吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (9): 2557-2567.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221390
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于悬锤系统的简支梁桥冲击系数测试方法适用性
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.青岛理工大学 土木工程学院,山东 青岛 266033
3.湖北省交通规划设计院股份有限公司,武汉 430051
Application of dynamic load allowance test method of simply supported girder bridge based on suspension hammer system
Yu-xin XUE1( ),Yong-jun ZHOU1(
),Yong-jun ZHOU1( ),Ye-lu WANG2,Kai-xiang FAN3,Yu ZHAO1
),Ye-lu WANG2,Kai-xiang FAN3,Yu ZHAO1
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.College of Civil Engineering,Qingdao University of Technology,Qingdao 266033,China
3.Hubei Communications Planning and Design Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Wuhan 430051,China
摘要:
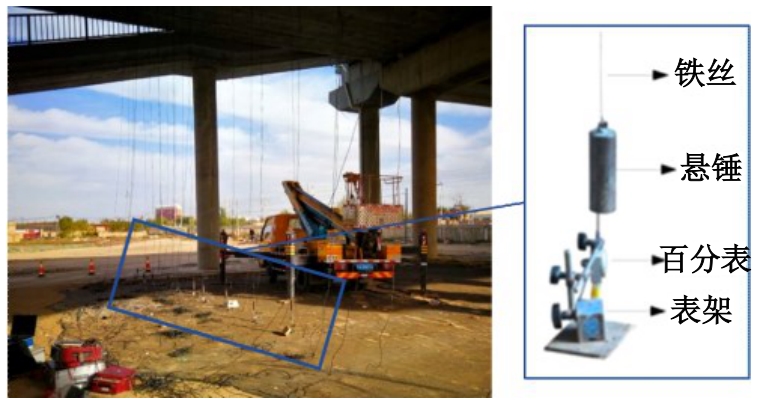
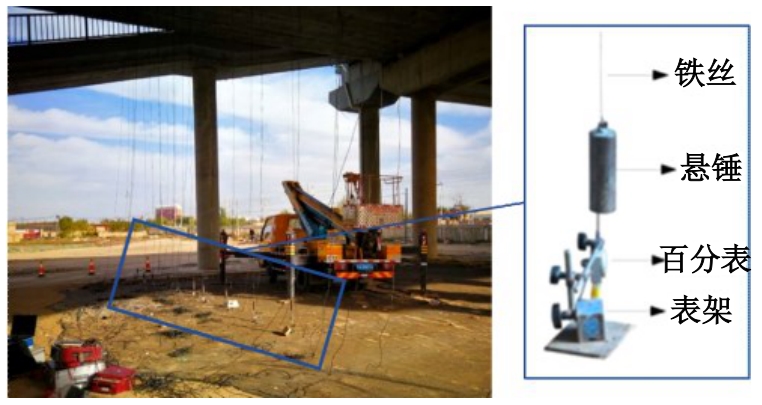
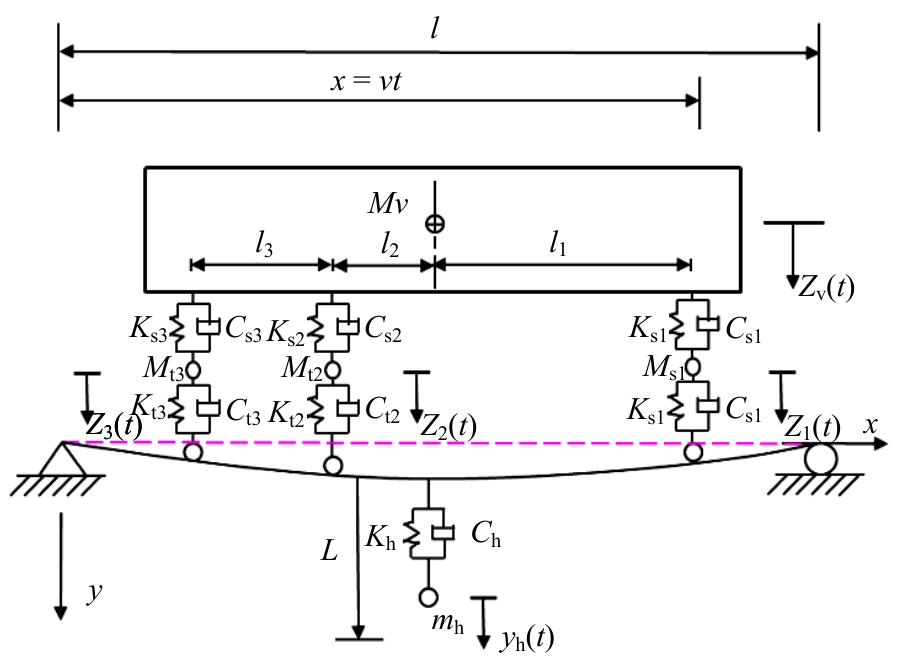
为研究悬锤系统在桥梁动力测试中的应用,以标准跨径简支梁/板桥为对象,采用理论推导、数值模拟与试验验证相结合的方法开展研究。首先,根据达朗贝尔原理推导了车-桥-悬锤系统耦合振动理论方程;然后,基于ANSYS软件编制分析程序进行数值计算,研究悬挂长度、铁丝直径、弹性模量以及悬锤质量对悬锤法测试冲击系数结果的影响,并与支架法测试结果对比,结合响应面分析,针对不同桥型提出了悬锤系统参数选型建议;最后,选取一座30 m简支箱梁桥进行动载试验,分别采用支架法与悬锤法测试挠度冲击系数,验证本文参数选型。结果表明:铁丝直径和悬锤质量交互作用显著;为满足悬锤法与支架法测量冲击系数差值小于5%的要求,铁丝直径以及悬锤质量的最佳取值应随悬挂长度增加而增大。
中图分类号:
- U44
| 1 | 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 2023年交通运输行业发展统计公报[N]. 中国交通报, 2024-6-18. |
| Ministry of Transport of the People's Republic of China.Ministry of transport statistical bulletin on the development of transportation industry in 2023[N]. China Transport News, 2024-06-18. | |
| 2 | .公路桥梁荷载试验规程 [S]. |
| 3 | 周勇军, 蔡军哲, 石雄伟, 等. 基于加权法的桥梁冲击系数计算方法[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2013, 13(4): 29-36. |
| Zhou Yong-jun, Cai Jun-zhe, Shi Xiong-wei, et al. Computing method of bridge impact factor based on weighted method[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2013, 13(4): 29-36. | |
| 4 | 周勇军, 薛宇欣, 李冉冉,等. 桥梁冲击系数理论研究和应用进展[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(4): 31-50. |
| Zhou Yong-jun, Xue Yu-xin, Li Ran-ran, et al. State-of-the-art of theory and applications of bridge dynamic load allowance[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(4): 31-50. | |
| 5 | 熊先才, 章鹏, 苻欲梅, 等. 光电液位传感器及其在桥梁挠度自动测量中的应用[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 2006, 26(4): 260-264. |
| Xiong Xian-cai, Zhang Peng, Fu Yu-mei, et al. Optoelectronic liquid-level sensor and its application for automatically measuring bridge deflection[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2006,26(4):260-264. | |
| 6 | 邵新星, 黄金珂, 员方, 等. 基于视觉的桥梁挠度测量方法与研究进展[J]. 实验力学, 2021, 36(1):29-42. |
| Shao Xin-xing, Huang Jin-ke, Yuan Fang, et al. Measurement method and recent progress of vision-based deflection measurement of bridges[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics, 2021,36(1):29-42. | |
| 7 | Huang J, Shao X X, Yang F J. Measurement method and recent progress of vision-based deflection measurement of bridges: a technical review[J]. Optical Engineering, 2022, 61(7): No. 070901. |
| 8 | 蓝章礼,杨小帆.非接触式张力线桥梁挠度测量系统[J].仪器仪表学报, 2008, 29(5): 1058-1062. |
