吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2182-2191.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220281
• • 上一篇
基于高阶燃料电池模型的多目标滑模控制
- 1.西南交通大学 机械工程学院,成都 610036
2.中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司,天津 300300
Multi⁃objective sliding mode control based on high⁃order fuel cell model
Guang-di HU1( ),Hao JING1,Cheng LI1,2,Biao FENG1,Xiao-dong LIU1
),Hao JING1,Cheng LI1,2,Biao FENG1,Xiao-dong LIU1
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610036,China
2.China Automotive Technology & Research Center Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300300,China
摘要:
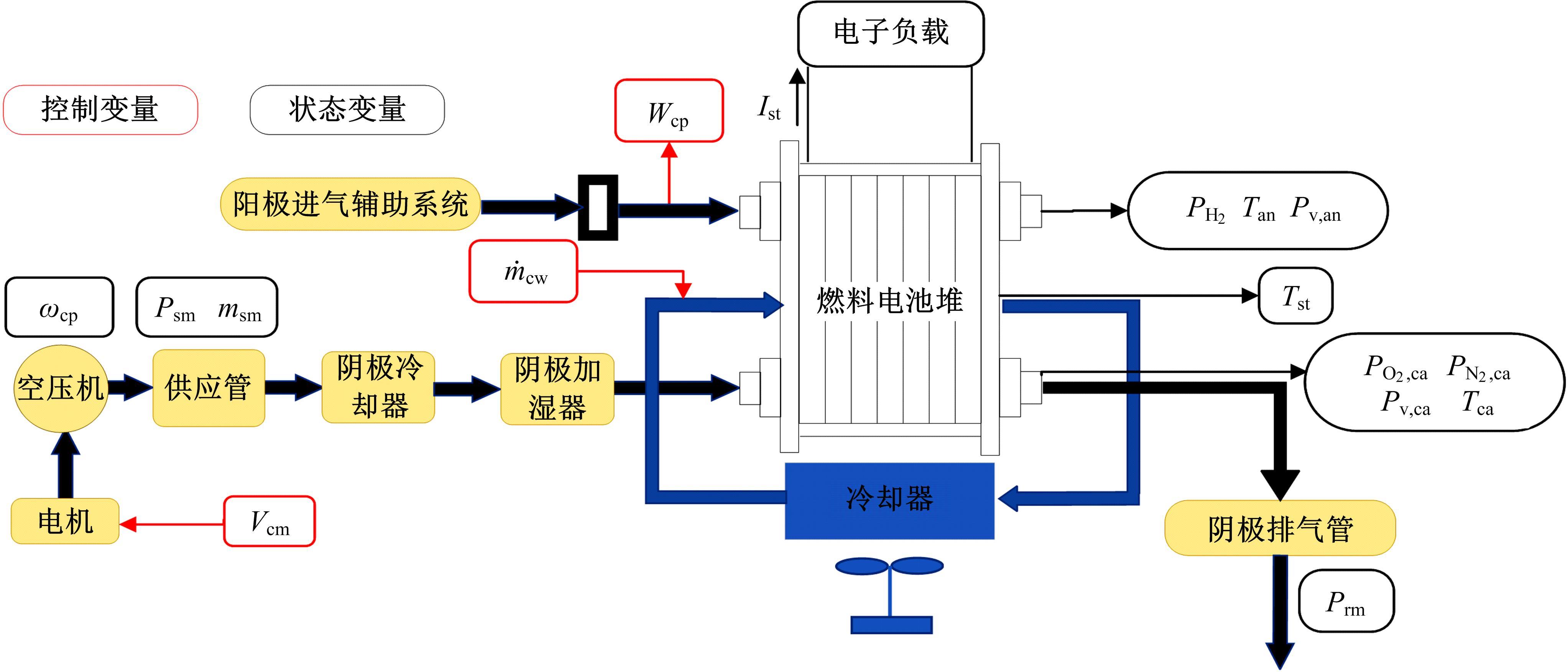
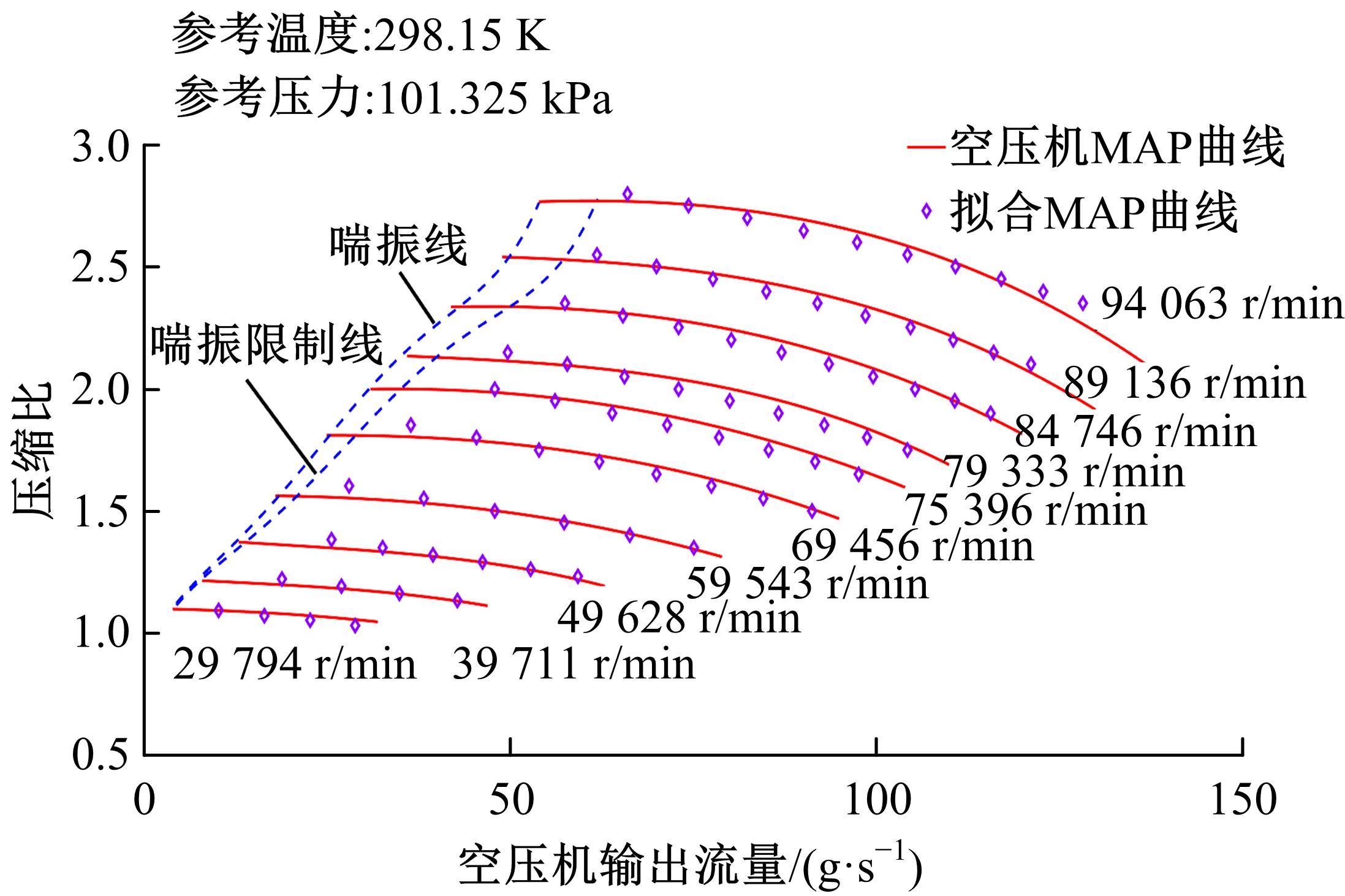
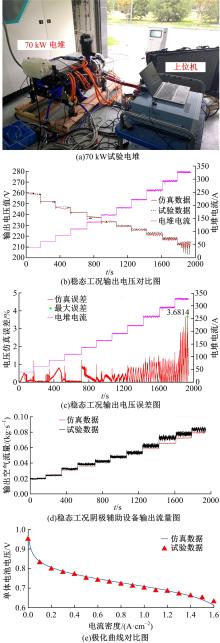
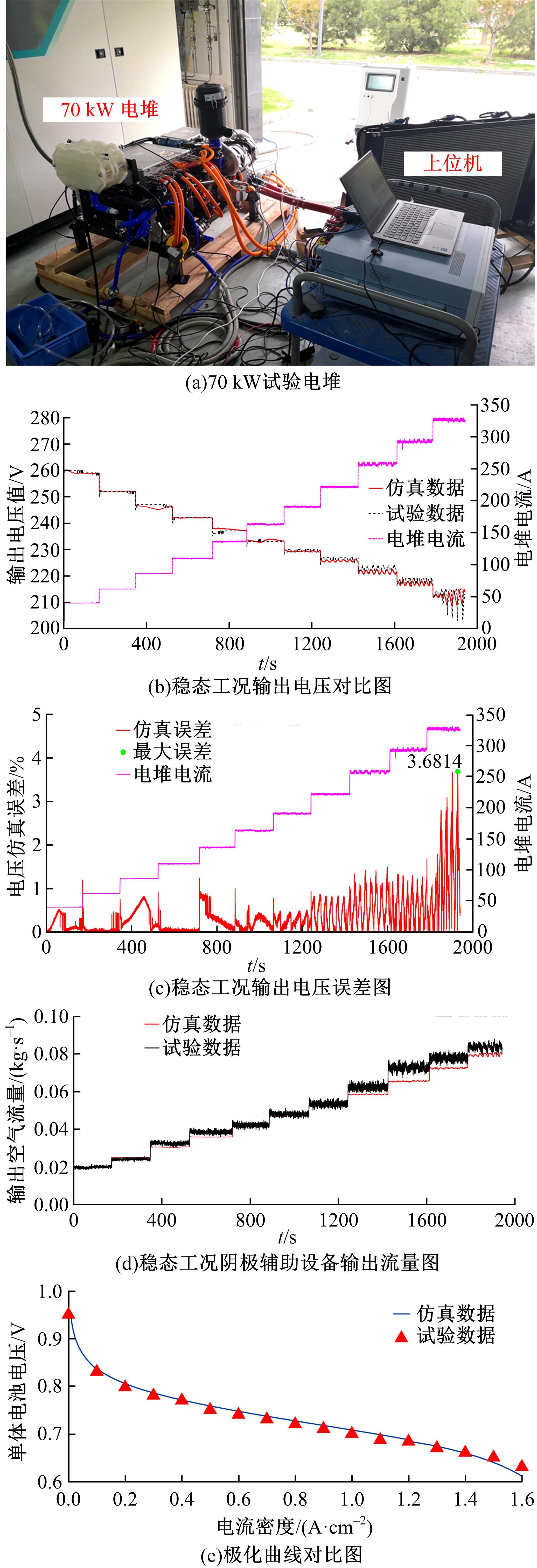
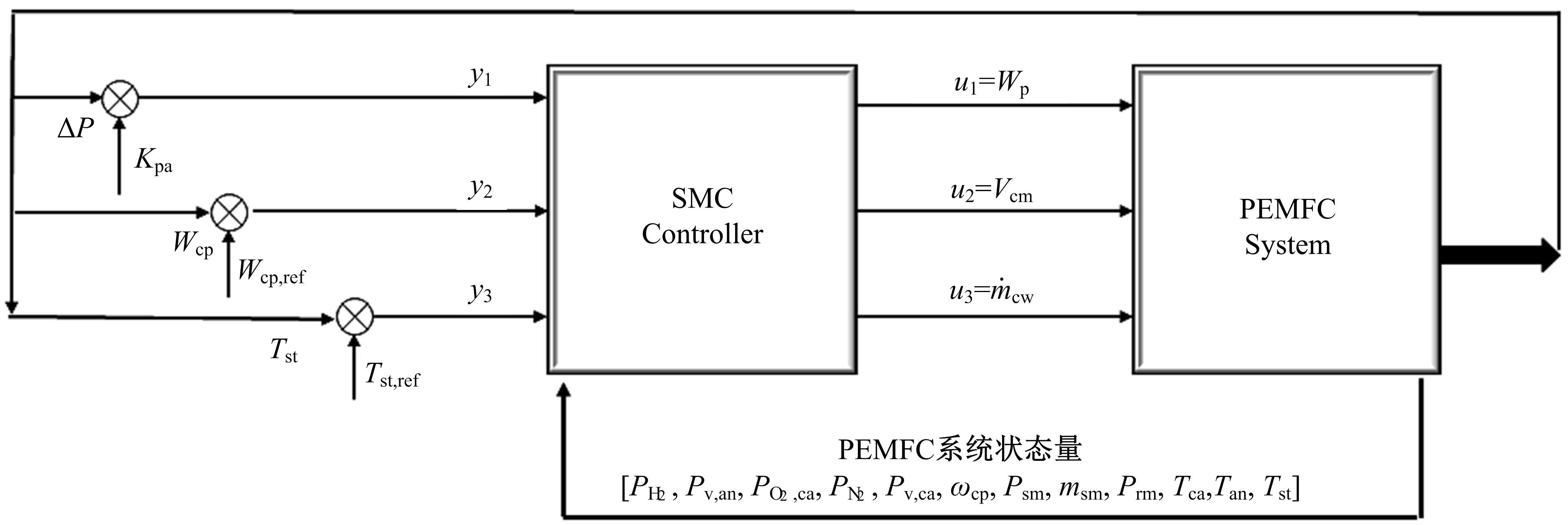
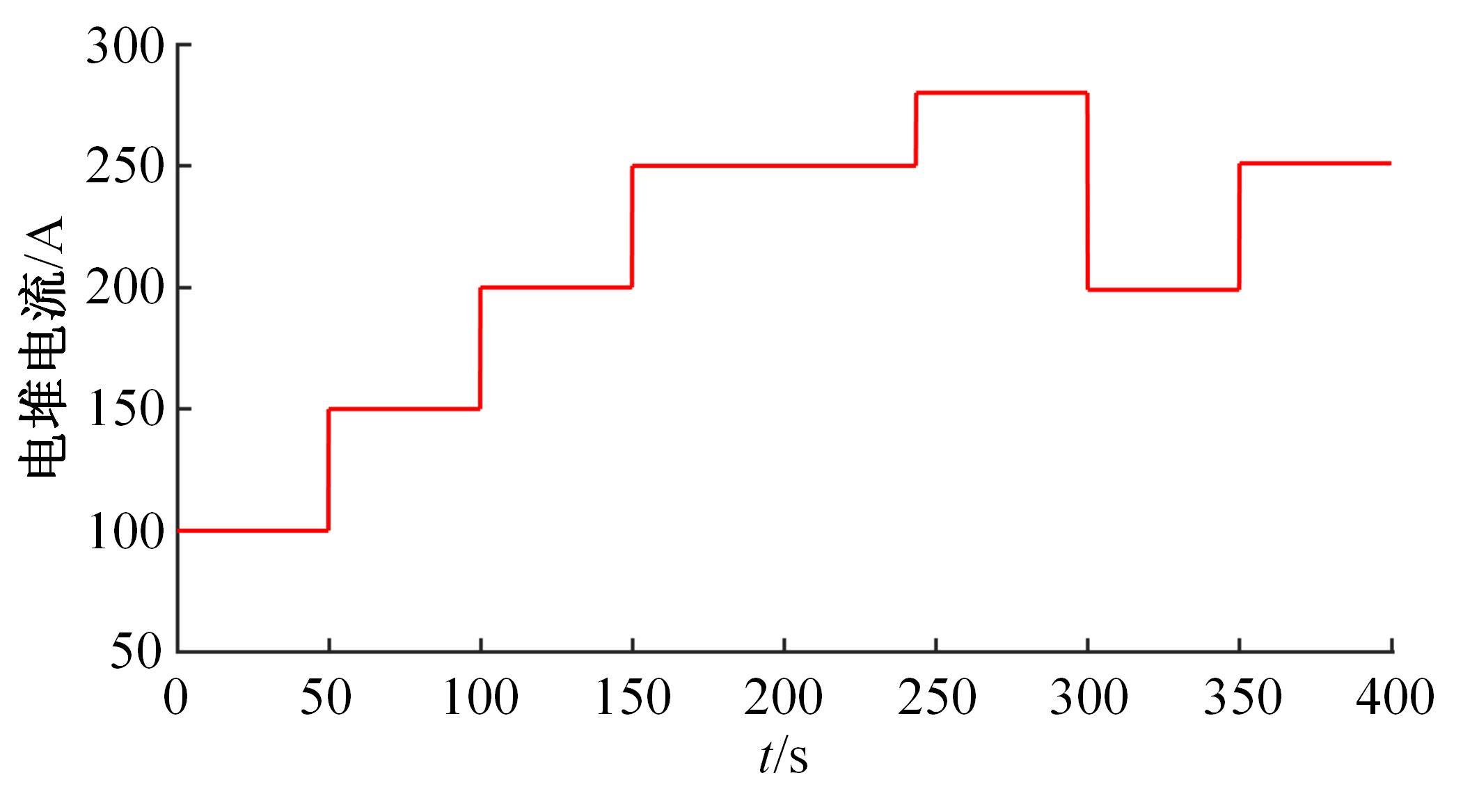
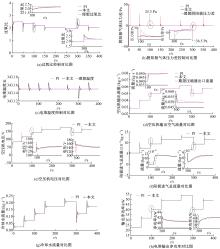
为了提高质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)的效率和寿命,对燃料电池的多个状态进行了精确控制。首先,在Simulink中建立了12阶燃料电池模型,运用试验数据对建模参数进行拟合,仿真模型的输出电压最大误差为3.68%。其次,基于所建立的模型设计了3输入、3输出滑模控制器,通过空压机电压、阳极进气流量和冷却水流量分别控制电堆过氧比、阴阳极气体压力差和温度。仿真结果表明:与PI控制器相比,当负载电流突变时,所设计的滑模控制器缩短了3 s的过氧比控制过渡时间,阴、阳极压力差波动从40 Pa降低至2 Pa左右,并且温度波动控制在0.05 K以内。
中图分类号:
- TM911.4
| 1 | 李佳琪,徐潇源,严正.大规模新能源汽车接入背景下的电氢能源与交通系统耦合研究综述[J].上海交通大学学报,2022,56(3):253-266. |
