吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 912-924.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230569
奥氏体不锈钢在单调和循环加载下的力学性能
颜建煌1( ),王志勇2,汤恩宏3,韩雪4,李海锋1(
),王志勇2,汤恩宏3,韩雪4,李海锋1( ),姜子钦5
),姜子钦5
- 1.华侨大学 土木工程学院,福建 厦门 361021
2.漳州城投设计咨询集团有限公司,福建 漳州 363007
3.福建宏昌建设集团有限公司,福建 龙岩 364030
4.厦门工学院 建筑科学与土木工程学院,福建 厦门 361021
5.北京工业大学 建筑工程学院,北京 100124
Mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steels under monotonic and cyclic loading
Jian-huang YAN1( ),Zhi-yong WANG2,En-hong TANG3,Xue HAN4,Hai-feng LI1(
),Zhi-yong WANG2,En-hong TANG3,Xue HAN4,Hai-feng LI1( ),Zi-qin JIANG5
),Zi-qin JIANG5
- 1.College of Civil Engineering,Huaqiao University,Xiamen 361021,China
2.Zhangzhou City Investment Design Consulting Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Zhangzhou 363007,China
3.Fujian Hongchang Construction Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Longyan 364030,China
4.School of Architecture and Civil Engineering,Xiamen Institute of Technology,Xiamen 361021,China
5.College of Architecture and Civil Engineering,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
摘要:
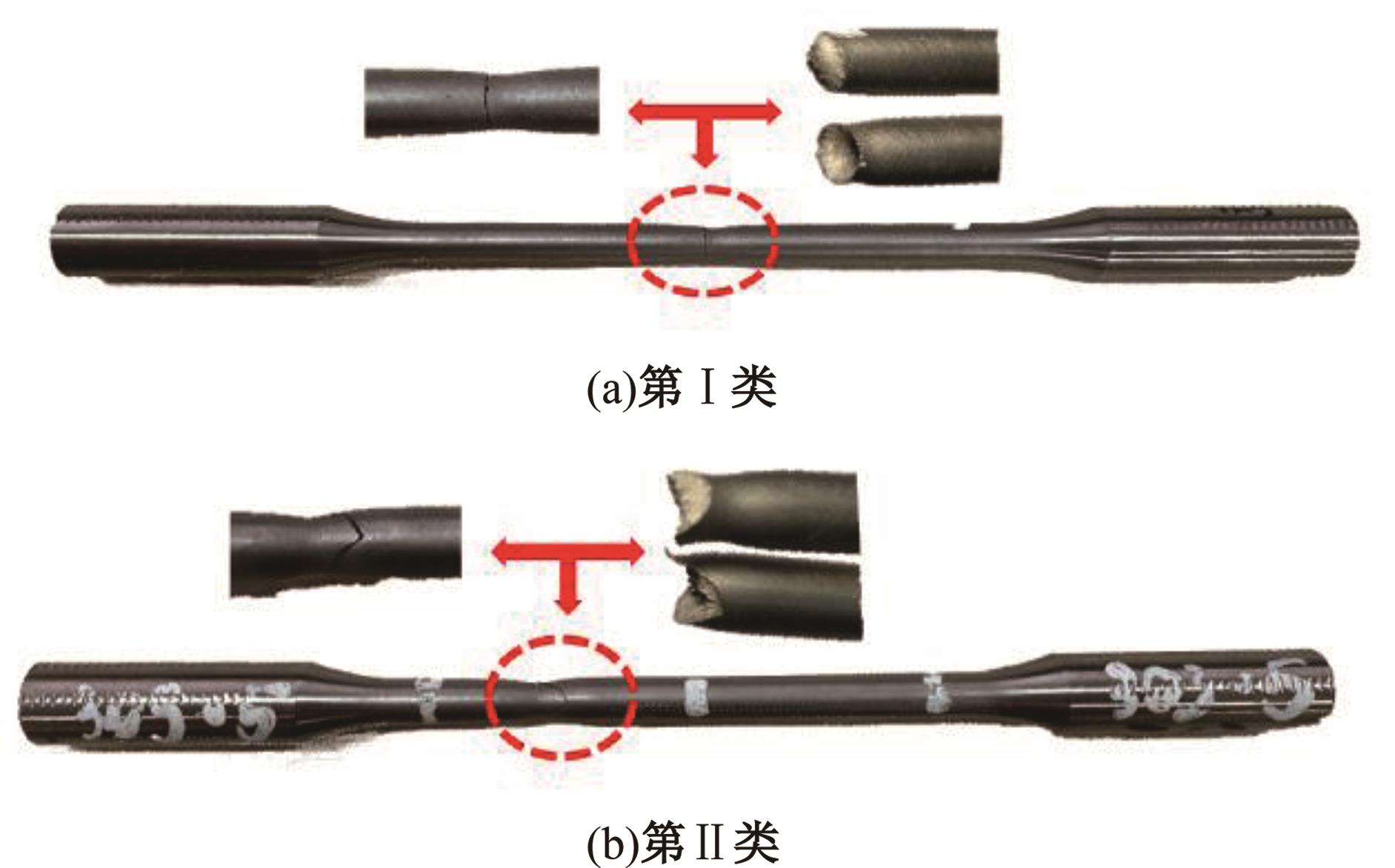
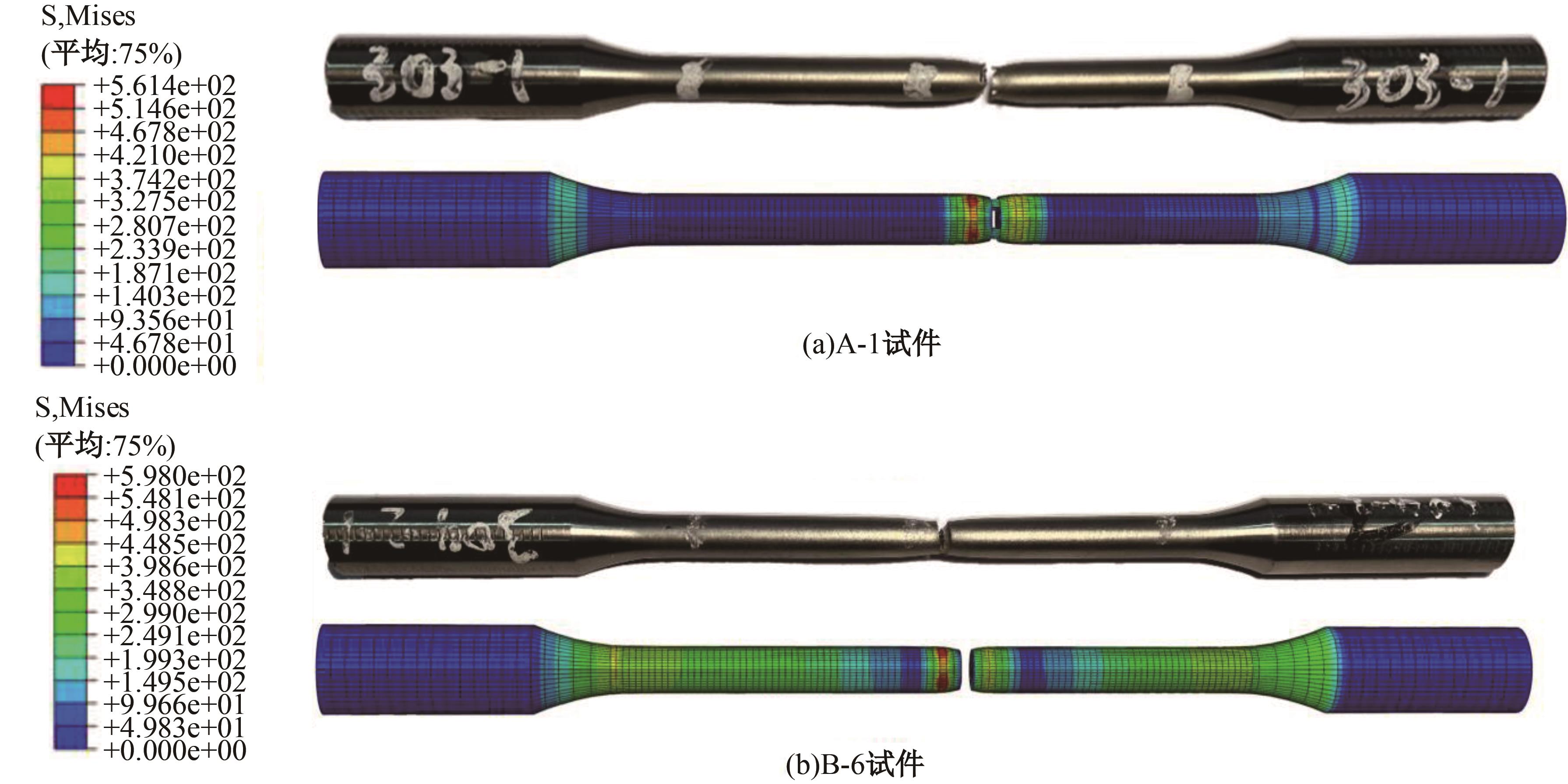
