吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (4): 764-772.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200887
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于改进海鸥算法的磁流变减振器模型辨识
- 吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
Parameter identification of magnetorheological damper model with modified seagull optimization algorithm
Wen-ku SHI( ),Shu-guang ZHANG,You-kun ZHANG(
),Shu-guang ZHANG,You-kun ZHANG( ),Zhi-yong CHEN,Yi-fei JIANG,Bin-bin LIN
),Zhi-yong CHEN,Yi-fei JIANG,Bin-bin LIN
- State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
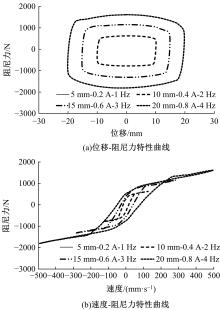
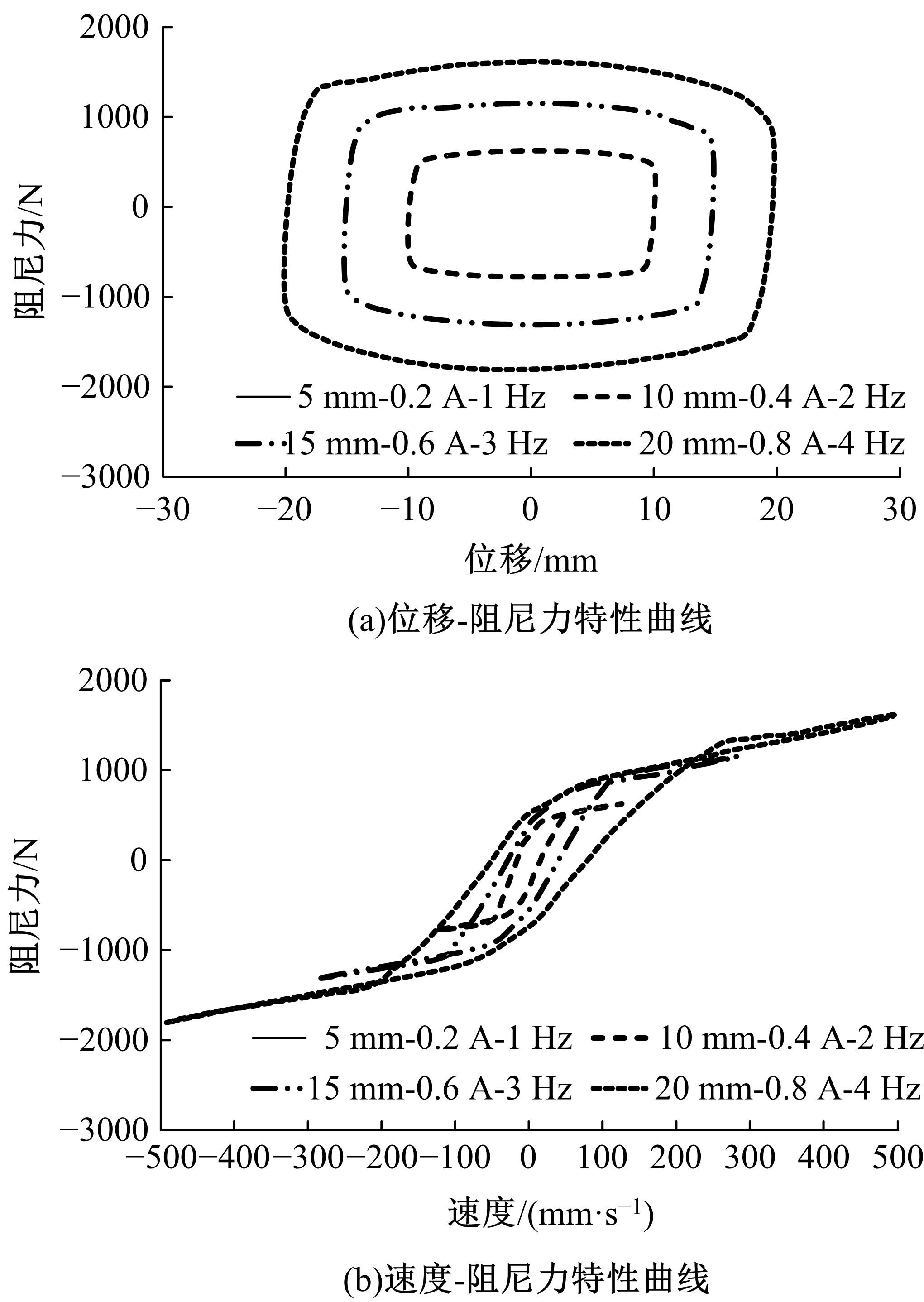
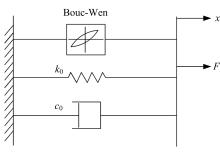
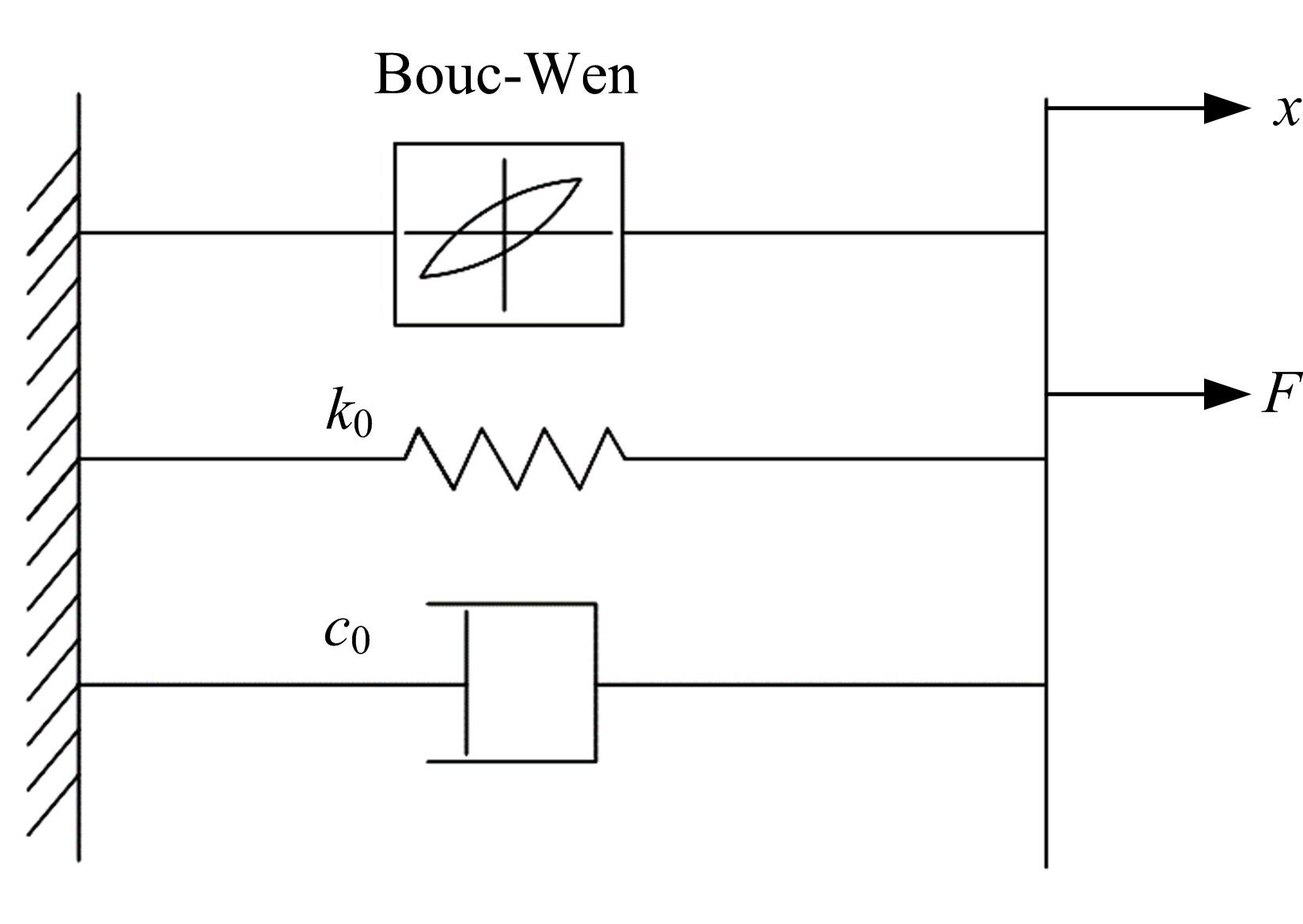
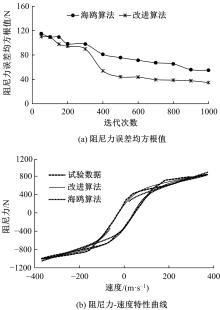
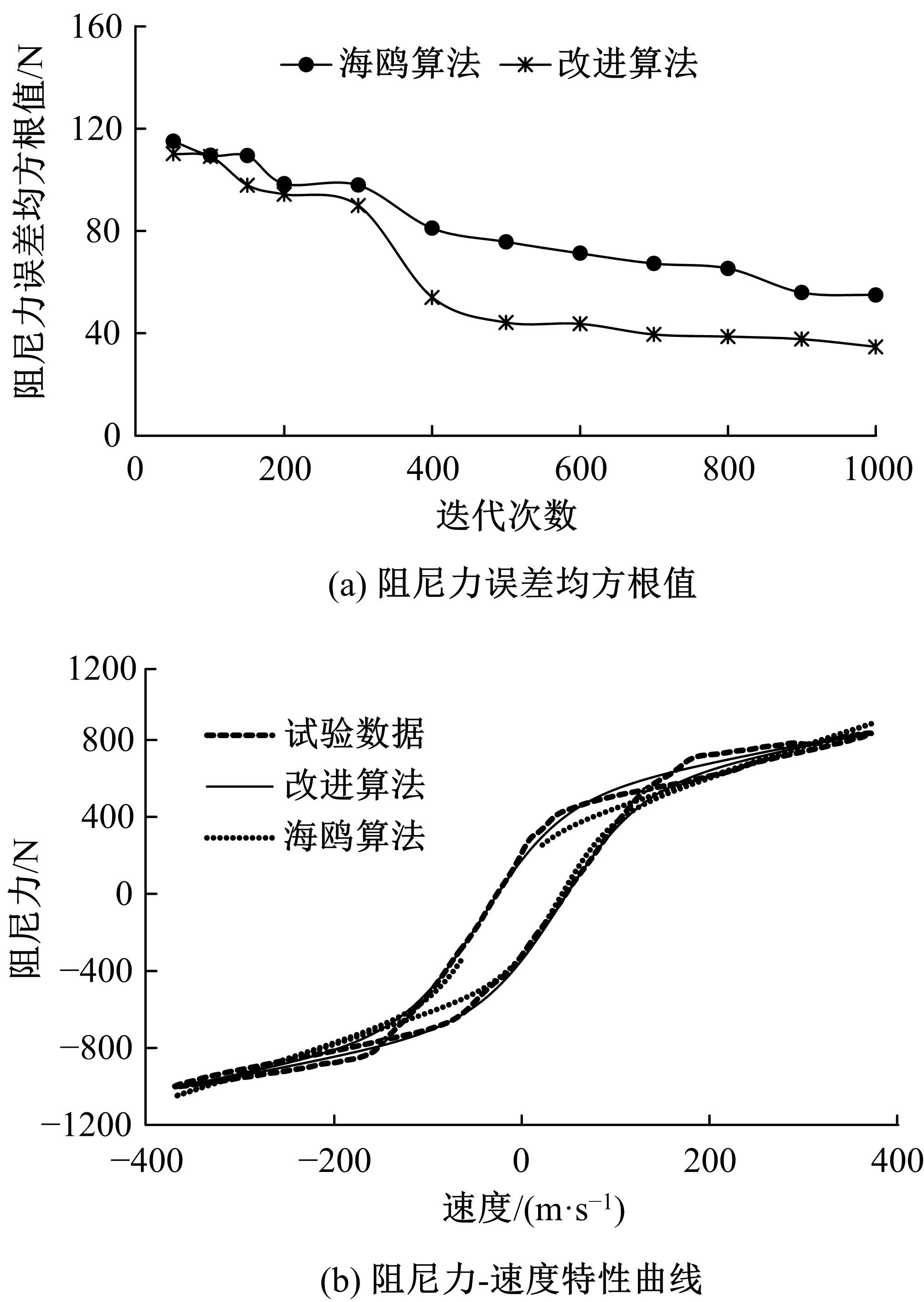
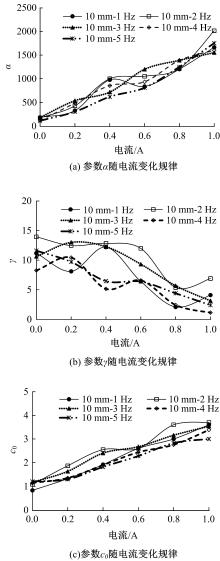
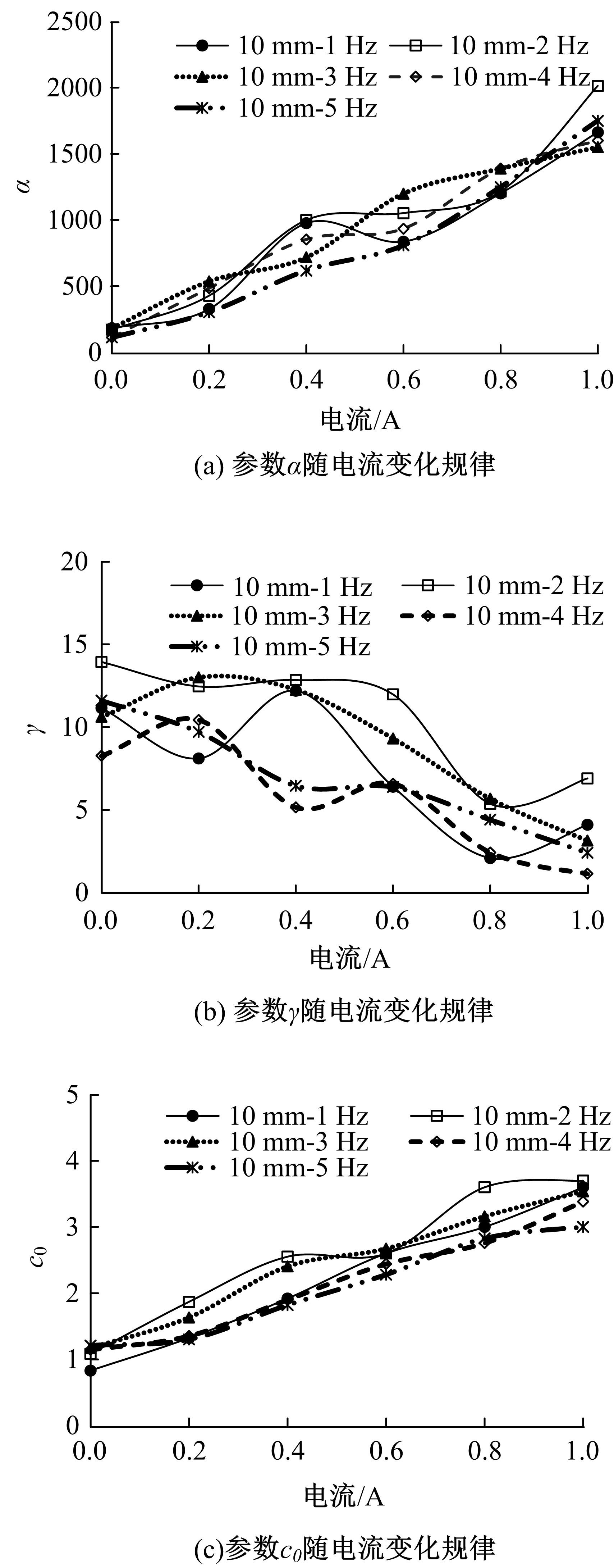
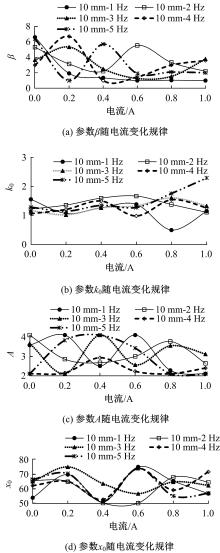
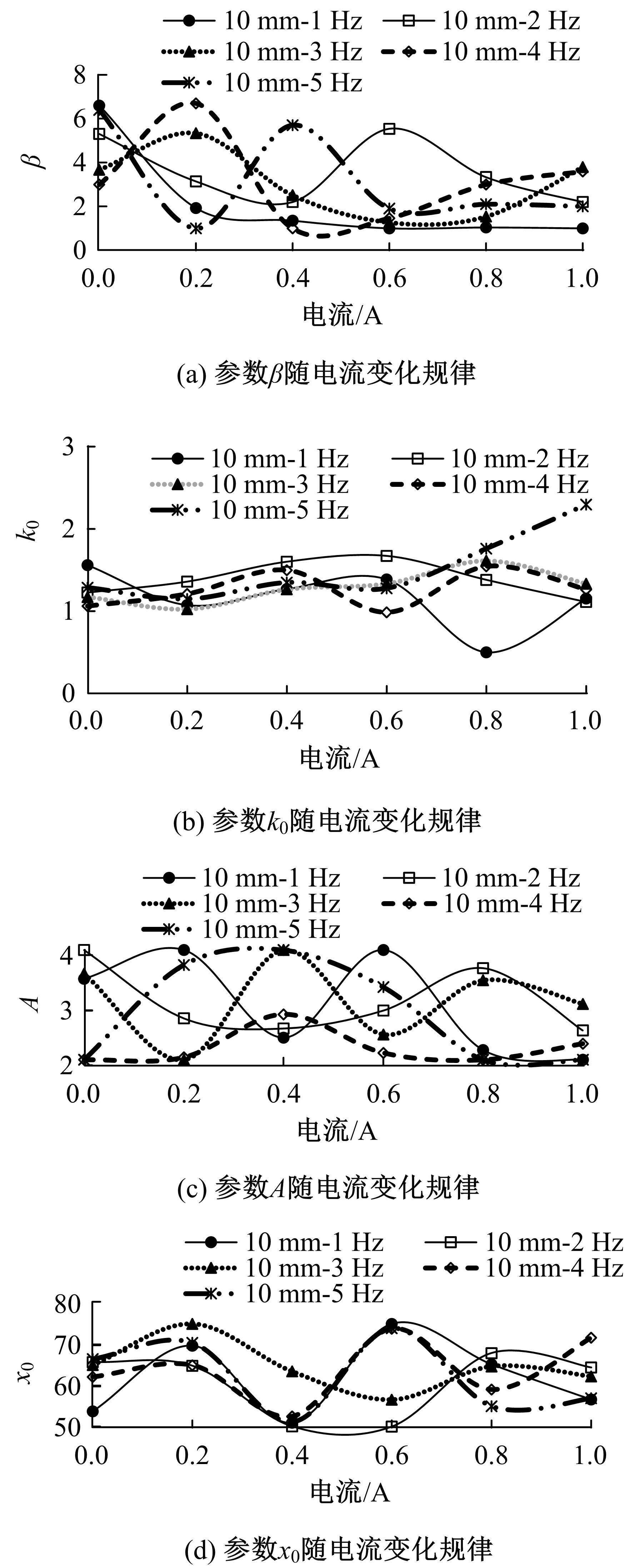
