吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2741-2751.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211344
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 下一篇
多孔吸声材料对轮胎空腔共振噪声的影响
- 1.江苏大学 汽车与交通工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
2.风神轮胎股份有限公司,河南 焦作 454003
Effects of porous sound absorbing materials on tire cavity noise
Jian YANG1( ),Hui-yun LI1,Hai-chao ZHOU1(
),Hui-yun LI1,Hai-chao ZHOU1( ),Guo-lin WANG1,Ling-xin ZHANG2
),Guo-lin WANG1,Ling-xin ZHANG2
- 1.School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
2.AEOLUS Tyre Co. ,Ltd. ,Jiaozuo 454003,China
摘要:
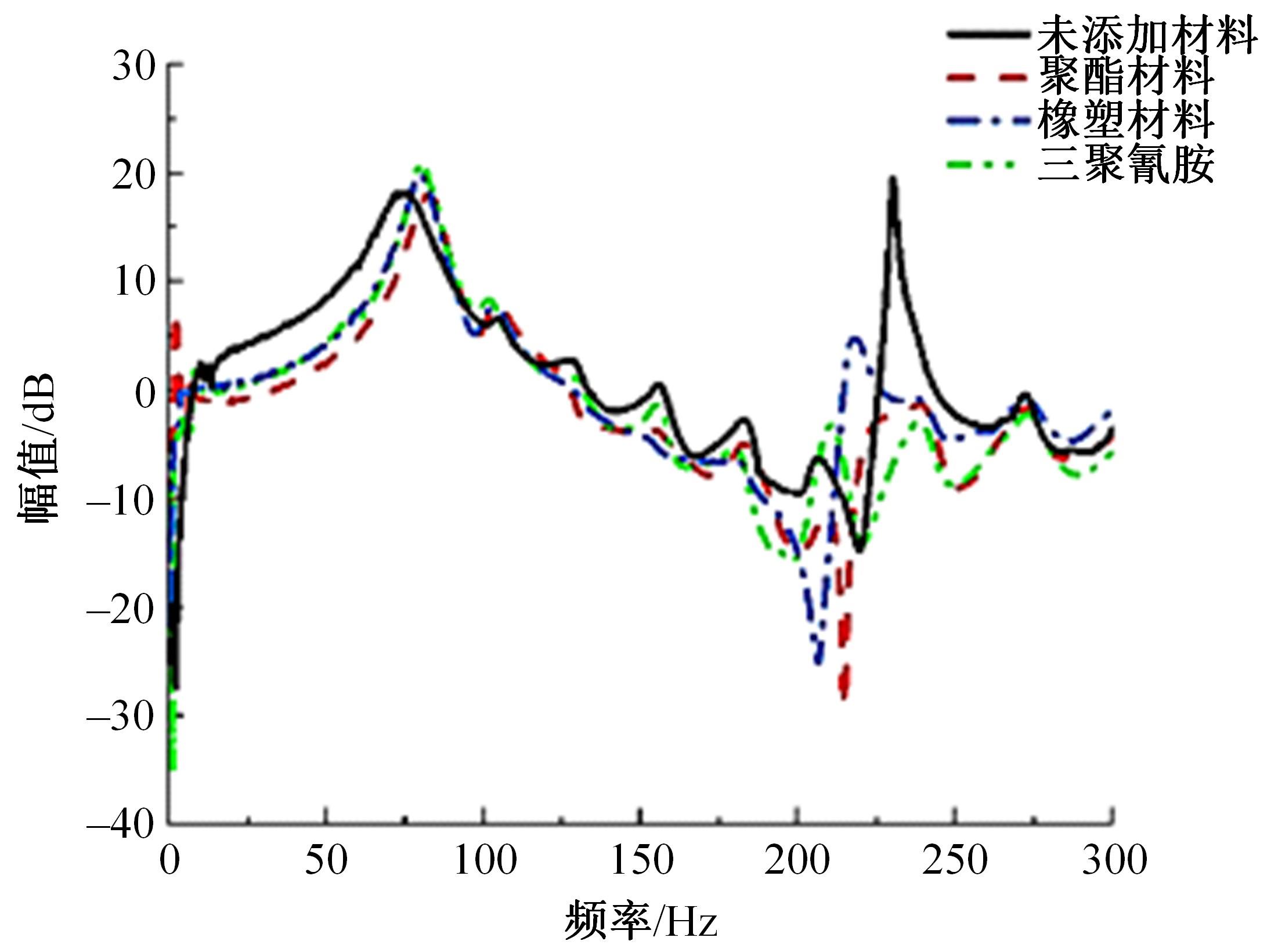
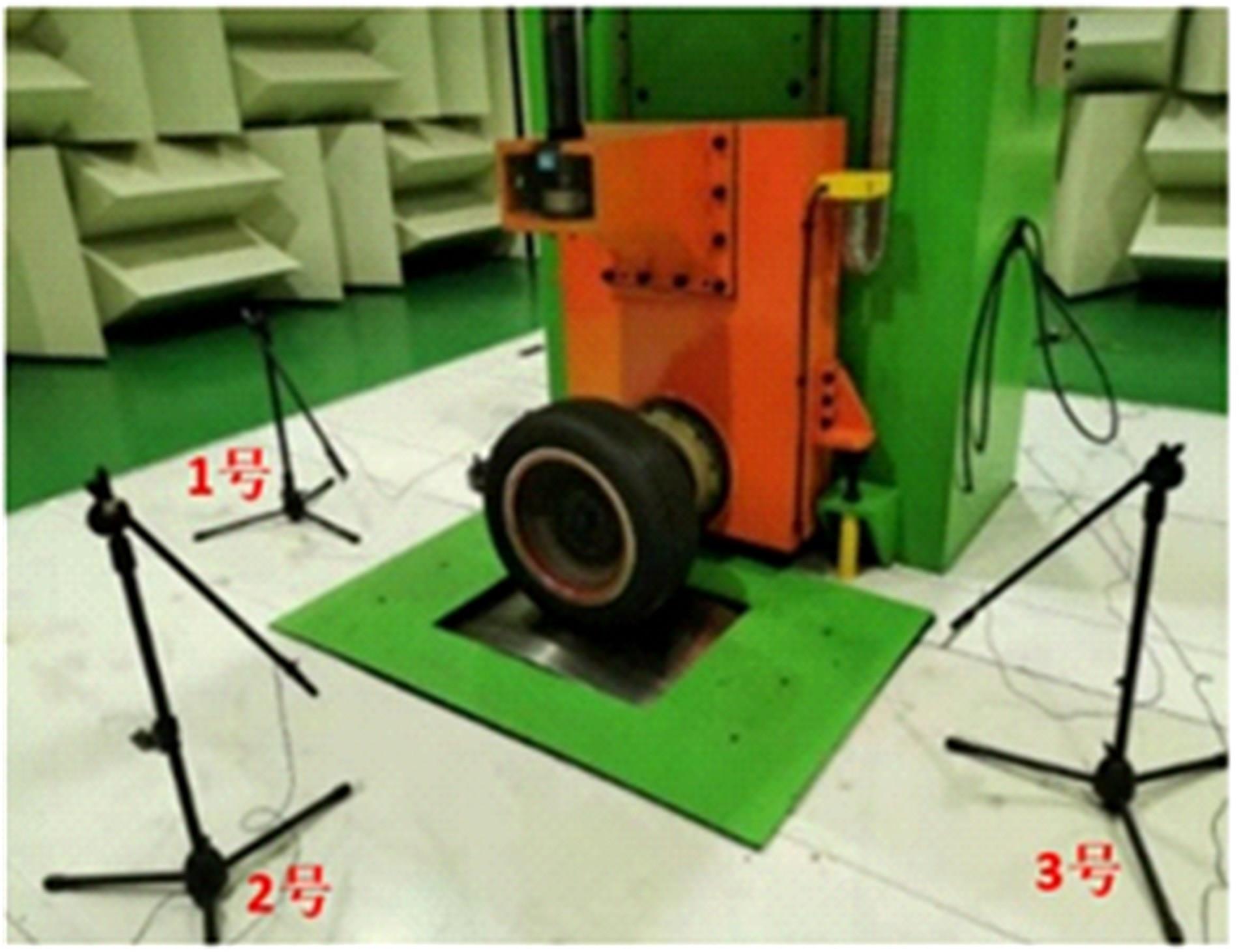
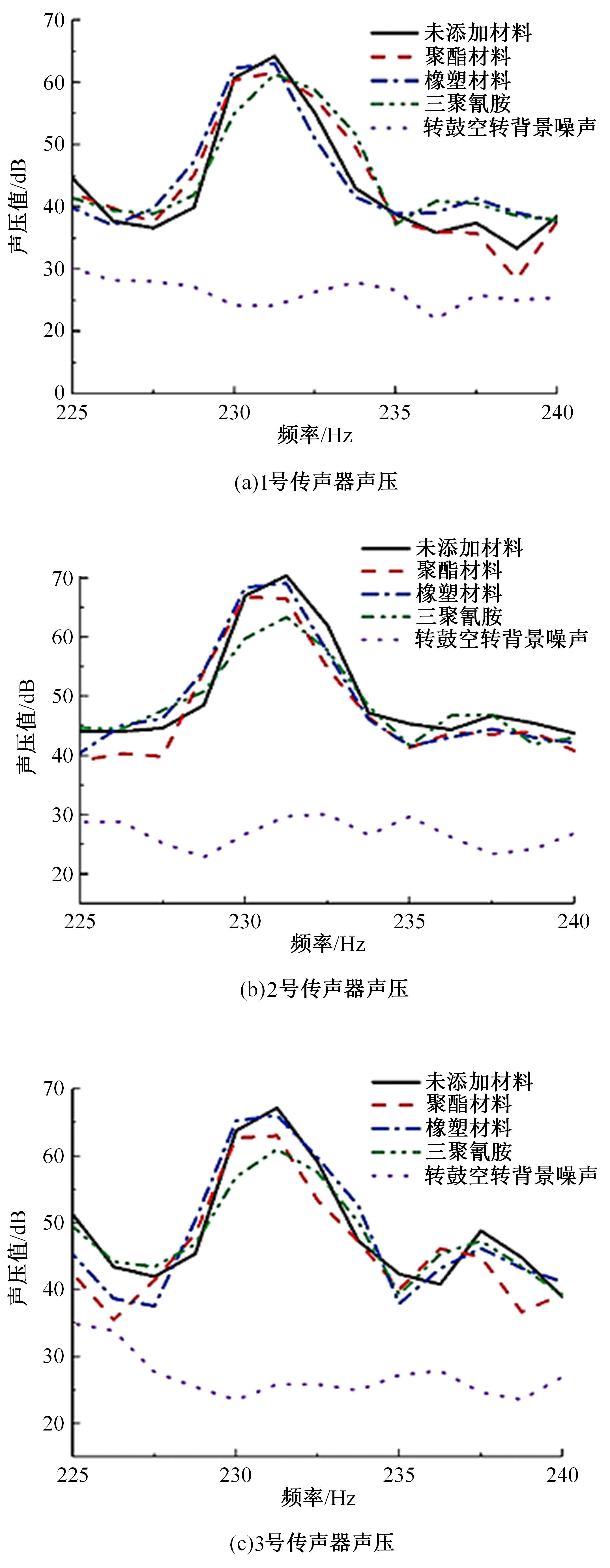
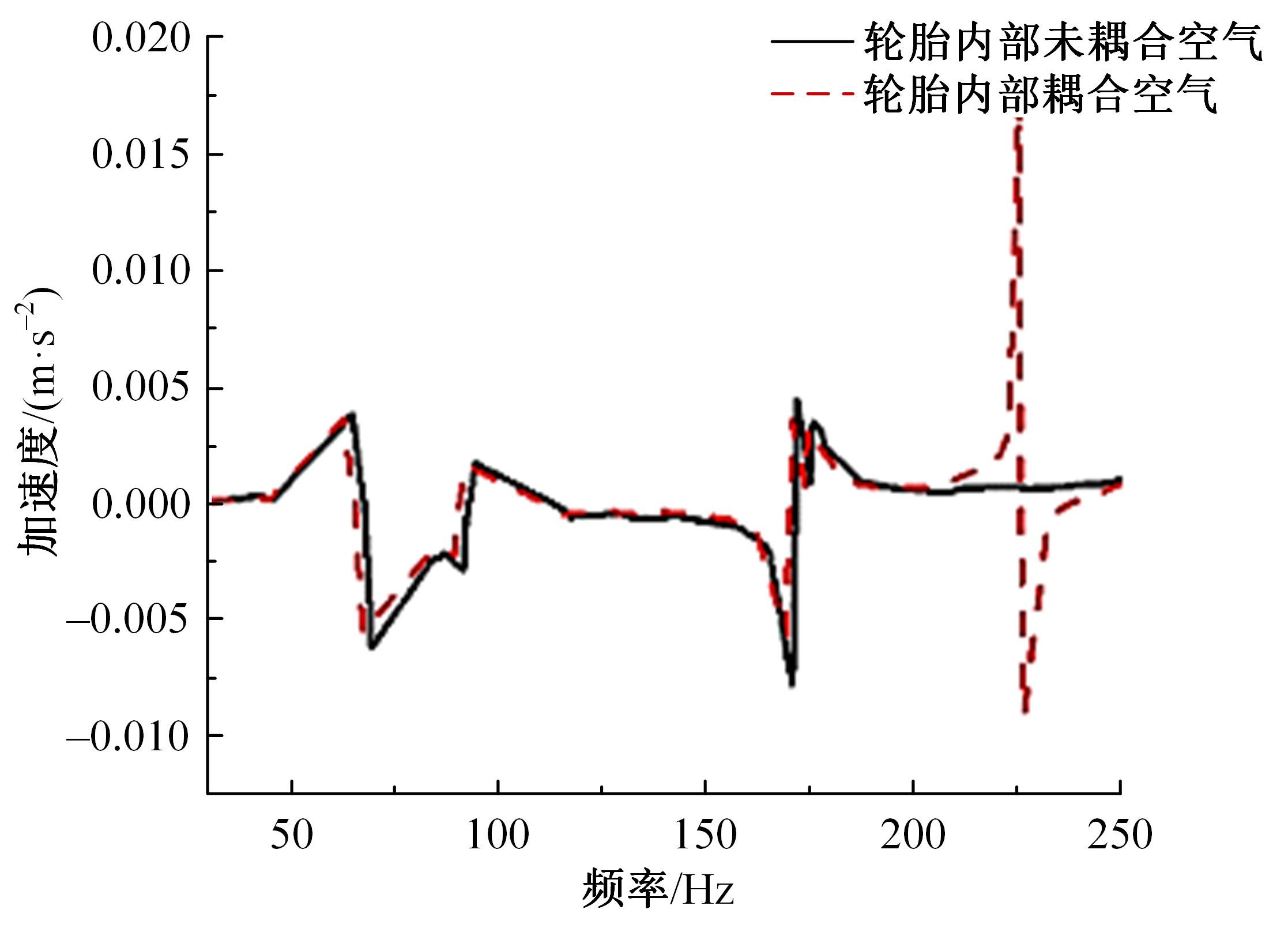
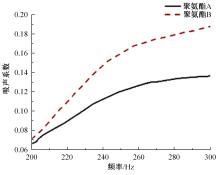
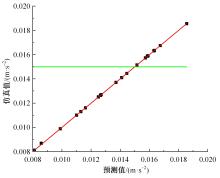
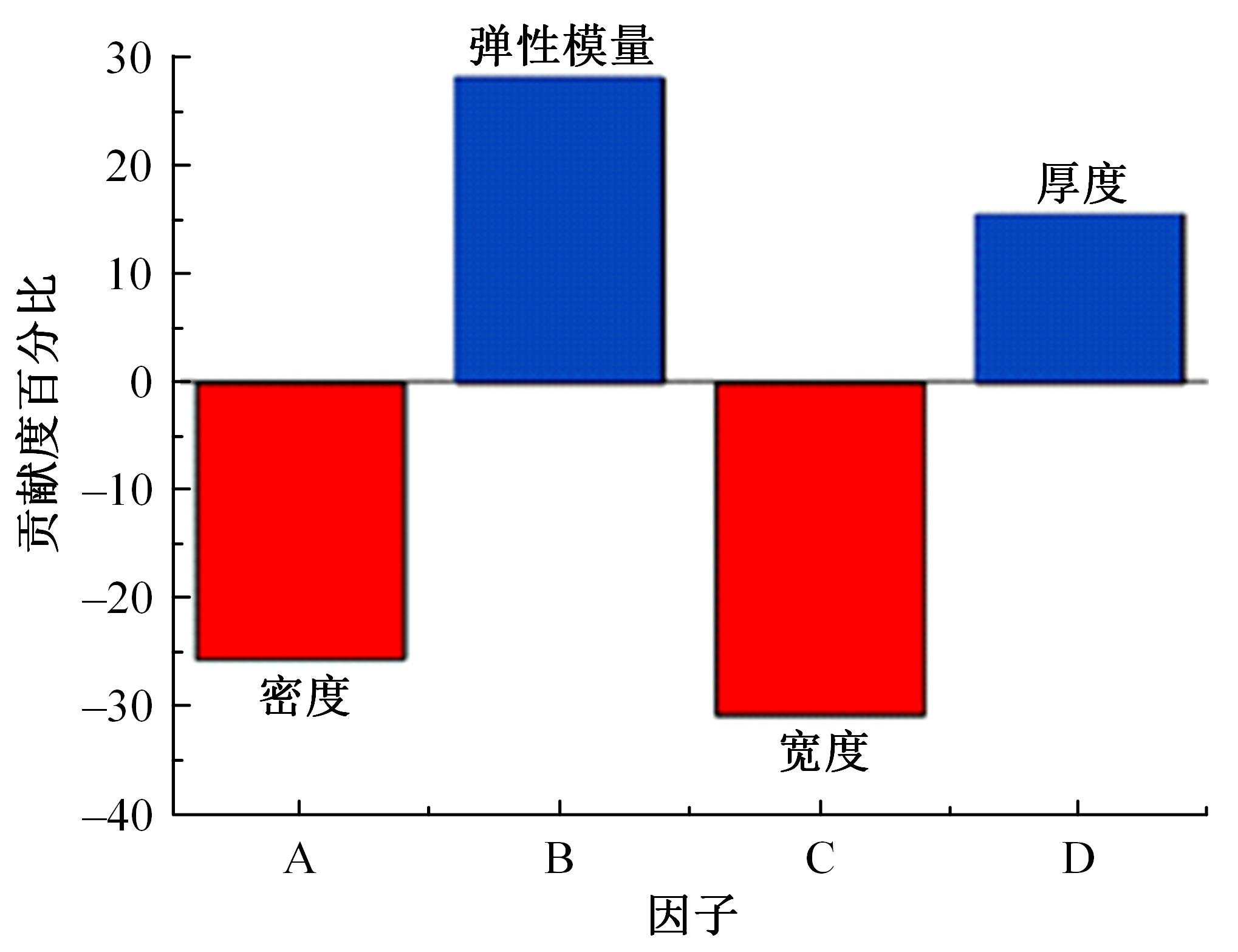
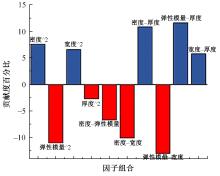
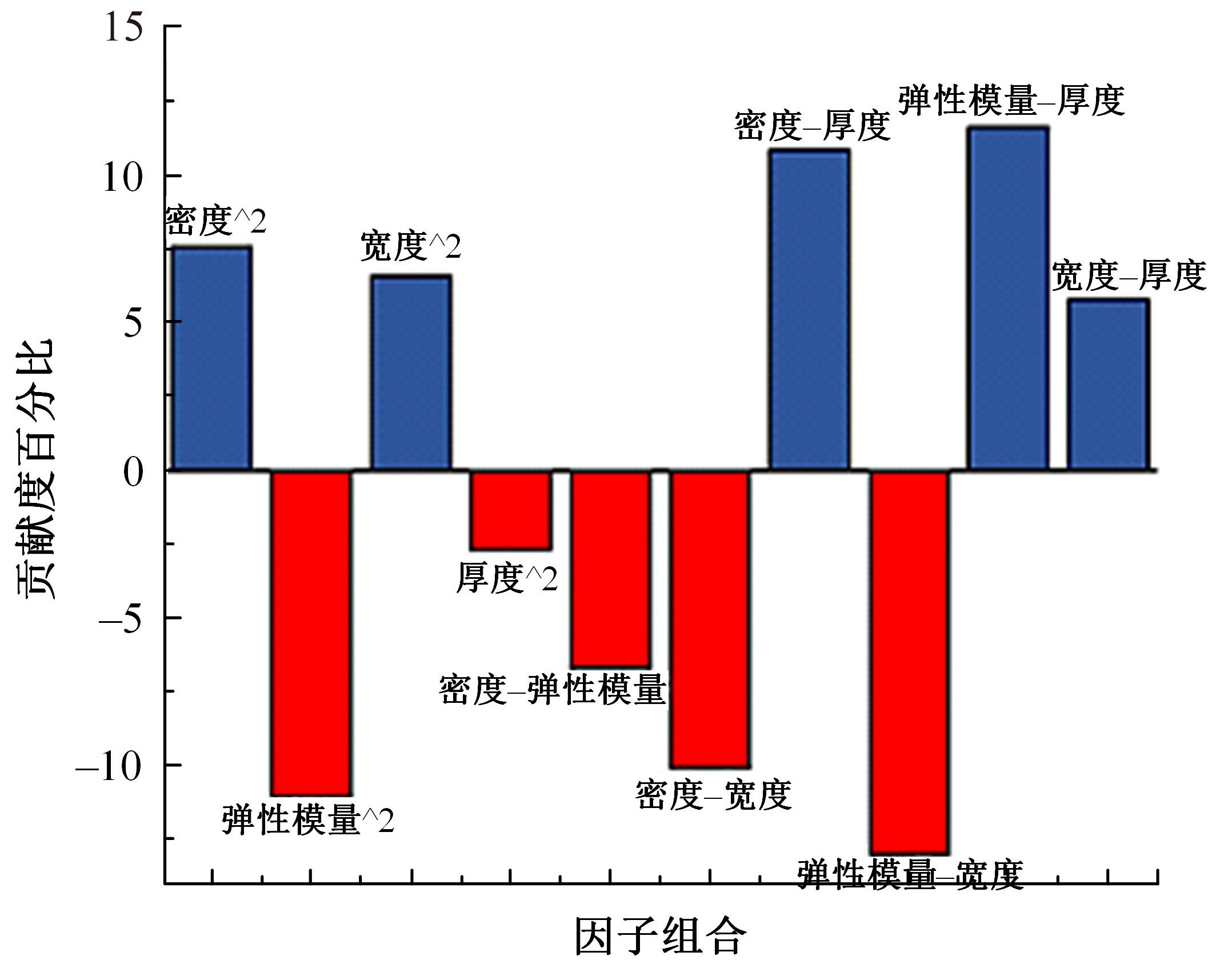
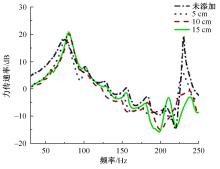
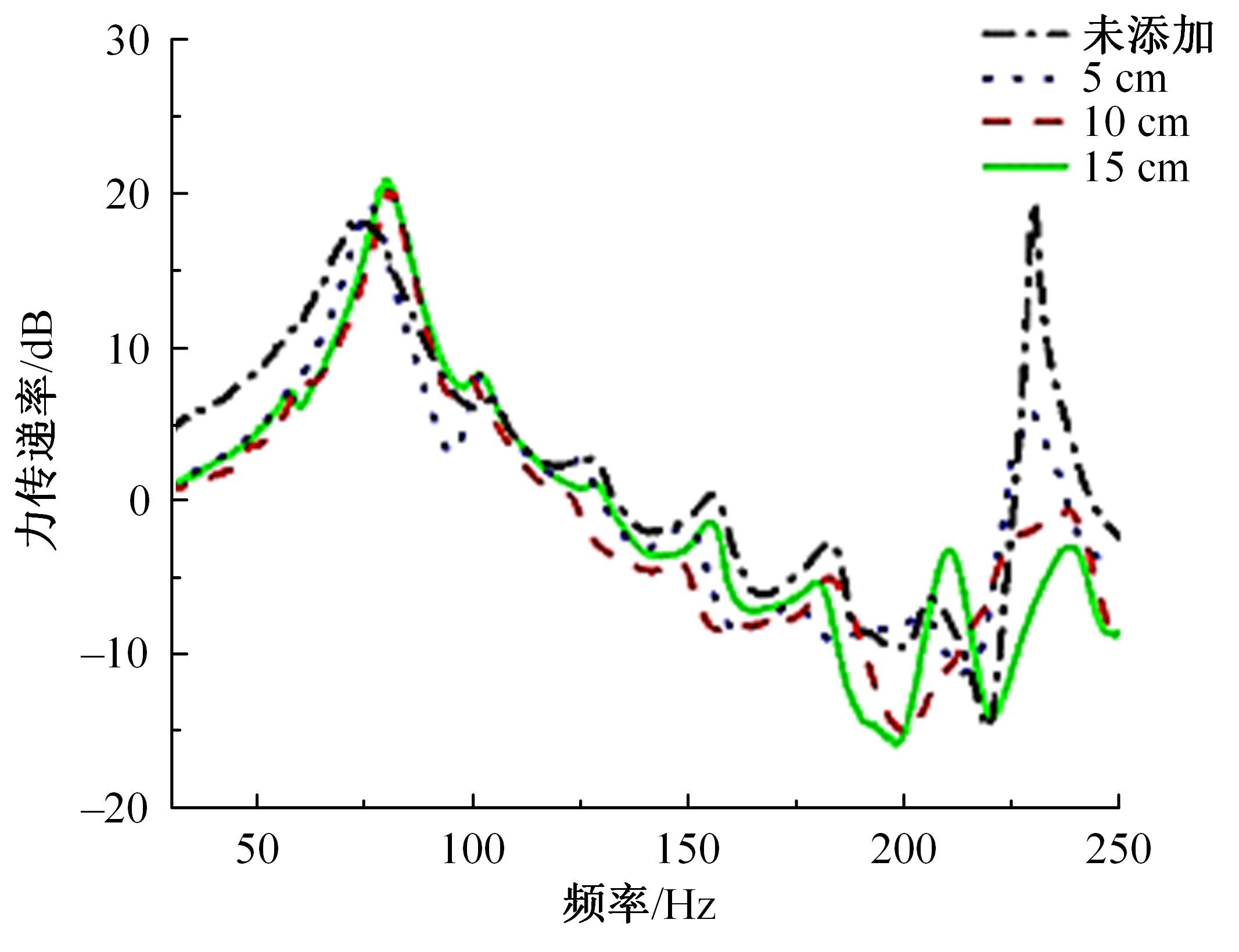