| Lan Zhang-li, Yang Xiao-fan. Non-contact bridge deflection measurement system using weighted- streched-wire[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2008, 29(5): 1058-1062. | |
| 9 | 王业路, 周勇军, 高徐军, 等. 基于预紧弹簧系统的桥梁挠度冲击系数量测方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2022, 35(10): 172-182. |
| Wang Ye-lu, Zhou Yong-jun, Gao Xu-jun, et al. Measurement method of the bridge deflection dynamic load allowance based on preloaded spring system[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022, 35(10): 172-182. | |
| 10 | Dong Y, Wang J Q, Ren W X, et al. A plastic optical fiber sensing system for bridge deflection measurement[J]. Sensors,2020,20(2):No.s20020480. |
| 11 | Alipour M, Washlesky S J, Harris D K. Field development and laboratory evaluation of 2D digital image correlation for deflection sensing in complex environments[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2019,24(4): No. 04019010. |
| 12 | Garg P, Moreu F, Ozdagli A, et al. Noncontact dynamic displacement measurement of structure using a moving laser doppler vibrometer[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2019, 24 (9): No.4019089. |
| 13 | Nie G Y, Bodda S S, Gupta A. Computer-vision- based vibration tracking using a digital camera: a sparse-optical- flow-based target tracking method[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(18): No.s22186869. |
| 14 | Cha G C, Park S, Oh T. A terrestrial lidar-based detection of shape deformation for maintenance of bridge structure[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2019, 145(12): No.4019075. |
| 15 | Xue M S, Yi T H, Qu C X, et al. Rapid estimation of bridge key deflection through optimized substructure impact testing[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering,2022, 27(10): No. 4022088. |
| 16 | 钟继卫, 王波, 王翔, 等. 桥梁智能检测技术研究与应用[J]. 桥梁建设, 2019, 49(): 1-6. |
| Zhong Ji-wei, Wang Bo, Wang Xiang, et al. Research of bridge intelligent inspection technology and application[J]. Bridge Construction, 2019,49(Sup.1):1-6. | |
| 17 | 李万恒, 申林, 王少鹏, 等. 基于多阶段分区域动力测试的桥梁结构损伤评估[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(3): 773-780. |
| Li Wan-heng, Shen Lin, Wang Shao-peng, et al. Damage assessment of bridge construction on multi-stage subregion mobile test[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 773-780. | |
| 18 | Yang D, Zhang S Q, Wang S, et al. Real-time illumination adjustment for video deflectometers[J]. Structure Control & Health Monitoring, 2022,29(5):No.e2930. |
| 19 | 王磊, 陈顺超, 袁胜涛, 等. 基于悬挂吊锤的桥梁动挠度测试[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(21): 9108-9115. |
| Wang Lei, Chen Shun-chao, Yuan Sheng-tao, et al. Test of bridge dynamic deflection based on suspended hammer[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(21): 9108-9115. | |
| 20 | 周勇军, 薛宇欣, 高徐军, 等. 基于模态叠加法的公路简支梁桥动力放大系数研究[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2023, 23(6): 146-155. |
| Zhou Yong-jun, Xue Yu-xin, Gao Xu-jun, et al. Research on dynamic amplification factor of highway simply supported girder bridge based on modal superposition method[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2023, 23(6): 146-155. | |
