吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 2254-2262.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211110
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于惯性基准多传感器耦合的路面谱测量方法
- 1.兰州交通大学 铁道技术学院,兰州 730070
2.兰州资源环境职业技术大学 机电工程学院,兰州 730021
Measurement method of pavement surface spectrum with multi⁃sensor coupling based on inertial benchmark
- 1.School of Railway Technical,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070,China
2.School of Mechanical & Electronical Engineering,Lanzhou Resources & Environment Voc-Tech University,Lanzhou 730021,China
摘要:
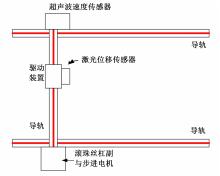
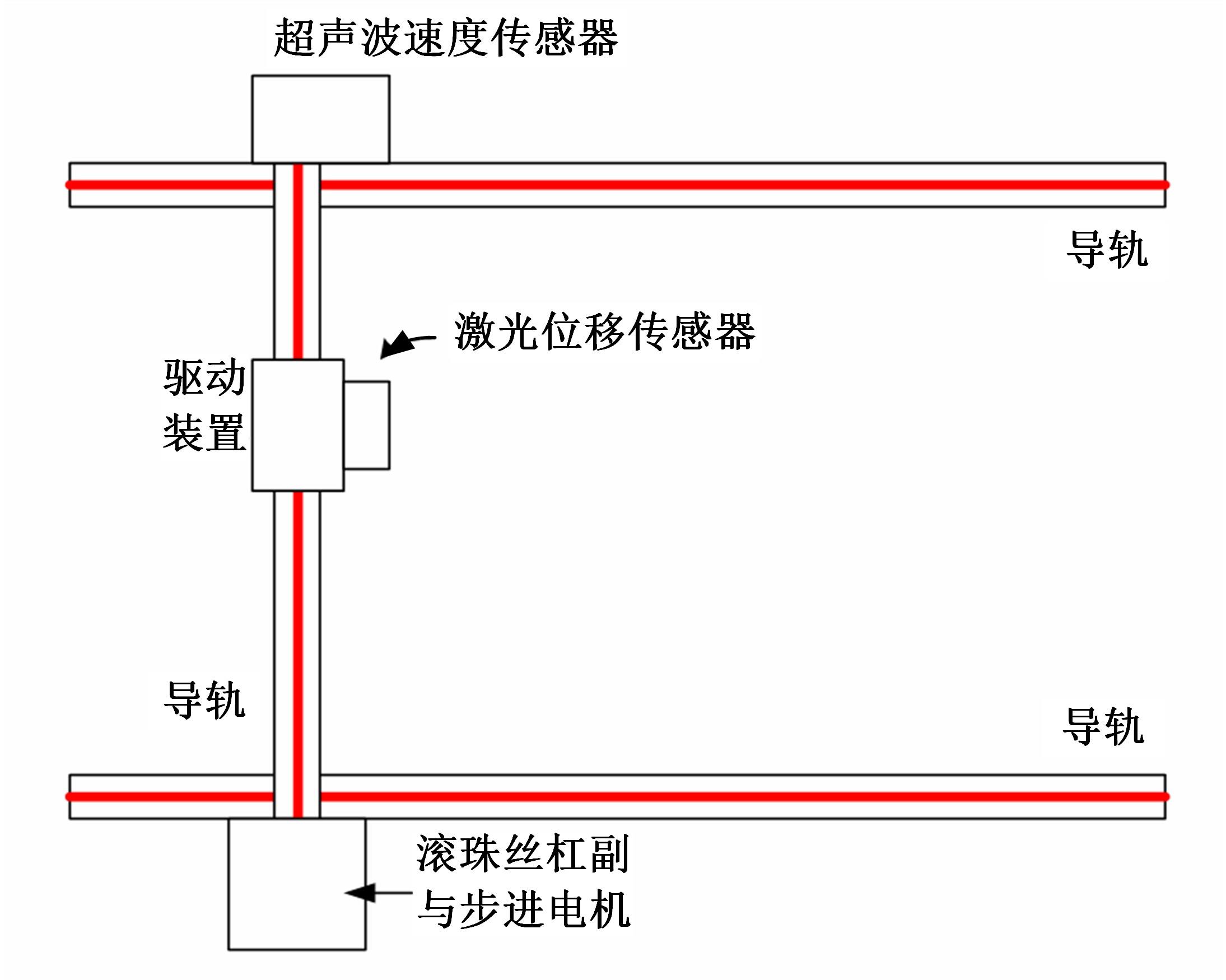
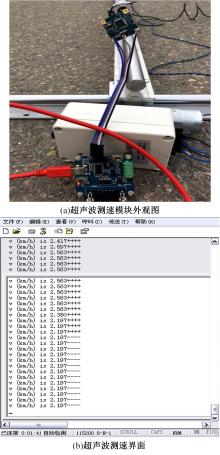
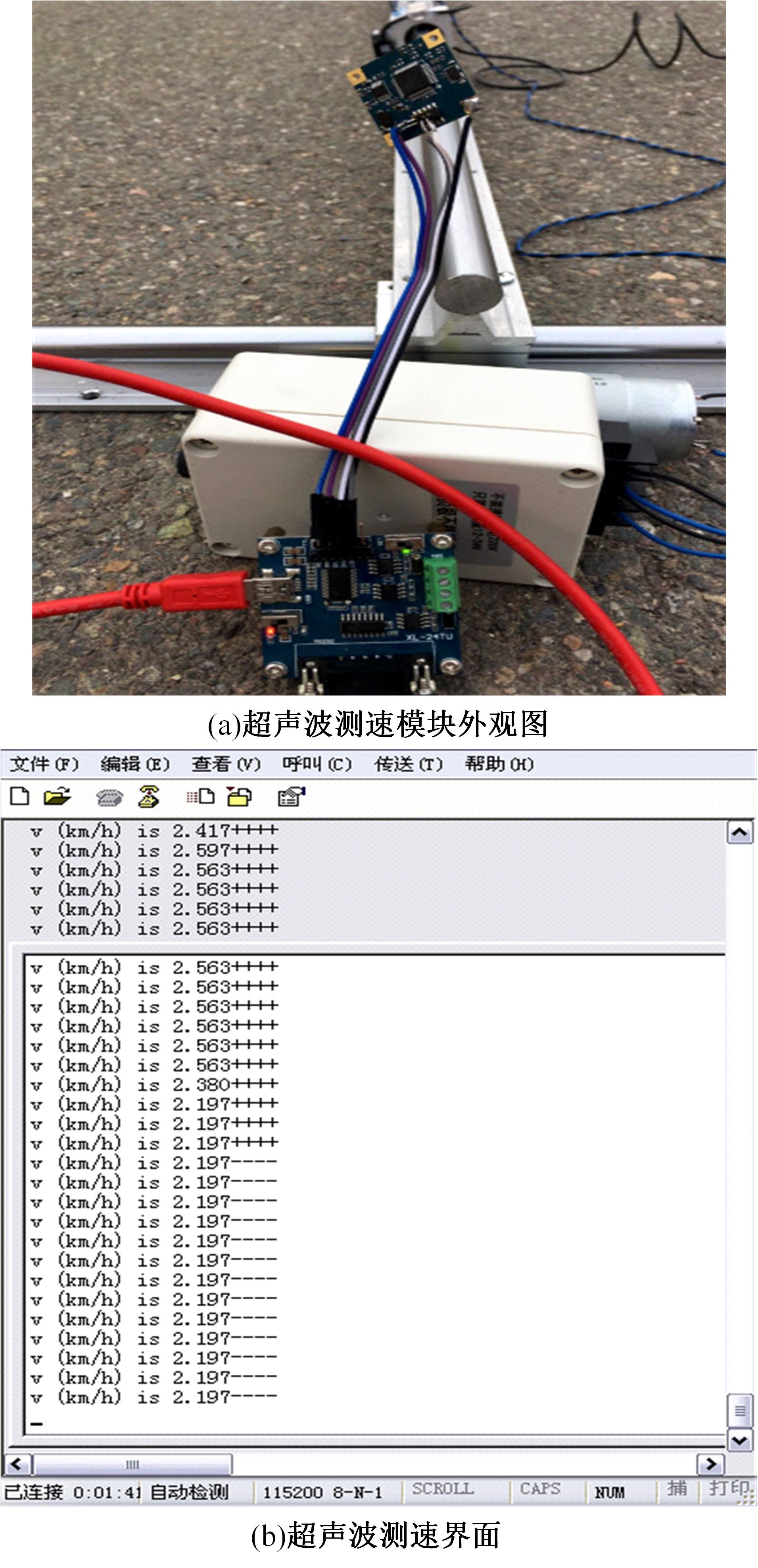
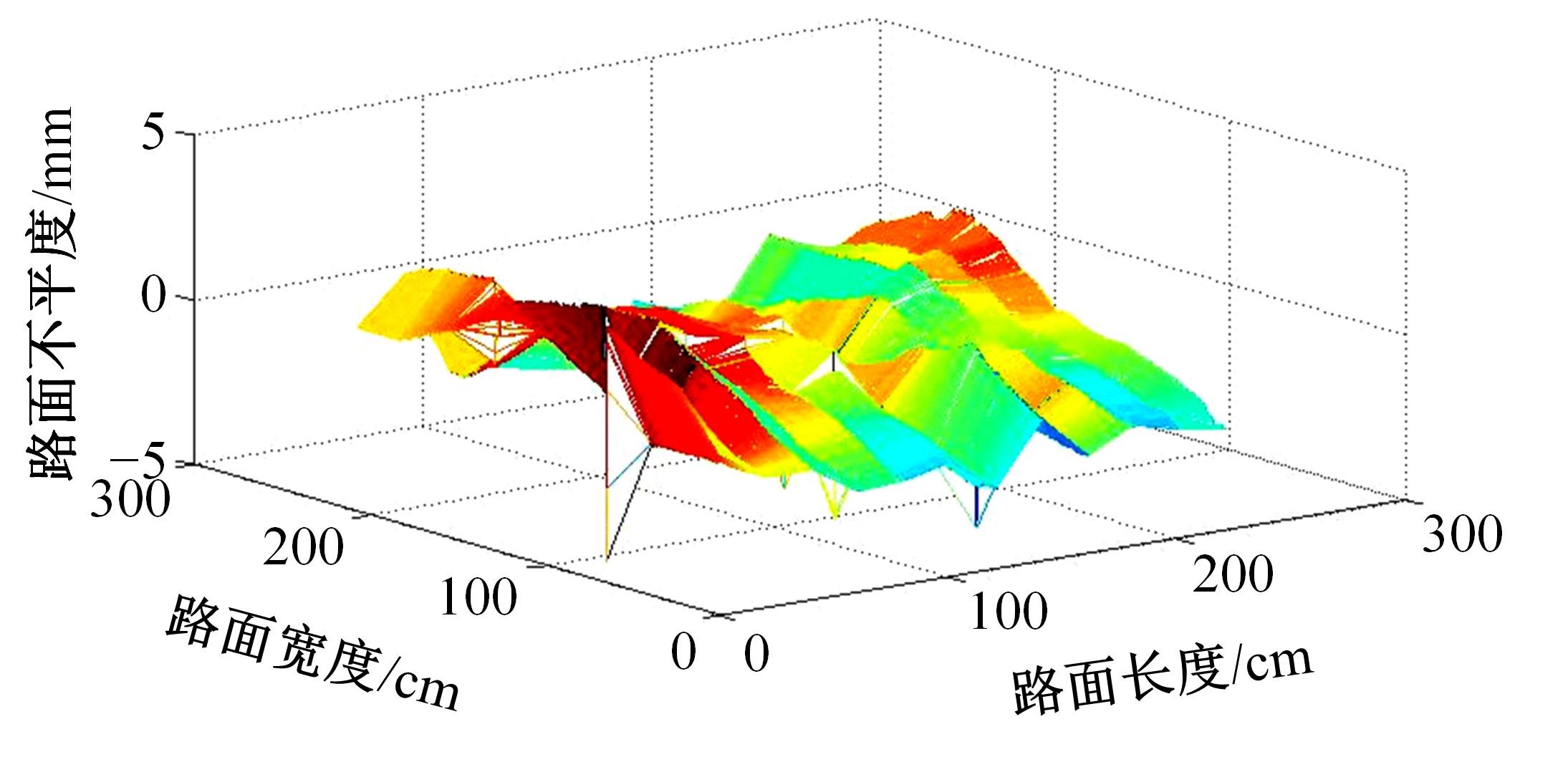
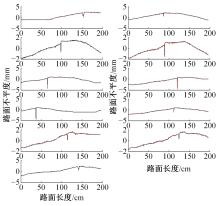
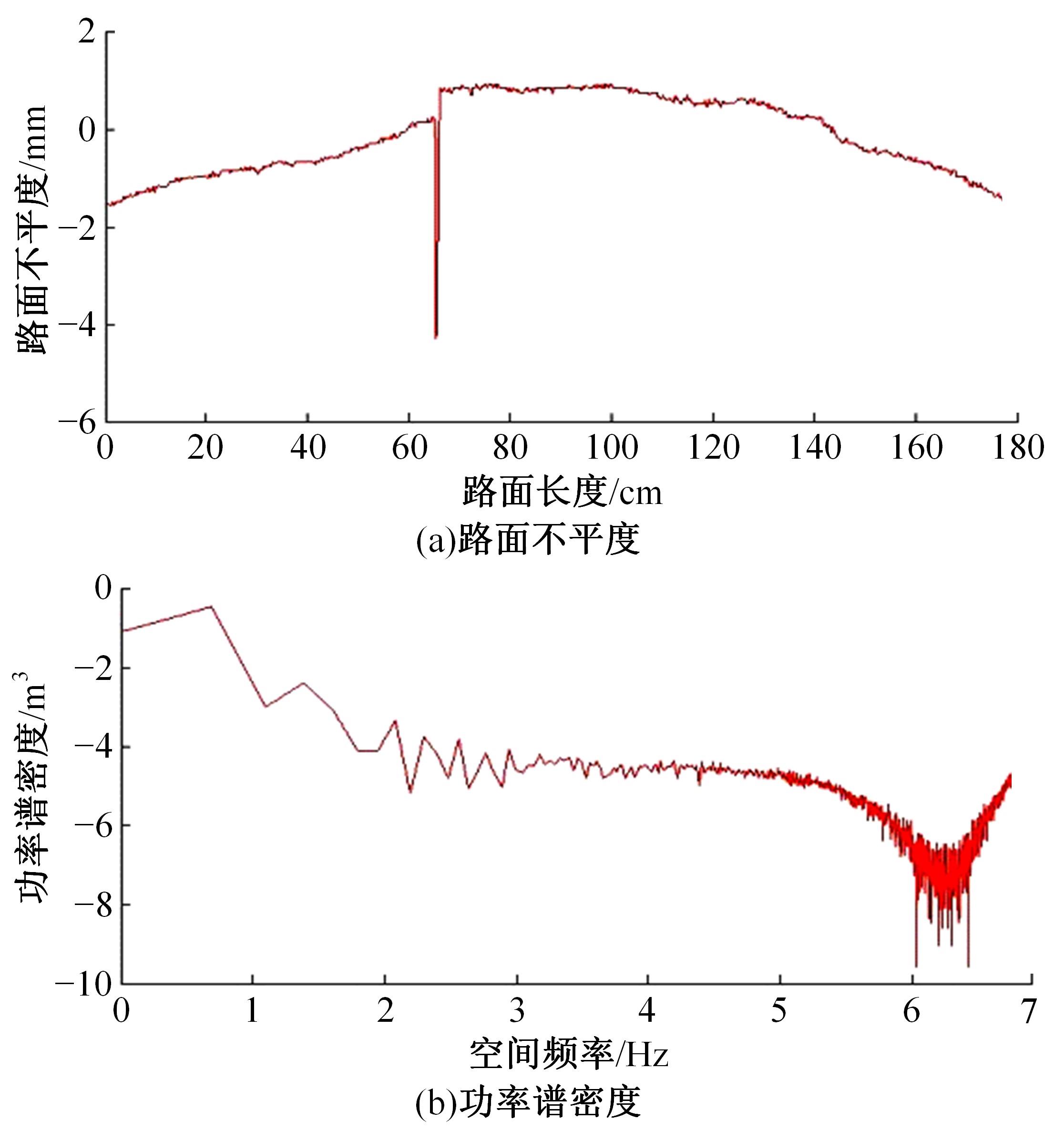
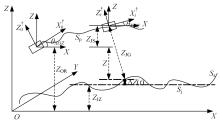