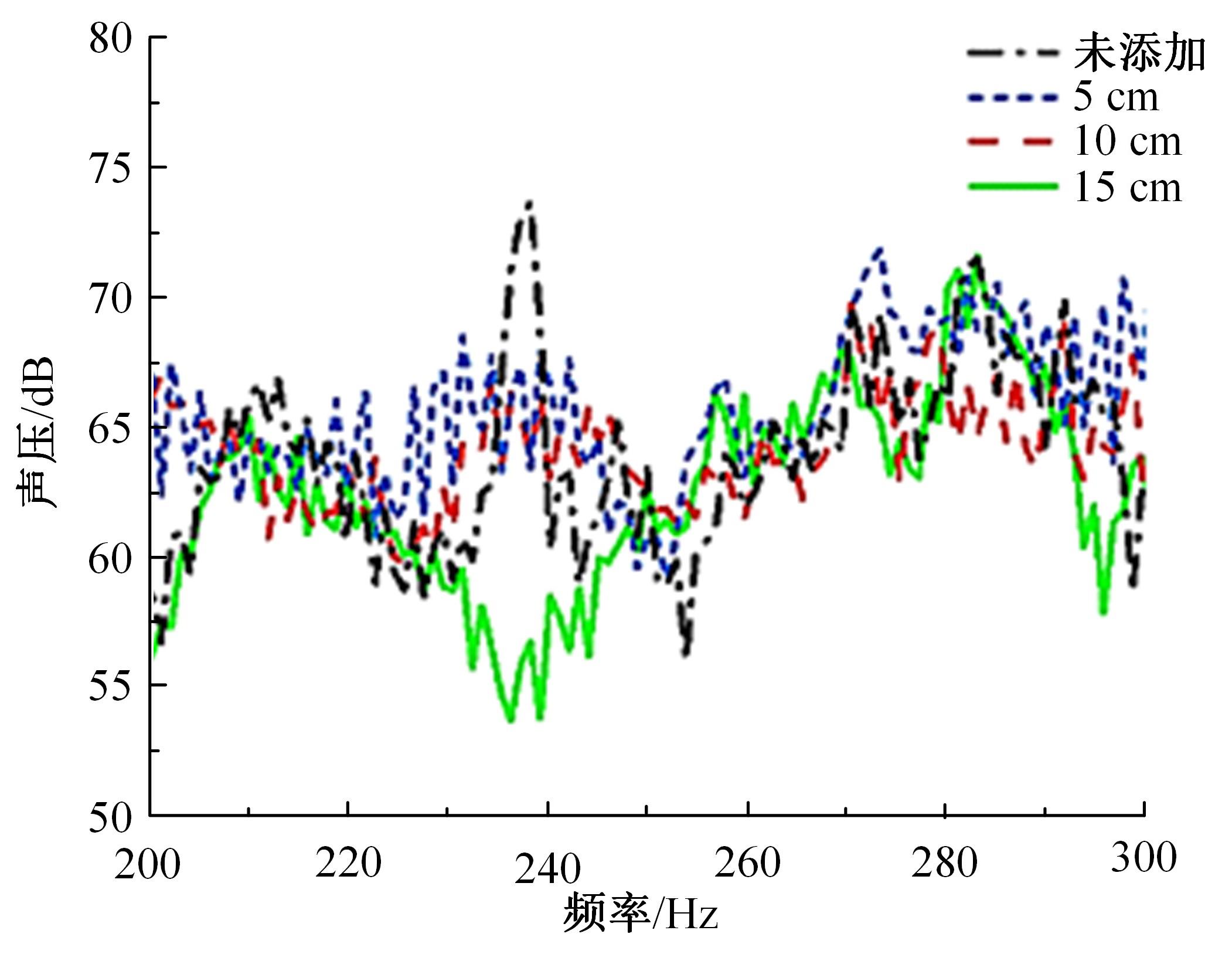
以乘用车205/55R16轮胎为研究对象,通过试验研究轮胎力传递率与轮胎空腔共振噪声关联关系。提出用轮胎力传递率幅值高低表征轮胎共振空腔噪声强弱;采用有限元方法建立轮胎力传递率仿真模型,指出多孔吸声材料的力学参数比其自身吸声系数对降噪效果影响更为显著;进而采用最优拉丁超立方试验方法、Kriging近似模型,探究多孔吸声材料的密度、弹性模量、宽度和厚度等4个参数对轮胎力传递率幅值的影响规律,借助多岛遗传优化算法获得多孔吸声材料最优设计参数,通过对多孔吸声材料宽度的轮胎力传递试验和跌落噪声试验验证了宽度参数影响规律的准确性。研究结果表明,相比于原始轮胎,带有优化后的多孔吸声材料的轮胎力传递率幅值明显降低,意味着轮胎空腔共振噪声也会得到有效改善。
中图分类号:
- U463
| 1 | 梁晨,赵璠,王国林,等. 基于新非自然平衡轮廓设计的载重子午线轮胎振动辐射噪声的研究[J]. 振动工程学报,2015,28(5):800-808. |
| Liang Chen, Zhao Fan, Wang Guo-lin, et al. Tire vibration noise study of radial truck tire based on a new non-natural equilibrium design[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2015,28(5):800-808. | |
| 2 | 刘伟,韩腾飞,刘二宝.轮胎空腔模态预测方法研究[J]. 轮胎工业,2018,38(8):456-458. |
| Liu Wei, Han Teng-fei, Liu Er-bao. Research on modal prediction method of tire cavity[J]. Tire Industry, 2018, 38(8): 456-458. | |
| 3 | Yamauchi H, Akiyoshi Y. Theoretical analysis of tire acoustic cavity noise and proposal of improvement technique[J]. JSAE Review, 2002, 23(1): 89-94. |
