吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1664-1674.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230845
基于知识蒸馏和评论时间的文本情感分类新方法
- 1.中央财经大学 信息学院,北京 100081
2.天津财经大学 统计学院,天津 300222
New method for text sentiment classification based on knowledge distillation and comment time
You-wei WANG1( ),Ao LIU1,Li-zhou FENG2
),Ao LIU1,Li-zhou FENG2
- 1.School of Information,Central University of Finance and Economics,Beijing 100081,China
2.School of Statistics,Tianjin University of Finance and Economics,Tianjin 300222,China
摘要:
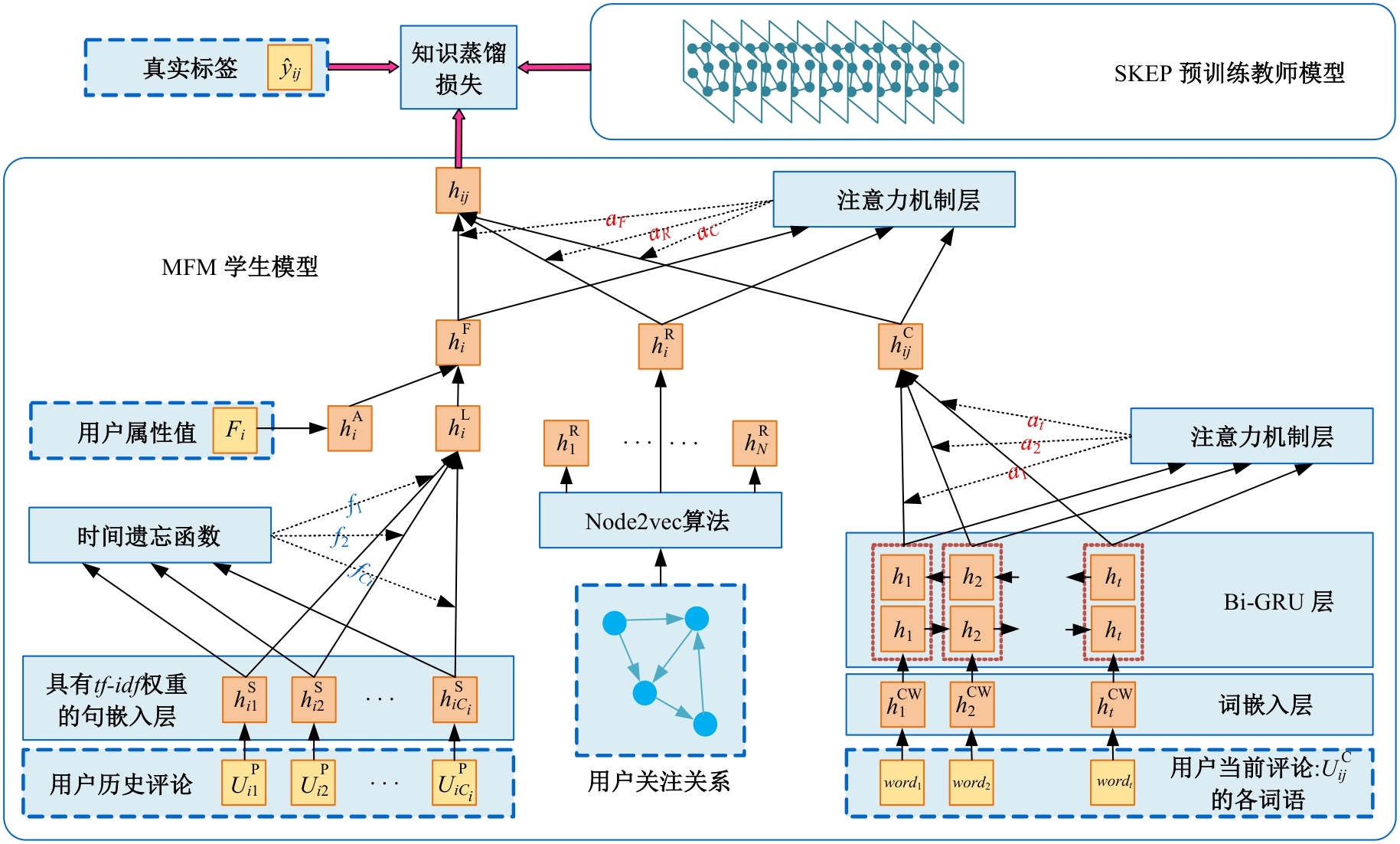
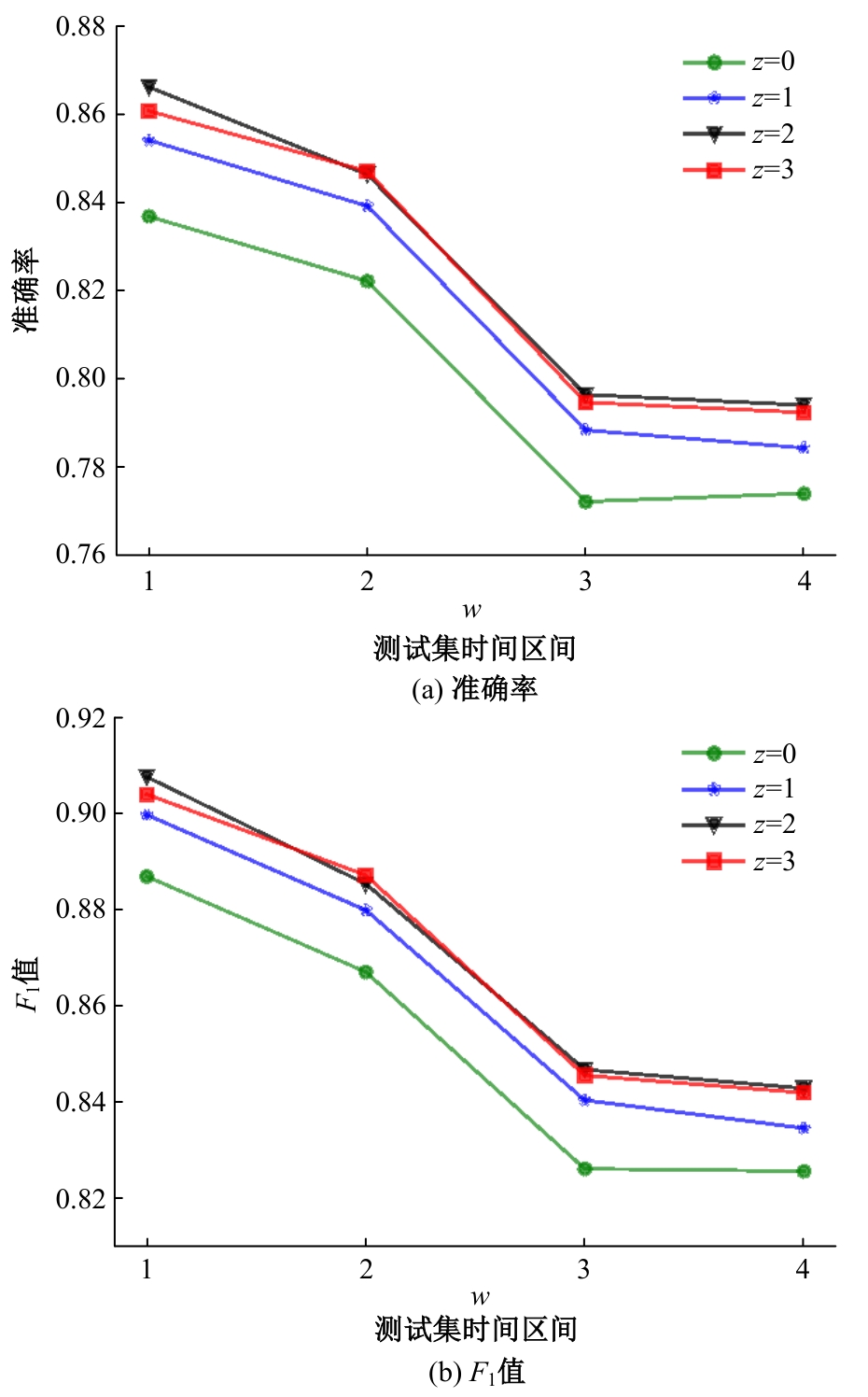
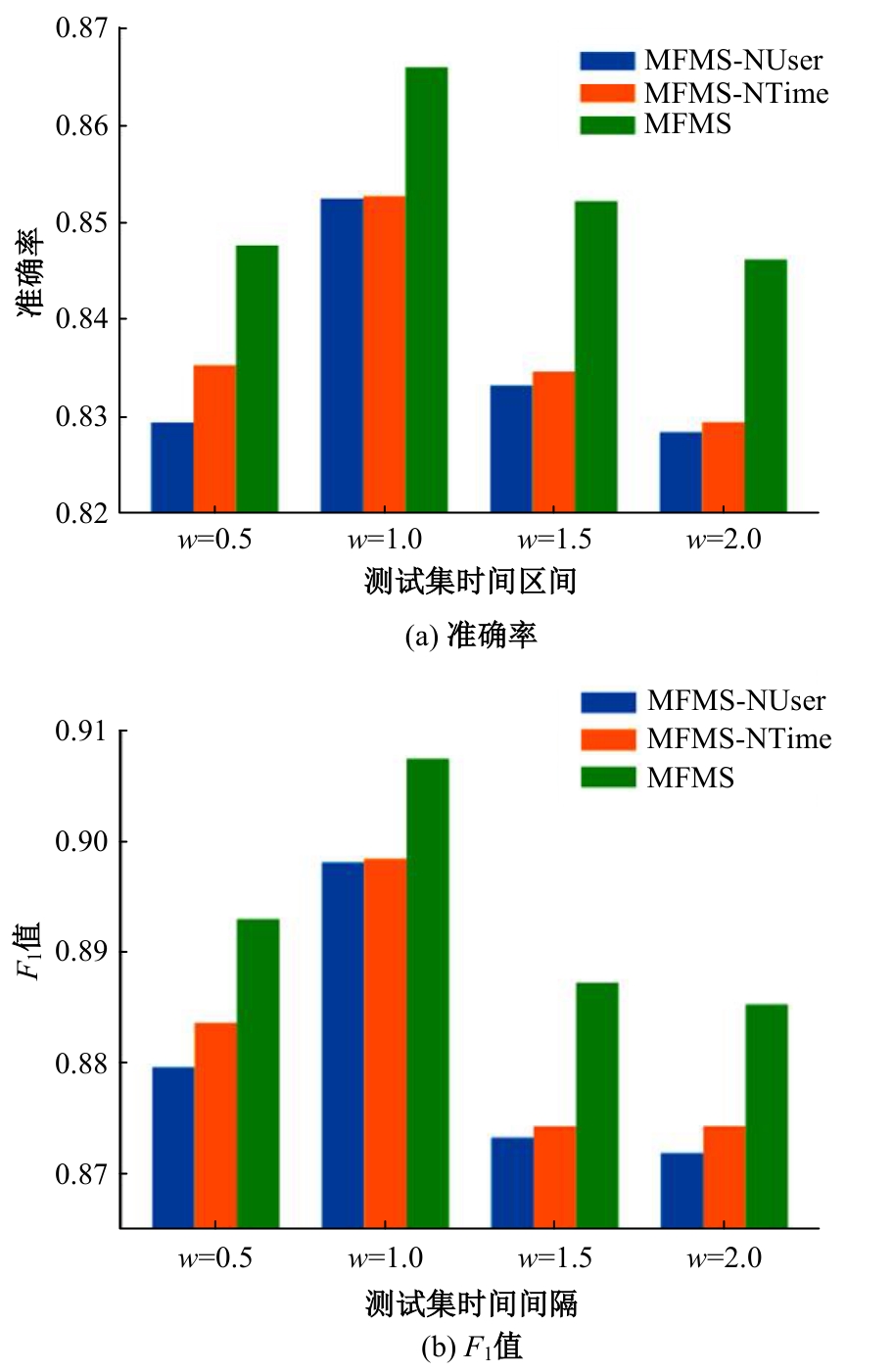
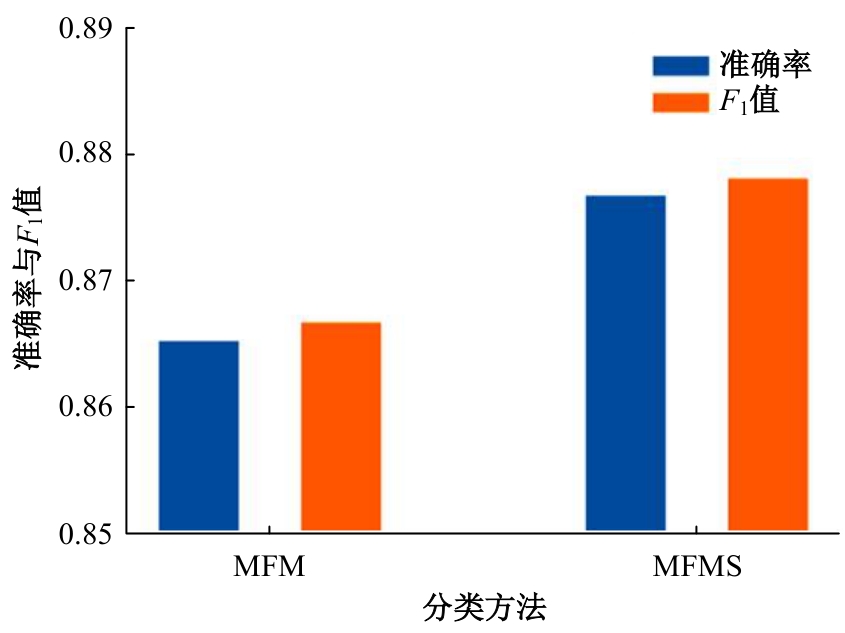
针对现有的情感分类方法普遍未能充分考虑用户个性化特征且忽略时间因素对情感分类结果的影响的问题,提出一种基于知识蒸馏和评论时间的文本情感分类新方法。首先,为解决数据集中高质量标注数据较少的问题,采用RoFormer-Sim生成模型对训练文本数据增强;然后,引入评论时间属性,从用户历史评论中提取用户的个性化信息,提出基于多特征融合的评论文本情感得分预测模型;最后,为提高针对冷启动用户的泛化性能,引入知识蒸馏理论,利用SKEP模型对基于多特征融合的情感分类模型进行通用性增强。在从中文股吧爬取的真实数据集上的实验结果表明:与SKEP、ELECTRA等典型方法相比,本文方法在准确率上分别提高了3.1%和0.9%,在F1值上分别提高了2.7%和1.0%,验证了其在改善情感分类表现方面的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TP391.1
| [1] | Umer M, Sadiq S, Nappi M, et al. ETCNN: extra tree and convolutional neural network-based ensemble model for COVID-19 tweets sentiment classification[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2022, 164: 224-231. |
| [2] | Lan Z, Chen M, Goodman S, et al. ALBERT: a lite bert for self-supervised learning of language representations[C]∥International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020: 1-17. |