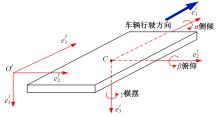
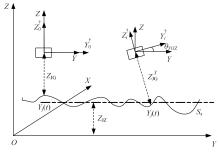
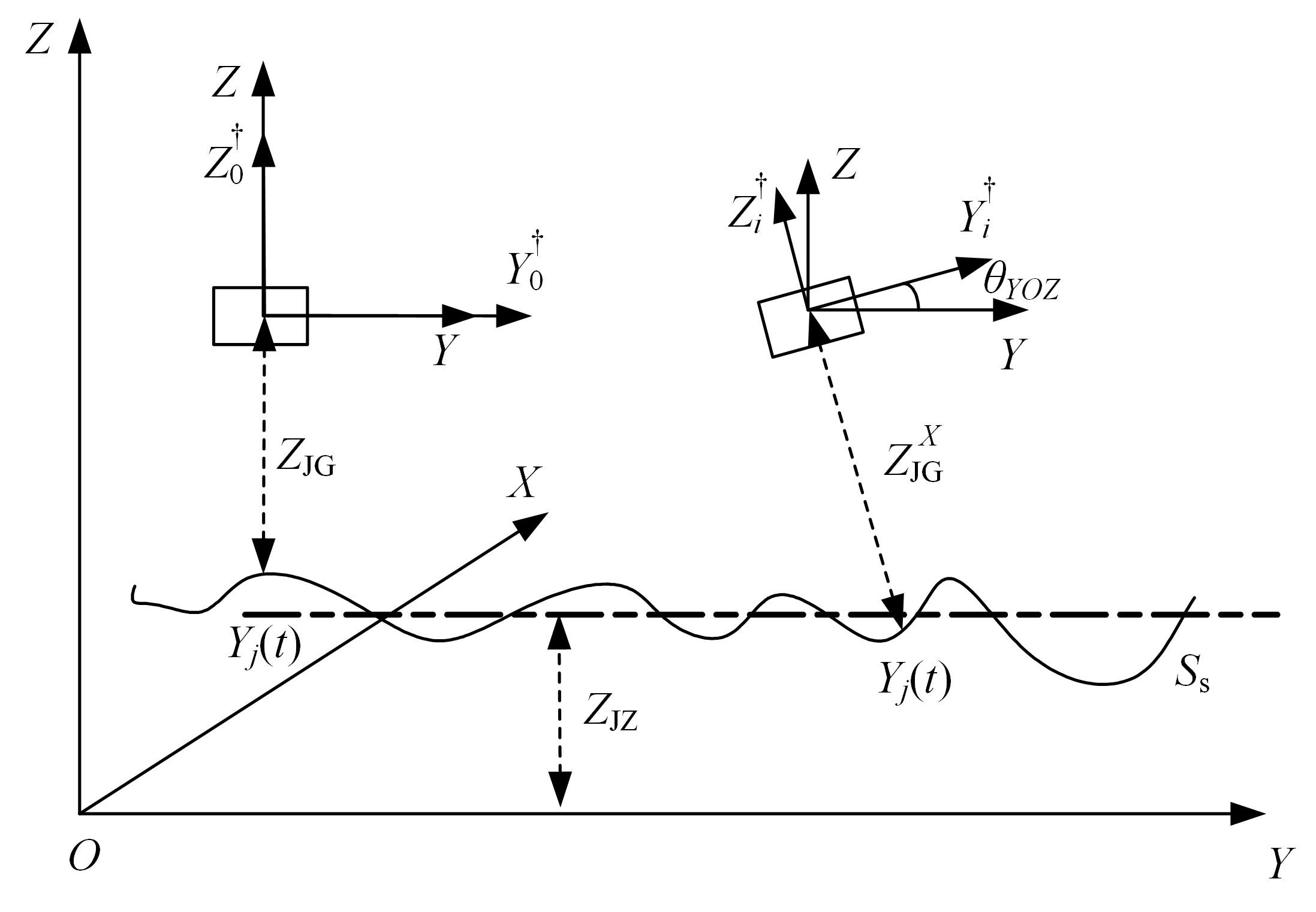
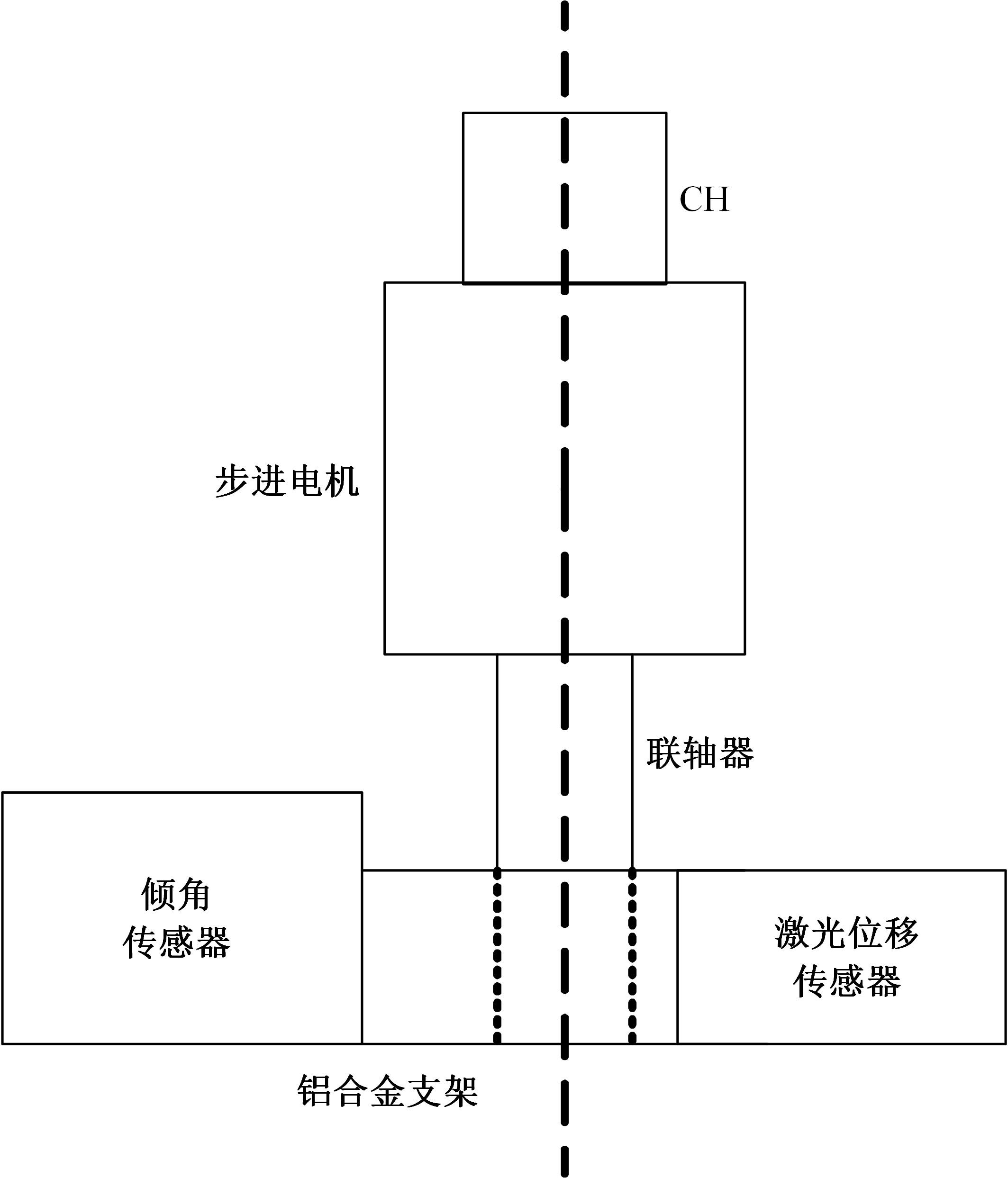
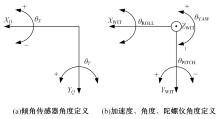
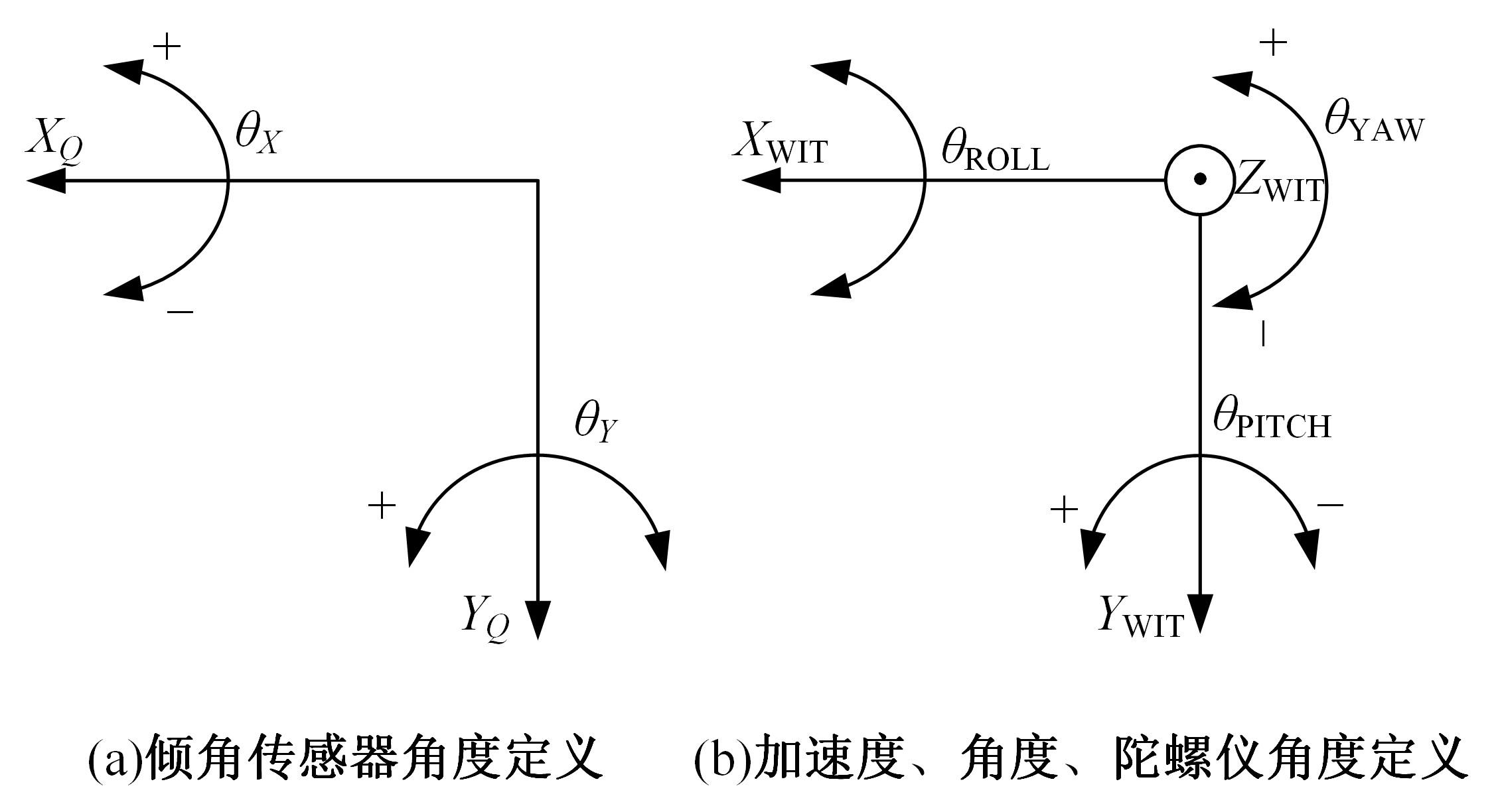
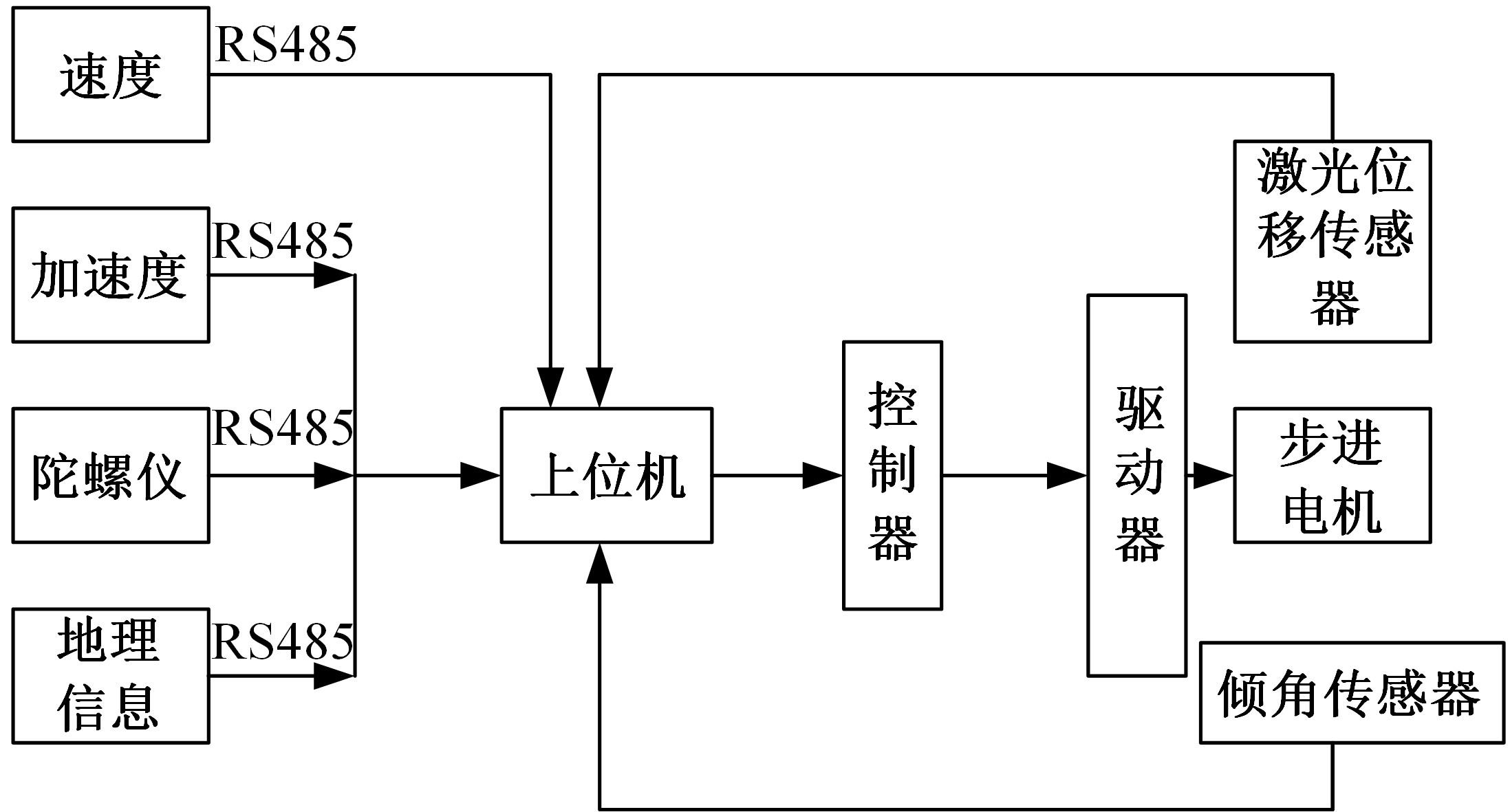
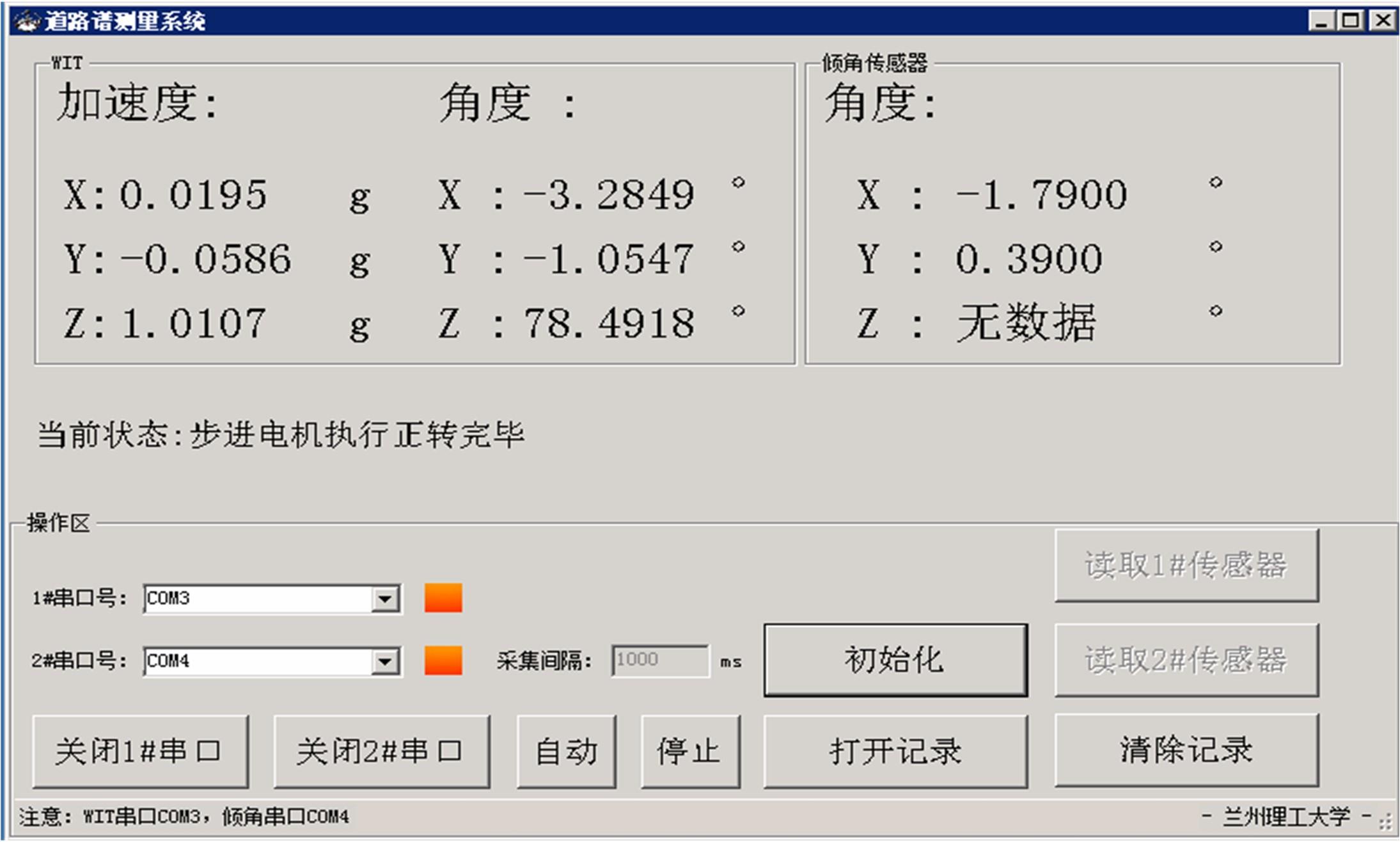
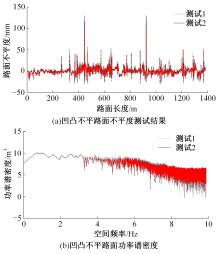
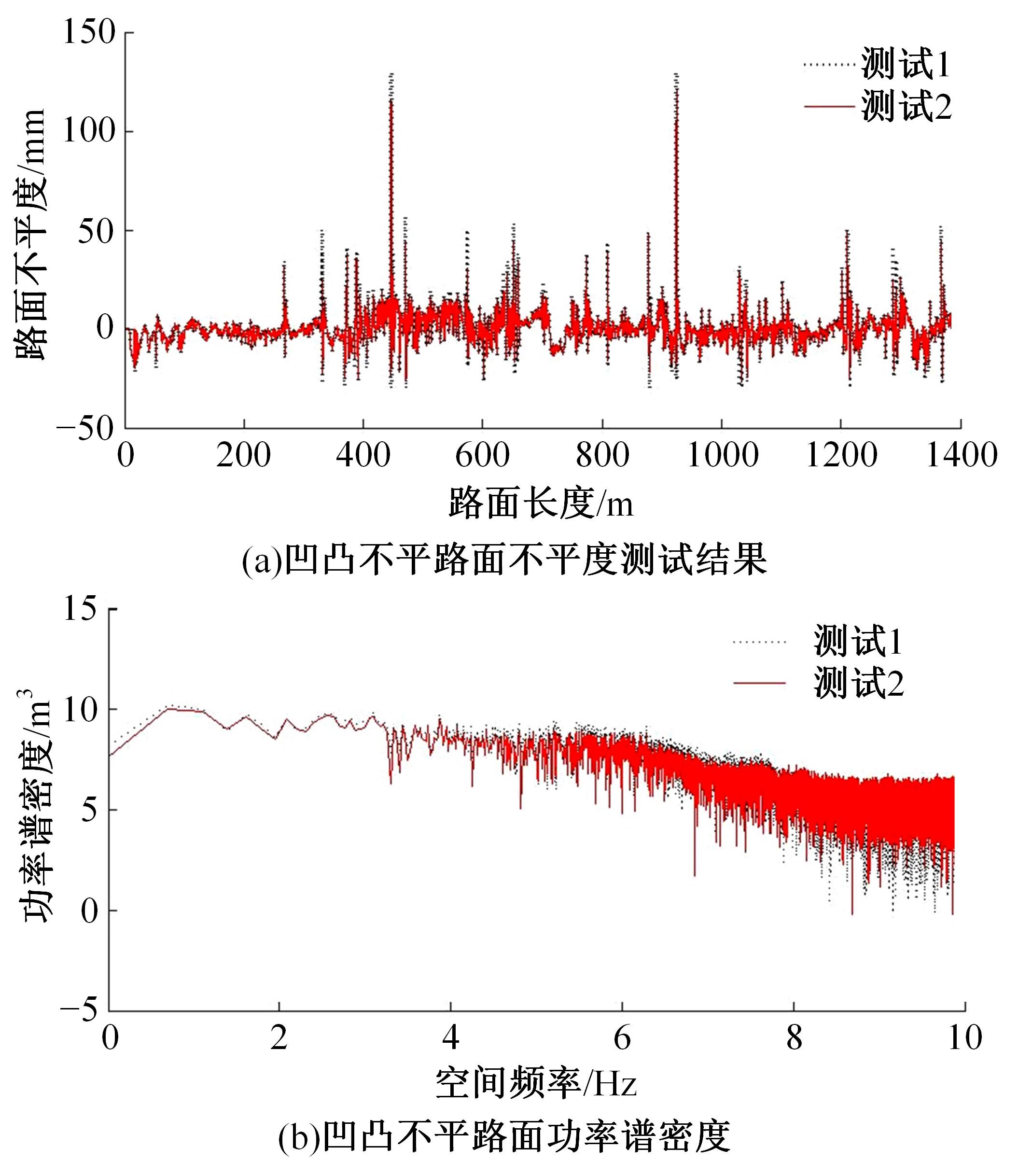
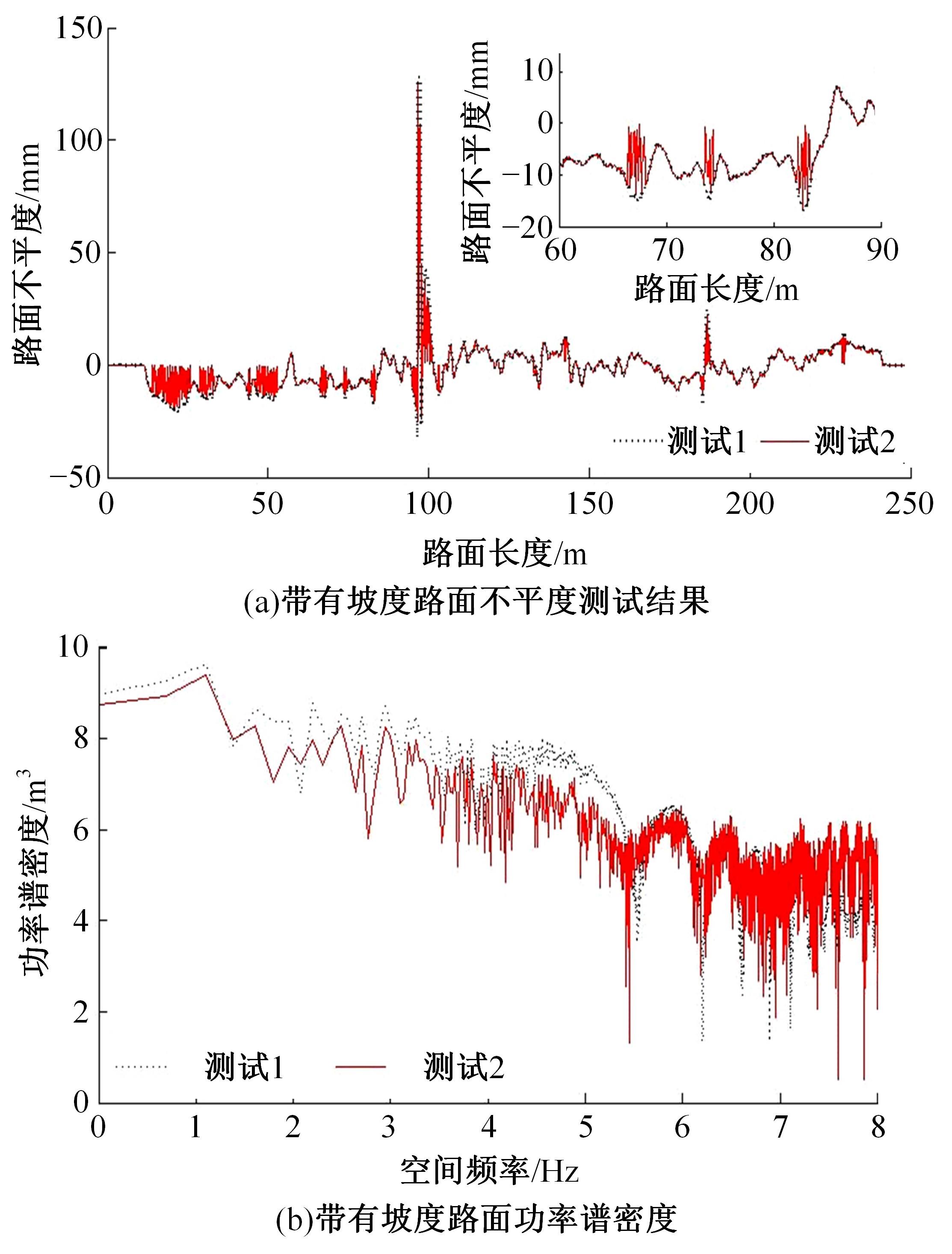
基于惯性坐标基准,结合多传感器耦合的路面谱测量方法,将测量系统平台搭载在移动设备(如车辆)上获取道路谱。采用车辆行驶过程中道路谱测量系统获取到的来自车辆瞬时加速度、俯仰角、实时位移与地理信息等数据来计算被测路面不平度;路面不平度以外激励方式引起车辆俯仰与侧倾运动,致使道路参数采集产生误差与错误。本文基于惯性坐标基准,采用多传感器与执行器耦合方法,利用PID控制算法,结合陀螺仪、加速度传感器、角度传感器数据对步进电机进行闭环控制,实时修正测量系统平台因车辆俯仰、侧倾和垂向运动对激光位移传感器姿态的影响,获取准确的道路谱数据。由测量平台获取的不同类型道路位移功率谱密度图像可知,本文方法具有一定的正确性与优越性。
中图分类号:
- U412.21
| 1 | 马建, 赵祥模, 贺拴海. 路面检测技术综述[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2017, 17(5): 121-137. |