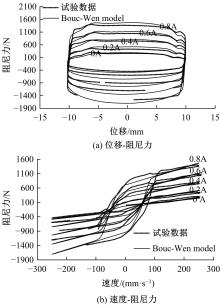
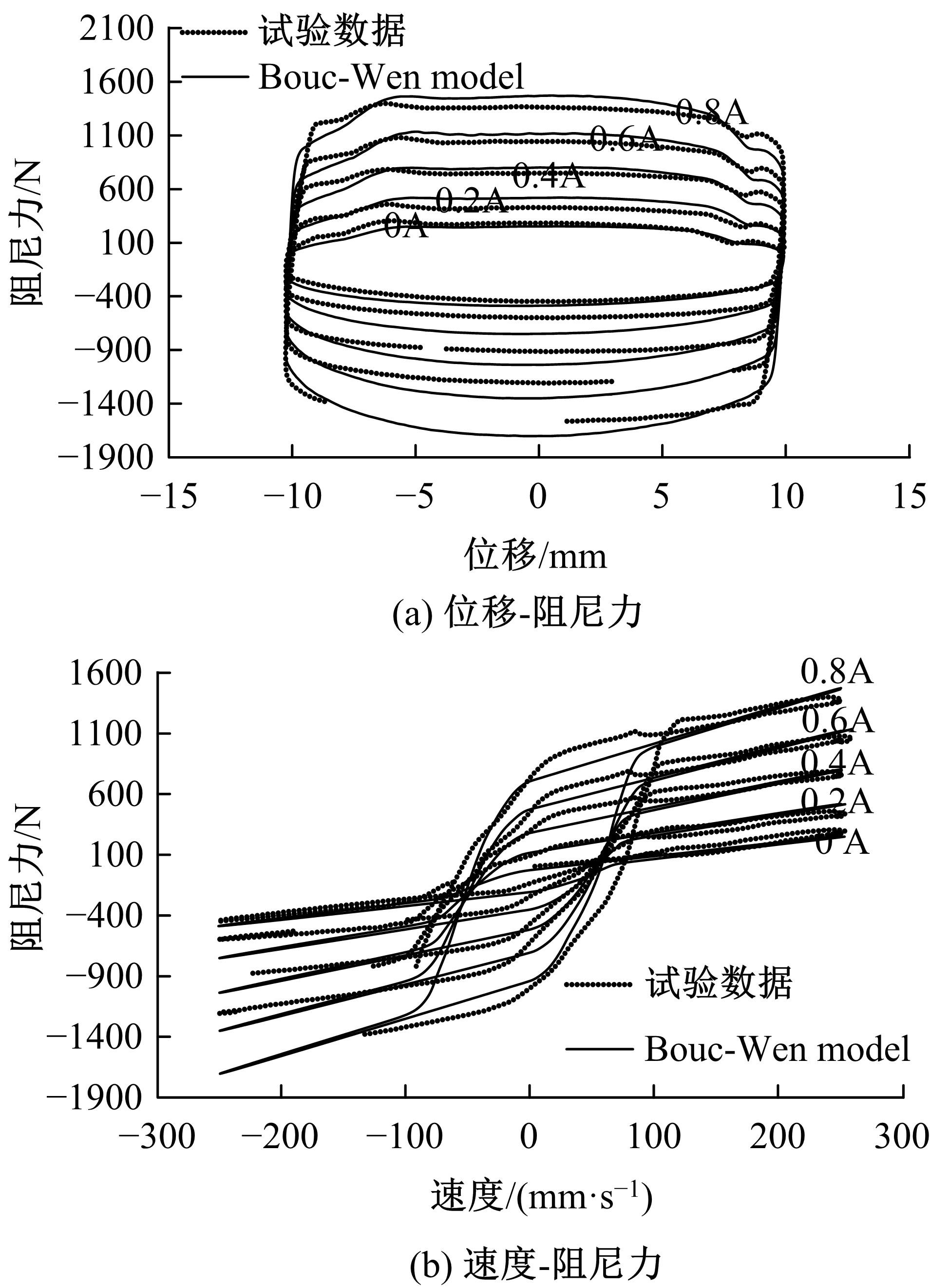
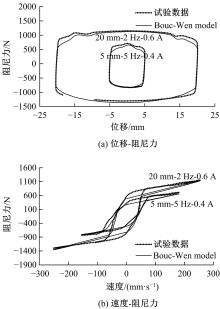
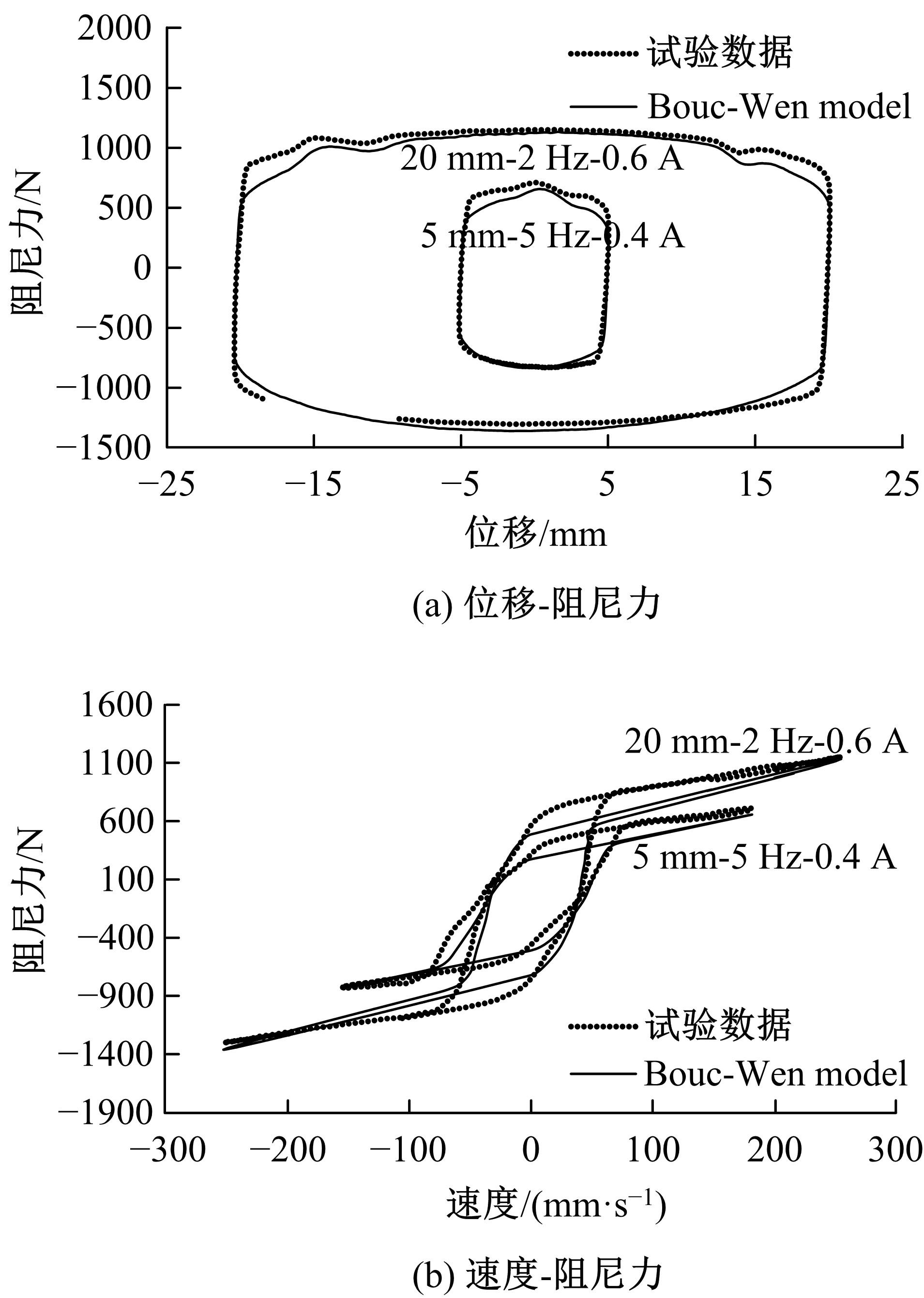
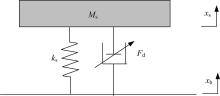
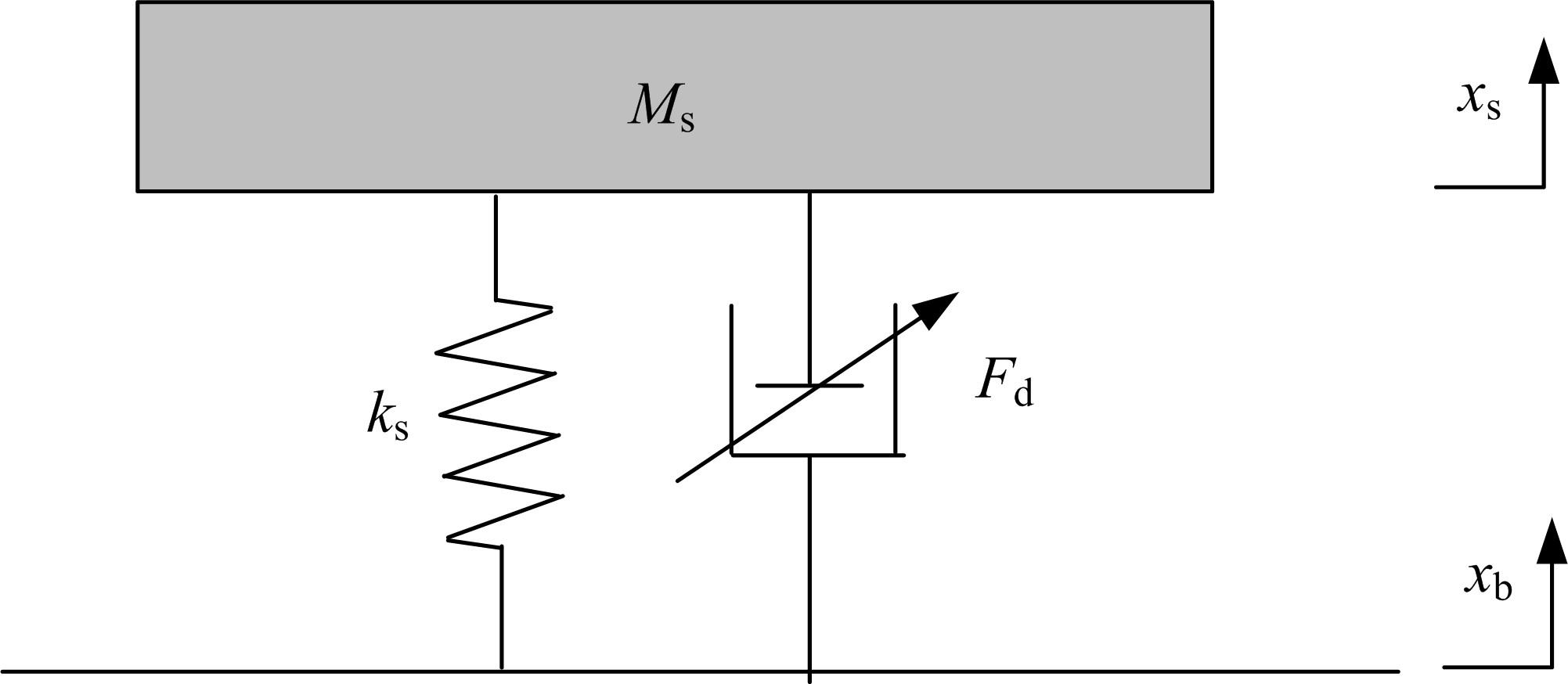
提出了一种磁流变减振器Bouc-Wen滞回模型参数的识别方法。基于新型元启发优化算法(海鸥算法),对描述磁流变减振器非线性力学特性的模型参数进行拟合识别,通过引入基于透镜折射成像的反向学习模型,改善了海鸥算法陷入局部最优的问题。该参数辨识方法计算结果准确,计算过程简单,计算结果鲁棒性强。通过对多工况下磁流变减振器力学特性试验数据进行拟合计算,建立了模型参数与控制电流之间的关系,进而建立了包含控制电流的磁流变减振器多工况通用模型,为磁流变半主动座椅悬架控制系统搭建提供了准确的力学模型。
中图分类号:
- U461.4
| 1 | Zong L H, Gong X L, Xuan S H, et al. Semi-active H infinity control of high-speed railway vehicle suspension with magnetorheological dampers[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2013, 51(5): 600-626. |
| 2 | Mai V N, Yoon D S, Choi S B, et al. Explicit model predictive control of semi-active suspension systems with magneto-rheological dampers subject to input constraints[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2020, 31(10): 1157-1170. |