| [3] | Liu Z, Huang D, Huang K, et al. Finbert: a pre-trained financial language representation model for financial text mining[C]∥Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth International Conference on International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 2021: 4513-4519. |
| [4] | 赵亚欧, 张家重, 李贻斌, 等. 基于ELMo和Transformer混合模型的情感分析[J]. 中文信息学报, 2021, 35(3): 115-124. |
| Zhao Ya-ou, Zhang Jia-chong, Li Yi-bin, et al. Sentiment analysis based on hybird model of elmo and transformer[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2021, 35(3): 115-124. | |
| [5] | Yang J, Zou X, Zhang W, et al. Microblog sentiment analysis via embedding social contexts into an attentive LSTM[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 97: 104048. |
| [6] | 蒋宗礼, 张静. 融合用户和产品信息的多头注意力情感分类模型[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2020, 29(7): 131-138. |
| Jiang Zong-li, Zhang Jing. Multi-head attention model with user and product information for sentiment classification[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2020, 29(7): 131-138. | |
| [7] | Hinton G, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network[J]. Computer Science, 2015, 14(7): 38-39. |
| [8] | 邵仁荣, 刘宇昂, 张伟, 等. 深度学习中知识蒸馏研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(8): 1638-1673. |
| Shao Ren-rong, Liu Yu-ang, Zhang Wei, et al. A survey of knowledge distillation in deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2022, 45(8): 1638-1673. | |
| [9] | Tian H, Gao C, Xiao X, et al. SKEP: sentiment knowledge enhanced pre-training for sentiment analysis[J/OL]. [2023-07-25].arXiv Preprint arXiv: 2005. 05635v2. |
