吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2563-2572.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211238
在役混凝土T梁疲劳刚度退化及寿命预测方法
- 交通运输部公路科学研究院 桥梁隧道研究中心,北京 100088
Fatigue stiffness degradation and life prediction method of in⁃service concrete T⁃beams
Xin-dai ZUO( ),Jin-quan ZHANG,Shang-chuan ZHAO
),Jin-quan ZHANG,Shang-chuan ZHAO
- Bridge Tunnel Research Center,Research Institute of Highway Ministry of Transport,Beijing 100088,China
摘要:
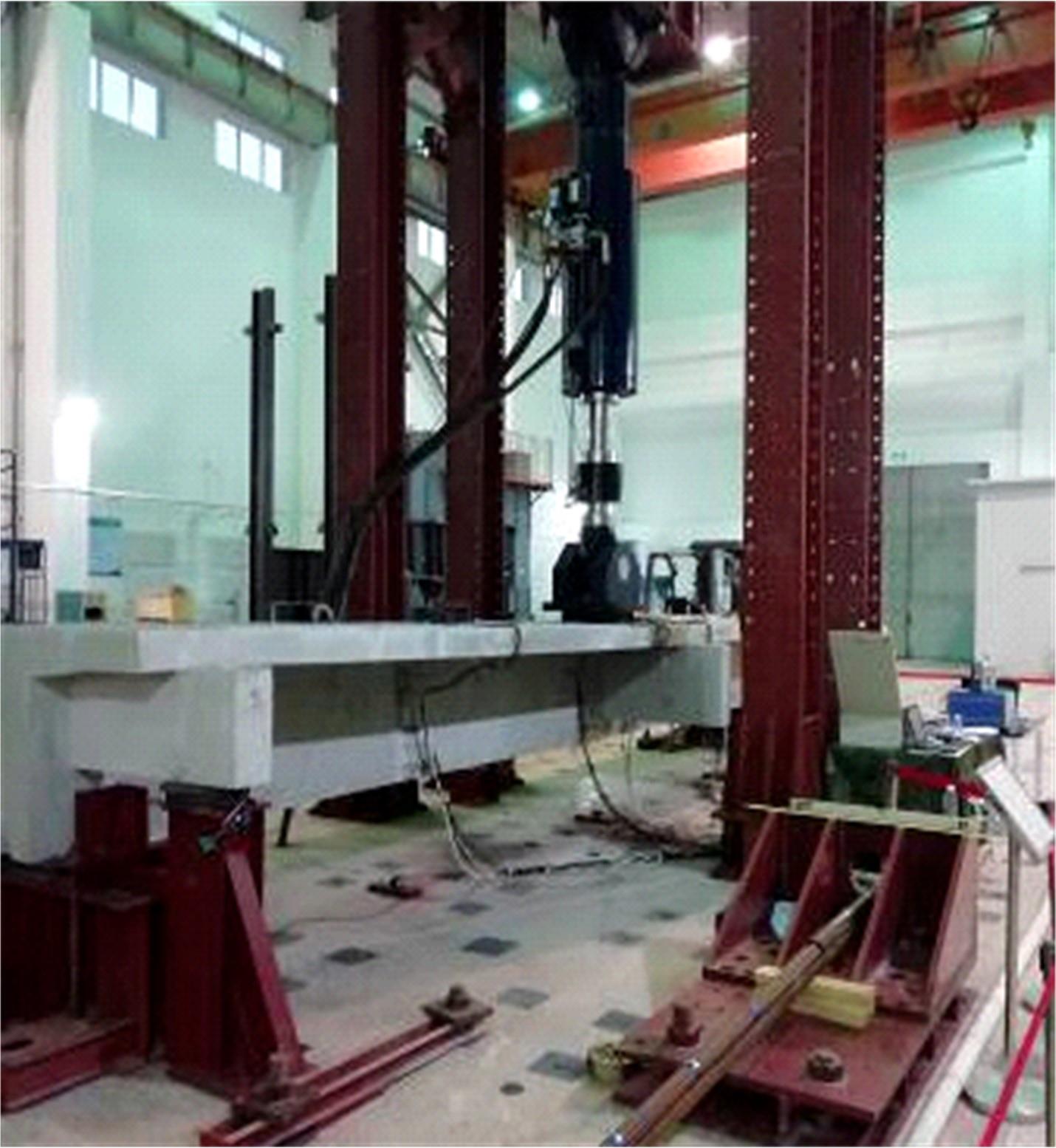
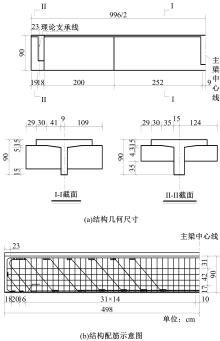
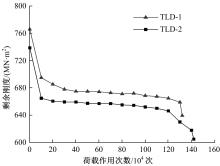
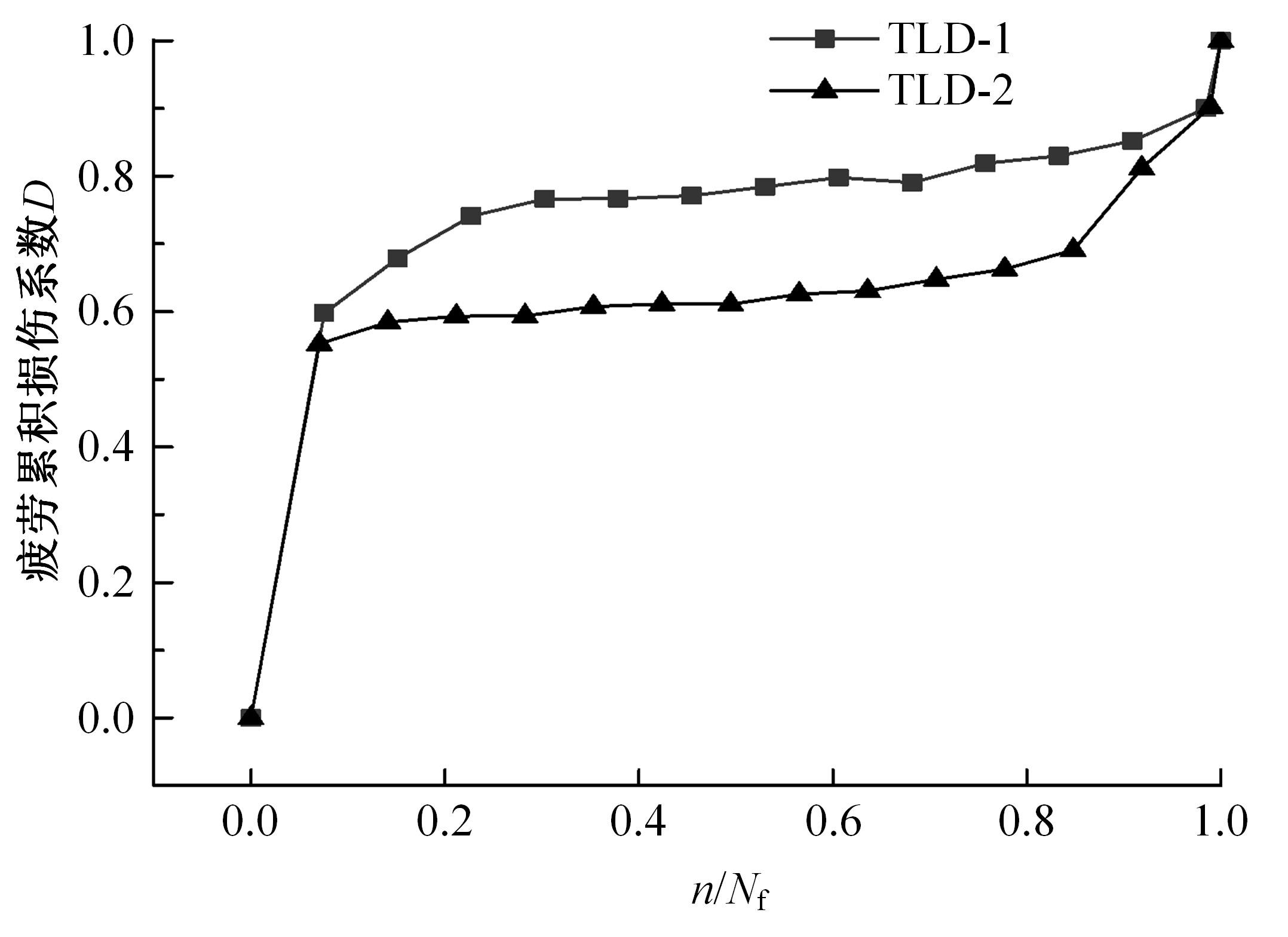
为获取在役混凝土T梁疲劳刚度退化规律,开展疲劳寿命预测,基于损伤力学理论构建了考虑开裂损伤的混凝土T梁阶梯刚度模型,通过对3根10 m钢筋混凝土T梁足尺模型进行静力和疲劳破坏试验,获取了疲劳剩余刚度随荷载作用次数的演化规律。引入疲劳损伤系数和刚度退化系数,建立了在役混凝土T梁疲劳寿命预测模型。分析结果表明:随着荷载作用次数的增加,桥梁剩余刚度呈现三阶段衰减,其中疲劳初期和后期阶段衰减较快,但占总寿命比重相对较小,而疲劳中期阶段呈线性稳定退化,约占疲劳总寿命的80%以上,为桥梁服役的主要阶段,疲劳破坏时剩余刚度约为初始刚度的82.7%。最终,针对在役混凝土T梁桥工作性状,提出了在役钢筋混凝土梁桥寿命预测方法,相关研究成果可为此类桥梁寿命预测研究提供理论支持。
中图分类号:
- U448.38
| 1 | 交通运输部. 2019年年交通运输行业发展统计公报[R]. 北京:交通运输部, 2020. |
| 2 | 宋秀华, 肖新辉, 鲁乃唯. 基于疲劳损伤的中小跨径桥梁限载取值研究[J]. 交通科学与工程, 2019, 35(2): 58-63. |
| Song Xiu-hua, Xiao Xin-hui, Lu Nai-wei. Study on vehicle load limit of medium and small span bridges based on fatigue damage[J]. Journal of Transport Science and Engineering, 2019,35(2): 58-63. | |
| 3 | 卫军, 杜永潇, 梁曼舒. 梁结构疲劳刚度退化对模态频率的影响[J] .浙江大学学报:工学版, 2019, 53(5): 899-909. |
| Wei Jun, Du Yong-xiao, Liang Man-shu. Influence of fatigue stiffness degradation for beam structure on modal frequency[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2019, 53(5): 899-909. | |
| 4 | 刘芳平, 易文韬. 钢筋混凝土梁基于疲劳刚度退化的承载力退化模型研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2020, 50(22): 99-104, 66. |
| Liu Fang-ping, Yi Wen-tao. Research on bearing capacity degr8dation model of reinforced concrete beams based on fatigue stiffness degradation[J]. Building Structure, 2020,50(22): 99-104, 66. | |