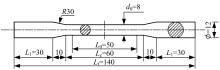
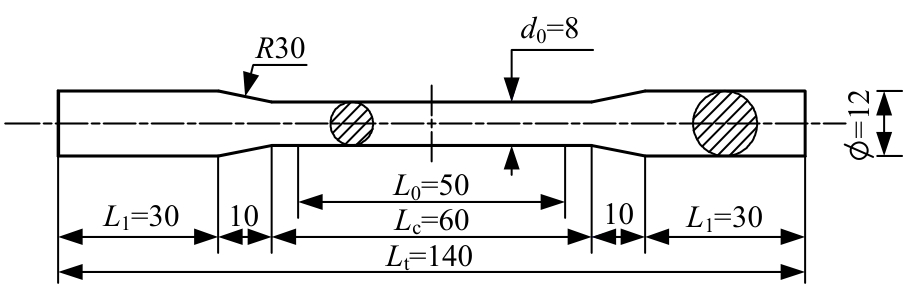
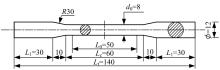
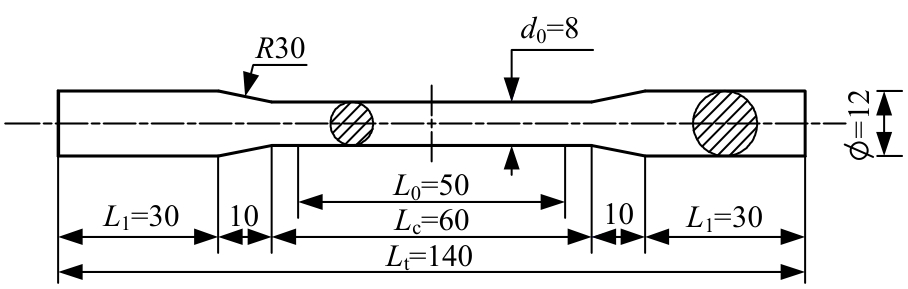
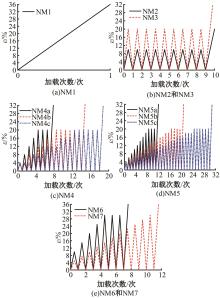
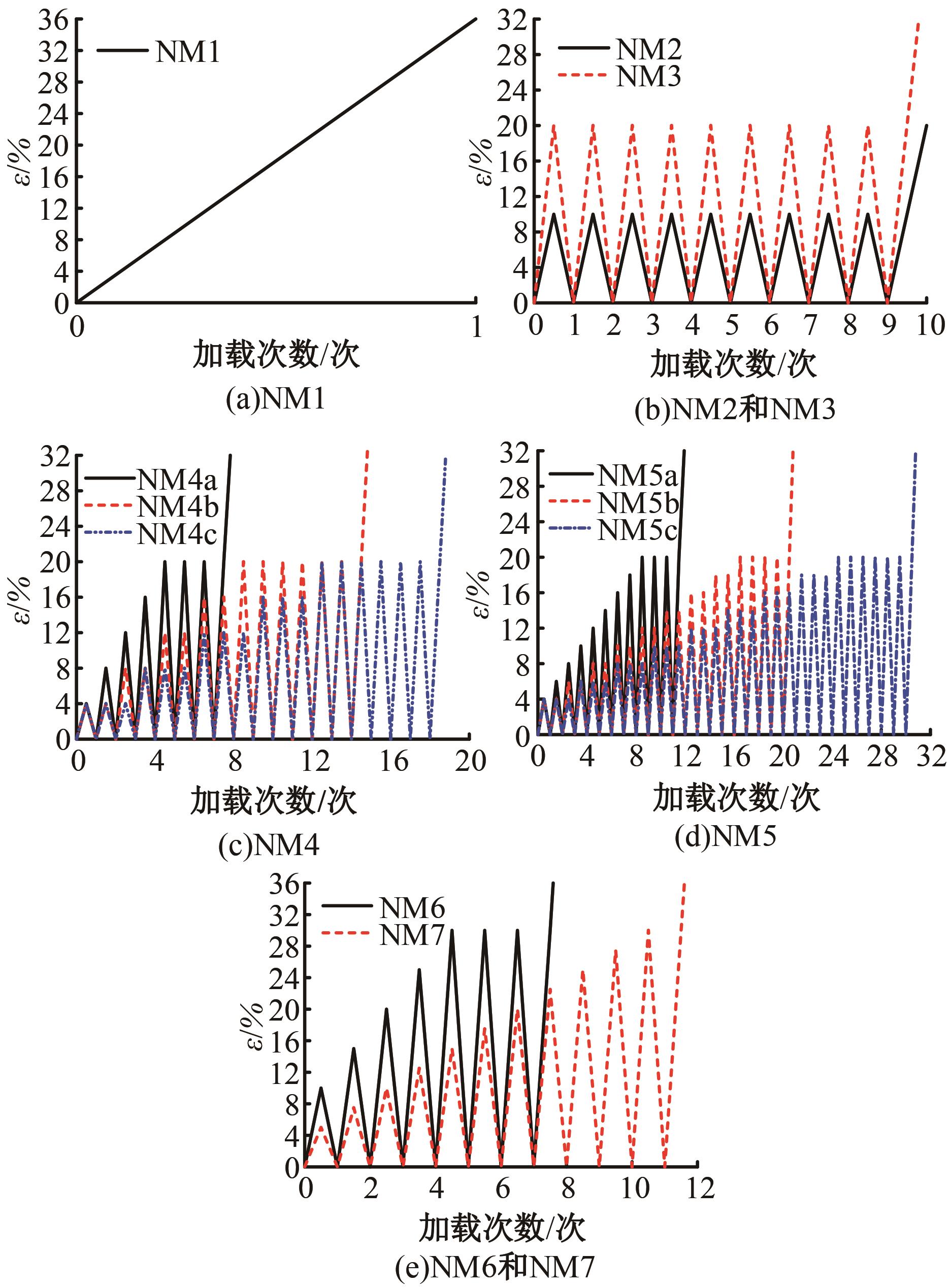
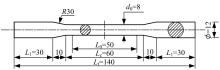
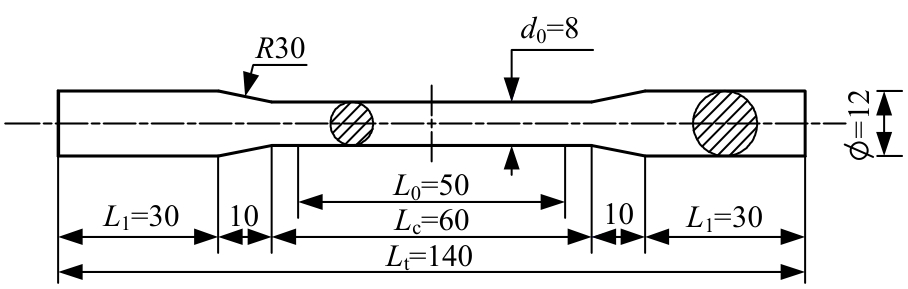
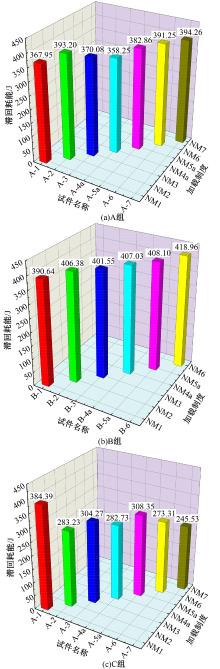
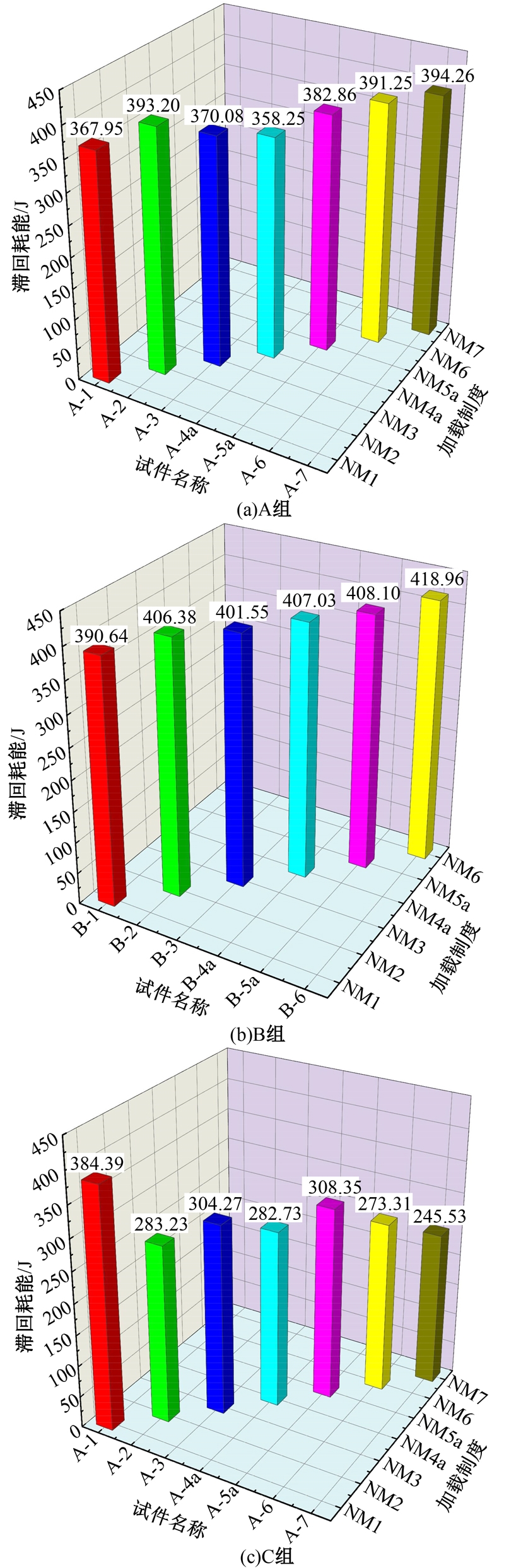
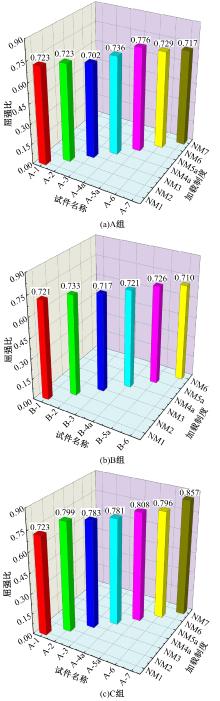
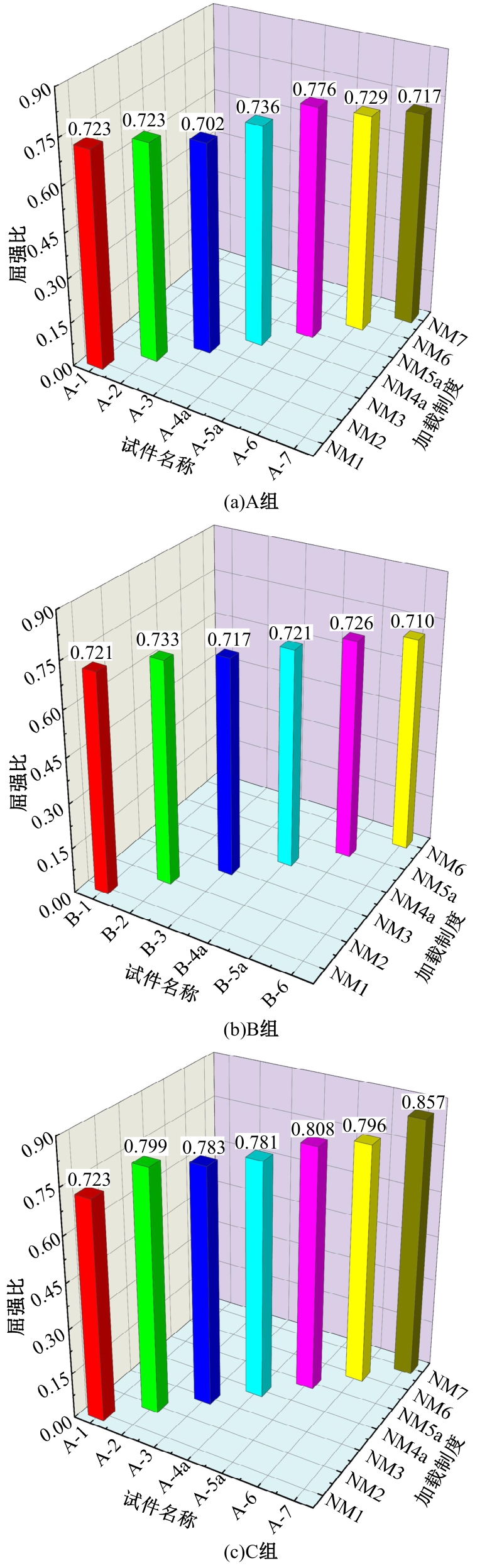
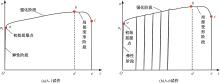
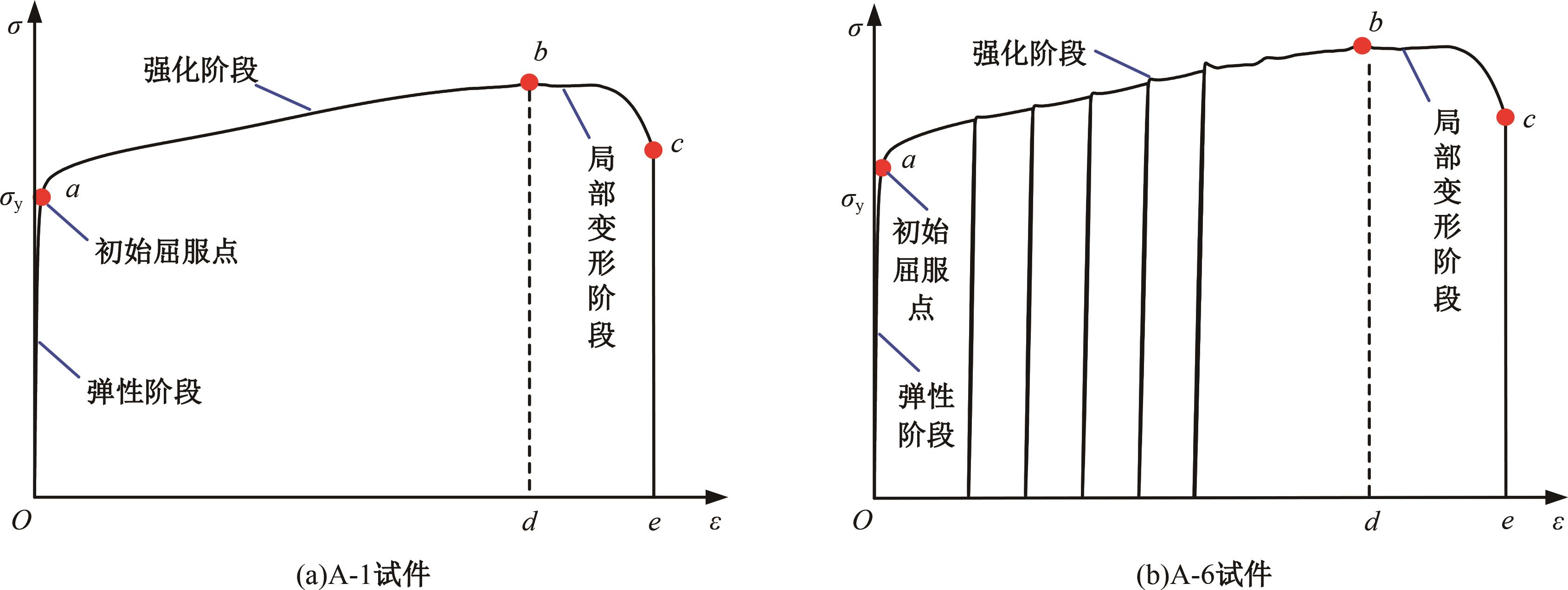
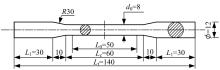
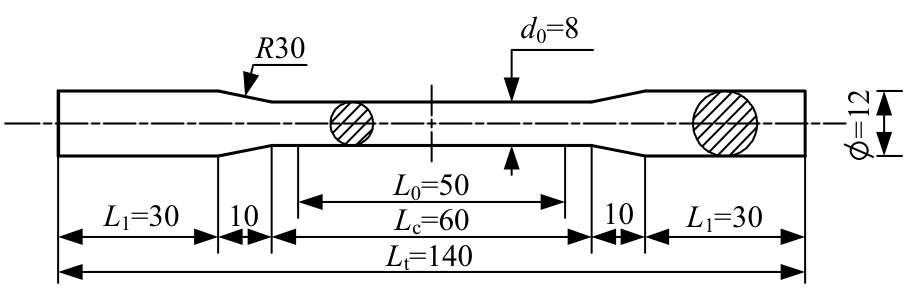
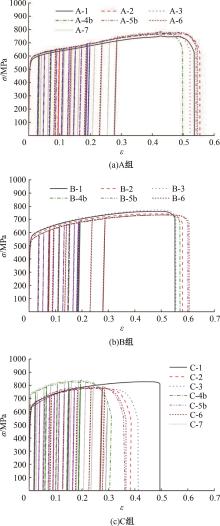
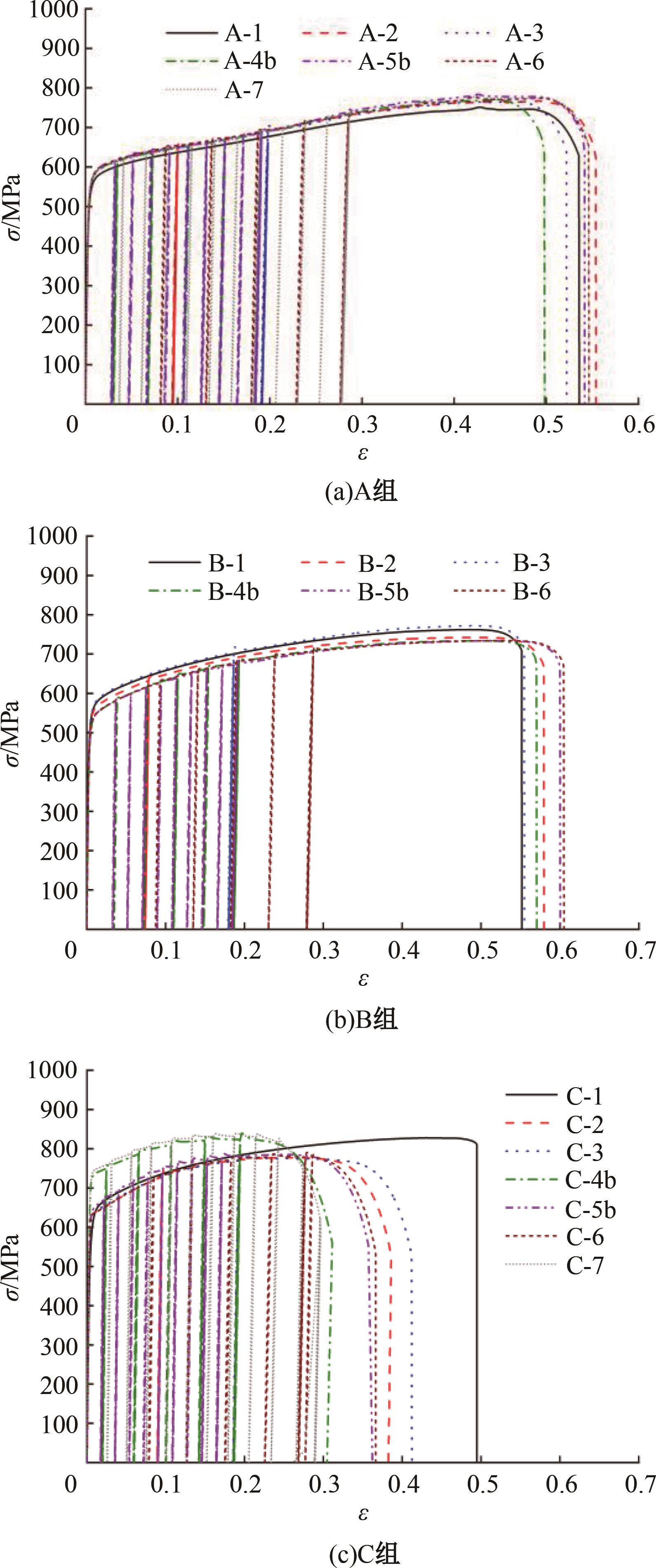
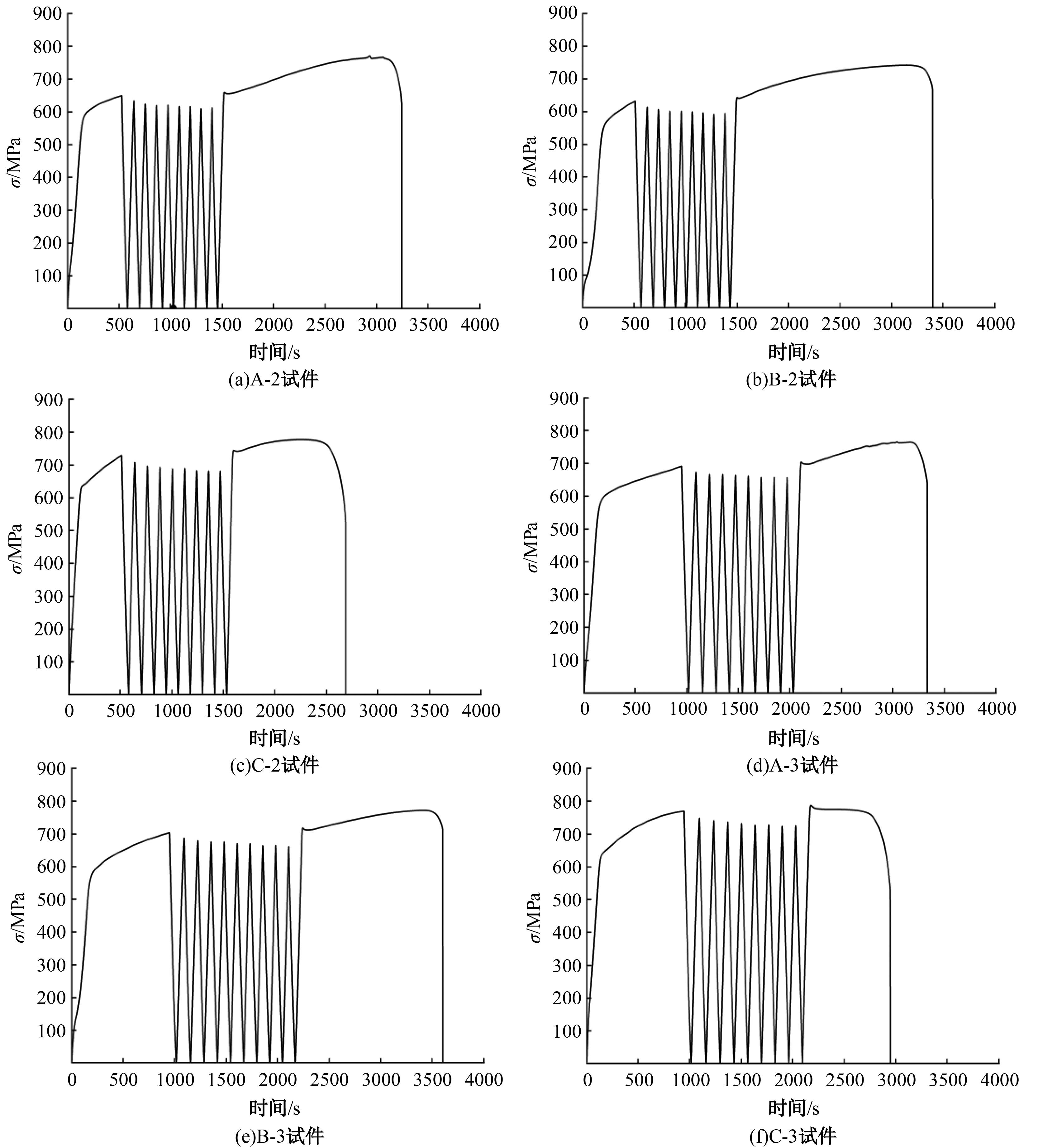
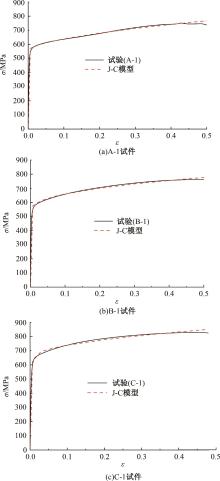
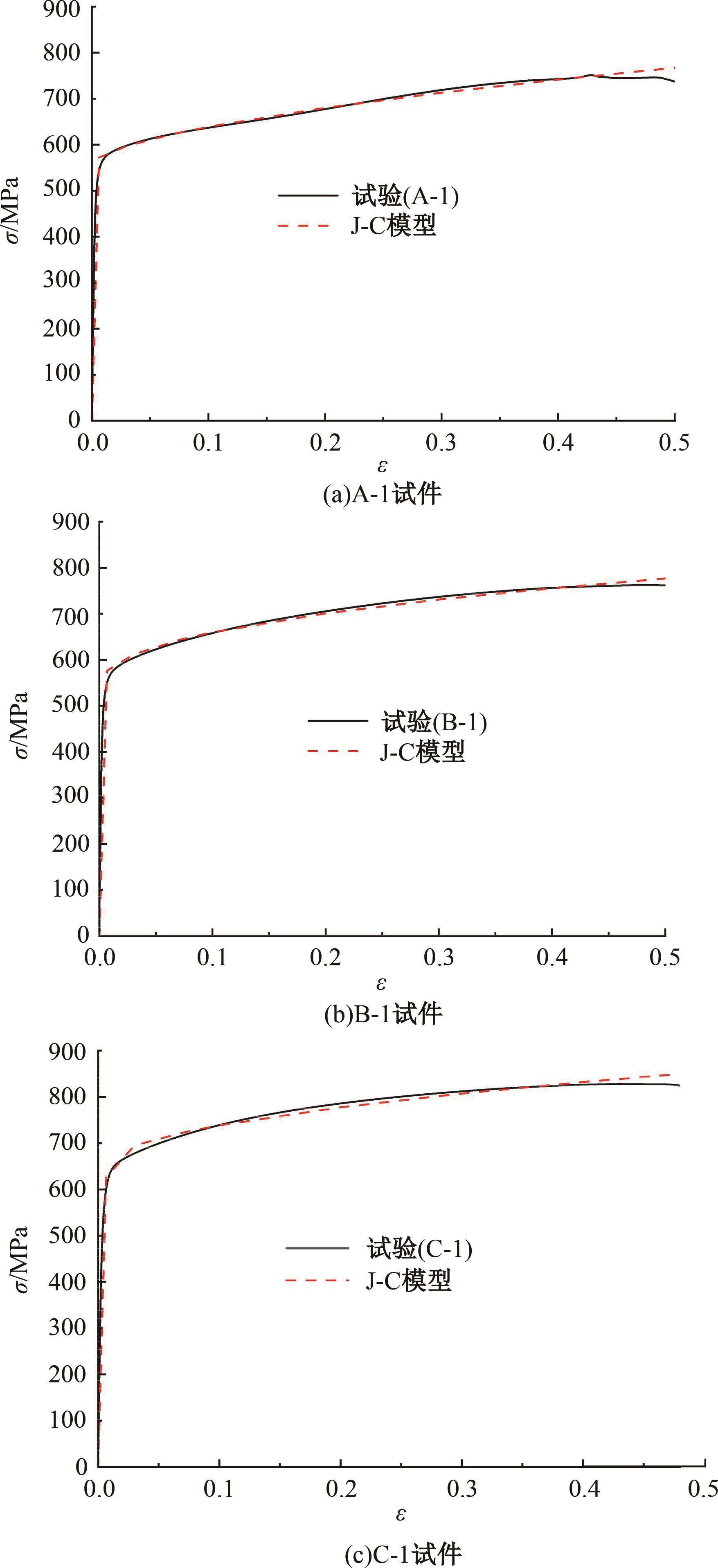
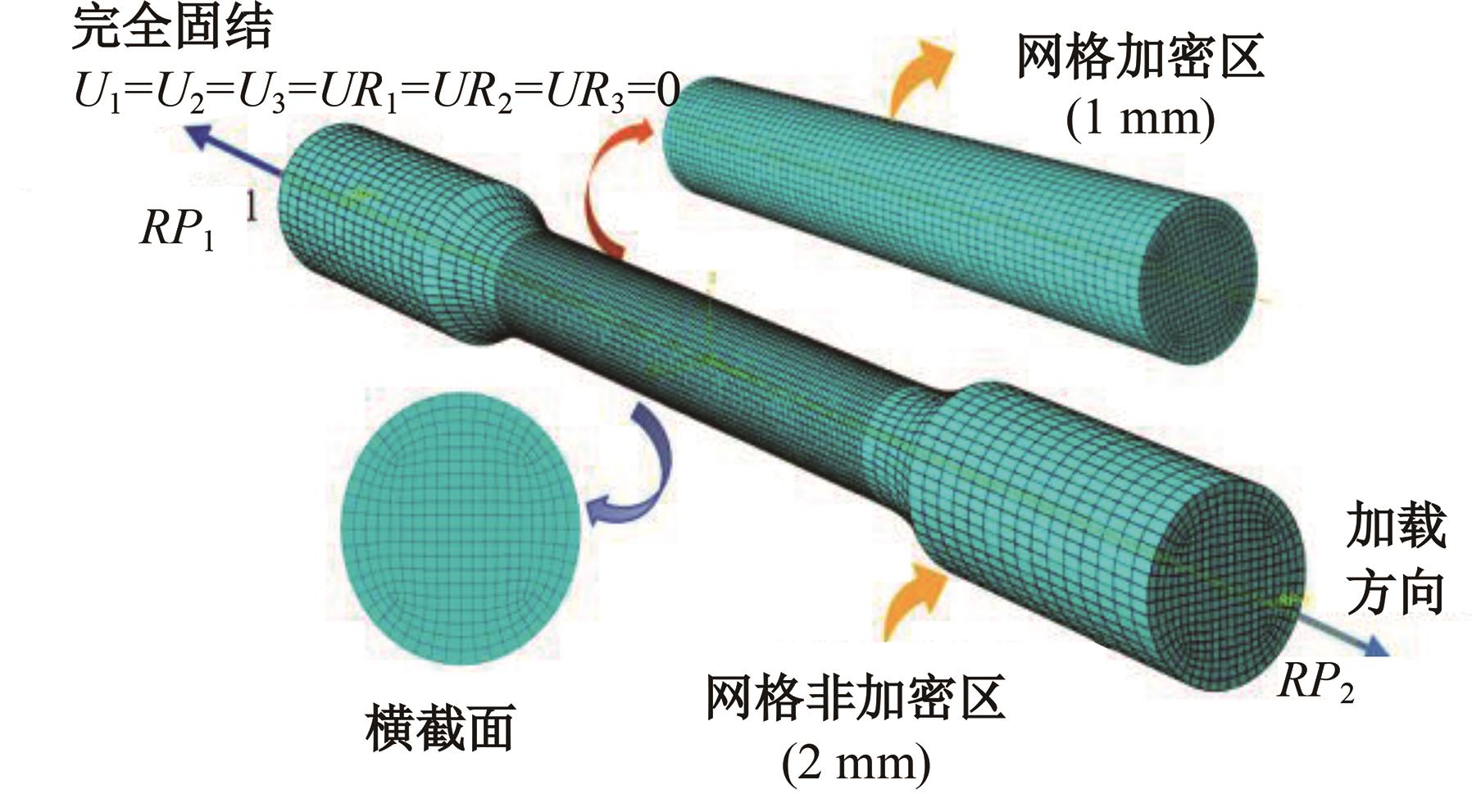
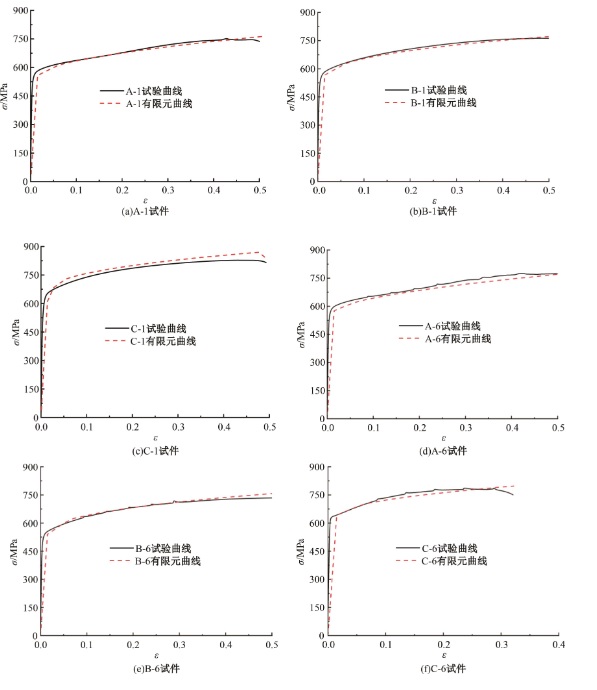
为促进奥氏体不锈钢在结构体系中应用,需要明确奥氏体不锈钢材料的力学性能。以材料类型和加载制度为变量,对33根棒状试件进行试验测试,获得了应力-应变曲线、应力-时间曲线以及骨架曲线,探讨了屈强比、滞回耗能和断后伸长率等力学性能指标的影响规律。在此基础上,拟合得出Johnson-Cook模型(J-C模型)的参数值,并采用ABAQUS软件建立了奥氏体不锈钢试件的有限元模型,数值模拟结果与试验结果吻合较好,验证了有限元建模方法的准确性以及J-C模型的适用性。