吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 2837-2848.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221523
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑小样本不确定性的土石坝压实质量智能评估
- 1.北京科技大学 土木工程系,北京 100083
2.水电水利规划设计总院,北京 100011
3.清华大学 水沙科学与水利水电工程国家重点实验室,北京 100084
4.中国水利水电科学研究院 水利部水工程建设与安全重点实验室,北京 100048
Intelligent compaction quality assessment of earth-rock dams considering small samples uncertainty
Qing-long ZHANG1( ),Nai-fu Deng1,Zai-zhan AN2,Rui MA3,Yu-fei ZHAO4(
),Nai-fu Deng1,Zai-zhan AN2,Rui MA3,Yu-fei ZHAO4( )
)
- 1.Department of Civil Engineering,University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083,China
2.China Electric Power Planning and Engineering Institute,Beijing 100011,China
3.State Key Laboratory of Hydroscience and Engineering,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
4.Key Laboratory of Construction and Safety of Water Engineering of the Ministry of Water Resources,China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research,Beijing 100048,China
摘要:
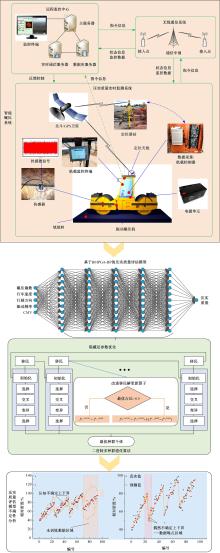
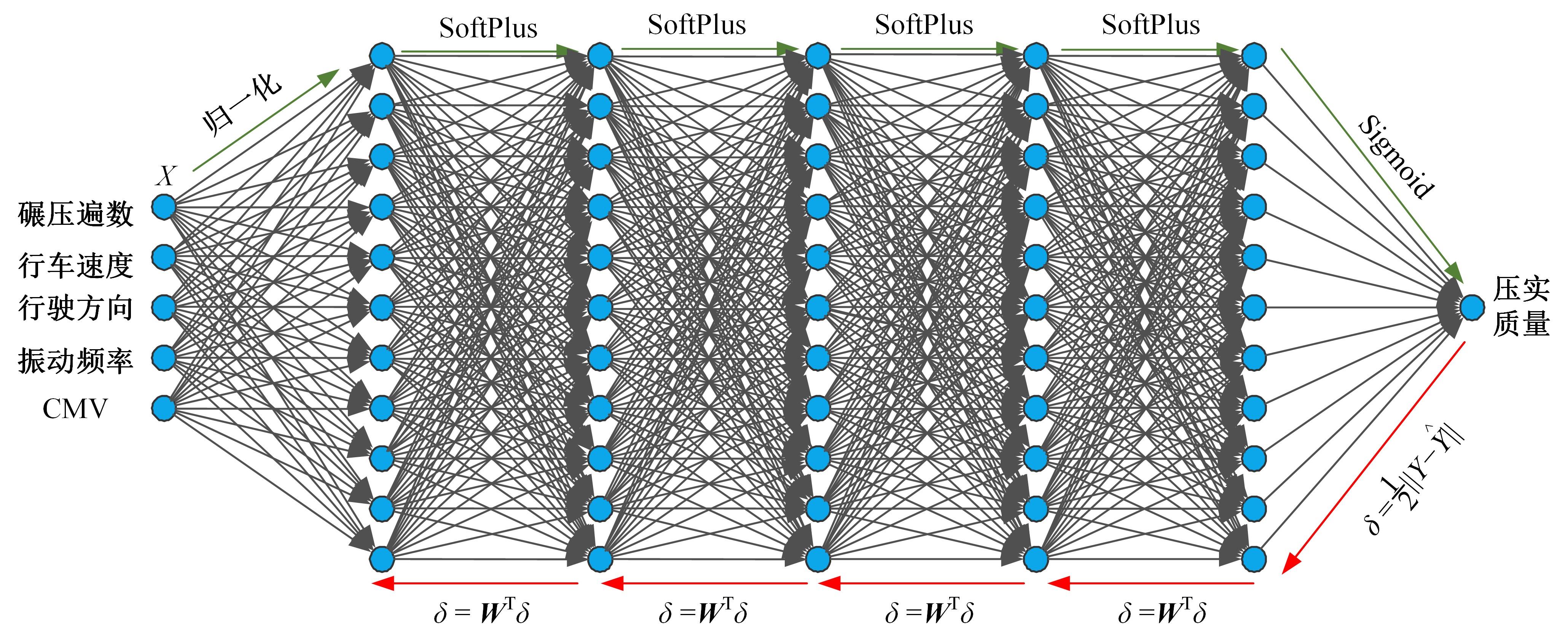
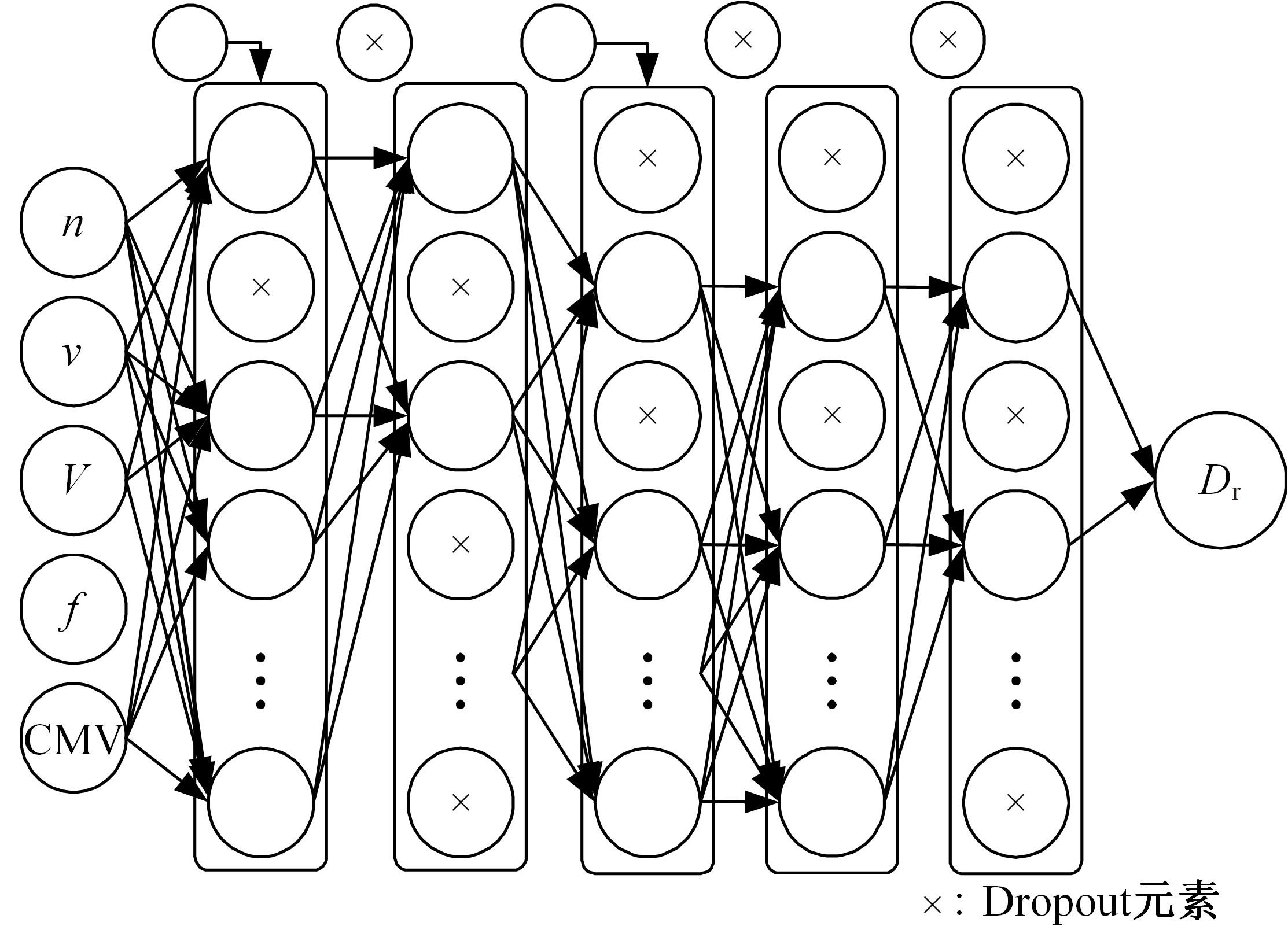
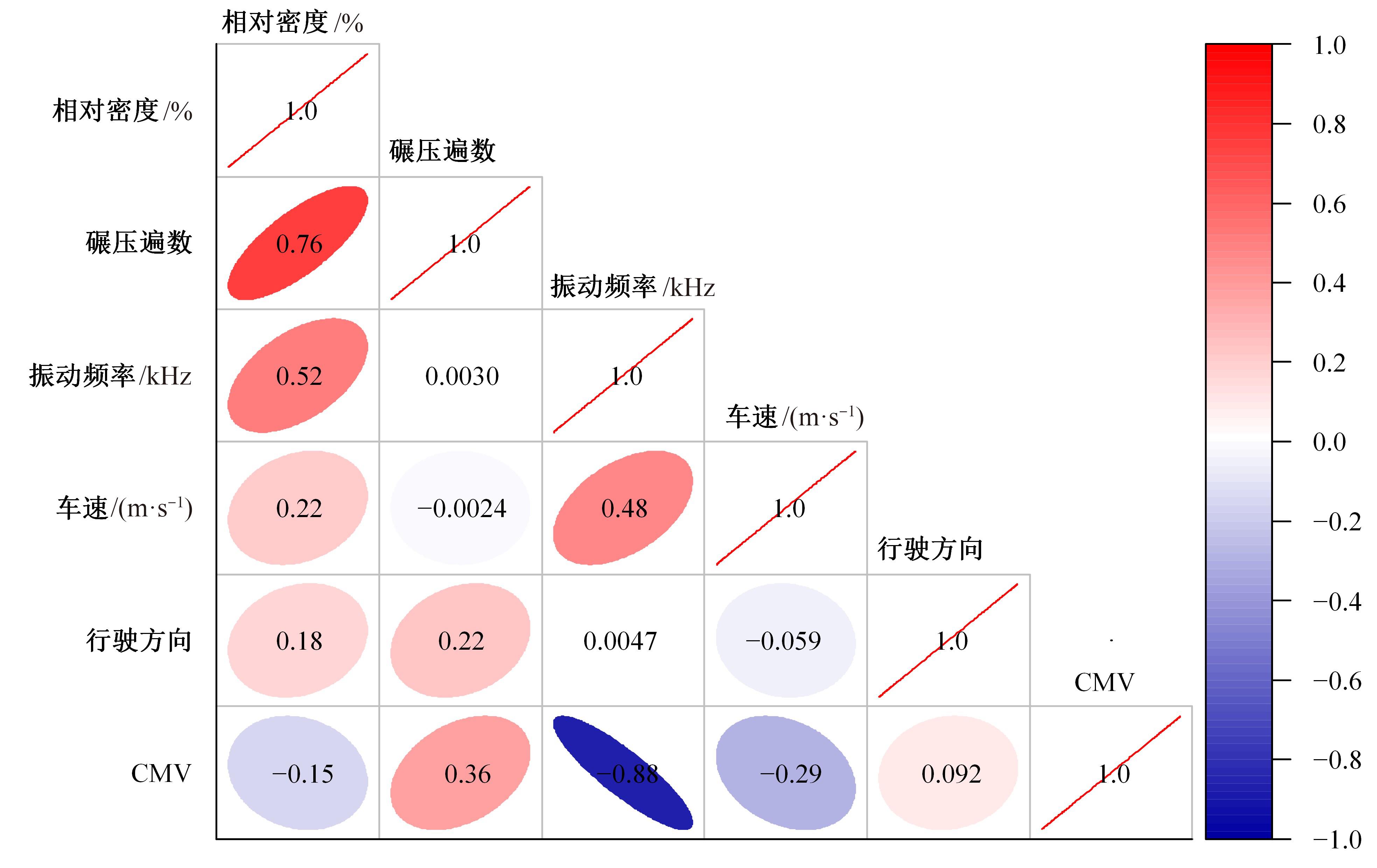
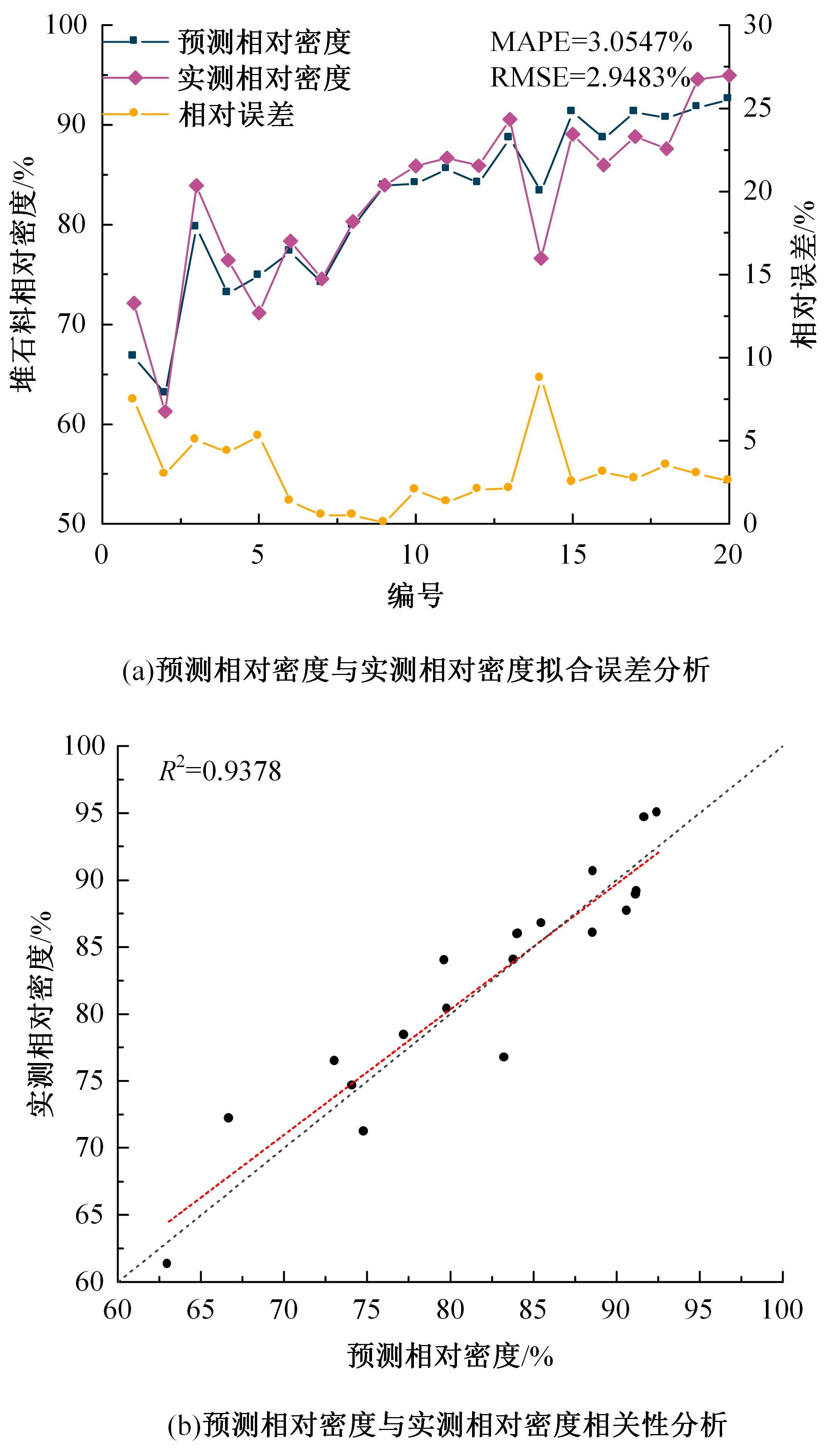
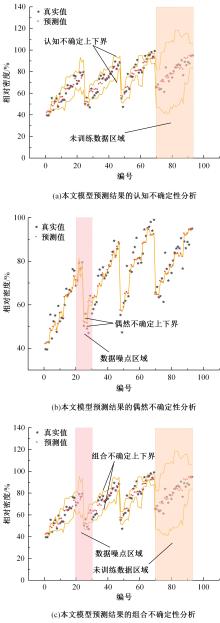
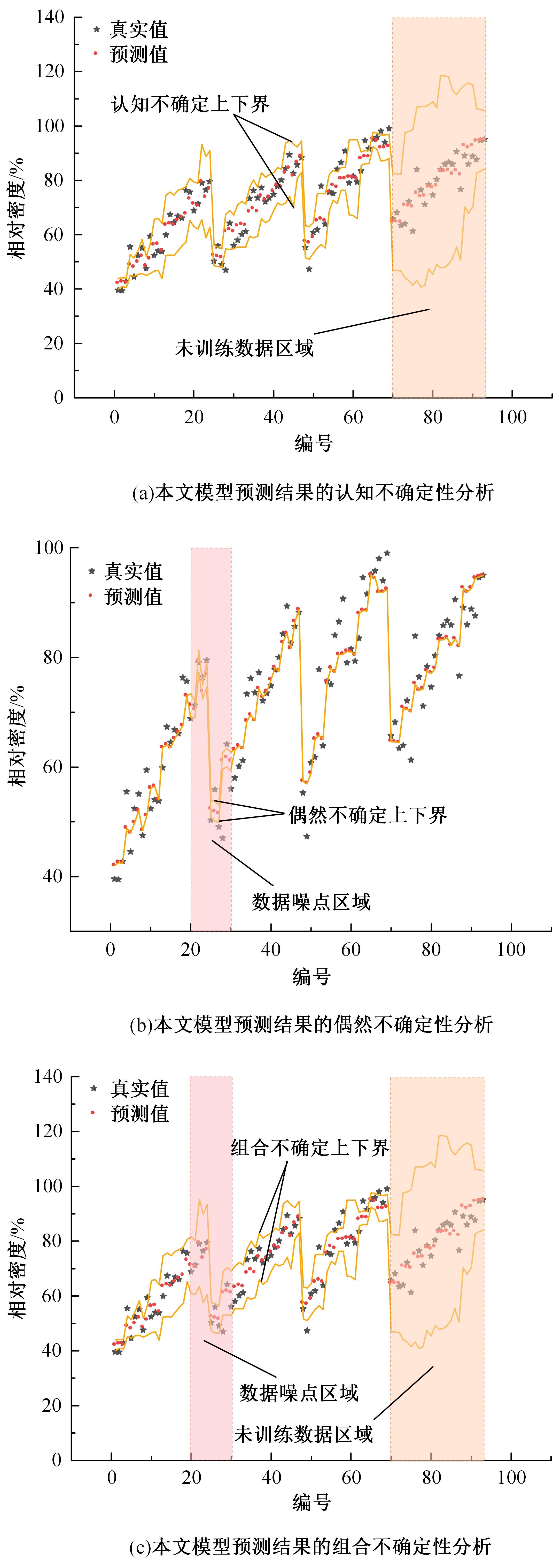
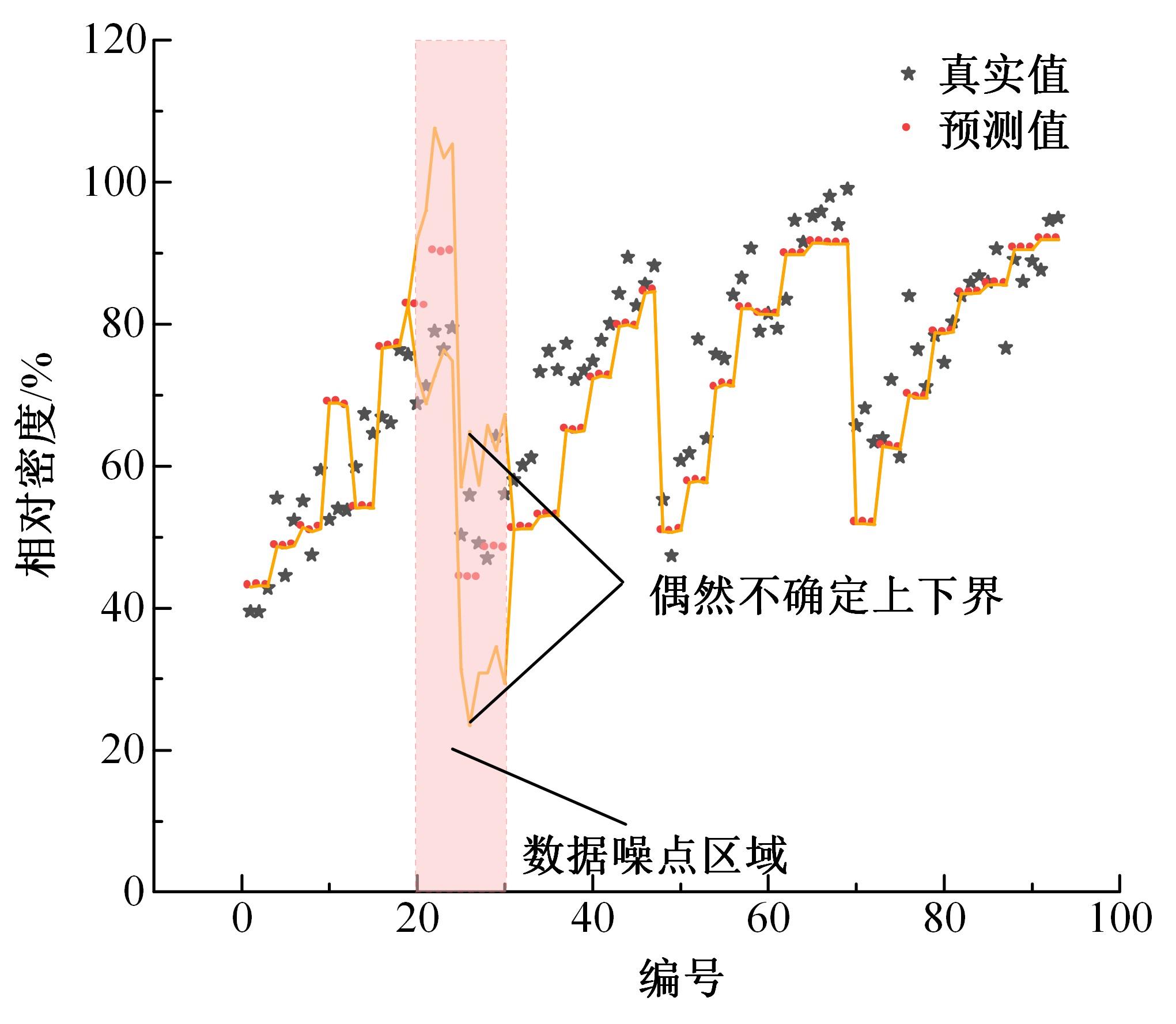
