吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 2380-2387.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211156
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法
- 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
Two-stage learning algorithm for biomedical named entity recognition
Xiang-jiu CHE( ),Huan XU,Ming-yang PAN,Quan-le LIU
),Huan XU,Ming-yang PAN,Quan-le LIU
- College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
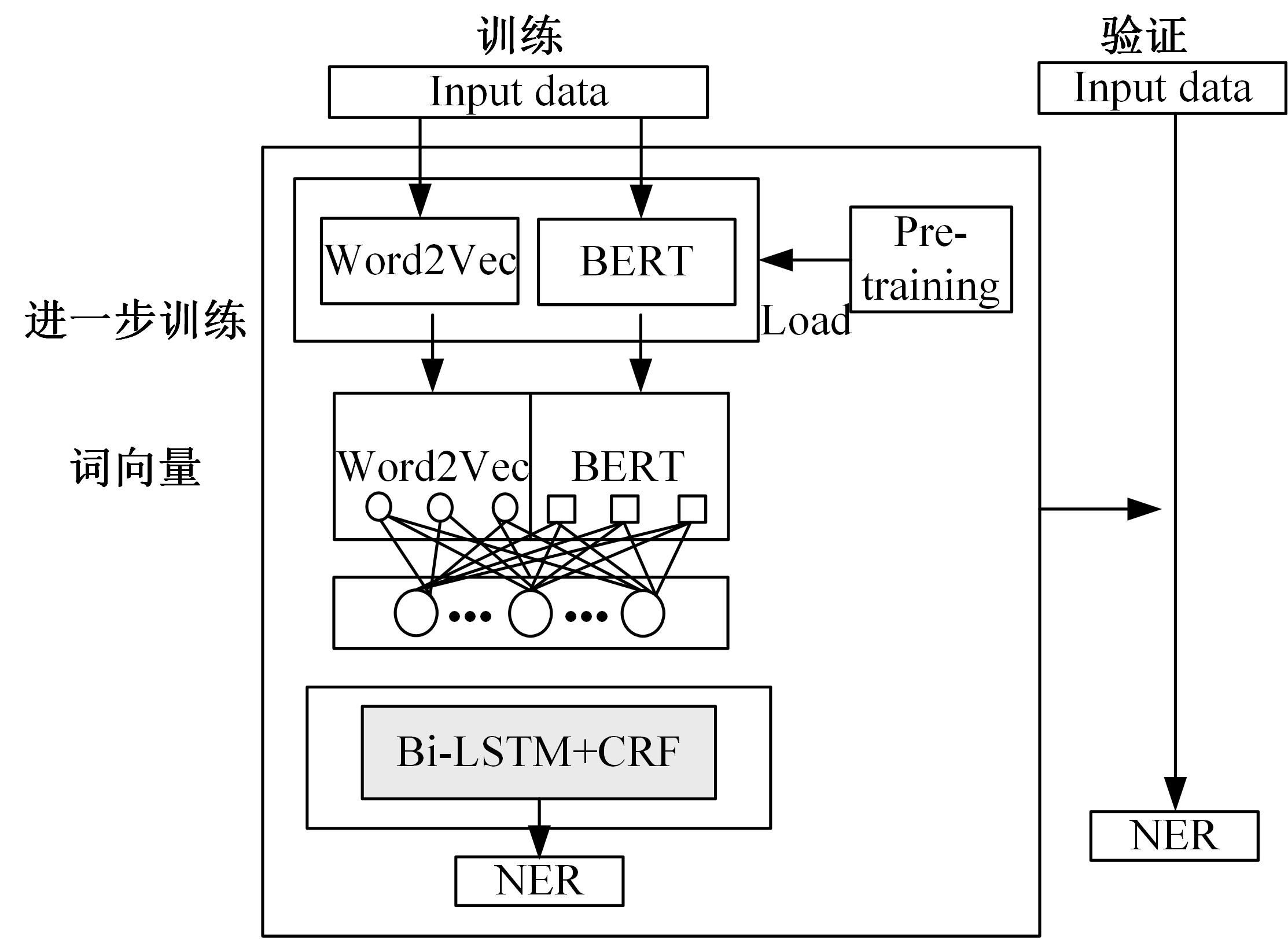
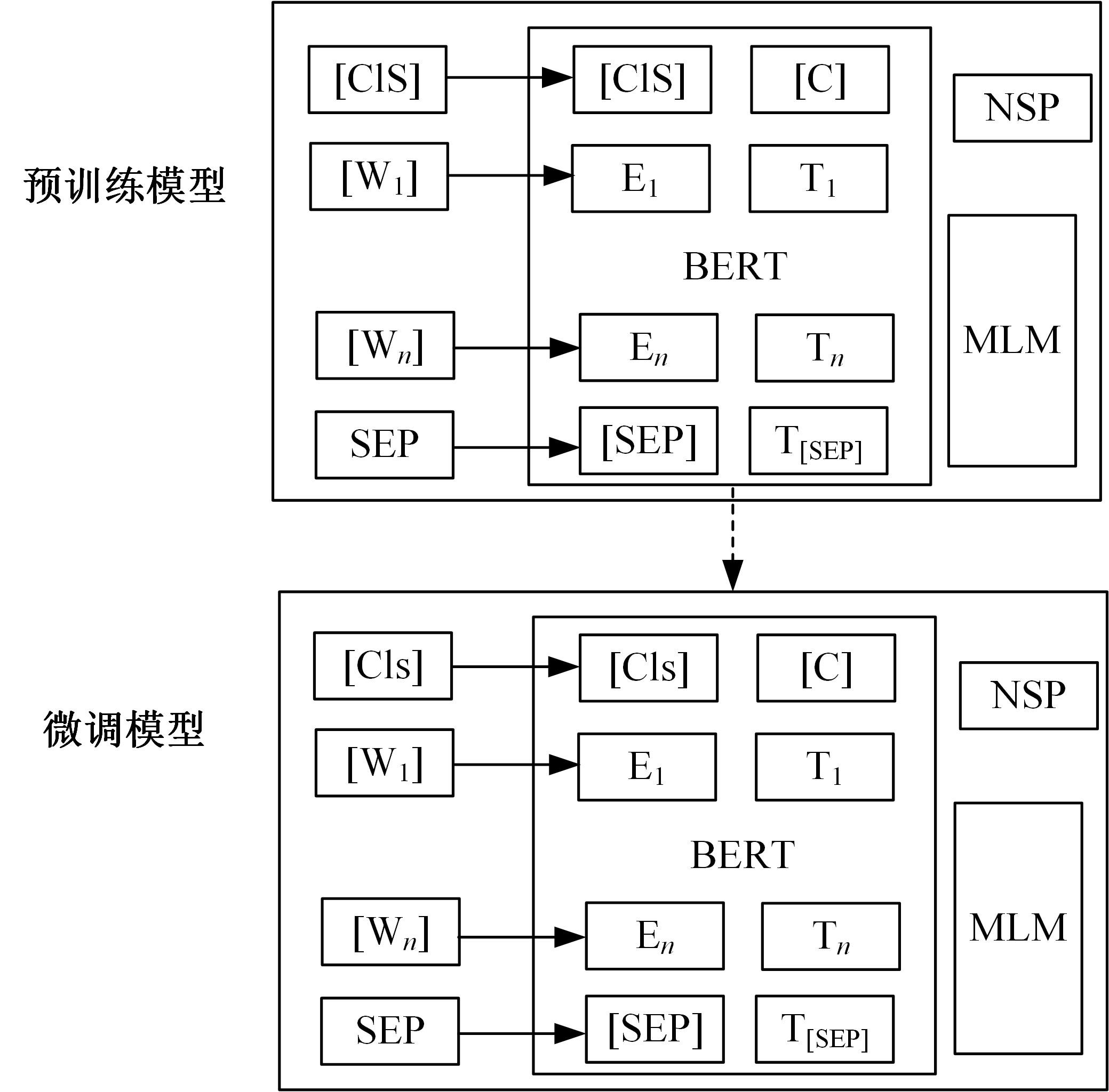
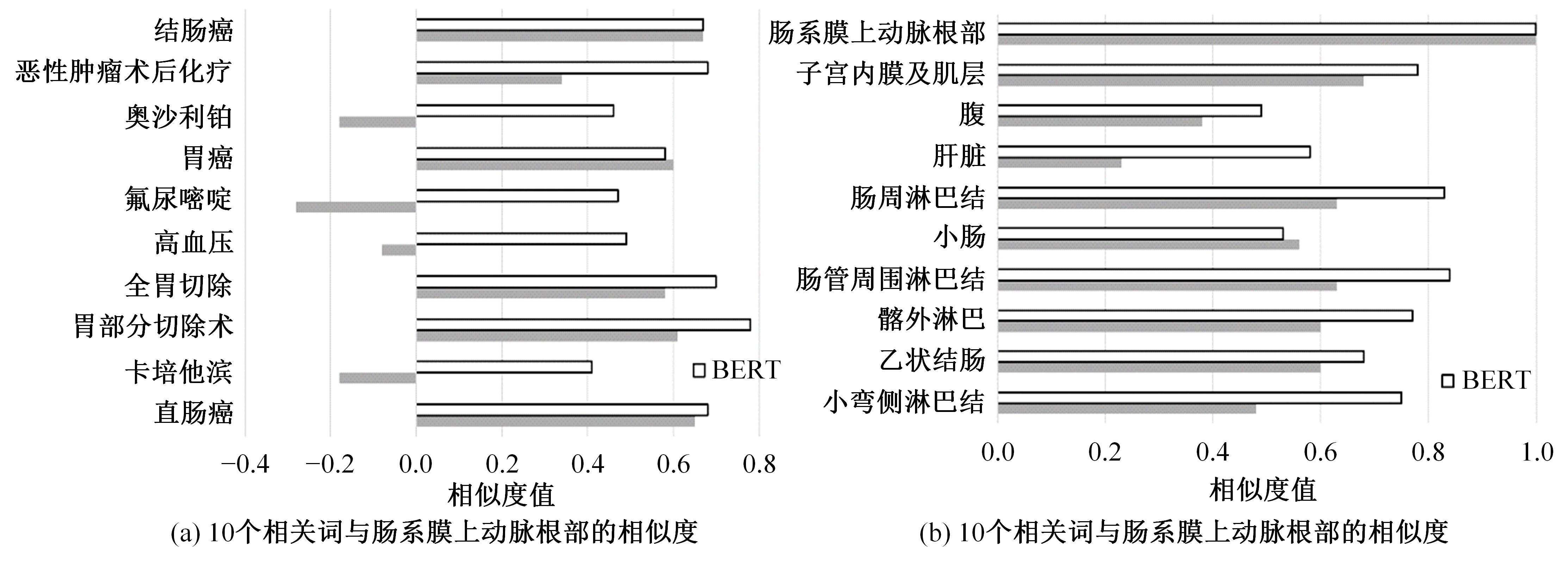
针对在生物医学领域中命名实体数据标注成本高、难以获取大量有标签数据的问题,提出了一个两阶段学习框架实现低资源下的中文生物医学命名实体识别。在第一阶段,利用Word2Vec和BERT为基础模型预训练并进行微调,获得特定领域的词向量表示;在第二阶段,将生成的词向量输入到由BiLSTM和条件随机场(Conditional random field,CRF)组成的神经网络中用于最终任务的训练。本文在Yidu-S4k数据集进行实验,结果表明本文算法在少量标签的情况下取得80.94%的准确率,具有较优性能。
中图分类号:
- TP391.1
| 1 | 何玉洁, 杜方, 史英杰, 等. 基于深度学习的命名实体识别研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021,7(11): 21-36. |
| He Yu-jie, Du Fang, Shi Ying-jie, et al. Review of named entity recognition based on deep learning[J]. Computer Engineering and Application, 2021,7(11): 21-36. | |
| 2 | Campos D, Matos S, Oliveira J L. Biomedical named entity recognition: a survey of machine-learning tools[J]. Theory and Applications for Advanced Text Mining, 2012, 11: 175-195. |
| 3 | Shen J, Wang X, Li S, et al. Exploiting rich features for Chinese named entity recognition[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering, Hangzhou, China, 2010: 278-282. |
| 4 | Soomro P D, Kumar S, Banbhrani A A S, et al. Bio-NER: biomedical named entity recognition using rulebased and statistical learners[J]. Int.J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl, 2017, 8: 163-170. |
| 5 | Durbin R, Eddy S R, Krogh A,et al. Biological sequence analysis: multiple sequence alignment methods[J/OL]. (2021-05-21). |