| [10] | Turney P D. Thumbs up or thumbs down? Semantic orientation applied to unsupervised classification of reviews[J]. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2002, 6: 417-424. |
| [11] | Xie W. Entity linking based on roformer-sim for chinese short texts[J]. Frontiers in Computing and Intelligent Systems, 2023, 4(1): 46-50. |
| [12] | Zhao Y, Liu S, Zhang Q, et al. Test case classification via few-shot learning[J]. Information and Software Technology, 2023, 160:107228. |
| [13] | Lewis M, Liu Y, Goyal N, et al. BART: denoising sequence-to-sequence pre-training for natural language generation, translation, and comprehension[C]∥Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020: 7871-7880. |
| [14] | Ebbinghaus H. Memory: a contribution to experimental psychology[J]. Annals of Neurosciences, 2013, 20(4): 2004155. |
| [15] | Grover A, Leskovec J. Node2vec: scalable feature learning for networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, New York, USA, 2016: 855-864. |
| [16] | 乔百友, 武彤, 杨璐, 等. 一种基于BiGRU和胶囊网络的文本情感分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024,54(7): 2026-2037. |
| Qiao Bai-you, Wu Tong, Yang Lu, et al. A text sentiment analysis method based on BiGRU and capsule network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(7): 2026-2037. | |
| [17] | 王友卫, 童爽, 凤丽洲, 等. 基于图卷积网络的归纳式微博谣言检测新方法[J].浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 56(5): 956-996. |
| Wang You-wei, Tong Shuang, Feng Li-zhou, et al. New inductive microblog rumor detection method based on graph convolutional network[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2022, 56(5): 956-996. | |
