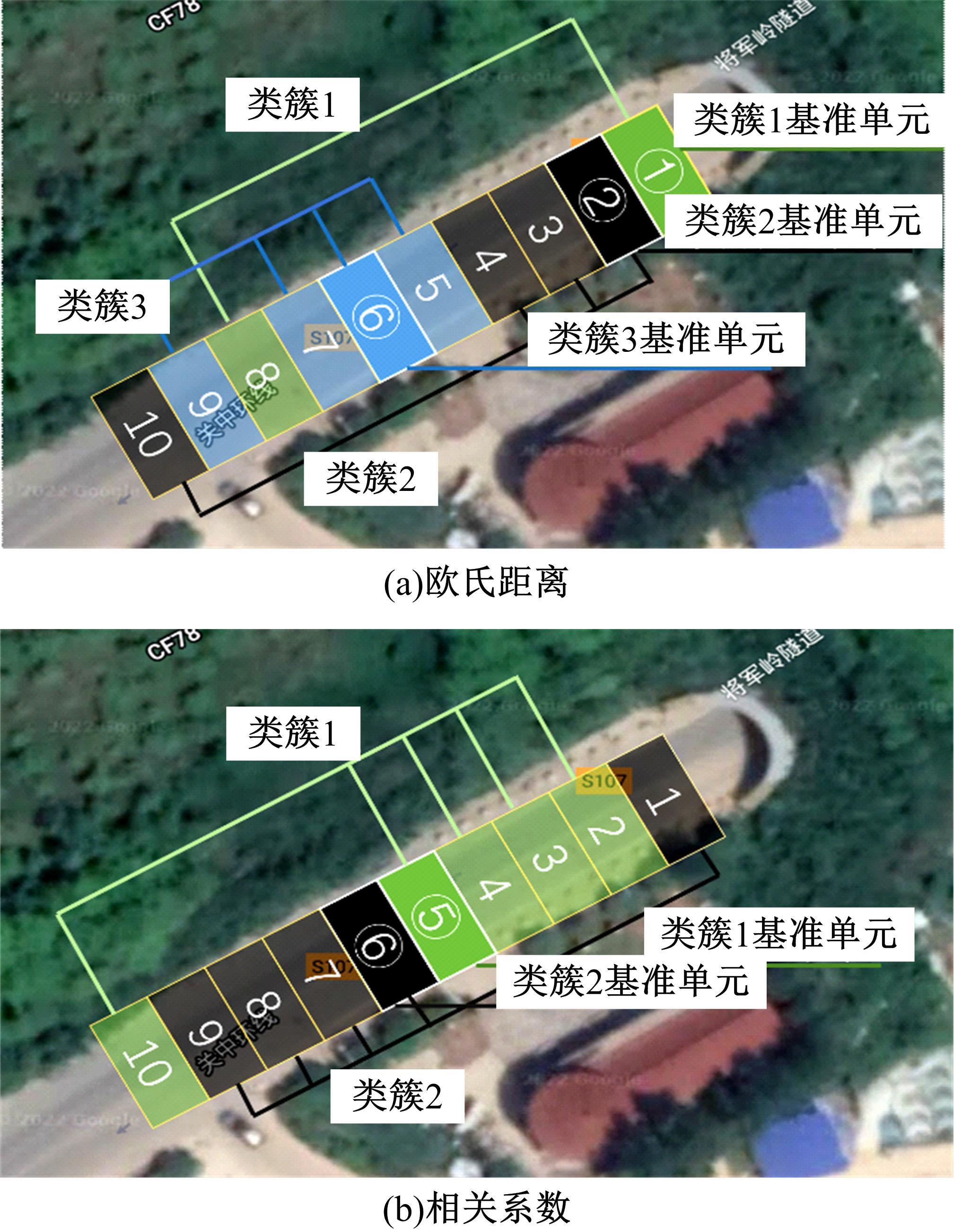
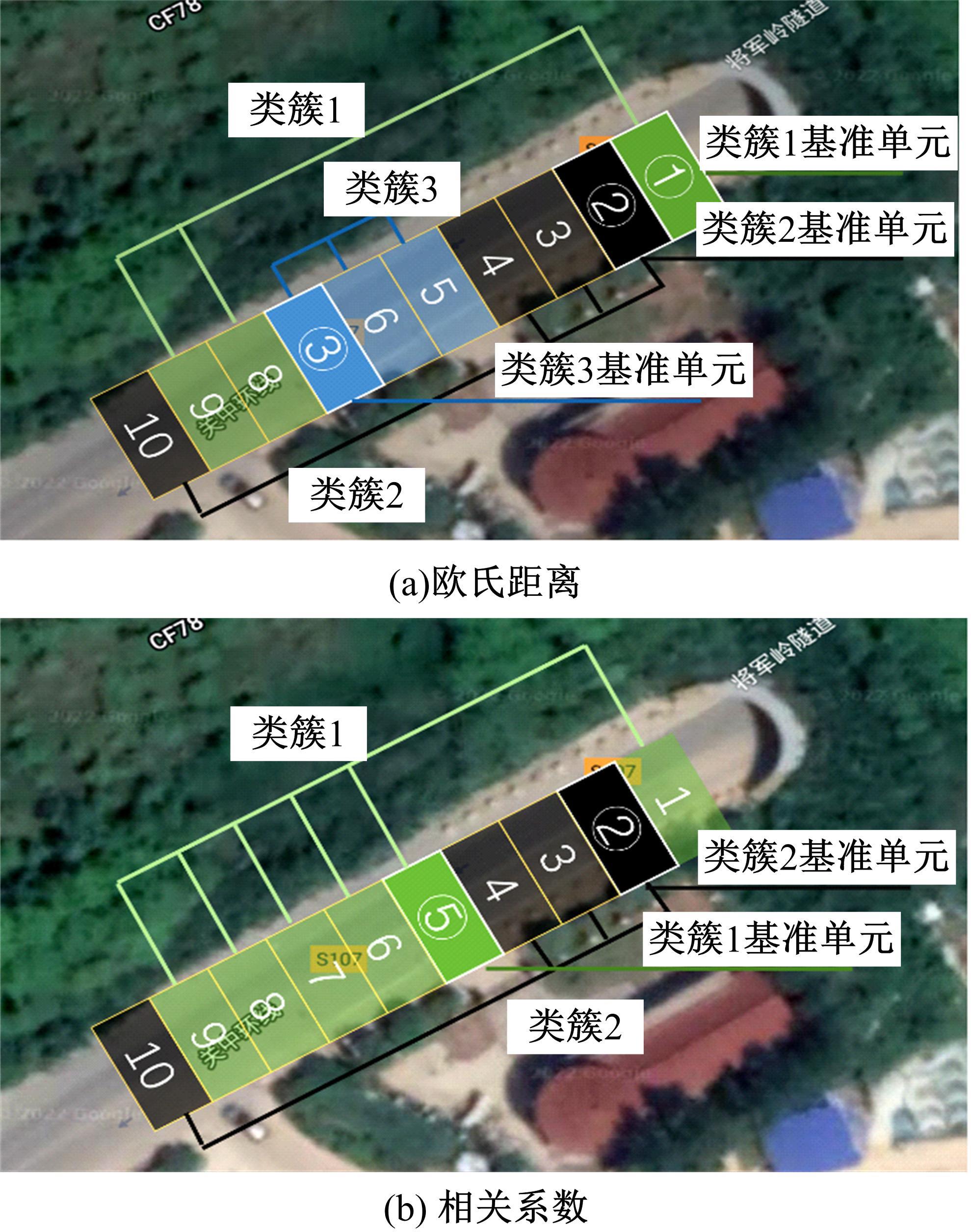
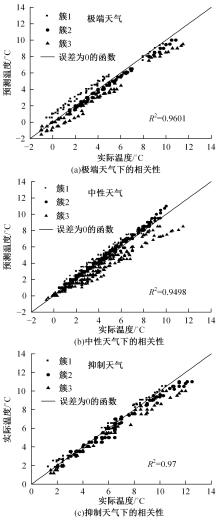
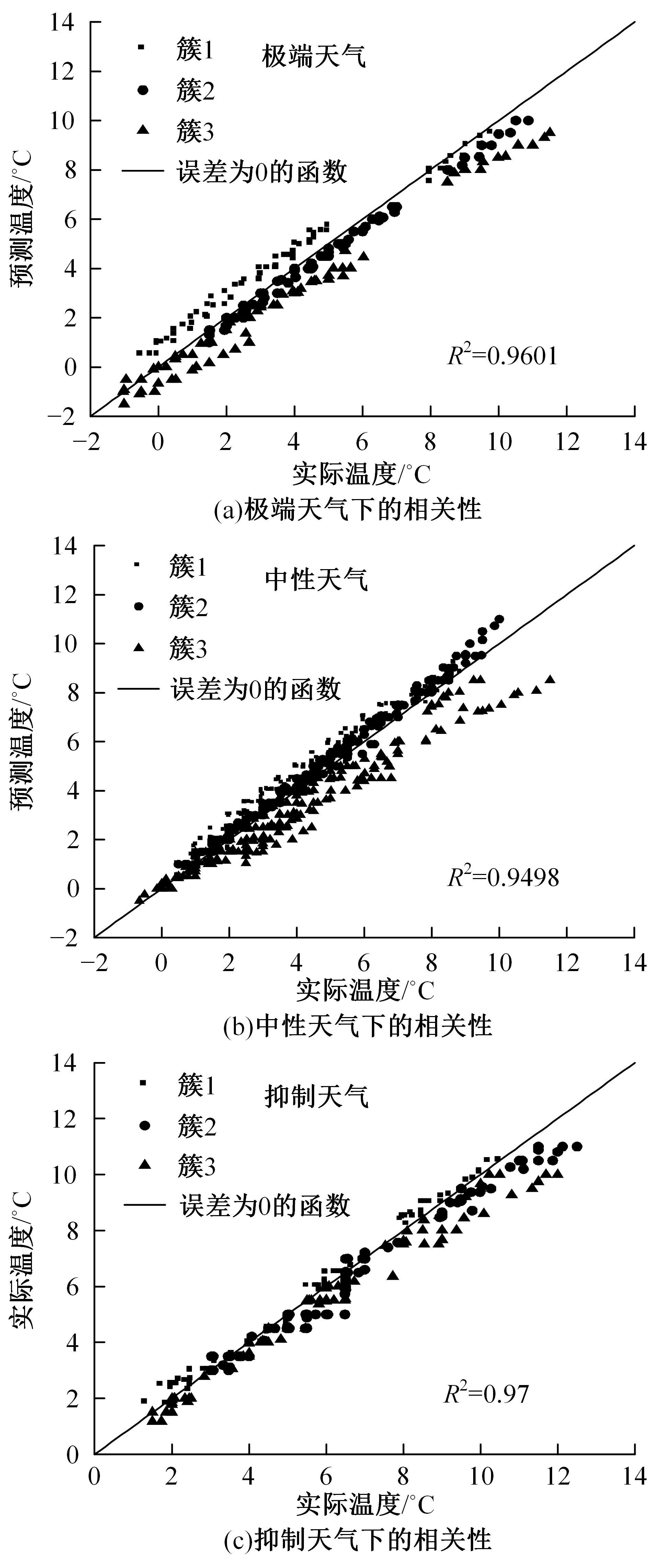
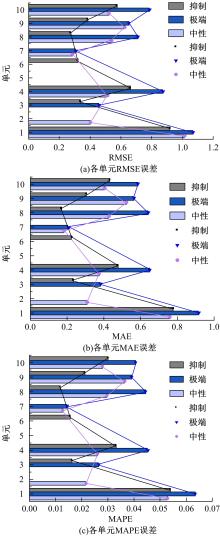
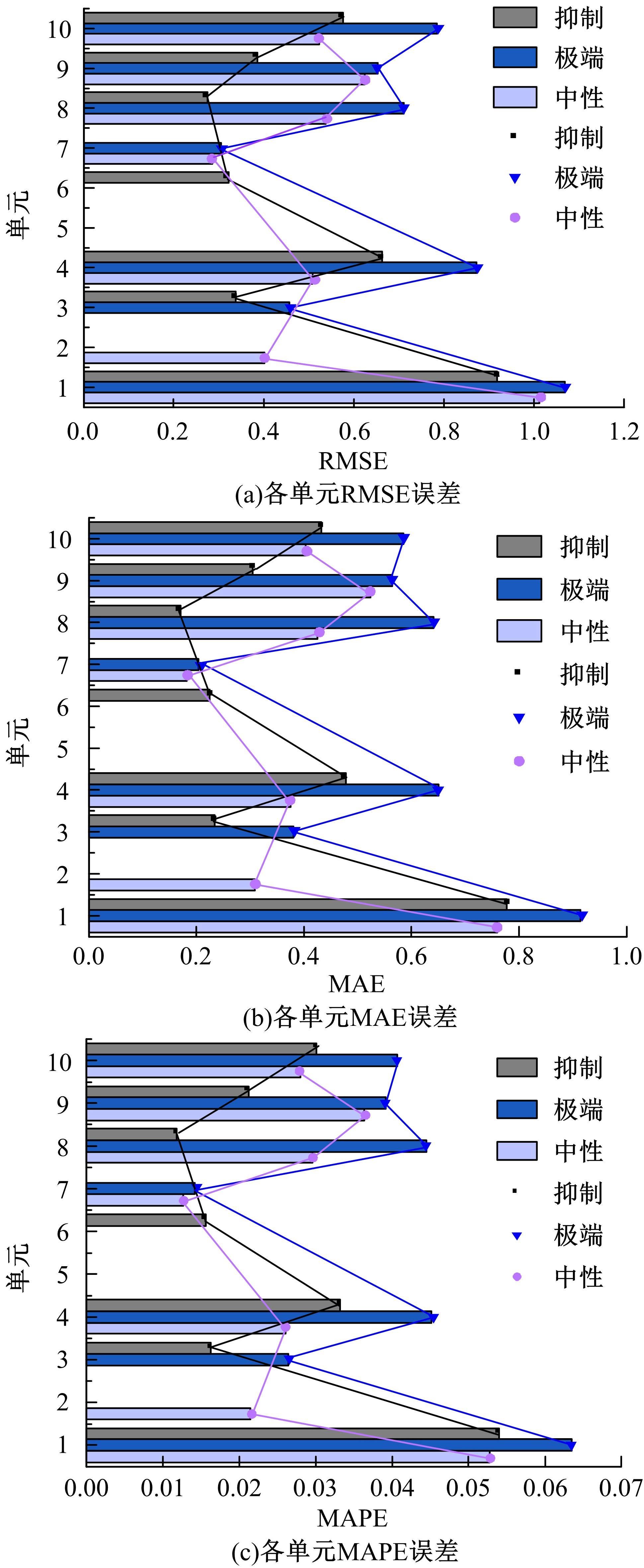
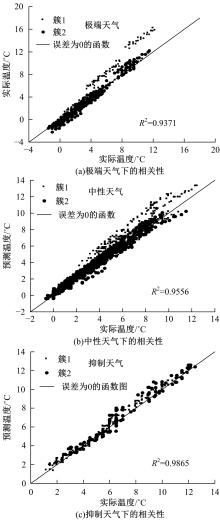
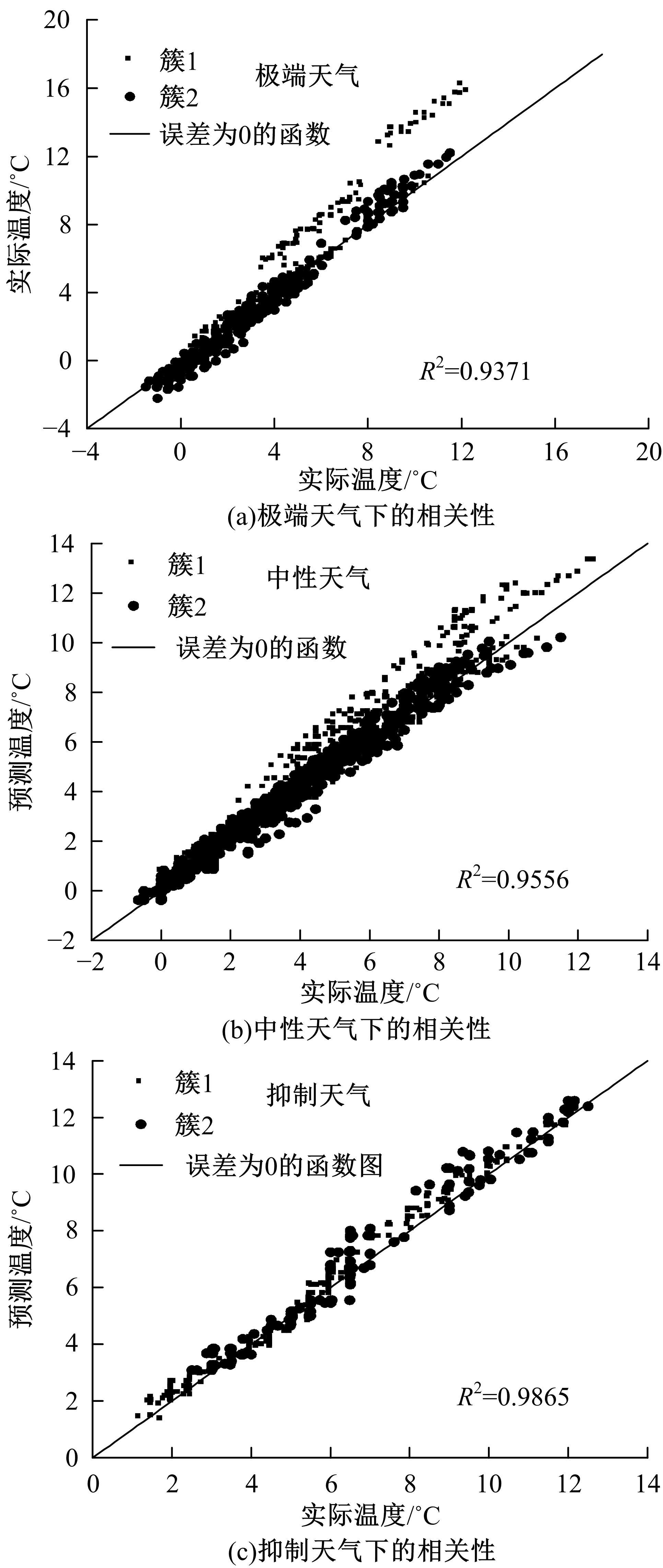
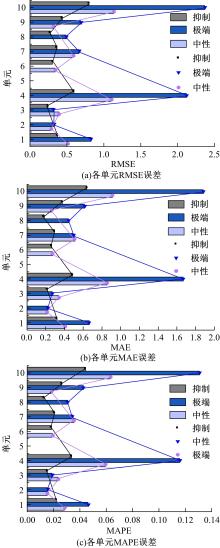
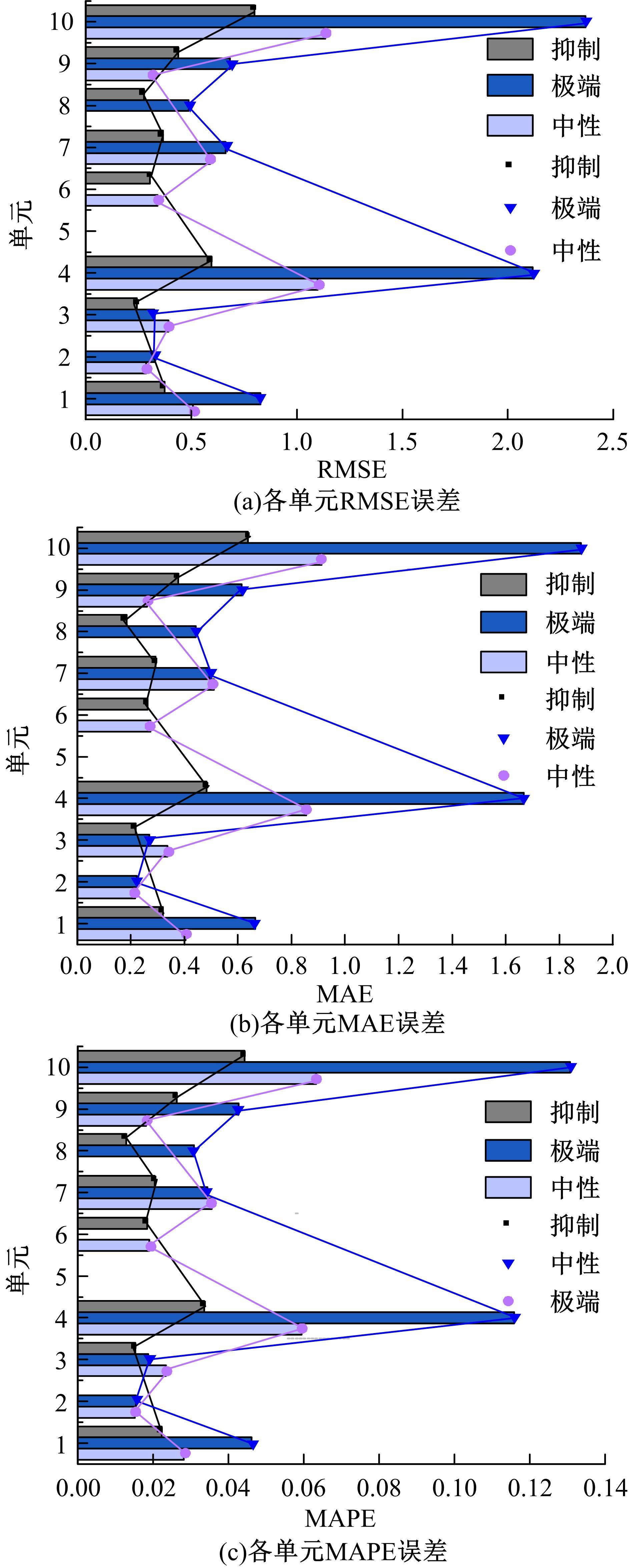
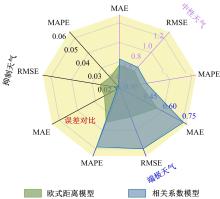
为实现路表温度的高精度预测,考虑路域环境的周期性和道路结构在纵向空间上的确定性特征,提出了包含天气模式的路表温度网格化感知方法,并基于试验路段的大量实测数据进行数据挖掘和分析。依据层次聚类算法的两种不同距离函数建立了两种感知网络模型(欧氏距离模型和相关距离模型)。利用平均绝对误差、均方根误差和平均相对误差对模型的预测效果进行评价。通过对3类天气模式下模型的预测误差水平进行分析,对预测值与实测值进行对比。结果显示:本文提出的网格化感知方法对天气模式较为敏感,两种模型均在抑制天气下的预测效果最好,抑制和中性天气下平均相对误差小于5%,极端天气下最大平均相对误差为5.43%。模型均方根误差在极端天气下最大为1.2 ℃,其他天气模式下均小于1 ℃。
中图分类号:
- U416.2
| 1 | 刘状壮, 沙爱民, 蒋玮. 蓄盐沥青路面研究进展:盐化物材料、混合料及其性能与评价[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(4): 18-31. |