| Li Jia-qi, Xu Xiao-yuan, Yan Zheng. A review of research on coupling electric-hydrogen energy and transportation system in the context of large-scale new energy vehicle access[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University,2022,56(3):253-266. | |
| 2 | 孙闫, 夏长高, 尹必峰, 等. 燃料电池电动汽车的能量管理[J/OL]. [2022-02-20]. |
| 3 | 高助威,李小高,刘钟馨,等.氢燃料电池汽车的研究现状及发展趋势[J].材料导报,2022,36(14):74-81. |
| Gao Zhu-wei, Li Xiao-gao, Liu Zhong-xin, et al. Research status and development trend of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles[J]. Materials Guide,2022,36(14):74-81. | |
| 4 | Murschenhofer D, Kuzdas D, Braun S, et al. A real-time capable quasi-2D proton exchange membrane fuel cell model[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 162: 159-175. |
| 5 | Pukrushpan J T, Peng H, Stefanopoulou A G. Simulation and analysis of transient fuel cell system performance based on a dynamic reactant flow model[C]∥ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, 2002: 637-648. |
| 6 | Pukrushpan J T, Stefanopoulou A G, Peng H. Control of fuel cell breathing[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2004, 24(2): 30-46. |
| 7 | Pukrushpan J T, Peng H, Stefanopoulou A G. Control-oriented modeling and analysis for automotive fuel cell systems[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems Measurement and Control, Control, 2004, 126(1): 14-25. |
