吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 346-355.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220364
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
高速列车转向架区域气动噪声源识别与分析
- 1.同济大学上海地面交通工具风洞中心,上海 201804
2.上海市地面交通工具空气动力与热环境模拟重点实验室,上海 201804
Identification and analysis of aerodynamic noise sources in the bogie area of high⁃speed trains
Yi-gang WANG1,2( ),Yu-peng WANG1,2,Hao ZHANG1,2,Si-an ZHAO1,2
),Yu-peng WANG1,2,Hao ZHANG1,2,Si-an ZHAO1,2
- 1.Shanghai Automotive Wind Tunnel Center,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.Shanghai Key Laboratory of Vehicle Aerodynamics and Vehicle Thermal Management Systems,Shanghai 201804,China
摘要:
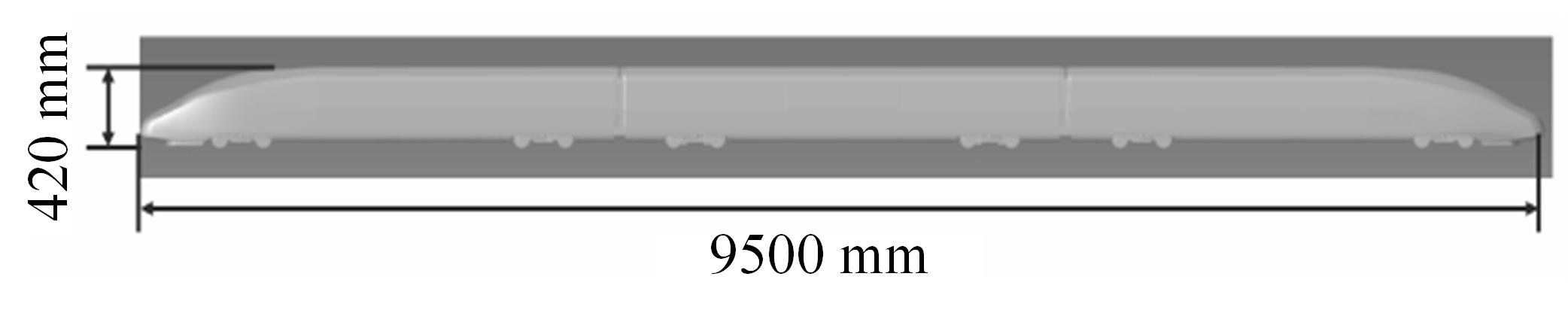