| 6 | Zhang Y, Wang X, Hou Z, et al. Clinical named entity recognition from Chinese electronic health records via machine learning methods (Preprint)[J]. JMIR Medical Informatics, 2018, 6(4): 30559093. |
| 7 | 燕杨, 文敦伟, 王云吉, 等. 基于层叠条件随机场的中文病历命名实体识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(6): 1843-1848. |
| Yan Yang, Wen Dun-wei, Wang Yun-ji, et al. Named entity recognition in Chinese medical records based on cascaded conditional random field[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1843-1848. | |
| 8 | Leaman R, Lu Z. TaggerOne: joint named entity recognition and normalization with semi-Markov models[J]. Bioinformatics, 2016, 32(18): 2839-46. |
| 9 | 潘国巍, 吉久明, 李楠, 等. 基于两类统计机器学习模型的中文化学物质名称识别研究[J]. 现代情报, 2011, 31(11): 163-165. |
| Pan Guo-wei, Ji Jiu-ming, Li Nan, et al. Research on Chinese chemical substance name recognition based on two types of statistical machine learning models[J]. Modern Information, 2011, 31(11): 163-165. | |
| 10 | Cotterell R, Duh K. Low-resource named entity recognition with cross-lingual, character-level neural conditional random fields[C]//Proceedings of the Eighth International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, 2017: 91-96. |
| 11 | Feng X, Feng X, Qin B, et al. Improving low resource named entity recognition using cross-lingual knowledge transfer[C]∥Proceedings of the Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence Main track, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 4071-4077. |
| 12 | Yu H, Mao X L, Chi Z, et al. A robust and domain-adaptive approach for low-resource named entity recognition[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Knowledge Graph, 2020: 297-304. |
| 13 | Fries J, Wu S, Ratner A, et al. Swellshark: a generative model for biomedical named entity recognition without labeled data[J/OL]. arXiv Preprint arXiv:, 2017. |