| 5 | 汪炳, 黄侨, 刘小玲. 组合梁疲劳后的刚度退化规律及计算模型[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(6): 265-271. |
| Wang Bing, Huang Qiao, Liu Xiao-ling. Stiffness degradation and its calculation model for composite beams after fatigue[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(6): 265-271. | |
| 6 | 周虎, 肖勇刚, 谭斌. 基于断裂力学的混凝土桥梁疲劳损伤及寿命评估分析[J]. 湖南城市学院学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 27(4): 6-10. |
| Zhou Hu, Xiao Yong-gang, Tan Bin. Fatigue damage and life evaluation of concrete bridges based on fracture mechanics[J]. Journal of Hunan City University (Natural Science), 2018, 27(4): 6-10. | |
| 7 | 陈万. 重载交通作用下桥梁结构的疲劳损伤数值分析[D].邯郸: 河北工业大学土木工程学院, 2015. |
| Chen Wan. Numerical analysis on fatigue damage of bridge caused by heavy load traffic[D]. Handan: School of Civil Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, 2015. | |
| 8 | 赵少杰, 任伟新. 超限超载交通对桥梁疲劳损伤及可靠度的影响[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 48(11): 3044-3050. |
| Zhao Shao-jie, Ren Wei-xin. Effect of overrun and overloaded vehicles on fatigue damage and reliability of highway bridges[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2017, 48(11): 3044-3050. | |
| 9 | Natário F, Fernández R M, Muttoni A. Experimental investigation on fatigue of concrete cantilever bridge deck slabs subjected to concentrated loads[J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 89: 191-203. |
| 10 | Liu Fang-ping, Zhou Jian-ting, Yan Lei. Study of stiffness and bearing capacity degradation of reinforced concrete beams under constant-amplitude fatigue[J]. PLoS ONE, 2018, 13(3): No.e0192797. |
| 11 | 朱红兵. 公路钢筋混凝土简支梁桥疲劳试验与剩余寿命预测方法研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学土木工程学院, 2011. |
| Zhu Hong-Bing. Method and experiment research on highway reinforced concrete simply-supported girder bridge's fatigue residual service life forecast[D]. Changsha: School of Civil Engineering, Central South University, 2011. | |
| 12 | 刘芳平, 周建庭. 基于疲劳应变演化的混凝土弯曲强度退化分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(4): 97-105. |