| 3 | Du X M, Yu M, Fu J, et al. Experimental study on shock control of a vehicle semi-active suspension with magneto-rheological damper[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2020, 29(7): No.074002. |
| 4 | Phu D X, Shin D K, Choi S B. Design of a new adaptive fuzzy controller and its application to vibration control of a vehicle seat installed with an MR damper[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2015, 24(8): No. 085012. |
| 5 | Bai X X, Chen P, Qian L J. Principle and validation of modified hysteretic models for magnetorheological dampers[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2015, 24(8): No. 085014. |
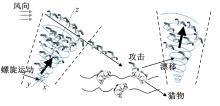
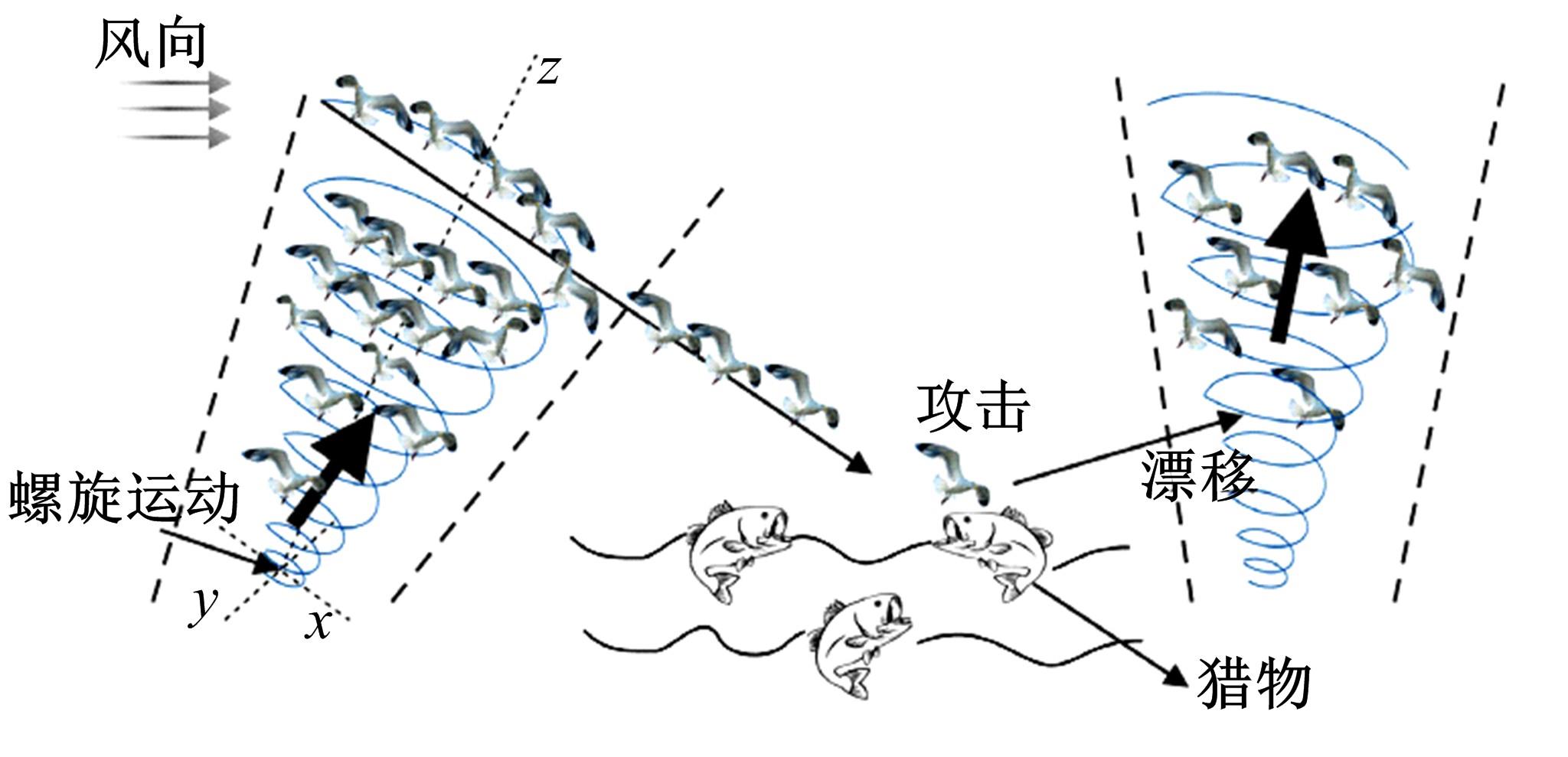
| 6 | Wang W X, Hua X G, Wang X Y, et al. Mechanical behavior of magnetorheological dampers after long-term operation in a cable vibration control system[J]. Structural Control and Health Monitoring, 2019, 26(1): No.e2280. |