针对土石坝压实质量评估存在实时性差、精确度低、泛化能力弱、训练数据不足、易受外部环境改变影响等问题,提出基于二进制多种群遗传算法的反向传播神经网络压实质量评估模型。通过调整传递激活函数,完善移民解更新机制,组合认知不确定性和偶然不确定性建立损失函数,解决了现场堆石料智能碾压评估中的小样本学习难题。研究表明:本文模型的评估性能优于9种对比模型,同时不确定性组合损失函数可提升模型的泛化能力和数据误差耐受度,具备在其他应用场景下的普适性和推广应用价值。
中图分类号:
- TV523
| 1 | 陈祖煜, 赵宇飞, 邹斌, 等. 大坝填筑碾压施工无人驾驶技术的研究与应用[J]. 水利水电技术, 2019, 50(8): 1-7. |
| Chen Zu-yu, Zhao Yu-fei, Zou Bin, et al. Study and application of unmanned driving technology or filling and rolling construction of earth-rockfill dam[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2019, 50(8): 1-7. | |
| 2 | 李庆斌, 马睿, 胡昱, 等. 大坝智能建造研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 62 (8): 1252-1269. |
| Li Qing-bin, Ma Rui, Hu Yu, et al. A review of intelligent dam construction techniques[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2022, 62(8): 1252-1269. | |
| 3 | 刘东海, 高雷. 基于碾振性态的土石坝料压实质量监测指标分析与改进[J]. 水力发电学报, 2018, 37(4): 111-120. |
| Liu Dong-hai, Gao Lei. Analysis and improvement of roller vibration behavior-based indexes for monitoring compaction quality of earth-rock dams[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2018, 37(4): 111-120. | |
| 4 | 王飞. 基于碾压质量实时监控的高心墙堆石坝沉降变形分析理论与应用[D]. 天津: 天津大学建筑工程学院,2017. |
| Wang Fei. Theory and application of high core rockfill dam settlement analysis based on real-time monitoring of rolling-compaction quality[D]. Tianjin: School of Civil Engineering,Tianjin University, 2017. | |
| 5 | 刘东海, 刘志磊, 冯友文. 堆石坝料压实监测指标影响因素及适用性分析[J]. 水力发电学报, 2019, 38(6): 1-10. |