试验结果表明:奥氏体不锈钢试件的应力-应变曲线具有显著的非线性特征,均有弹性阶段、强化阶段以及局部变形阶段,但没有明显的屈服平台;316型号奥氏体不锈钢试件在循环加载下的屈强比达到了0.857,滞回耗能和断后伸长率明显下降,其塑性变形能力逐渐减弱;303、304型号奥氏体不锈钢试件在单调和循环加载下的屈强比、滞回耗能以及断后伸长率等力学性能指标较为接近,二者具有良好的塑性变形能力。
中图分类号:
- TU391
| 1 | 郑宝锋, 舒赣平, 沈晓明. 不锈钢材料常温力学性能试验研究[J]. 钢结构, 2011, 26(5): 1-6, 55. |
| Zheng Bao-feng, Shu Gan-ping, Shen Xiao-ming. Experimental study on material properties of stainless steel at room temperature[J]. Steel Construction (Chinese & English), 2011, 26(5): 1-6, 55. | |
| 2 | 陈乐, 何琨, 梁波, 等. 316不锈钢室温和350 ℃低周疲劳性能研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2017, 38(3): 51-55. |
| Chen Le, He Kun, Liang Bo, et al. Study on low-cycle fatigue property of 316 stainless steel at room temperature and 350 ℃[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2017, 38(3): 51-55. | |
| 3 | 王文权, 王岩新, 王洪潇, 等. SUS301L不锈钢激光焊缝缺陷修复工艺[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2022, 52(1): 79-90. |
| Wang Wen-quan, Wang Yan-xin, Wang Hong-xiao, et al. Defects repair technology of SUS301L stainless steel laser weld[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(1): 79-90. | |