| 7 | Zhang C, Wang L X. Dynamic models for magnetorheological dampers and its feedback linearization[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2009, 79-82: 1205-1208. |
| 8 | 左曙光, 毛钰, 吴旭东, 等. 磁流变减振器高频硬化特性建模及优化[J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(10): 120-125, 150. |
| Zuo Shu-guang, Mao Yu, Wu Xu-dong, et al. Modelling and optimization of high frequency hardening characteristics of magneto rheological damper [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(10): 120-125, 150. | |
| 9 | 彭虎, 张进秋, 刘义乐, 等. 基于改进双Sigmoid模型的磁流变减振器力学建模研究[J].振动与冲击, 2019, 38(15): 216-222. |
| Peng Hu, Zhang Jin-qiu, Liu Yi-le,et al. MR damper's modeling based on improved dual-sigmoid model [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(15): 216-222. | |
| 10 | 薛兵, 杜永昌, 刘源, 等. 基于机理的磁流变减震器滞回特性魔术公式模型[J]. 振动工程学报, 2017, 30(5): 774-780. |
| Xue Bing, Du Yong-chang, Liu Yuan, et al. Magic formula model of hysteresis characteristics of magnetorheological damper based on mechanism[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 30(5): 774-780. | |
| 11 | Charalampakis A E, Koumousis V K. Identification of bouc–wen hysteretic systems by a hybrid evolutionary algorithm[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 314(3-5): 571-585. |
| 12 | Kwok N M, Ha Q P, Nguyen T H, et al. A novel hysteretic model for magnetorheological fluid dampers and parameter identification using particle swarm optimization[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2006, 132(2): 441-451. |
| 13 | 郑玲, 牛伯瑶, 李以农, 等. 基于遗传算法的汽车磁流变减振器多目标优化[J]. 汽车工程, 2016, 38(7): 871-877. |
| Zheng Ling, Niu Bo-yao, Li Yi-nong, et al. Multi-objective optimization of vehicle MR damper based on genetic algorithm[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2016, 38(7): 871-877. | |
| 14 | 刘永强, 杨绍普, 廖英英. 一种磁流变减震器模型参数识别新方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(6): 62-68. |
| Liu Yong-qiang, Yang Shao-pu, Liao Ying-ying. A new method of parameters identification for magnetorheological damper model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(6): 62-68. | |