| [18] | 陈洁, 王思雨, 赵姝, 等. 基于多粒度用户偏好的文档级情感分析[J]. 中文信息学报, 2023, 37(7): 122-130. |
| Chen Jie, Wang Si-yu, Zhao Shu, et al. Multi-granular user preferences for document-level sentiment analysis[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2023, 37(7): 122-130. | |
| [19] | Li Y, Ni P, Li G, et al. Inter-personal relation extraction model based on bidirectional GRU and attention mechanism[C]∥IEEE 5th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Harbin, China, 2019: 1867-1871. |
| [20] | Guo B, Zhang C, Liu J, et al. Improving text classification with weighted word embeddings via a multi-channel textcnn model[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 363: 366-374. |
| [21] | Clark K, Luong M T, Le Q V, et al. Electra: pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators[J/OL]. [2023-07-26]. arXiv Preprint arXiv: 2003. 10555. |
| [22] | Kamal A, Abulaish M. Cat-bigru: convolution and attention with bi-directional gated recurrent unit for self-deprecating sarcasm detection[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2022, 14: 91-109. |
| [23] | Ahmad W, Wang B, Martin P, et al. Enhanced sentiment analysis regarding COVID-19 news from global channels[J]. Journal of Computational Social Science, 2023, 6: 19-57. |
| [24] | Gao Z, Li Z, Luo J, et al. Short text aspect-based sentiment analysis based on CNN + BiGRU[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(5): 12052707. |
| [25] | Aslam N, Rustam F, Lee E, et al. Sentiment analysis and emotion detection on cryptocurrency related tweets using ensemble LSTM-GRU model[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 39313-39324. |
