吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2752-2760.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211358
双电机驱动履带车辆直驶稳定性分层控制策略
- 1.北京科技大学 机械工程学院 北京 100083
2.中国北方车辆研究所,北京 100072
Straight driving stability hierarchical control for dual-motor driving electric tracked vehicle
Bing CHEN1( ),Kai-xuan MA1,Yang LIU1,Jiang REN1,Chen-xi ZHANG2,Tao-shuo ZHAO2
),Kai-xuan MA1,Yang LIU1,Jiang REN1,Chen-xi ZHANG2,Tao-shuo ZHAO2
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083,China
2.China North Vehicle Research Institute,Beijing 100072,China
摘要:
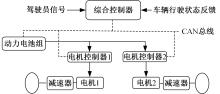
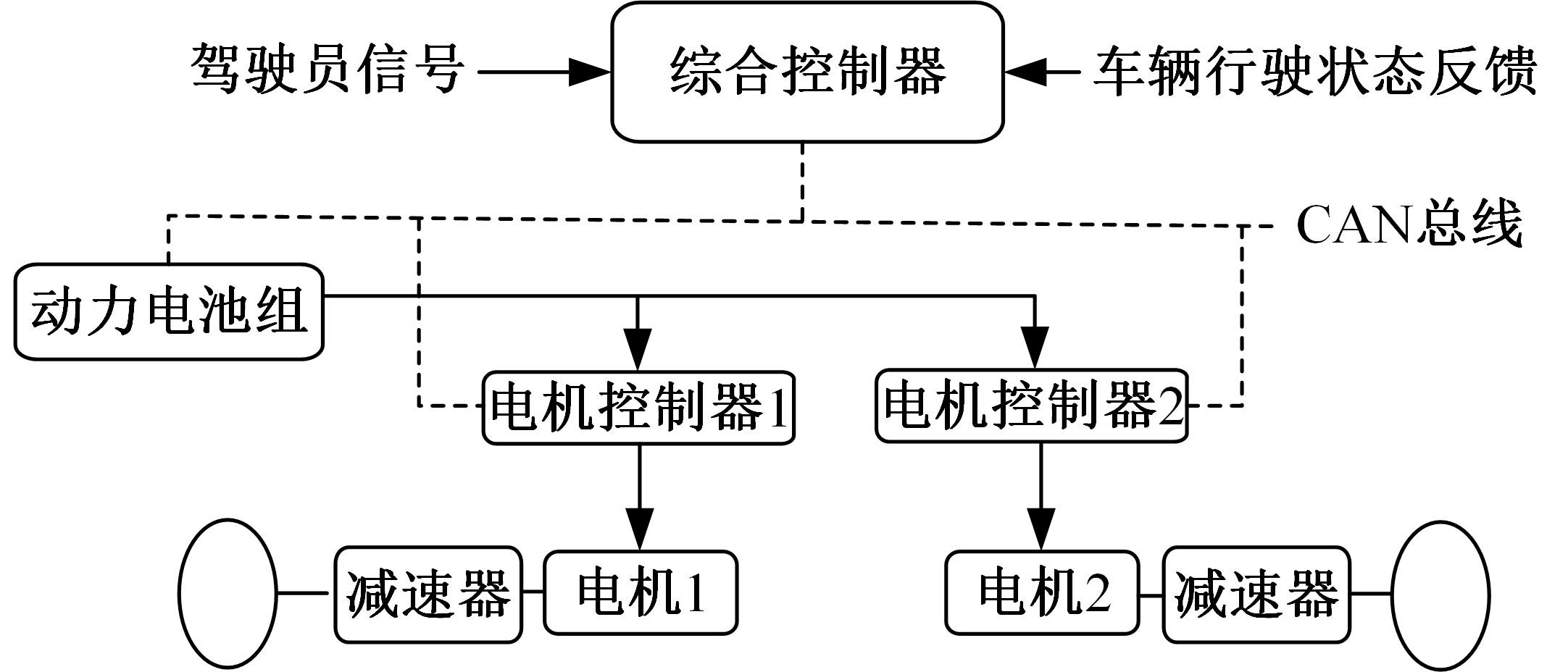
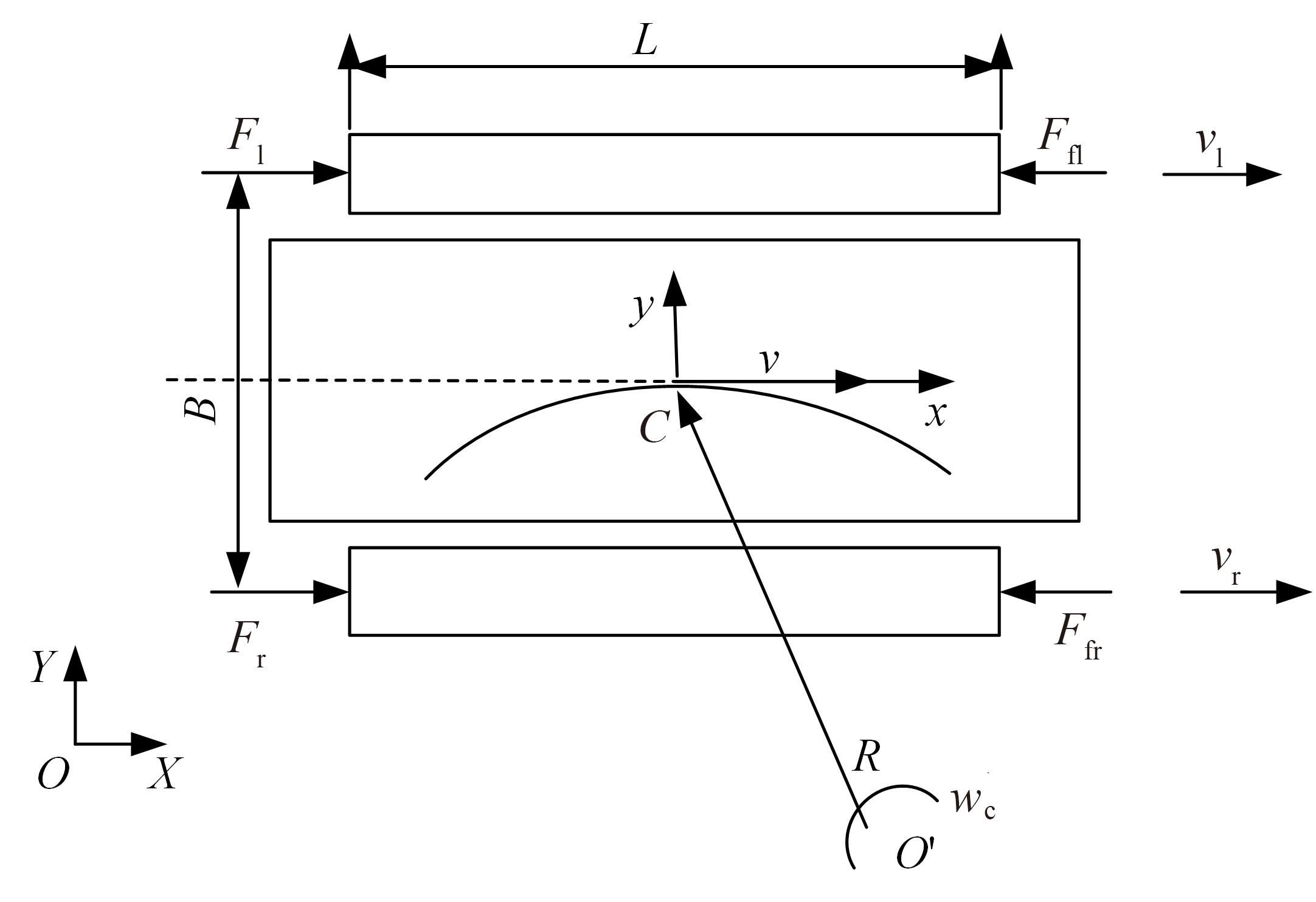
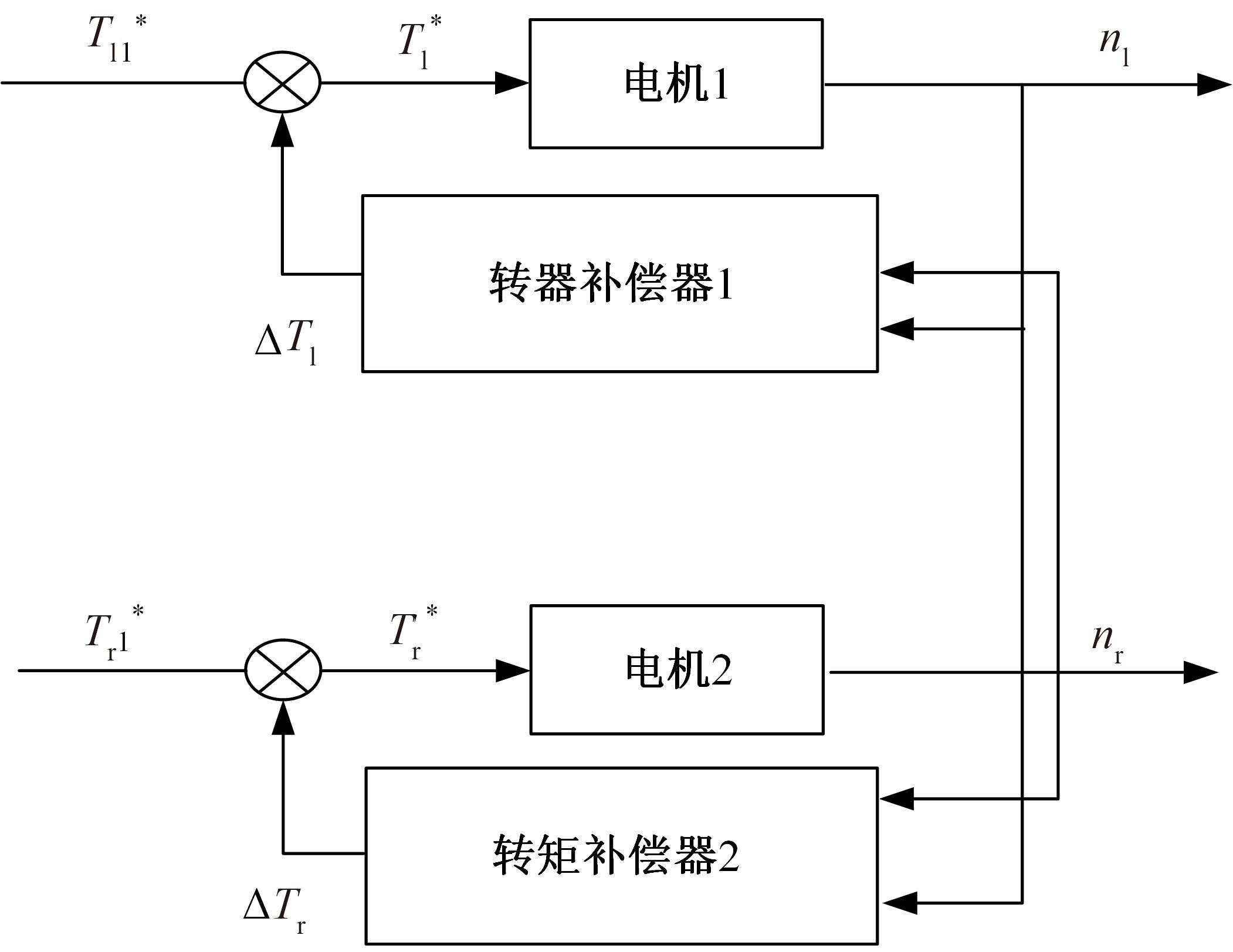
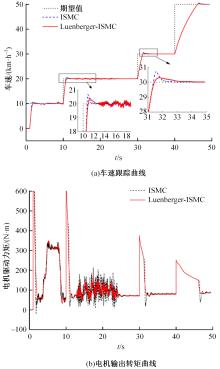
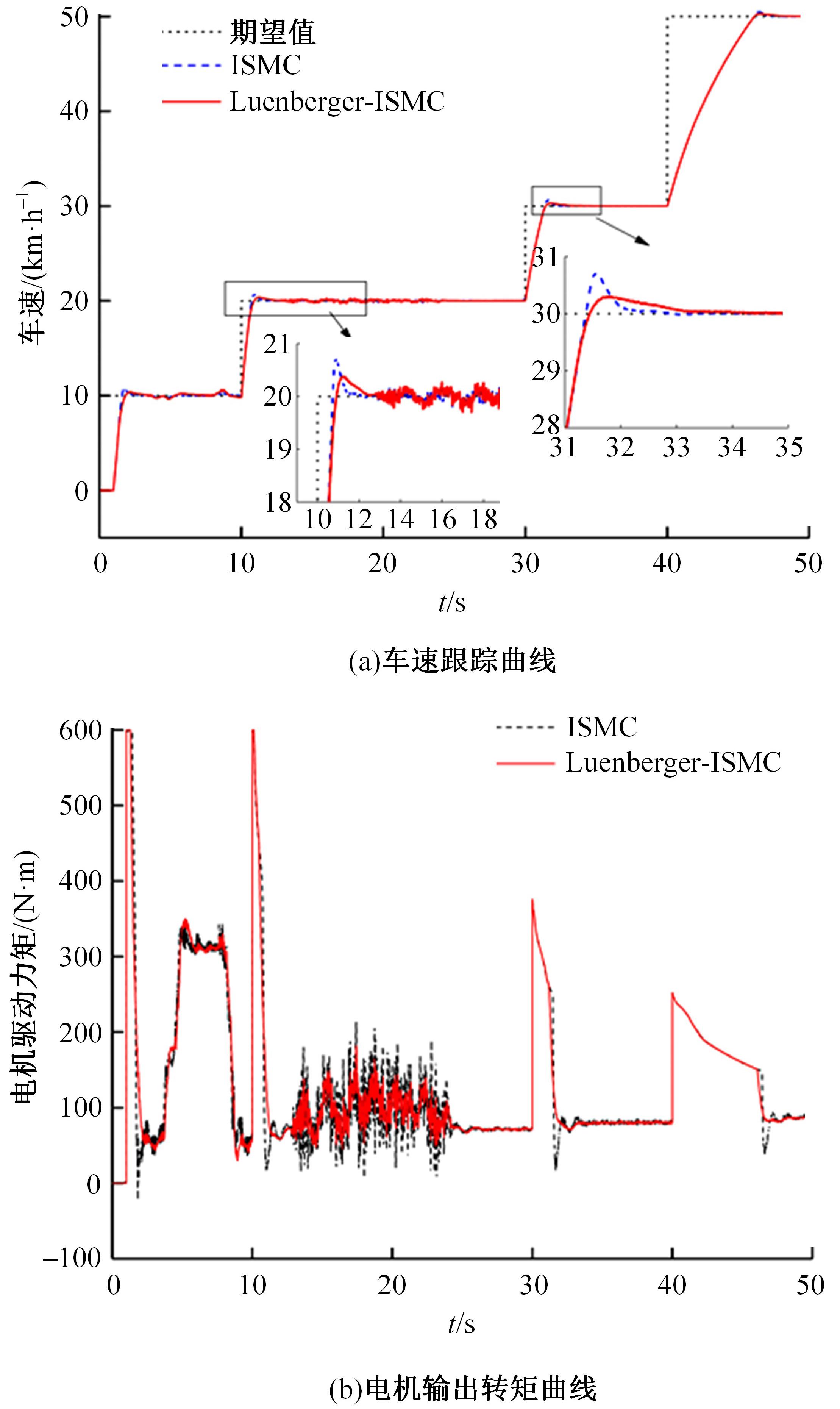
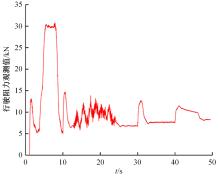