| Ma Jian, Zhao Xiang-mo, He Shuan-hai. Review of pavement detection technology[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2017, 17(5) :121-137. | |
| 2 | 张宝振, 王汉平, 张哲, 等. 二维路面不平度的分形构造方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(12): 2389-2396. |
| Zhang Bao-zhen, Han-ping Whang, Zhang Zhe, et al. Fractal construction method of 2D road roughness[J]. Acta Armamentarii,2020, 41(12):2389-2396. | |
| 3 | 段虎明, 石峰, 谢飞,等. 道路谱测量检测技术研究综述[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2010, 24(1): 72-79. |
| Duan Hu-ming, Shi Feng, Xie Fei, et al. Summary of research on road spectrum measurement[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrument, 2010, 24(1): 72-79. | |
| 4 | Jiang M, Gielen G, Deng B, et al. A fast learning algorithm for time-delay neural networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2002, 148(1-4): 27-39. |
| 5 | Kim J, Lee H D. Development of new automated crack measurement algorithm to analyze laser images of pavement surface[C]∥Transportation Research Board Meeting, Washington,USA, 2009: 093672. |
| 6 | Broberg P. Surface crack detection in welds using thermography[J]. Ndt & E International, 2013, 57: 69-73. |
| 7 | Wang K, Engineering K, Arkansas U O, et al. Elements of automated survey of pavements and a 3D methodology[J]. Journal of Modern Transportation, 2011, 19: 51-57. |
| 8 | Mohan A, Poobal S. Crack detection using image processing: a critical review and analysis[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2017, 57(2): 787-798. |
| 9 | Wang K, Gong W. Real-time automated survey system of pavement cracking in parallel environment[J]. Journal of Infrastructure Systems, 2005, 11(3): 154-164. |
| 10 | Huang Y X. Automatic inspection of pavement cracking distress [J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2006, 15(1): 013017. |
| 11 | 李杰, 郭文翠, 赵旗, 等. 基于车辆响应的路面不平度识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(6): 1810-1817. |