| 4 | Tanaka Y, Horikawa S, Murata S. An evaluation method for measuring SPL and mode shape of tire cavity resonance by using multi-microphone system[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2016, 105: 171-178. |
| 5 | Lee H, Kim M T, Taheri S. Estimation of tire-road contact features using strain-based intelligent tire[J]. Tire Science and Technology, 2018, 46(4): 276-293. |
| 6 | Sakata T, Morimura H, Ide H. Effects of tire cavity resonance on vehicle road noise[J]. Tire Science and Technology, 1990, 18(2): 68-79. |
| 7 | Molisani L R, Burdisso R A, Tsihlas D. A coupled tire structure/acoustic cavity model[J]. International Journal of Solids And Structures, 2003, 40(19): 5125-5138. |
| 8 | Mohamed Z. A study of tyre cavity resonance noise mechanism and countermeasures using vibroacoustic analysis[D]. Kuala Lumpur: University Putra Malaysia, 2014. |
| 9 | Thomas S. A new analytical tire model for determining the effect of damping foam on tire/vehicle vibration[D]. Akron: The University of Akron, 2019. |
| 10 | Periyathamby H. Helmholtz resonator for reducing tire cavity resonance and in-vehicle noise[J]. Canadian Acoustics, 2004, 32(4): 27-31. |
| 11 | Mohamed Z, Wang X. A study of tyre cavity resonance and noise reduction using inner trim[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 50: 498-509. |
| 12 | Li T. Literature review of tire-pavement interaction noise and reduction approaches[J]. Journal of Vibroengineering, 2018, 20(6): 2424-2452. |
| 13 | Hatch Daniel. Hankook unveils “sound absorber” tech for quieter drive[EB/OL]. [2018-04-01]. . |
| 14 | Zhang Y B, Yao Q, Xiao L, et al. On the resonance of a lined tire cavity[J]. Acta Acustica united with Acustica, 2019, 105(6): 1237-1242. |
| 15 | Mohamed Z. Tire cavity resonance mitigation using acoustic absorbent materials[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2017, 23(10): 1607-1622. |
| 16 | Baro S, Abom M. Tyre cavity noise: porous materials as a countermeasure[C]∥The 45th International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering: Towards a Quieter Future, Hamburg, Germany, 2016: 6730-6735. |