| Liu Fang-ping, Zhou Jian-ting. Concrete bending strength degradation analysis based on fatigues strain evolution[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(4): 97-105. | |
| 13 | Cheng L J. Flexural fatigue analysis of a CFRP form reinforced concrete bridge deck[J]. Composite Structures, 2011, 93(11):2895-2902. |
| 14 | Neild S A, Williams M S, Mcfadden P D. Nonlinear vibration characteristics of damaged concrete beams[J]. Journal of Structural Engineering ASCE, 2003, 129(2): 260-268. |
| 15 | 曹晖, 郑星, 华建民, 等. 基于非线性振动特性的预应力混凝土 梁损伤识别[J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(2): 190-194. |
| Cao Hui, Zheng Xing, Hua Jian-min, et al. Damage detection of prestressed concrete beams based on non-linger dynamic characteristics[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(2): 190-194. | |
| 16 | 卫军, 杜永潇. 基于固有频率的梁结构疲劳损伤演化规律[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 50(8): 1866-1875. |
| Wei Jun, Du Yong-xiao. Fatigue damage evolution of Timoshenko beams based on natural frequency[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2019, 50(8): 1866-1875. | |
| 17 | 朱红兵, 赵耀, 李秀, 等. 疲劳荷载作用下钢筋混凝土梁的刚度退化规律及计算公式[J].土木建筑与环境工程, 2014, 36(2): 1-13. |
| Zhu Hong-bing, Zhao Yao, Li Xiu, et al. Reinforced concrete beam's stiffness degeneration regulation and its calculation formula under the action of fatigue load[J]. Journal of Civil, Architectural & Environment Engineering, 2014, 36(2): 1-13. | |
| 18 | 姚恒盈. 装配式预应力混凝土箱梁静动刚度足尺试验全过程分析[D]. 西安:长安大学公路学院, 2020. |
| Yao Heng-ying. Dynamic and static stiffness analysis of full-scale prefabricated prestressed concrete girder[D]. Xi′an: School of Highway, Chang'an University, 2020. | |
| 19 | 廉伟, 姚卫星.复合材料层压板剩余刚度-剩余强度关联模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008, 25(5): 151-156. |
| Lian Wei, Yao Wei-xing. Residual stiffness-residual strength coupled model of composite laminates[J]. Acta Materiae Composites Sinica, 2008, 25(5): 151-156. | |