| 8 | Grujicic M, Chittajallu K M, Law E H, et al. Model-based control strategies in the dynamic interaction of air supply and fuel cell[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part A: Journal of Power and Energy, 2004, 218(7): 487-499. |
| 9 | Kunusch C, Puleston P, Mayosky M. Sliding-Mode Control of PEM Fuel Cells[M]. London: Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. |
| 10 | Sankar K, Jana A K. Nonlinear multivariable sliding mode control of a reversible PEM fuel cell integrated system[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 171: 541-565. |
| 11 | Wang Y, Li H, Feng H, et al. Simulation study on the PEMFC oxygen starvation based on the coupling algorithm of model predictive control and PID[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 249: No. 114851. |
| 12 | 李奇, 冯嘉, 尹良震, 等. 基于多阶滑模观测器的PEMFC发电系统输出净功率优化控制方法[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46(3): 1005-1015. |
| Li Qi, Feng Jia, Yin Liang-Zhen, et al. A multi-order sliding mode observer-based optimal control method for net power output of PEMFC power generation system[J]. Power Grid Technology, 2022, 46(3): 1005-1015. | |
| 13 | 洪凌. 车用燃料电池发电系统氢气回路控制[D]. 杭州:浙江大学控制科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Hong Ling. Hydrogen circuit control for automotive fuel cell power generation system[D]. Hangzhou: School of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2017. | |
| 14 | Zhang Q, Tong Z, Tong S, et al. Modeling and dynamic performance research on proton exchange membrane fuel cell system with hydrogen cycle and dead-ended anode[J]. Energy, 2021, 218(C): No. 119476. |
| 15 | Matraji I, Laghrouche S, Wack M. Pressure control in a PEM fuel cell via second order sliding mode[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(21): 16104-16116. |
| 16 | Quan S, Wang Y X, Xiao X, et al. Feedback linearization-based MIMO model predictive control with defined pseudo-reference for hydrogen regulation of automotive fuel cells[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 293: No. 116919. |
| 17 | 申小玲, 刘朝晖, 郭昌海. 温控系统对质子交换膜燃料电池性能影响[J]. 电源技术, 2017, 41(1): 54-56. |
| Shen Xiao-ling, Liu Zhao-hui, Guo Chang-hai. Effect of temperature control system on the performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Power Technology, 2017, 41(1): 54-56. | |
| 18 | 程珍, 陈科, 罗超. 基于模糊预测控制的燃料电池温度控制系统的研究[J]. 仪表技术, 2012, 40(8): 1-4, 8. |
| Cheng Zhen, Chen Ke, Luo Chao. Study of fuel cell temperature control system based on fuzzy predictive control[J]. Instrumentation Technology, 2012, 40(8): 1-4, 8. | |