| Li Jie, Guo Wen-cui, Zhao Qi,et al. Road roughness identification based on vehicle responses[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2019,49(6) :1810-1817. | |
| 12 | 牛治慧, 苏建, 张益瑞, 等. 基于转向架试验台的轨道不平顺模拟试验[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(2): 400-407. |
| Niu Zhi-hui, Su Jian, Zhang Yi-rui, et al. Track irregularity simulation based on bogie test rig[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2017,47(2):400-407. | |
| 13 | Chen H, Jin W Y. Dynamic response of a semiactive suspension system with hysteretic nonlinear energy sink based on random excitation by means of computer simulation[J]. Complexity, 2020(2): 3181423. |
| 14 | 段虎明, 石锋, 谢飞, 等. 道路谱测量系统的误差与精度分析[J]. 汽车工程, 2010, 32(9): 783-788. |
| Duan Hu-ming, Shi Feng, Xie Fei, et al. Error and accuracy analysis on road spectra measurement system[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2010, 32(9): 783-788. | |
| 15 | 王建锋, 李平, 韩毅. 基于多传感器综合的路面不平度测量[J]. 武汉大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 45(3): 361-365. |
| Wang Jian-feng, Li Ping, Han Yi. Road roughness measurement based on multi-sensor data comprehension[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2012, 45(3): 361-365. | |
| 16 | Liu X D, Wang H X, Shan Y C, et al. Construction of road roughness in left and right wheel paths based on PSD and coherence function[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 60/61: 668-677. |
| 17 | 赵济海. 路面不平度的测量分析与应用[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2000. |
| 18 | 刘玉梅, 庄娇娇, 曹晓宁. 基于小波理论的双六自由度试验台轨道不平顺模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(1): 30-38. |
| Liu Yu-mei, Zhuang Jiao-jiao, Cao Xiao-ning. Track irregularity simulation of dual 6-DOF test-bed based on wavelet theory[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 30-38. | |