| Liu Dong-hai, Liu Zhi-lei, Feng You-wen. Analysis on applicability and influence factors of real-time monitoring compaction indexes for rockfill dam materials[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2019, 38(6): 1-10. | |
| 6 | 林威伟, 钟登华, 胡炜, 等. 基于随机森林算法的土石坝压实质量动态评价研究[J]. 水利学报, 2018, 49(8): 945-955. |
| Lin Wei-wei, Zhong Deng-hua, Hu Wei, et al. Study on dynamic evaluation of compaction quality of earth rock dam based on random forest[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 49(8): 945-955. | |
| 7 | 潘恒彦, 张文会, 梁婷婷, 等. 基于MIMIC与机器学习的出租车驾驶员交通事故诱因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(2): 457-467. |
| Pan Heng-yan, Zhang Wen-hui, Liang Ting-ting, et al. Inducement analysis of taxi drivers' traffic accidents based on MIMIC and machine learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 532(2):457-467. | |
| 8 | Wang J J, Zhong D H, Wu B P, et al. Evaluation of compaction quality based on SVR with CFA: case study on compaction quality of earth-rock dam[J]. J Comput Civ Eng, 2018, 32(3): No.05018001. |
| 9 | 朱冰, 范天昕, 赵健, 等. 基于危险边界搜索的自动驾驶系统加速测试方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(3): 704-712. |
| Zhu Bing, Fan Tian-xin, Zhao Jian, et al. Accelerate test method of automated driving system based on hazardous boundary search[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 704-712. | |