| 17 | Baro S, Corradi R, Abom M, et al. Modelling of a lined tyre for predicting cavity noise mitigation[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2019, 155: 391-400. |
| 18 | 赵阳阳, 李俊鹏, 张芳. 车轮轮胎力传递率试验和计算方法研究[J]. 上海汽车, 2015(12): 24-28. |
| Zhao Yang-yang, Li Jun-peng, Zhang Fang. Research on test and calculation method of wheel tire force transmissibility[J]. Shanghai Auto, 2015(12): 24-28. | |
| 19 | 明杰婷. 橡胶材料粘弹性本构模型的研究及其在胎面橡胶块上的应用[D]. 长春:吉林大学汽车工程学院,2016. |
| Ming Jie-ting. The research of viscoelastic constitutive model for rubber material and its application in tread block of tires[D]. Changchun: College of Automotive Engineering, Jilin University, 2016. | |
| 20 | 丁凤龙. 子午线轮胎动力学与滚动噪声的分析研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学材料科学与工程学院,2018. |
| Ding Feng-long. Study of radial tire dynamics and rolling noise analysis[D]. Beijing: College of Material Sciences and Engineering, Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2018. | |
| 21 | 王国林, 丁俊杰, 周海超, 等. 智能轮胎力的敏感响应区域及变量[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(6): 1983-1990. |