| 19 | 过学迅, 徐占, 李孟良, 等. 路面不平度测量技术研究综述[J]. 中外公路, 2009, 39(5): 47-51. |
| Guo Xue-xun, Xu Zhan, Li Meng-liang, et al. Review on measurement technology of pavement roughness[J]. Journal of China & Foreign Highway, 2009, 39(5): 47-51. | |
| 20 | 机械振动道路路面谱测量数据报告: [S]. |
| [1] | 张树培,夏明悦,张玮,陈钊,陈义祥. 考虑非线性刚度的间隙球铰碰撞动力学建模与仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2227-2235. |
| [2] | 刘平义,李晓婷,高偌霖,李海涛,魏文军,王亚. 车辆侧倾驱动机构设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2185-2192. |
| [3] | 黄学劲,钟锦星,路京雨,赵霁,肖伟,袁新枚. 基于用户画像的电动汽车充电负荷预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2193-2200. |
| [4] | 张青霞,侯吉林,安新好,胡晓阳,段忠东. 基于车辆脉冲响应的路面不平度识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1765-1772. |
| [5] | 陈鑫,张冠宸,赵康明,王佳宁,杨立飞,司徒德蓉. 搭接焊缝对铝合金焊接结构轻量化设计的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1282-1288. |
| [6] | 张勇,毛凤朝,刘水长,王青妤,潘神功,曾广胜. 基于Laplacian算法的汽车外流场畸变网格优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1289-1296. |
| [7] | 汪少华,储堃,施德华,殷春芳,李春. 基于有限时间扩张状态观测的HEV鲁棒复合协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [8] | 陈磊,王杨,董志圣,宋亚奇. 一种基于转向意图的车辆敏捷性控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1257-1263. |
| [9] | 尹燕莉,黄学江,潘小亮,王利团,詹森,张鑫新. 基于PID与Q⁃Learning的混合动力汽车队列分层控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1481-1489. |
| [10] | 于贵申,陈鑫,武子涛,陈轶雄,张冠宸. AA6061⁃T6铝薄板无针搅拌摩擦点焊接头结构及性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
| [11] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [12] | 杨红波,史文库,陈志勇,郭年程,赵燕燕. 基于NSGA⁃II的斜齿轮宏观参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [13] | 赵睿,李云,胡宏宇,高镇海. 基于V2I通信的交叉口车辆碰撞预警方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1019-1029. |
| [14] | 陈小波,陈玲. 定位噪声统计特性未知的变分贝叶斯协同目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1030-1039. |
| [15] | 田彦涛,季言实,唱寰,谢波. 深度强化学习智能驾驶汽车增广决策模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
|
||