| 10 | 王佳俊, 钟登华, 关涛, 等. 基于KM和AC-BFA模糊逻辑的土石坝压实质量实时评价[J]. 水力发电学报, 2019, 38(3): 165-178. |
| Wang Jia-jun, Zhong Deng-hua, Guan Tao, et al. Real-time evaluation of compaction quality of earth-rock dams using fuzzy logic based on KM and AC-BFA[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2019, 38(3): 165-178. | |
| 11 | Wang F, Zhong D H, Yan Y L, et al. Rockfill dam compaction quality evaluation based on cloud-fuzzy model[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A, 2018, 19(4): 289-303. |
| 12 | 安再展, 刘天云, 皇甫泽华, 等. 利用CMV评估堆石料压实质量的神经网络模型[J]. 水力发电学报, 2020,39(4): 110-120. |
| An Zai-zhan, Liu Tian-yun, Ze-hua Huangpu, et al. Neural network model for evaluating compaction quality of rockfill materials by compaction meter value[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2020, 39(4): 110-120. | |
| 13 | 刘彪, 赵宇飞, 陈祖煜, 等. 基于碾压波速的堆石坝压实质量实时监测指标的研究[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2022, 20(1): 20-29. |
| Liu Biao, Zhao Yu-fei, Chen Zu-yu, et al. Study on real-time monitoring index for rockfil dam compaction quality based on rolling wave velocity[J]. Journal of China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2022, 20(1): 20-29. | |
| 14 | Wang X, Dong X, Zhang Z, et al. Compaction quality evaluation of subgrade based on soil characteristics assessment using machine learning[J]. Transportation Geotechnics, 2022, 32: No.100703. |