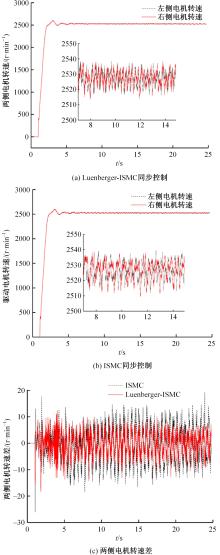
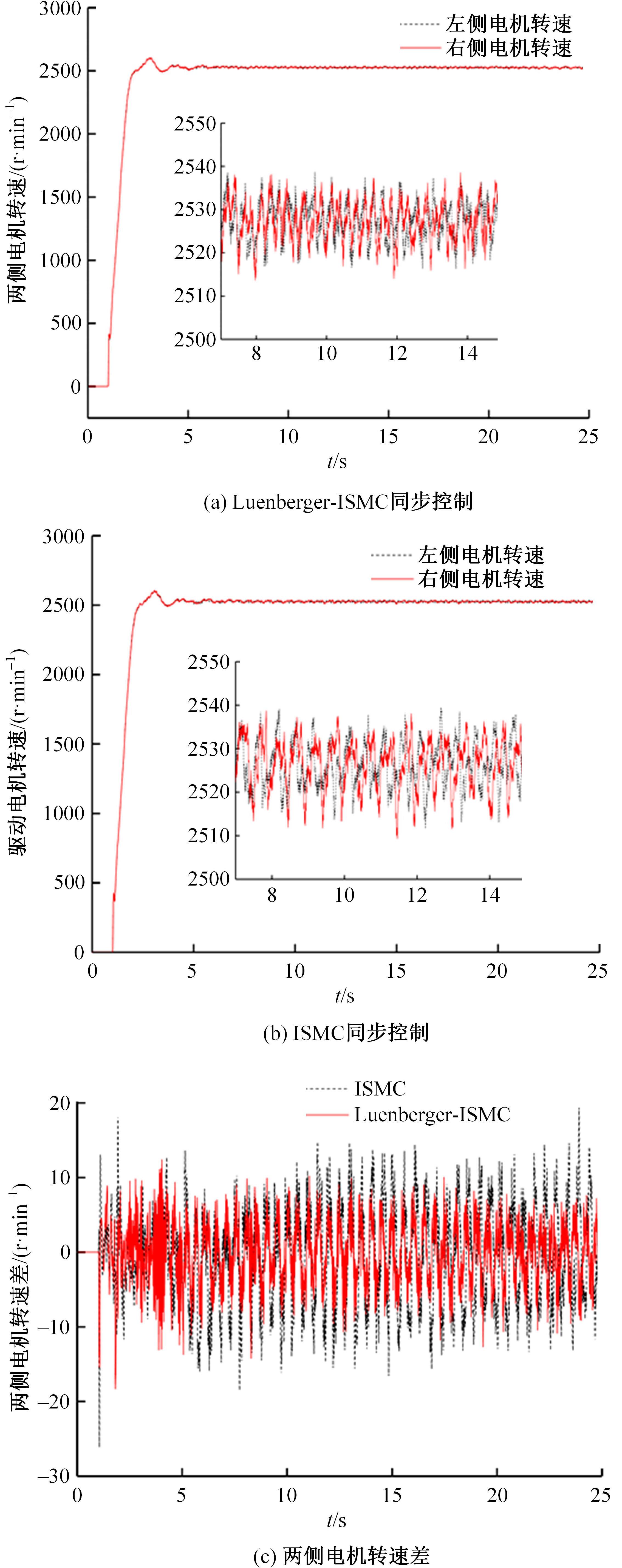
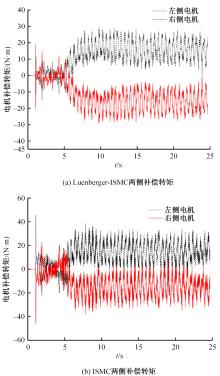
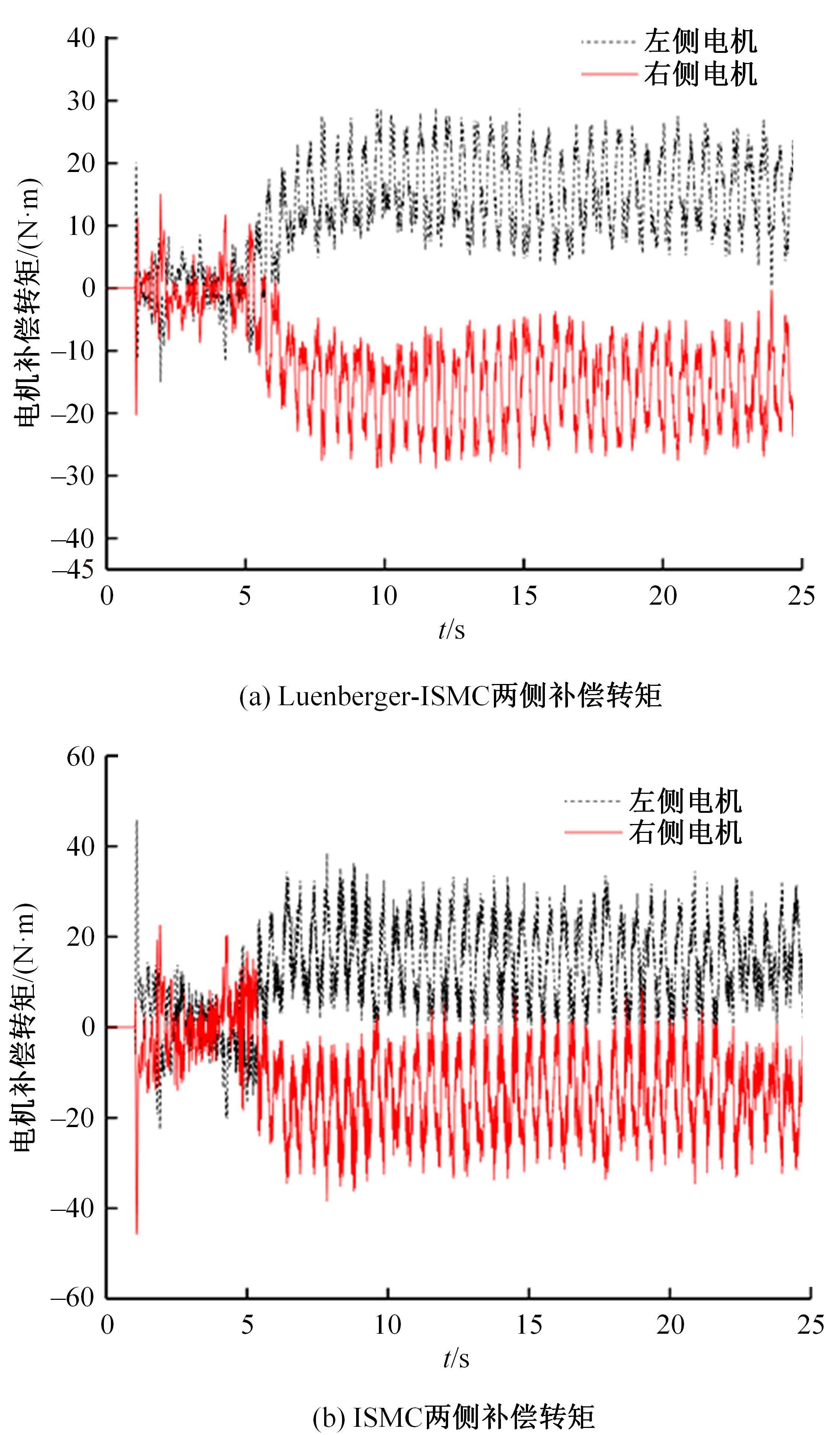
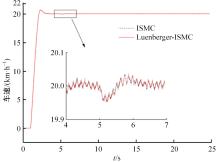
针对双电机独立驱动履带车辆直线行驶车速往往会由于路面结构、参数的剧烈变化而失去稳定性,以及车辆两侧行驶阻力不同也会造成驱动电机转速不同而出现车辆偏驶现象的问题,提出了一种车辆直线行驶整车分层控制策略,上层控制车辆直线行驶车速稳定性,下层控制双侧电机转速同步,提高车辆直线行驶车速抗干扰性的同时减少行驶偏移量。围绕外界行驶阻力扰动问题,设计了Luenberger阻力观测器,并将其观测值反馈到上层积分滑模车速控制器中,以提高车速抗干扰性;下层控制器采用交叉耦合同步控制,补偿两侧电机输出转矩,以提高两侧电机的同步性。最后,通过RecurDyn+Matlab/Simulink联合仿真验证了本文控制策略的有效性。
中图分类号:
- U469.694
| 1 | 邹渊,胡晓松.地面车辆混合驱动系统建模与控制优化[M]. 北京:北京理工大学出版社,2015:240-245. |
| 2 | Randive V, Subramanian S C, Thondiyath A. Component sizing of single and dual drive series hybrid electric powertrain for military tracked vehicles[C]∥IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Wuhan,China,2019: 1-6. |