| 4 | 景强, 方翔, 倪静姁, 等. 2304不锈钢钢筋在港珠澳大桥的应用——钢筋耐蚀性能研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2017, 34(10): 51-56. |
| Jing Qiang, Fang Xiang, Ni Jing-ye, et al. Use of 2304 stainless steel reinforcement in Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau bridge—Corrsion behaviors of 2304 stainless steel reinforcement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2017, 34(10): 51-56. | |
| 5 | Morgenthal G, Sham R, West B. Engineering the tower and main span construction of stonecutters bridge[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2010, 15(2): 144-152. |
| 6 | Nakajima M, Uematsu Y, Kakiuchi T, et al. Effect of quantity of martensitic transformation on fatigue behavior in type 304 stainless steel[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 10(7): 299-304. |
| 7 | Lee W S, Lin R F, Chen R H, et al. Effects of prestrain on high temperature impact properties of 304L stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2010, 25(4): 754-763. |
| 8 | 刘俭辉, 王生楠, 韦尧兵, 等. 304不锈钢低周疲劳断裂特性的研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2013(17): 84-88. |
| Liu Jian-hui, Wang Sheng-nan, Wei Yao-bing, et al. Study on low cycle fatigue fracture properties of 304 stainless steel[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 437(17): 84-88. | |