| 15 | Terbuch A, Zöhrer A, Winter V, et al. Quality monitoring in vibro ground improvement—a hybrid machine learning approach[J]. Geomechanics and Tunnelling, 2022, 15(5): 658-664. |
| 16 | Wang X F, Cheng C, Li J L, et al. Automated monitoring and evaluation of highway subgrade compaction quality using artificial neural networks[J]. Automation in Construction, 2023, 145:No.104663. |
| 17 | An Z Z, Liu T Y, Zhang Z S, et al. Dynamic optimization of compaction process for rockfill materials[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 110: No.103038. |
| 18 | Liu B, Zhao Y, Wang W, et al. Compaction density evaluation model of sand-gravel dam based on Elman neural network with modified particle swarm optimization[J]. Frontiers in Physics, 2022, 9:No.806231. |
| 19 | Hong Y, Tian Z H, Sun X. Dynamic evaluation for compaction quality of roller compacted concrete based on reliability metrics[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2020, 146 (10): No.4020123. |
| 20 | Wang J J, Zhong D H, Adeli H, et al. Smart bacteria-foraging algorithm‐based customized kernel support vector regression and enhanced probabilistic neural network for compaction quality assessment and control of earth-rock dam[J]. Expert Systems, 2018, 35(6): No.e12357. |
| 21 | Zhang Q, Zhu Y, He L, et al. Assessment of roller-integrated compaction monitoring indexes for low-liquid-limit silt based on roller vibratory acceleration analysis[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part B: Pavements, 2023,149(4): No.04023020. |