| 19 | Cheng S, Fang C, Xu L, et al. Model-based temperature regulation of a PEM fuel cell system on a city bus[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(39): 13566-13575. |
| 20 | 梁鹏.车用水冷燃料电池用户手册[Z]. |
| 21 | Slotine J J E, Li W. Applied Nonlinear Control[M]. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1991. |
| 22 | Lu X Y, Spurgeon S K. Output feedback stabilization of MIMO non-linear systems via dynamic sliding mode[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control: IFAC-Affiliated Journal, 1999, 9(5): 275-305. |
| 23 | 邓惠文, 李奇, 陈维荣. 适用于PEMFC系统过氧化估计的HOSM观测器研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(17): 5058-5068, 5225. |
| Deng Hui-wen, Li Qi, Chen Wei-rong. Research on HOSM observer applicable to peroxide estimation of PEMFC system[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2017, 37(17): 5058-5068, 5225. |
| [1] | 王克勇,鲍大同,周苏. 基于数据驱动的车用燃料电池故障在线自适应诊断算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2107-2118. |
| [2] | 曹起铭,闵海涛,孙维毅,于远彬,蒋俊宇. 质子交换膜燃料电池低温启动水热平衡特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2139-2146. |
| [3] | 杨子荣,李岩,冀雪峰,刘芳,郝冬. 质子交换膜燃料电池运行工况参数敏感性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1971-1981. |