| 15 | Zeinali M, Mazlan S A, Fatah A Y A, et al. A phenomenological dynamic model of a magnetorheological damper using a neuro-fuzzy system[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2013, 22(12): No. 125013. |
| 16 | 王戡, 郑玲, 刘非. 基于广义回归神经网络的磁流变减振器模型辨识[J]. 汽车工程, 2013, 35(7): 619-623, 634. |
| Wang Kan, Zheng Ling, Liu Fei. Model identification of mr damper based on generalized regression neural network[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2013, 35(7): 619-623, 634. | |
| 17 | Spencer B F, Dyke S J. Phenomenological model for magnetorheological dampers[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1997, 123(3): 230-237. |
| 18 | Dhiman G, Kumar V. Seagull optimization algorithm: theory and its applications for large-scale industrial engineering problems[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 165: 169-196. |
| 19 | Cao Y, Li Y Q, Zhang G, et al. Experimental modeling of PEM fuel cells using a new improved seagull optimization algorithm[J]. Energy Reports, 2019, 5: 1616-1625. |
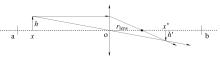
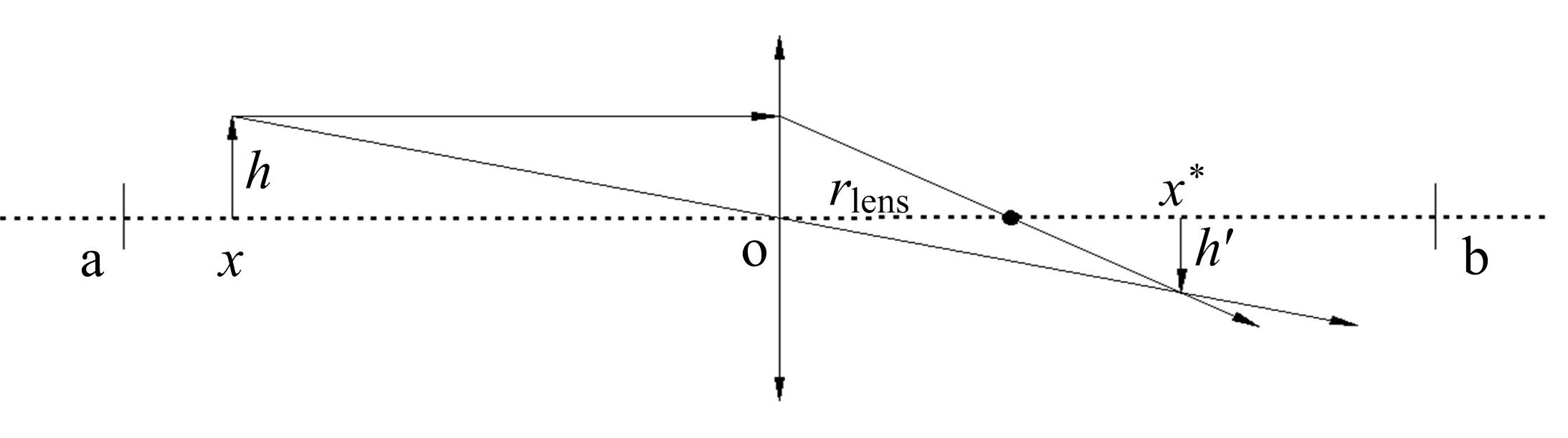
| 20 | 喻飞,李元香,魏波, 等.透镜成像反学习策略在粒子群算法中的应用[J]. 电子学报, 2014, 42(2): 230-235. |
| Yu Fei, Li Yuan-xiang, Wei Bo, et al. The application of a novel obl based on lens imaging principle in PSO[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2014, 42(2): 230-235. |
| [1] | 李杰,陈涛,郭文翠,赵旗. 汽车非平稳随机振动空间域虚拟激励法及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 738-744. |
| [2] | 张英朝,李昀航,郭子瑜,王国华,张喆,苏畅. 长头重型卡车气动减阻优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 745-753. |
| [3] | 段亮,宋春元,刘超,魏苇,吕成吉. 基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 53-62. |
| [4] | 庄蔚敏,陈沈,王楠. 温度对车身钢铝胶铆连接结构热应力变化的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 70-78. |
| [5] | 陈剑斌,周宋泽,费峰永,陈永龙,凌国平. 过盈量及滚花方式对装配式凸轮轴压装失效的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1959-1966. |
| [6] | 胡兴军,张靖龙,罗雨霏,辛俐,李胜,胡金蕊,兰巍. 冷却管结构及进气方向对空冷中冷器性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 1933-1942. |
| [7] | 罗勇,韦永恒,黄欢,肖人杰,任淋,崔环宇. 驾驶员意图识别的P2.5插混构型双离合器起步控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1575-1582. |
| [8] | 曾小华,宋美洁,宋大凤,王越. 基于车联网信息的公交客车行驶工况数据处理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| [9] | 马超,高云凯,刘哲,段月星,田林雳. 骨架式车身多材料及梁截面形状和尺寸优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1583-1592. |
| [10] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [11] | 杨建,夏琦,周海超,王国林. 修正胎体弦轮廓载重子午线轮胎的降噪机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1198-1203. |
| [12] | 龙江启,向锦涛,俞平,王骏骋. 适用于非线性主动悬架滑模控制的线性干扰观测器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1230-1240. |
| [13] | 陈鑫,于贵申,张彪,潘凯旋,杨立飞. 搅拌摩擦点焊接头拉伸-剪切行为的等效建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1190-1197. |
| [14] | 宋大凤,杨丽丽,曾小华,王星琦,梁伟智,杨南南. 基于行驶工况合成的混合动力汽车电池寿命优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 781-791. |
| [15] | 何仁,赵晓聪,杨奕彬,王建强. 基于驾驶人风险响应机制的人机共驾模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 799-809. |
|
||