| 22 | Zhang Q, Liu T, Zhang Z, et al. Compaction quality assessment of rockfill materials using roller-integrated acoustic wave detection technique[J]. Automation in Construction, 2019, 97: 110-121. |
| 23 | Wang X, Cheng C, Zhang J, et al. Real-time monitoring and quality assessment of subgrade compaction: key factors and ANN model[J]. Acta Geotechnica, 2022: 1-18. |
| 24 | Liu M, Wang X, Wang J, et al. Comprehensive evaluation for real-time compaction quality using i-AHP and i-GAM: case study of earth-rock dam[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(8): No.1543. |
| 25 | Zhang Q, An Z, Liu T, et al. Intelligent rolling compaction system for earth-rock dams[J]. Automation in Construction, 2020, 116:No.103246. |
| 26 | Committe D. Test method for unconfined compressive strength of cohesive soil[J]. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, USA, 2016:1-22. |
| 27 | White D J, Rupnow T D, Ceylan H. Influence of Subgrade/subbase Non-uniformity on PCC Pavement Performance[M]. New York: American Society of Civil Engineers(ASCE), 2004: 1058-1065. |
| 28 | Anderegg R, Kaufmann K. Intelligent compaction with vibratory rollers: feedback control systems in automatic compaction and compaction control[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2004, 1868(1): 124-134. |