| 3 | Sivakumar P, Reginald R, Viswanath G,et al. Configuration study of hybrid electric power pack for tracked combat vehicles[J]. Defence Science Journal,2017,67(4): 354-364. |
| 4 | 马晓军,苏建强,魏曙光,等. 双侧电驱动装甲车辆直驶转矩补偿控制[J]. 兵工学报,2013,34(11): 1373-1379. |
| Ma Xiao-jun, Su Jian-qiang, Wei Shu-guang,et al. Torque compensate control of dual-motor electric drive armored vehicle[J]. Acta Armamentarii,2013,34(11): 1373-1379. | |
| 5 | 李春明,盖江涛,袁艺,等. 履带车辆双电机耦合驱动系统同步特性[J]. 兵工学报,2020,41(10): 1930-1938. |
| Li Chun-ming, Gai Jiang-tao, Yuan Yi,et al. Synchronization characteristics of dual-motor coupled driving system of tracked vehicle[J]. Acta Armamentarii,2020,41(10):1930-1938. | |
| 6 | Li P, Yan J, Tu Q,et al. A steering control strategy based on torque fuzzy compensation for dual electric tracked vehicle[J]. Filomat,2018,32(5): 1953-1963. |
| 7 | Ziye Z, Haiou L, Huiyan C,et al. Tracking control of unmanned tracked vehicle in off-road conditions with large curvature[C]∥IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC),Auckland, New Zealand, 2019: 3867-3873. |
| 8 | Ji X, He X, Lv C,et al. A vehicle stability control strategy with adaptive neural network sliding mode theory based on system uncertainty approximation[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics,2018,56(6): 923-946. |
| 9 | Guo H, Liu J, Cao D,et al. Dual-envelop-oriented moving horizon path tracking control for fully automated vehicles[J]. Mechatronics,2018,50: 422-433. |
| 10 | 刘金琨,孙富春. 滑模变结构控制理论及其算法研究与进展[J]. 控制理论与应用,2007,24(3): 407-418. |
| Liu Jin-kun, Sun Fu-chun. Research and development on theory and algorithms of sliding mode control[J]. Control Theory & Applications,2007,24(3): 407-418. | |
