吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (11): 3238-3245.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220007
基于混合特征的特征选择神经肽预测模型
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 软件学院,长春 130012
A model for identifying neuropeptides by feature selection based on hybrid features
Feng-feng ZHOU1( ),Zhen-wei YAN2
),Zhen-wei YAN2
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.College of Software,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
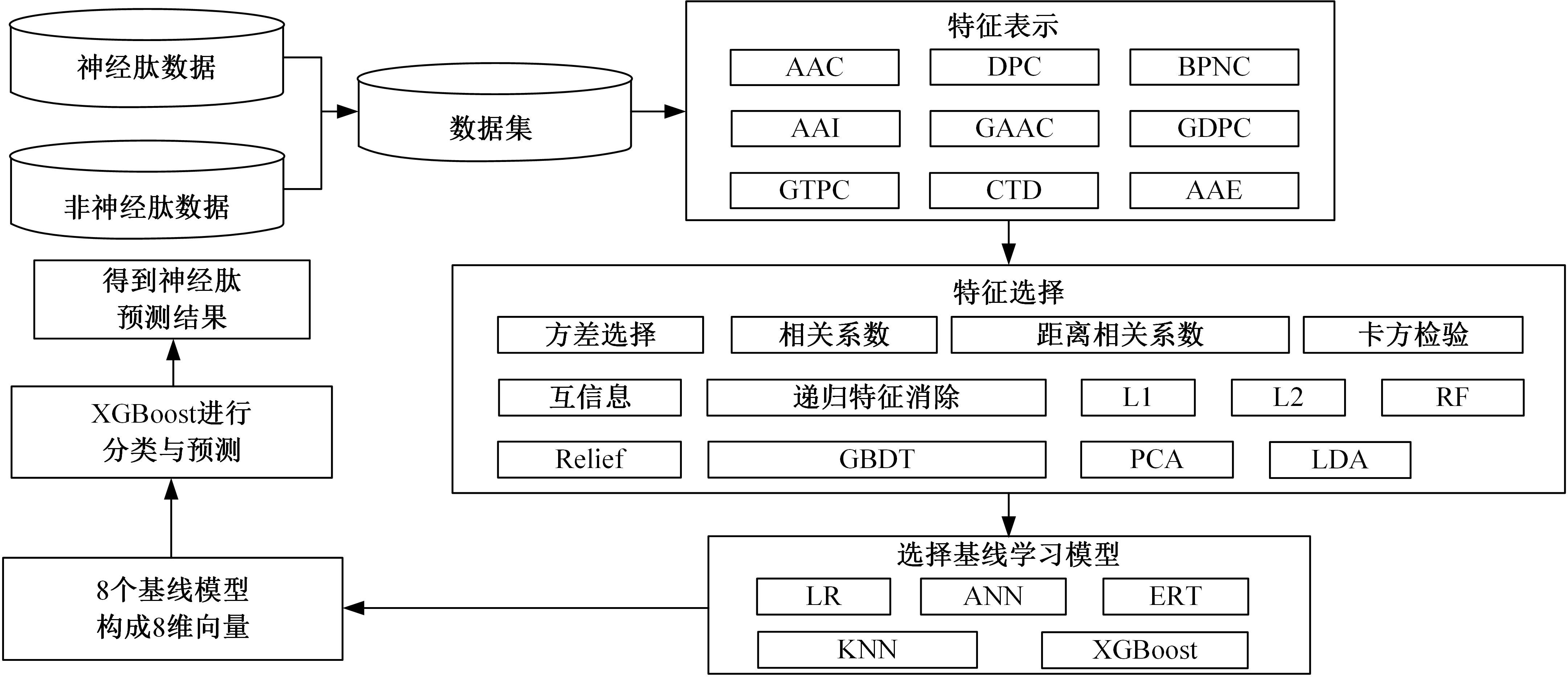
提出了一种神经肽预测集成算法。整合了9个特征描述符与5个机器学习算法,生成了45个基线学习模型。第一层对这45个基线模型进行特征选择;第二层根据基线模型对的准确度和皮尔森(Pearson)相关系数之和选择8个基本学习模型;第三层将这些学习者的输出输入到逻辑回归,极限梯度提升等分类器中进行最后一步的选择用以训练最终模型,并将输出作为最终预测结果。在测试数据集上的准确度为0.9169,高于现有的模型。
中图分类号:
- TP399
| 1 | 王莹. 基于机器学习的神经肽前体及其剪切位点的预测[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学生物科学与技术学院, 2021. |
| Wang Ying. Prediction of neuropeptide precursor and its cleavage site based on machine learning[D]. Chengdu: School of Life Science and Technology, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021. | |
| 2 | Bin Y N, Zhang W, Tang W D, et al. Prediction of neuropeptides from sequence information using ensemble classifier and hybrid features[J]. Journal of Proteome Research, 2020, 19(9): 3732-3740. |
| 3 | Hayakawa E, Watanabe H, Menschaert G, et al. A combined strategy of neuropeptide prediction and tandem mass spectrometry identifies evolutionarily conserved ancient neuropeptides in the sea anemone Nematostella vectensis[J]. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14(9): 0215185. |
| 4 | Manayalan B, Basith S, Shin T H, et al. mAHTPred: a sequence-based meta-predictor for improving the prediction of anti-hypertensive peptides using effective feature representation[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(16): 2757-2765. |
| 5 | Akbar S, Hayat M, Iqbal M, et al. iACP-GAEnsC: evolutionary genetic algorithm based ensemble classification of anticancer peptides by utilizing hybrid feature space[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2017, 79: 62-70. |
| 6 | Karsenty S, Rappoport N, Ofer D, et al. NeuroPID: a classifier of neuropeptide precursors[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(1): 182-186. |
| 7 | Kang J J, Fang Y W, Yap P C, et al. NeuroPP: a tool for the prediction of neuropeptide precursors based on optimal sequence composition[J]. Interdisciplinary Sciences-Computational Life Sciences, 2019, 11(1): 108-114. |
| 8 | Agrawal P, Kumar S, Singh A, et al. NeuroPIpred: a tool to predict, design and scan insect neuropeptides[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 20195129. |