| 9 | 姜公锋, 孙亮, 陈钢. 304不锈钢应变强化疲劳寿命的试验研究[J]. 机械强度, 2014, 36(6): 850-855. |
| Jiang Gong-feng, Sun Liang, Chen Gang. Experimental study of 304 stainless steel fatigue life considering material pre-strain hardening effect[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2014, 36(6): 850-855. | |
| 10 | Zhou F, Li L. Experimental study on hysteretic behavior of structural stainless steels under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2016, 122(7): 94-109. |
| 11 | 钟巍华, 鱼滨涛, 佟振峰, 等. 国产316LN不锈钢的室温低周疲劳行为研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(8): 66-68, 73. |
| Zhong Wei-hua, Yu Bin-tao, Tong Zhen-feng, et al. Research on low cycle fatigue behavior of domestic 316LN stainless steel at room temperature[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2017, 46(8): 66-68, 73. | |
| 12 | Hasunuma S, Ogawa T. Crystal plasticity FEM analysis for variation of surface morphology under low cycle fatigue condition of austenitic stainless steel[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2019, 127(10): 488-499. |
| 13 | 王元清, 常婷, 石永久. 循环荷载下奥氏体不锈钢的本构关系试验研究[J]. 东南大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 42(6): 1175-1179. |
| Wang Yuan-qing, Chang Ting, Shi Yong-jiu. Experimental study on constitutive relationship in austenitic stainless steel under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 42(6): 1175-1179. | |
| 14 | 王萌, 杨维国, 王元清, 等. 奥氏体不锈钢滞回本构模型研究[J]. 工程力学, 2015, 32(11): 107-114. |
| Wang Meng, Yang Wei-guo, Wang Yuan-qing, et al. Study on hysteretic constitutive model of austenitic stainless steel[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2015, 32(11): 107-114. | |
| 15 | Obunai K, Kawase K, Fukuta T, et al. Low cycle fatigue life estimation of stainless steel[J]. Advanced Experimental Mechanics, 2018, 3(1): 152-156. |
| 16 | Abarkan I, Shamass R, Achegaf Z, et al. Numerical and analytical studies of low cycle fatigue behavior of 316 LN austenitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 2020, 144(6): No.061507. |
| 17 | 孙治国, 杨葆洋, 张震威, 等. 循环荷载下不锈钢力学性能建模方法[J]. 地震工程学报, 2022, 44(4): 759-767. |
| Sun Zhi-guo, Yang Bao-yang, Zhang Zhen-wei, et al. Modeling method for mechanical behavior of stainless steel under cyclic loading[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2022, 44(4): 759-767. | |