| Wang Guo-lin, Ding Jun-jie, Zhou Hai-chao, et al. Force-sensitive response area and variable of intelligent tire[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(6): 1983-1990. | |
| 22 | Cao L, Fu Q, Si Y, et al. Porous materials for sound absorption[J]. Composites Communications, 2018, 10: 25-35. |
| 23 | 杨永宝. 轮胎空腔振动模型与降噪研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学车辆与运载学院,2018. |
| Yang Yong-bao. Study on the tire cavity vibration model and noise reduction[D]. Beijing: College of Vehide and Mobility, Tsinghua University,2018. | |
| 24 | Brennan M J, To W M. Acoustic properties of rigid-frame porous materials—an engineering perspective[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2001, 62(7): 793-811. |
| 25 | Simpson T W, Mauery T M, Korte J J, et al. Kriging models for global approximation in simulation-based multidisciplinary design optimization[J]. AIAA journal, 2001, 39(12):2233-2241. |
| 26 | 马芳武,韩露,周阳,等. 采用聚乳酸复合材料的汽车零件多材料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(5):1385-1391. |
| Ma Fang-wu, Han Lu, Zhou Yang, et al. Multi material optimal design of vehicle product using polylactic acid composites[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019,49(5):1385-1391. | |
| 27 | 周海超, 夏琦, 王国林, 等.轮胎空腔共振噪声与力传递率关系的试验研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(3): 429-436, 449. |
| Zhou Hai-chao, Xia Qi, Wang Guo-lin, et al. Experimental study on the relationship between tire cavity resonance noise and tire force transmissibility[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(3): 429-436, 449. |
| [1] | 陈兆玮,蒲前华. 弹性车轮对大跨斜拉桥车桥耦合振动的抑制特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2519-2532. |
| [2] | 刘平义,李晓婷,高偌霖,李海涛,魏文军,王亚. 车辆侧倾驱动机构设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2185-2192. |
| [3] | 黄学劲,钟锦星,路京雨,赵霁,肖伟,袁新枚. 基于用户画像的电动汽车充电负荷预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2193-2200. |
| [4] | 张树培,夏明悦,张玮,陈钊,陈义祥. 考虑非线性刚度的间隙球铰碰撞动力学建模与仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2227-2235. |
| [5] | 陈辉,邵亚军. 基于惯性基准多传感器耦合的路面谱测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2254-2262. |