| 9 | Cheng N, Li M L, Zhao L, et al. Comparison and integration of computational methods for deleterious synonymous mutation prediction[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2020, 21(3): 970-981. |
| 10 | Wang Y, Wang M X, Yin S W, et al. NeuroPep: a comprehensive resource of neuropeptides[J]. Database-the Journal of Biological Databases and Curation, 2015, 2015: 25931458. |
| 11 | Matallana-Surget S, Chang R L, Chan A. Protein structure, amino acid composition and sequence determine proteome vulnerability to oxidation-induced damage[J]. The EMBO Journal, 2020, 39(23): 33073387. |
| 12 | Petrilli P. Classification of protein sequences by their dipeptide composition[J]. Computer Application in the Biosciences, 1993, 9(2): 205-209. |
| 13 | Kawashima S, Pokarowski P, Pokarowska M, et al. AAindex: amino acid index database, progress report 2008[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2008, 36: 202-205. |
| 14 | Ken N, Yasushi K, Tatsuo O. Classification of proteins into groups based on amino acid composition and other characters. II. grouping into four types[J]. Journal of Biochemistry, 1983, 94(3): 997-1007. |
| 15 | Lee T Y, Lin Z Q, Hsieh S J, et al. Exploiting maximal dependence decomposition to identify conserved motifs from a group of aligned signal sequences[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(13): 1780-1787. |
| 16 | Yang L W, Gao H, Wu K Y, et al. Identification of cancerlectins by using cascade linear discriminant analysis and optimal g-gap tripeptide composition[J]. Current Bioinformatics, 2020, 15(6): 528-537. |
| 17 | Xia J F, Zhao X M, Huang D S. Predicting protein-protein interactions from protein sequences using meta predictor[J]. Amino Acids, 2010, 39(5): 1595-1599. |
| 18 | 施启军, 潘峰, 龙福海, 等. 特征选择方法研究综述[J]. 微电子学与计算机, 2022, 39(3): 1-8. |
| Shi Qi-jun, Pan Feng, Long Fu-hai, et al. Summary of research on feature selection methods[J]. Microelectronics & Computer, 2022, 39(3): 1-8. | |
| 19 | 吴璐. 基于SVM-RFE特征选择的规则提取方法[J]. 微型电脑应用, 2021, 37(9): 150-154. |
| Wu Lu. Rule extraction method based on SVM-RFE feature selection[J]. Microcomputer Application, 2021, 37(9): 150-154. | |
| 20 | 赵若宇. Lasso及其相关优化模型在临床预测中的应用[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学数学科学学院, 2021. |
| Zhao Ruo-yu, Lasso and its related optimization models in clinical prediction[D]. Dalian: School of Mathematical Science, Dalian University of Technology, 2021. | |
| 21 | 张保华, 黄文倩, 李江波, 等. 基于I-RELIEF和SVM的畸形马铃薯在线分选[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2014, 44(6): 1811-1817. |