| 14 | Liu A L, Du J F, Stoyanov V. Knowledge-augmented language model and its application to unsupervised namedentity recognition[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2019. |
| 15 | Shang J B, Liu L Y, Ren X, et al. Learning named entity tagger using domain-specific dictionary[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv:, 2018. |
| 16 | Xiao Z F. Towards a two-phase unsupervised system for cybersecurity concepts extraction[C]//13th International Conference on Natural Computation, Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery, Guilin, China, 2017: 2161-2168. |
| 17 | Ji B, Li S S, Yu J, et al. Research on Chinese medical named entity recognition based on collaborative cooperation of multiple neural network models[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2020, 104: 103395. |
| 18 | Zhao Q, Wang D, Li J Q, et al. Exploiting the concept level feature for enhanced name entity recognition in Chinese EMRs[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2020, 76: 63991-6420. |
| 19 | Wang Q, Zhou Y M, Ruan T, et al. Incorporating dictionaries into deep neural networks for the Chinese clinical named entity recognition[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2019, 92: 103133. |
| 20 | 郭晓然, 罗平, 王维兰. 基于Transformer编码器的中文命名实体识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(3): 989-995. |
| Guo Xiao-ran, Luo Ping, Wang Wei-lan. Chinese named entity recognition based on Transformer encoder[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 989-995. | |
| 21 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K, et al. Bert: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[OL]. arXiv Preprint arXiv:, 2018. |
| 22 | Mikolov T, Chen K, Corrado G, et al. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space[OL]. arXiv Preprint arXiv:, 2013. |