| 21 | 周勇军, 赵洋, 赵煜, 等. 基于动载试验荷载效率的简支梁桥冲击系数研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(20): 207-216. |
| Zhou Yong-jun, Zhao Yang, Zhao Yu, et al. A study on dynamic load allowance of a simply supported girder bridge based on load efficiency of a dynamic load test[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2021,40(20): 207-216. | |
| 22 | 韩智强, 谢刚, 周勇军, 等. 曲线桥梁车桥耦合振动数值分析方法[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(2): 515-522. |
| Han Zhi-qiang, Xie Gang, Zhou Yong-jun, et al. Numerical analysis method of vehicle-bridge coupling vibration of curved bridge[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 515-522. | |
| 23 | 沈火明, 肖新标. 求解车桥耦合振动问题的一种数值方法[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2003, 38(6): 658-662. |
| Shen Huo-ming, Xiao Xin-biao. Numerical method for vehicle bridge coupled vibrations[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2003,38(6):658-662. | |
| 24 | Won K L, Hae D P. Chaotic dynamics of a harmonically excited spring-pendulum system with internal resonance[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 1997, 14(3): 211 -229. |
| 25 | 姚玉权, 仰建岗, 高杰, 等. 基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
| Yao Yu-quan, Yang Jian-gang, Gao Jie, et al. Optimal design on recycled hot-mix asphalt mixture based on performance-cost model[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022,52(3): 585-595. |
| [1] | 郭雪莲,韩万水,王涛,周恺,张修石,张书颖. 大件车通行弯桥抗倾覆稳定安全系数评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2229-2237. |
| [2] | 肖林,魏欢博,卫星,康志锐. 钢混组合梁栓钉锈胀下混凝土板开裂行为数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1958-1965. |
| [3] | 张春雷,邵长宇,苏庆田,戴昌源. 球扁钢肋钢纤维混凝土组合桥面板正弯矩受力性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1634-1642. |
| [4] | 张彦玲,贾云飞,贾晓远,郑旺,李运生. 装配式小箱梁桥内力横向分布系数建议公式[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1688-1700. |
| [5] | 黄汉辉,陈康明,吴庆雄. 钢管混凝土桁式弦杆组合连续梁抗弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1665-1676. |
| [6] | 邵长江,崔皓蒙,漆启明,庄卫林. 近断层大跨RC轻柔拱桥纵向阻尼器减震研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1355-1367. |
| [7] | 赵秋,陈鹏,赵煜炜,余澳. 台后设置拱形结构的无缝桥梁整体受力性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1016-1027. |
| [8] | 张洪,朱志伟,胡天宇,龚燕峰,周建庭. 基于改进YOLOv5s的桥梁螺栓缺陷识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 749-760. |
| [9] | 韩智强,谢刚,卓亚娟,骆佐龙,李华腾. 基于车轮-桥面相干激励的大跨连续梁桥振动响应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 436-444. |
| [10] | 杨国俊,齐亚辉,石秀名. 基于数字图像技术的桥梁裂缝检测综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [11] | 谭国金,欧吉,艾永明,杨润超. 基于改进DeepLabv3+模型的桥梁裂缝图像分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 173-179. |
| [12] | 龙关旭,张修石,辛公锋,王涛,杨干. 融合机器视觉的桥梁动态称重方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 188-197. |
| [13] | 卫星,高亚杰,康志锐,刘宇辰,赵骏铭,肖林. 低温环境下栓钉环焊缝焊接残余应力场数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 198-208. |
| [14] | 安然,王有志. 剪力钉连接件拉剪共同作用抗剪性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2554-2562. |
| [15] | 左新黛,张劲泉,赵尚传. 在役混凝土T梁疲劳刚度退化及寿命预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2563-2572. |
|
||