| [4] | 隗海林,王泽钊,张家祯,刘洋. 基于Avl-Cruise的燃料电池汽车传动比及能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [5] | 肖阳,王洁,刘孟军,杨发庆,张天瑶,兰巍. 质子交换膜燃料电池气体扩散层的力学改进模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2147-2155. |
| [6] | 刘岩,丁天威,王宇鹏,都京,赵洪辉. 基于自适应控制的燃料电池发动机热管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2168-2174. |
| [7] | 张佩,王志伟,杜常清,颜伏伍,卢炽华. 车用质子交换膜燃料电池空气系统过氧比控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [8] | 高金武,王义琳,刘华洋,王艺达. 基于滑模观测器的质子交换膜燃料电池阴极进气系统解耦控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2156-2167. |
| [9] | 陈凤祥,张俊宇,裴冯来,侯明涛,李其朋,李培庆,王洋洋,张卫东. 质子交换膜燃料电池氢气供应系统的建模及匹配设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1982-1995. |
| [10] | 刘镇宁,江柯,赵韬韬,樊文选,卢国龙. 大功率质子交换膜燃料电池测试系统的开发及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2025-2033. |
| [11] | 池训逞,侯中军,魏伟,夏增刚,庄琳琳,郭荣. 基于模型的质子交换膜燃料电池系统阳极气体浓度估计技术综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [12] | 裴尧旺,陈凤祥,胡哲,翟双,裴冯来,张卫东,焦杰然. 基于自适应LQR控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [13] | 张恒,詹志刚,陈奔,隋邦杰,潘牧. 气体扩散层各向异性传输特性的孔尺度模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2055-2062. |
| [14] | 陈凤祥,伍琪,李元松,莫天德,李煜,黄李平,苏建红,张卫东. 2.5吨燃料电池混合动力叉车匹配、仿真及优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
| [15] | 武小花,余忠伟,朱张玲,高新梅. 燃料电池公交车模糊能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2077-2084. |
|
||