| 29 | Thompson M J, White D J. Estimating compaction of cohesive soils from machine drive power[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2008, 134(12): 1771-1777. |
| 30 | 张家玲, 徐光辉, 蔡英. 连续压实路基质量检验与控制研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2015, 36(4): 1141-1146. |
| Zhang Jia-ling, Xu Guang-hui, Cai Ying. An investigation on quality inspection and control for continuously compacting subgrade[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(4): 1141-1146. | |
| 31 | Liu D H, Lin M, Li S. Real-time quality monitoring and control of highway compaction[J]. Automation in Construction, 2016, 62: 114-123. |
| 32 | 王涛. 动态系统思想: 理论和语言研究[M]. 南京:东南大学出版社, 2014. |
| 33 | Van Ravenzwaaij D, Cassey P, Brown S D. A simple introduction to Markov Chain Monte-Carlo sampling[J]. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 2018, 25 (1): 143-154. |
| 34 | Gal Y, Ghahramani Z. Dropout as a bayesian approximation: representing model uncertainty in deep learning[DB/OL].[2022-10-26].. |
| 35 | Lakshminarayanan B, Pritzel A, Blundell C. Simple and scalable predictive uncertainty estimation using deep ensembles[C]∥Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017. |
| [1] | 商蕾,杨萍,杨祥国,潘建欣,杨军,张梦如. 基于APSO-BP-PID控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2401-2413. |
| [2] | 杨军,韩鹏飞. 采用神经网络架构搜索的高分辨率遥感影像目标检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2646-2657. |