| Liu Zhuang-zhuang, Sha Ai-min, Jiang Wei. Advances in asphalt pavements containing salts:additives, mixtures,performances,and evaluation[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(4): 18-31. | |
| 2 | 刘状壮, 张有为, 季鹏宇, 等. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| Liu Zhuang-zhuang, Zhang You-wei, Ji Peng-yu, et al. Study on heat transfer characteristics of electric heating snow melting[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. | |
| 3 | Kwon T J, Fu Li-ping. Spatiotemporal variability of road weather conditions and optimal RWIS density— an empirical investigation[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2017, 44(9): 691-699. |
| 4 | Jin P J, Walker A, Cebelak M, et al. Determining strategic locations for environmental sensor stations with weather-related crash data[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2014(2440): 34-42. |
| 5 | Kwon T J, Fu Li-ping, Melles S J. Location optimization of road weather information system (RWIS) network considering the needs of winter road maintenance and the traveling public[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2017, 32(1): 57-71. |
| 6 | Biswas S, Wu Ming-jian, Melles S J, et al. Use of topography, weather zones, and semivariogram parameters to optimize road weather information system station density across large spatial scales[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2019, 2673(12): 301-311. |
| 7 | Feng Feng, Fu Li-ping. Winter road surface condition forecasting[J]. Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 2015, 21(3): No. 04014049. |
| 8 | 张昌利, 孟颖, 温立民, 等. 面向CPS的高速公路凝冰短时预测与主动式防冰控制[J]. 北京交通大学学报, 2017, 41(3): 47-54. |
| Zhang Chang-li, Meng Ying, Wen Li-min, et al. CPS-oriented short-term icing events prediction and proactive anti-ice control for highway systems[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017, 41(3): 47-54. | |
| 9 | Gu Lian, Wu Ming-jian, Kwon T J. An enhanced spatial statistical method for continuous monitoring of winter road surface conditions[J]. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2020, 47(10): 1154-1165. |