| 20 | Ma Y, Xiang Y, Wang L, et al. Fatigue life prediction for aging RC beams considering corrosive environments[J]. Engineering Structures, 2014(79): 211-221. |
| [1] | 安然,王有志. 剪力钉连接件拉剪共同作用抗剪性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2554-2562. |
| [2] | 王峰,刘双瑞,王佳盈,宋佳玲,王俊,张久鹏,黄晓明. 尺寸和形状效应对多孔结构风阻系数的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1677-1685. |
| [3] | 王俊,李加武,王峰,张久鹏,黄晓明. 简化U形峡谷风速分布及其对悬索桥抖振响应的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1658-1668. |
| [4] | 王华,王龙林,张子墨,何昕. 基于裂缝宽度变化的连续刚构桥安全性预警技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1650-1657. |
| [5] | 冯宇,郝键铭,王峰,张久鹏,黄晓明. 非平稳极端风作用下大跨桥梁瞬态风致效应分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1638-1649. |
| [6] | 顾正伟,张攀,吕东冶,吴春利,杨忠,谭国金,黄晓明. 基于数值仿真的简支梁桥震致残余位移分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1711-1718. |
| [7] | 吴春利,黄诗茗,李魁,顾正伟,黄晓明,张炳涛,杨润超. 基于数值仿真和统计分析的洪水作用下桥墩作用效应分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1612-1620. |
| [8] | 谭国金,孔庆雯,何昕,张攀,杨润超,朝阳军,杨忠. 基于动力特性和改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷深度识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1592-1600. |
| [9] | 江辉,李新,白晓宇. 桥梁抗震结构体系发展述评:从延性到韧性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1550-1565. |
| [10] | 袁野. 温度和车辆作用下梁式桥梁结构固有频率分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1702-1710. |
| [11] | 刘子玉,陈士通,支墨墨,黄晓明,陈哲心. 可“临-永”转换抢修钢墩应急使用极限承载力[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1601-1611. |
| [12] | 张玥,刘传森,宋飞. 桥台背墙对连续梁桥地震易损性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1372-1380. |
| [13] | 兰树伟,周东华,陈旭,莫南明. 双柱式高墩桥梁整体稳定性的实用算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1105-1111. |
| [14] | 孙琪凯,张楠,刘潇,周子骥. 基于Timoshenko梁理论的钢-混组合梁动力折减系数[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 488-495. |
| [15] | 回丽,陆家琛,周松,安金岚,周冠妍,刘小鹏. 热处理对TC4钛合金激光双束焊接接头疲劳性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 105-110. |
|