| [3] | 特木尔朝鲁朝鲁,张亚萍. 基于卷积神经网络的无线传感器网络链路异常检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2295-2300. |
| [4] | 赵宏伟,武鸿,马克,李海. 基于知识蒸馏的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2307-2312. |
| [5] | 张锦洲,姬世青,谭创. 融合卷积神经网络和双边滤波的相贯线焊缝提取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2313-2318. |
| [6] | 朱圣杰,王宣,徐芳,彭佳琦,王远超. 机载广域遥感图像的尺度归一化目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2329-2337. |
| [7] | 李光保,高栋,路勇,平昊,周愿愿. 基于改进神经网络和Fluent的气液固技术的内表面处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1537-1547. |
| [8] | 张玺君,余光杰,崔勇,尚继洋. 基于聚类算法和图神经网络的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1593-1600. |
| [9] | 魏晓辉,王晨洋,吴旗,郑新阳,于洪梅,岳恒山. 面向脉动阵列神经网络加速器的软错误近似容错设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1746-1755. |
| [10] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [11] | 黄玲,崔躜,游峰,洪佩鑫,钟浩川,曾译萱. 适用于多车交互场景的车辆轨迹预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1188-1195. |
| [12] | 张西广,张龙飞,马钰锡,樊银亭. 基于密度峰值的海量云数据模糊聚类算法设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1401-1406. |
| [13] | 夏超,王梦佳,朱剑月,杨志刚. 基于分层卷积自编码器的钝体湍流流场降阶分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 874-882. |
| [14] | 杨国俊,齐亚辉,石秀名. 基于数字图像技术的桥梁裂缝检测综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [15] | 高海龙,徐一博,刘坤,李春阳,卢晓煜. 基于多源数据融合的高速公路路网短时交通流参数实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 155-161. |
|
||