| 11 | Qi G, Fan X, Zhao Z. Fuzzy and sliding mode variable structure control of vehicle active steering system[J]. Recent Patents on Mechanical Engineering,2021,14(2): 226-241. |
| 12 | 李静,余春贤,陆辉,等. 基于模型预测的车辆稳定控制[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2013, 43(): 504-508. |
| Li Jing, Yu Chun-xian, Lu Hui, et al. Vehicle stability control based on model prediction[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition),2013,43(Sup.1): 504-508. | |
| 13 | Li S T, Liu H, Zhao D . et al. Adaptive sliding mode control of lateral stability of four-wheel hub electric vehicles[J]. International Journal of Automotive Technology,2020,21(3): 739-747. |
| 14 | Chen Dong-dong, Li Zong-wei, Chen Ying. PMSM double loop predictive control based on Luenberger observer[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,2021,1754(1): No.012091. |
| 15 | Zhang Y, An Y, Wang G, Kong X. Multi motor neural PID relative coupling speed synchronous control[J]. Archives of Electrical Engineering,2020,69(1): 69-78. |
| 16 | 王建红,陈耀忠,陈桂,等. 基于交叉耦合控制的双电机同步控制系统研究[J]. 南京理工大学学报,2017,41(6): 693-697. |
| Wang Jian-hong, Chen Yao-zhong, Chen Gui. Dual-motor synchronous control system based on cross-coupled control[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology,2017,41(6): 693-697. | |
| 17 | Li L B, Sun L L, Zhang S Z,et al. Speed tracking and synchronization of multiple motors using ring coupling control and adaptive sliding mode control[J]. ISA Transactions,2015,58: 635-649. |
| 18 | 李金子,肖炯然,潘剑飞,等. 多永磁同步直线电机协同控制研究[J]. 吉林大学学报:信息科学版,2019,37(1): 32-39. |
| Li Jin-zi, Xiao Jiong-ran, Pan Jian-fei,et al. Research on cooperative control of multi-PMSM linear motors [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Information Science Edition),2019,37(1): 32-39. |