| [1] | 侯越,郭劲松,林伟,张迪,武月,张鑫. 分割可跨越车道分界线的多视角视频车速提取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1692-1704. |
| [2] | 赵宏伟,周明珠,刘萍萍,周求湛. 基于置信学习和协同训练的医学图像分割方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1675-1681. |
| [3] | 申自浩,高永生,王辉,刘沛骞,刘琨. 面向车联网隐私保护的深度确定性策略梯度缓存方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1638-1647. |
| [4] | 王军,司昌馥,王凯鹏,付强. 融合集成学习技术和PSO-GA算法的特征提取技术的入侵检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1396-1405. |
| [5] | 徐涛,孔帅迪,刘才华,李时. 异构机密计算综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 755-770. |
| [6] | 赵孟雪,车翔玖,徐欢,刘全乐. 基于先验知识优化的医学图像候选区域生成方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 722-730. |
| [7] | 蔡晓东,周青松,张言言,雪韵. 基于动静态和关系特征全局捕获的社交推荐模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 700-708. |
| [8] | 车翔玖,武宇宁,刘全乐. 基于因果特征学习的有权同构图分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 681-686. |
| [9] | 郭晓然,王铁君,闫悦. 基于局部注意力和本地远程监督的实体关系抽取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 307-315. |
| [10] | 汪豪,赵彬,刘国华. 基于时间和运动增强的视频动作识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 339-346. |
| [11] | 刘元宁,臧子楠,张浩,刘震. 基于深度学习的核糖核酸二级结构预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 297-306. |
| [12] | 李路,宋均琦,朱明,谭鹤群,周玉凡,孙超奇,周铖钰. 基于RGHS图像增强和改进YOLOv5网络的黄颡鱼目标提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [13] | 赵宏伟,武鸿,马克,李海. 基于知识蒸馏的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2307-2312. |
| [14] | 张云佐,郑宇鑫,武存宇,张天. 基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902. |
| [15] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
|