| 10 | Hermansson A. Simulation model for calculating pavement temperatures including maximum temperature[J]. Pavement Management and Monitoring: Pavement Design, Management, and Performance, 2000, 1699(1): 134-141. |
| 11 | 陈嘉祺, 罗苏平, 李亮, 等. 沥青路面温度场分布规律与理论经验预估模型[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 44(4): 1647-1656. |
| Chen Jia-qi, Luo Su-ping, Li Liang, et al. Temperature distribution and method-experience prediction model of asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2013, 44(4): 1647-1656. | |
| 12 | 谈至明, 马正军, 邹晓翎. 基于路表实测温度的路面温度场估计模型[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 41(5): 700-704. |
| Tan Zhi-ming, Ma Zheng-jun, Zou Xiao-ling. Pavement temperature estimation model based on field temperature data[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2013, 41(5): 700-704. | |
| 13 | 庄传仪, 王林, 申爱琴, 等. 沥青路面路表温度预估模型研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(3): 39-43, 48. |
| Zhuang Chuan-yi, Wang Lin, Shen Ai-qin, et al. Prediction model of surface temperature of asphalt pavement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2010, 27(3): 39-43, 48. | |
| 14 | Khan Z H, Islam M R, Tarefder R A. Determining asphalt surface temperature using weather parameters[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering—English Edition, 2019, 6(6): 577-588. |
| 15 | Liu Bo, Yan Shuo, You Huan-ling, et al. Road surface temperature prediction based on gradient extreme learning machine boosting[J]. Computers in Industry, 2018, 99: 294-302. |
| 16 | Tabrizi S E, Xiao K, The J V, et al. Hourly road pavement surface temperature forecasting using deep learning models[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 603: No. 126877. |
| 17 | 杨书杰, 彭嫣. 基于机器学习的路表温度预估方法研究[J]. 交通科技, 2022(2): 5-8. |