| [1] | 陈兆玮,蒲前华. 弹性车轮对大跨斜拉桥车桥耦合振动的抑制特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2519-2532. |
| [2] | 刘平义,李晓婷,高偌霖,李海涛,魏文军,王亚. 车辆侧倾驱动机构设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2185-2192. |
| [3] | 黄学劲,钟锦星,路京雨,赵霁,肖伟,袁新枚. 基于用户画像的电动汽车充电负荷预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2193-2200. |
| [4] | 张树培,夏明悦,张玮,陈钊,陈义祥. 考虑非线性刚度的间隙球铰碰撞动力学建模与仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2227-2235. |
| [5] | 陈辉,邵亚军. 基于惯性基准多传感器耦合的路面谱测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2254-2262. |
| [6] | 陈磊,王杨,董志圣,宋亚奇. 一种基于转向意图的车辆敏捷性控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1257-1263. |
| [7] | 陈鑫,张冠宸,赵康明,王佳宁,杨立飞,司徒德蓉. 搭接焊缝对铝合金焊接结构轻量化设计的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1282-1288. |
| [8] | 张勇,毛凤朝,刘水长,王青妤,潘神功,曾广胜. 基于Laplacian算法的汽车外流场畸变网格优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1289-1296. |
| [9] | 汪少华,储堃,施德华,殷春芳,李春. 基于有限时间扩张状态观测的HEV鲁棒复合协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [10] | 尹燕莉,黄学江,潘小亮,王利团,詹森,张鑫新. 基于PID与Q⁃Learning的混合动力汽车队列分层控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1481-1489. |
| [11] | 于贵申,陈鑫,武子涛,陈轶雄,张冠宸. AA6061⁃T6铝薄板无针搅拌摩擦点焊接头结构及性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
| [12] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [13] | 杨红波,史文库,陈志勇,郭年程,赵燕燕. 基于NSGA⁃II的斜齿轮宏观参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1007-1018. |
| [14] | 赵睿,李云,胡宏宇,高镇海. 基于V2I通信的交叉口车辆碰撞预警方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1019-1029. |
| [15] | 陈小波,陈玲. 定位噪声统计特性未知的变分贝叶斯协同目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1030-1039. |
|
||