| 18 | . 金属材料拉伸试验第1部分: 室温试验方法 [S]. |
| 19 | . 钢结构设计标准 [S]. |
| 20 | Koplik J, Needleman A. Void growth and coalescence in porous plastic solids[J]. International Journal of Solids & Structures, 1988, 24(8): 835-853. |
| 21 | Johnson G R, Cook W H. A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1983, 21: 541-548. |
| 22 | 李云飞, 曾祥国, 盛鹰, 等. 基于实验的钛合金优化动态本构模型与有限元模拟[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(24): 137-142. |
| Li Yun-fei, Zeng Xiang-guo, Sheng Ying, et al. An optimal dynamic constitutive modeling of titanium alloy and FE simulation[J]. Materials Reports, 2016, 30(24): 137-142. |
| [1] | 刁延松,任义建,杨元强,赵凌云,刘秀丽,刘芸. 带有摩擦耗能组件的可更换钢梁柱拼接节点抗震性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1643-1656. |
| [2] | 刘一凡,缪志伟,申晨,耿祥东. 基于蒙特卡罗法的不均匀锈蚀钢筋力学性能评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1007-1015. |
| [3] | 许良,边钰博,周松,肖景厚. 高温水浸对T800/环氧树脂基复合材料性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1943-1950. |
| [4] | 王卫华,朱勇斌,祁神军,霍静思,郭秀泉,钟振安. 摩擦耗能型翼缘削弱式钢梁连接的承载性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1400-1410. |
| [5] | 魏丽丽,胡明玉. 砂浆碱集料反应细观数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3501-3507. |