| Yang Shu-jie, Peng Yan. Research on road surface temperature estimation method based on machine learning[J]. Transportation Science & Technology, 2022(2): 5-8. | |
| 18 | Fujimoto A, Akira S, Teruyuki F, et al. Heat transfer analysis on road surface temperature near a traffic light[C]∥17th ITS World Congress, Busan, Korea, South, 2010: No. 01354757. |
| 19 | Gustavsson T. A study of air and road-surface temperature variations during clear windy nights[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2010, 18(8): 919-932. |
| 20 | Rodriguez M Z, Comin C H, Casanova D, et al. Clustering algorithms: a comparative approach[J]. PLoS ONE, 2016, 14(1): 1-34. |
| 21 | Trevor H, Robert T, Jerome F. The Elements of Statistical Learning[M]. Berlin: Springer-verlag, 2003. |
| 22 | 林子静, 胡继超, 朱承瑛. 高速公路路面夜间逐时温度预报方法研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(8): 23-29. |
| Lin Zi-Jing, Hu Ji-chao, Song Cheng-ying. A method for forecasting hourly expressway surface temperature during night time[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2021, 38(8): 23-29. | |
| 23 | 王可心, 包云轩, 朱承瑛, 等. 随机森林回归法在冬季路面温度预报中的应用[J]. 气象, 2021, 47(1): 82-93. |
| Wang Ke-xin, Bao Yun-xuan, Zhu Cheng-ying, et al. Forecasts of road surface temperature in winter based on random forests regression[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2021, 47(1): 82-93. |
| [1] | 杨柳,王创业,王梦言,程阳. 设置自动驾驶小客车专用车道的六车道高速公路交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [2] | 周正峰,于晓涛,陶雅乐,郑茂,颜川奇. 基于灰色关联分析的树脂与弹性体高黏沥青高温性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2078-2088. |
| [3] | 马涛,马源,黄晓明. 基于多元非线性回归的智能压实关键参数最优解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [4] | 黄晓明,赵润民. 道路交通基础设施韧性研究现状及展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1529-1549. |
| [5] | 司春棣,崔亚宁,许忠印,凡涛涛. 层间粘结失效后桥面沥青铺装层细观力学行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1719-1728. |
| [6] | 李岩,张久鹏,陈子璇,黄果敬,王培. 基于PCA-PSO-SVM的沥青路面使用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1729-1735. |
| [7] | 赵晓康,胡哲,张久鹏,裴建中,石宁. 基于光纤传感技术的路面结冰智能监测研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1566-1579. |
| [8] | 郑睢宁,何锐,路天宇,徐紫祎,陈华鑫. RET/胶粉复合改性沥青制备及其混合料性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1381-1389. |
| [9] | 魏海斌,韩栓业,毕海鹏,刘琼辉,马子鹏. 智能感知道路主动除冰雪系统及实验技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1411-1417. |
| [10] | 杨帆,李琛琛,李盛,刘海伦. 温缩作用下双层连续配筋混凝土路面配筋率设计参数对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1122-1132. |
| [11] | 关博文,邸文锦,王发平,吴佳育,张硕文,贾治勋. 干湿循环与交变荷载作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1112-1121. |
| [12] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,曹素娥. 基于谱聚类的不确定数据集中快速离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1181-1186. |
| [13] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [14] | 魏海斌,马子鹏,毕海鹏,刘汉涛,韩栓业. 基于力学响应分析方法的导电橡胶复合路面铺装技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 531-537. |
| [15] | 陈栩,曹超飞,尚静,黄明星,艾长发,任东亚. 动静水环境作用下级配离析对沥青混合料水损害的影响评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 210-219. |
|
||