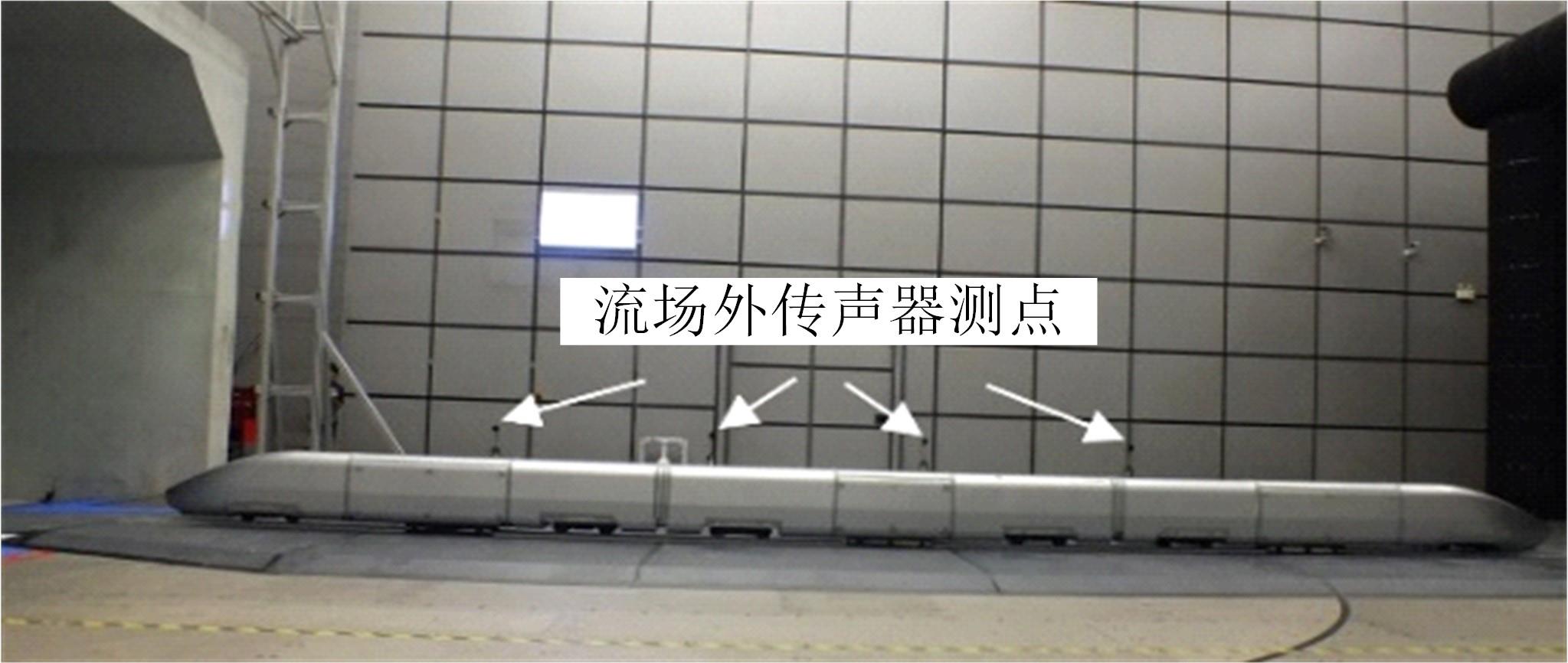
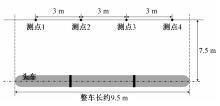
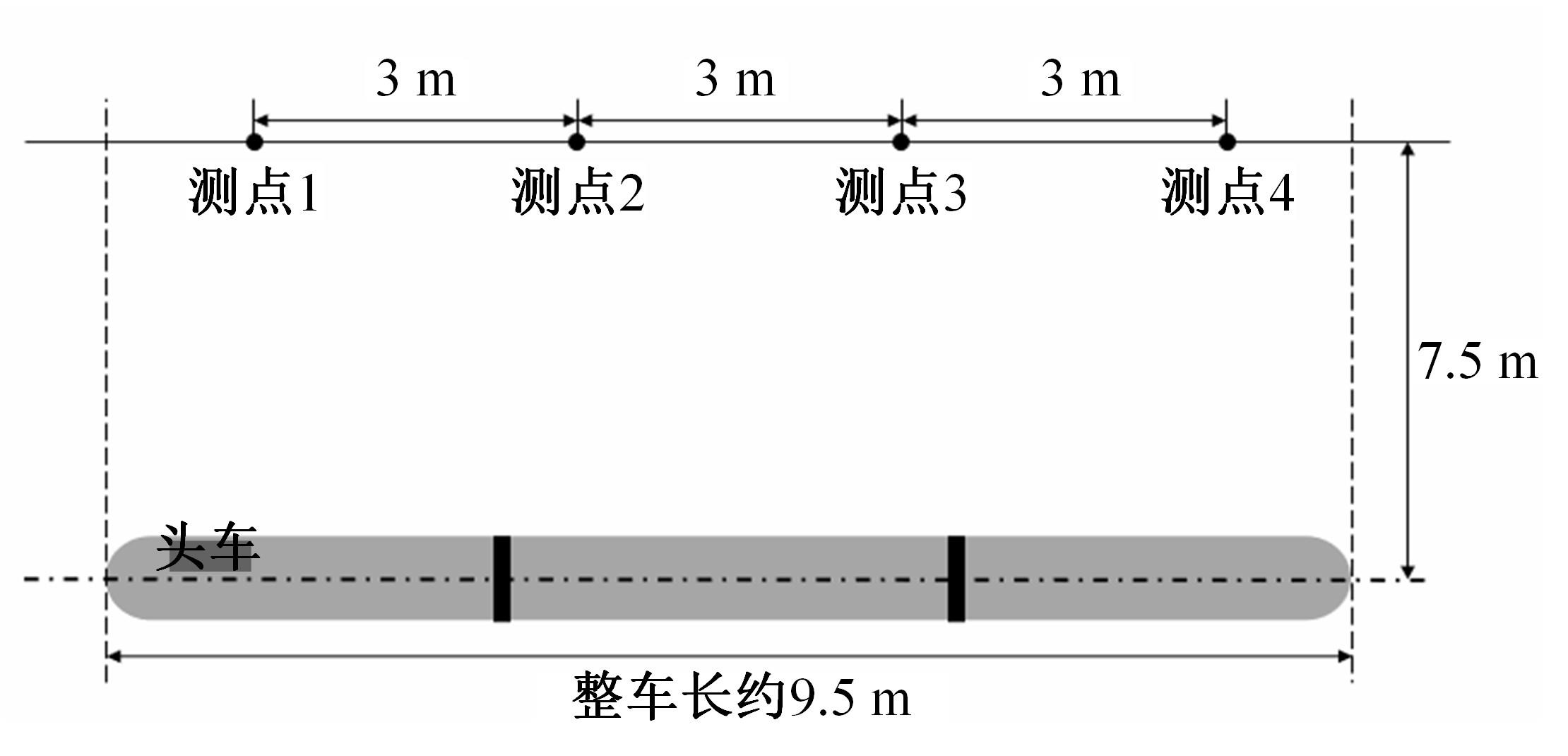
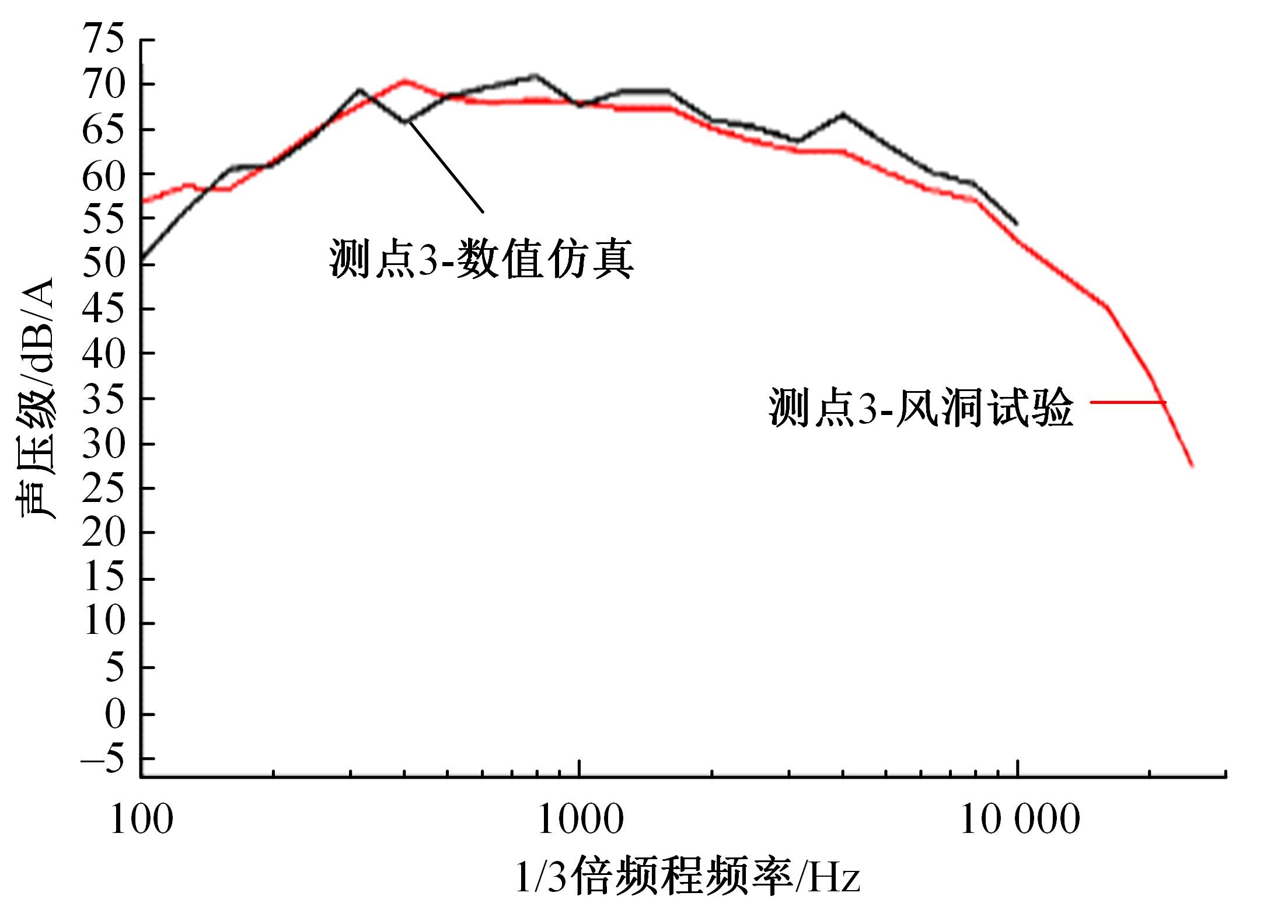
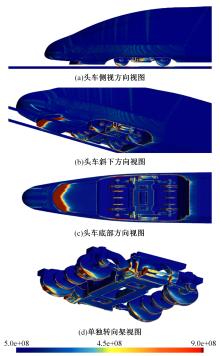