| Zhang Bao-hua, Huang Wen-qian, Li Jiang-bo,et al. Online sorting of irregular potatoes based on I-RELIEF and SVM method[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2014,44(6): 1811-1817. | |
| 22 | 杨玉玲. 特征选择与集成方法的研究及应用[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学数学与统计学院, 2021. |
| Yang Yu-ling. Research on feature selection and integration method and it's applications[D]. Lanzhou: School of mathematics and statistics, Lanzhou University, 2021. | |
| 23 | 曲铭. 基于集成学习特征选择的新闻流行度预测研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学中泰证券金融研究院, 2021. |
| Qu Ming. Research on news popularity prediction based on ensemble learning feature selection[D]. Jinan: Zhongtai Securities Finance Research Institute, Shandong University, 2021. | |
| 24 | 王斌, 何丙辉, 林娜, 等. 基于随机森林特征选择的茶园遥感提取[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(7): 1719-1732. |
| Wang Bin, He Bing-hui, Lin Na, et al. Tea plantation remote sensing extraction based on random forest[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1719-1732. | |
| 25 | Tang J J, Liang J, Han C Y, et al. Crash injury severity analysis using a two-layer Stacking framework[J]. Accident Analysis and Prevention, 2019, 122: 226-238. |
| [1] | 耿庆田,刘植,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [2] | 薛珊,张亚亮,吕琼莹,曹国华. 复杂背景下的反无人机系统目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 891-901. |
| [3] | 潘恒彦,张文会,梁婷婷,彭志鹏,高维,王永岗. 基于MIMIC与机器学习的出租车驾驶员交通事故诱因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 457-467. |
| [4] | 时小虎,吴佳琦,吴春国,程石,翁小辉,常志勇. 基于残差网络的弯道增强车道线检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 584-592. |
| [5] | 耿庆田,赵杨,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于注意力机制的LSTM和ARIMA集成方法在土壤温度中应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2973-2981. |
| [6] | 郭辉,付接递,李振东,严岩,李虓. 基于改进鲸鱼算法优化SVM参数和特征选择[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2952-2963. |
| [7] | 朱冰,李紫薇,李奇. 基于改进SegNet的遥感图像建筑物分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 248-254. |
| [8] | 王俊杰,农元君,张立特,翟佩臣. 基于施工场景的视觉关系检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 226-233. |
| [9] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [10] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [11] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [12] | 李佩泽,赵世舜,翁小辉,蒋鑫妹,崔洪博,乔建磊,常志勇. 基于多传感器优化的农药残留快速检测新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1951-1956. |
| [13] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [14] | 王斌,何丙辉,林娜,王伟,李天阳. 基于随机森林特征选择的茶园遥感提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1719-1732. |
| [15] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
|