| 23 | Lample G, Ballesteros M, Subramanian S, et al. Neural architectures for named entity recognition[J]. arXiv Preprint arXiv:, 2016. |
| 24 | Matthew E P, Mark N, Mohit I, et al. Deep contextualized word representations[OL]. arXiv Preprint arXiv:, 2018. |
| 25 | Zhang S, Zhang X, Wang H, et al. Multi-scale attentive interaction networks for chinese medical question answer selection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 74061-74071. |
| [1] | 赵亚慧,李飞雨,崔荣一,金国哲,张振国,李德,金小峰. 基于跨语言预训练模型的朝汉翻译质量评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [2] | 王连明,吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [3] | 张则强,梁巍,谢梦柯,郑红斌. 混流双边拆卸线平衡问题的精英差分进化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1297-1304. |
| [4] | 李健,熊琦,胡雅婷,刘孔宇. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [5] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [6] | 刘培勇,董洁,谢罗峰,朱杨洋,殷国富. 基于多支路卷积神经网络的磁瓦表面缺陷检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1449-1457. |
| [7] | 姜宇,潘家铮,陈何淮,符凌智,齐红. 基于分割方法的繁体中文报纸文本检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1146-1154. |
| [8] | 于鹏,朴燕. 基于多尺度特征的行人重识别属性提取新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1155-1162. |
| [9] | 潘弘洋,刘昭,杨波,孙庚,刘衍珩. 基于新一代通信技术的无人机系统群体智能方法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 629-642. |
| [10] | 何颖,樊俊松,王巍,孙庚,刘衍珩. 无人机空地安全通信与航迹规划的多目标联合优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 913-922. |
| [11] | 吴振宇,刘小飞,王义普. 基于DKRRT*-APF算法的无人系统轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 781-791. |
| [12] | 陶博,颜伏伍,尹智帅,武冬梅. 基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 802-809. |
| [13] | 薛珊,张亚亮,吕琼莹,曹国华. 复杂背景下的反无人机系统目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 891-901. |
| [14] | 祁贤雨,王巍,王琳,赵玉飞,董彦鹏. 基于物体语义栅格地图的语义拓扑地图构建方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 569-575. |
| [15] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
|
||