| [6] | 陈磊,王杨,董志圣,宋亚奇. 一种基于转向意图的车辆敏捷性控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1257-1263. |
| [7] | 陈鑫,张冠宸,赵康明,王佳宁,杨立飞,司徒德蓉. 搭接焊缝对铝合金焊接结构轻量化设计的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1282-1288. |
| [8] | 张勇,毛凤朝,刘水长,王青妤,潘神功,曾广胜. 基于Laplacian算法的汽车外流场畸变网格优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1289-1296. |
| [9] | 汪少华,储堃,施德华,殷春芳,李春. 基于有限时间扩张状态观测的HEV鲁棒复合协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [10] | 尹燕莉,黄学江,潘小亮,王利团,詹森,张鑫新. 基于PID与Q⁃Learning的混合动力汽车队列分层控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1481-1489. |
| [11] | 于贵申,陈鑫,武子涛,陈轶雄,张冠宸. AA6061⁃T6铝薄板无针搅拌摩擦点焊接头结构及性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
| [12] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [13] | 杨红波,史文库,陈志勇,郭年程,赵燕燕. 基于NSGA⁃II的斜齿轮宏观参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [14] | 赵睿,李云,胡宏宇,高镇海. 基于V2I通信的交叉口车辆碰撞预警方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1019-1029. |
| [15] | 陈小波,陈玲. 定位噪声统计特性未知的变分贝叶斯协同目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1030-1039. |
|
||