| [6] | 匡亚川,宋哲轩,刘胤虎,莫小飞,伏亮明,罗时权. 新型装配式双舱综合管廊力学性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 596-603. |
| [7] | 魏海斌,王相焱,王富玉,张勇. 基于振动成型AC-25沥青混合料力学性能及细观分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1269-1276. |
| [8] | 程永春,李赫,李立顶,王海涛,白云硕,柴潮. 基于灰色关联度的矿料对沥青混合料力学性能的影响分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 925-935. |
| [9] | 刘寒冰,高鑫,宫亚峰,刘诗琪,李文俊. 表面处理对玄武岩纤维活性粉末混凝土力学性能的影响及断裂特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 936-945. |
| [10] | 张广泰,张路杨,邢国华,曹银龙,易宝. 钢-聚丙烯混杂纤维混凝土剪力墙抗震性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 946-955. |
| [11] | 向红亮,陈盛涛,邓丽萍,张伟,詹土生. 微合金化2205双相不锈钢组织及性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1645-1652. |
| [12] | 王金国,王志强,任帅,闫瑞芳,黄恺,郭劲. Ti添加量对球墨铸铁组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1653-1662. |
| [13] | 李明,王浩然,赵唯坚. 单向带抗剪键叠合板的受力性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 654-667. |
| [14] | 修文翠,吴化,韩英,刘云旭. 等温热处理温度对超级贝氏体组织与性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 520-525. |
| [15] | 佟鑫,张雅娇,黄玉山,胡正正,王庆,张志辉. 选区激光熔化304L不锈钢的组织结构及力学性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1615-1621. |
|
||