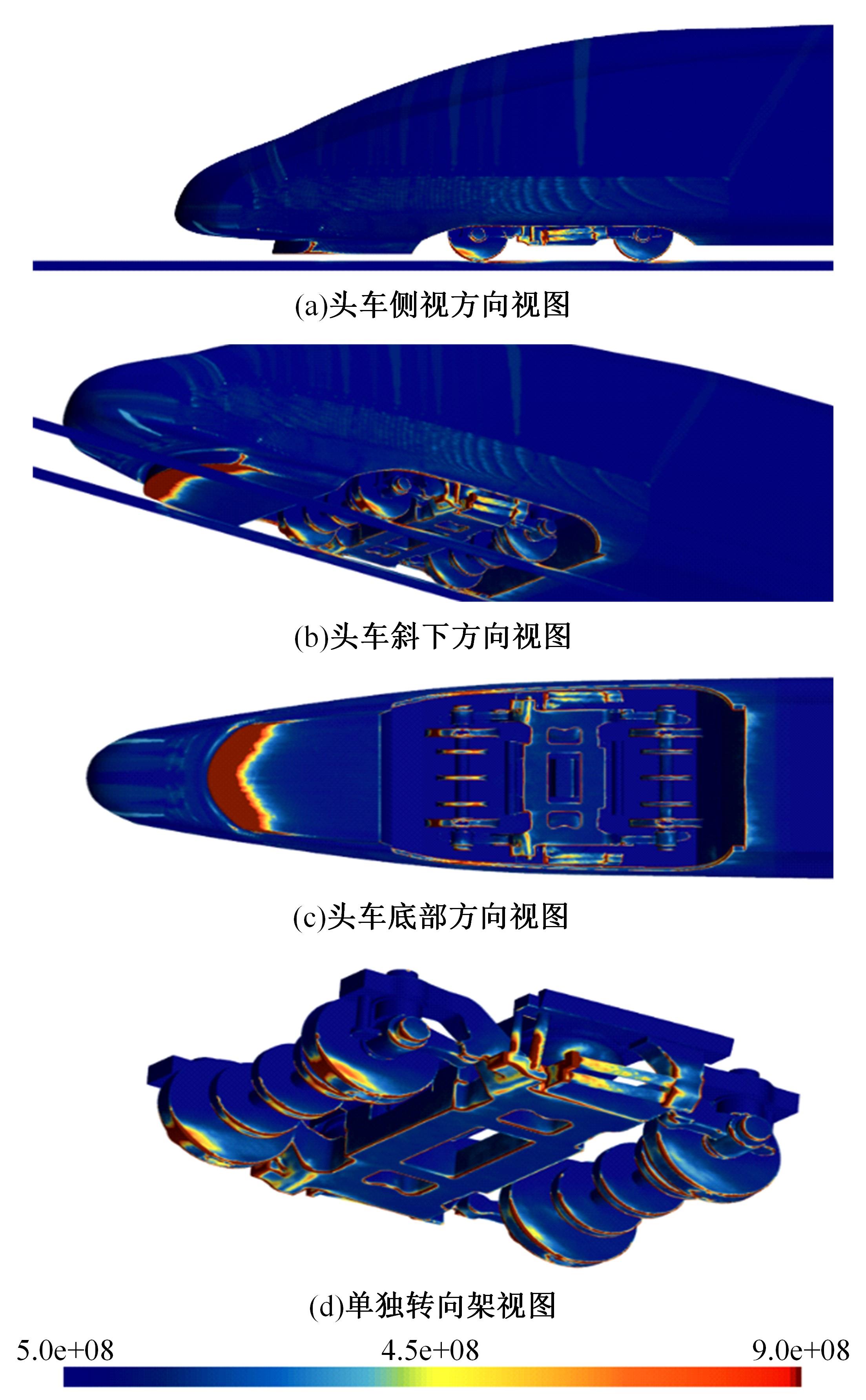
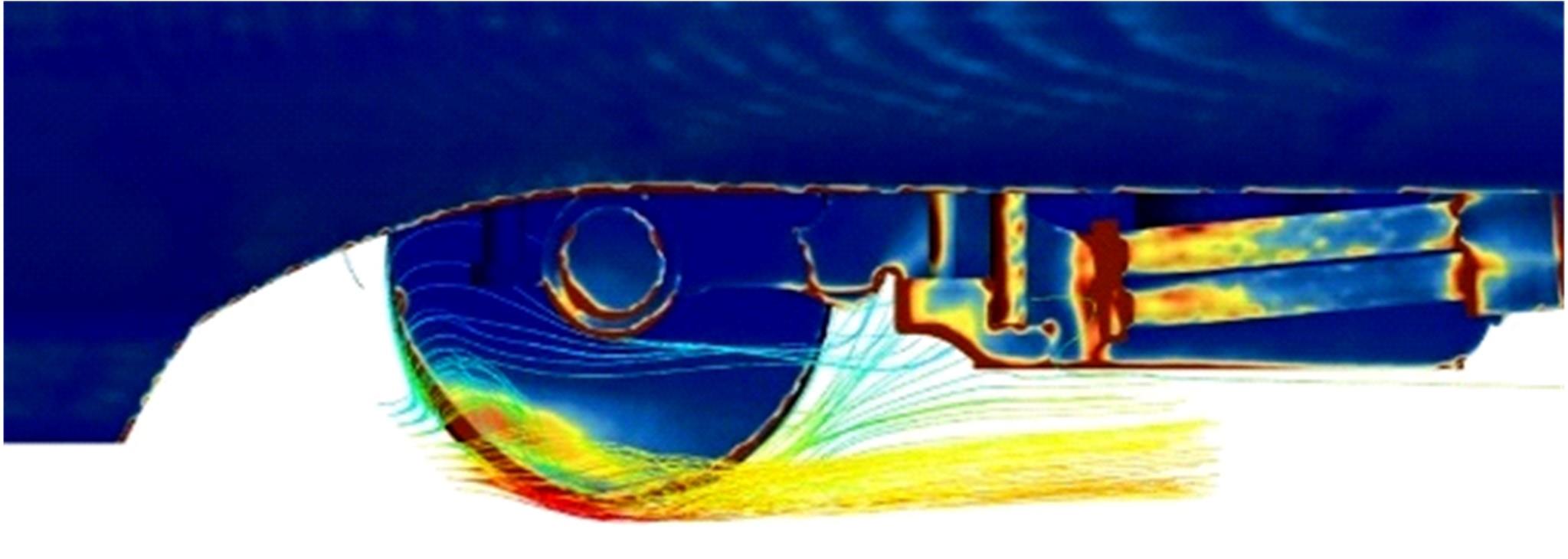
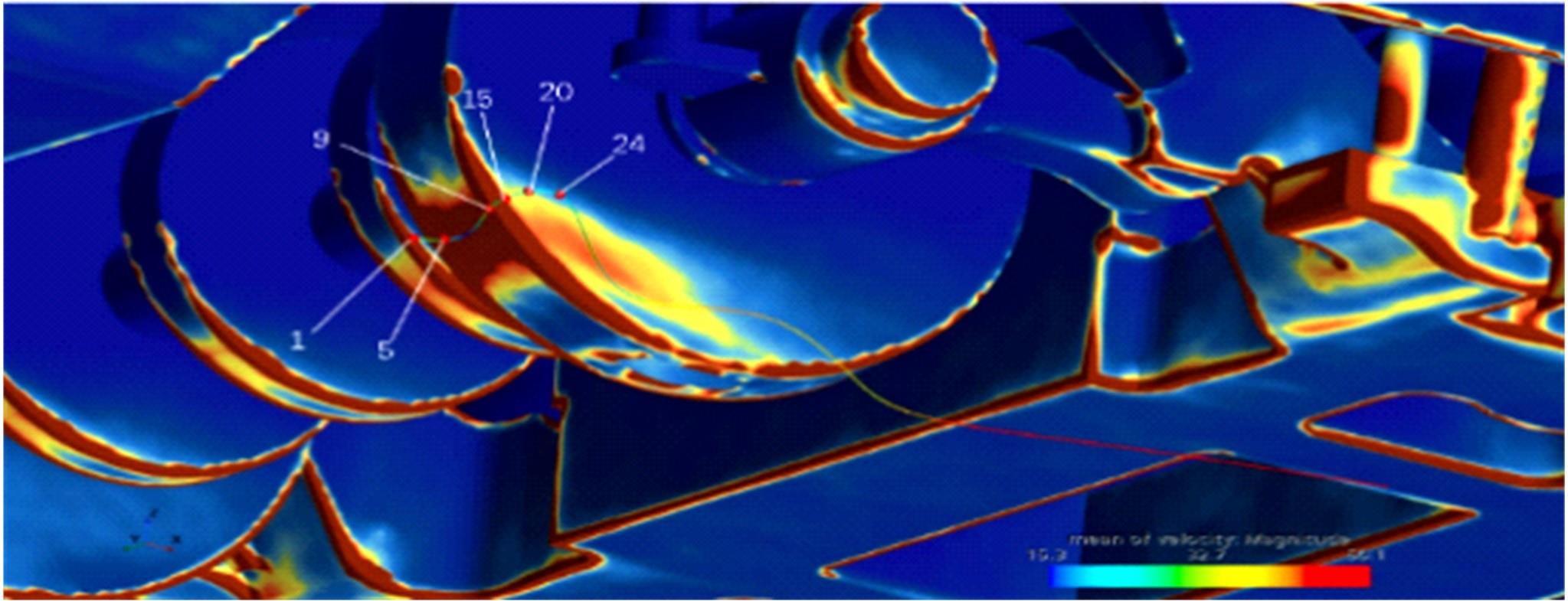
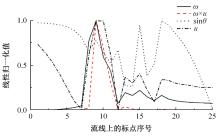
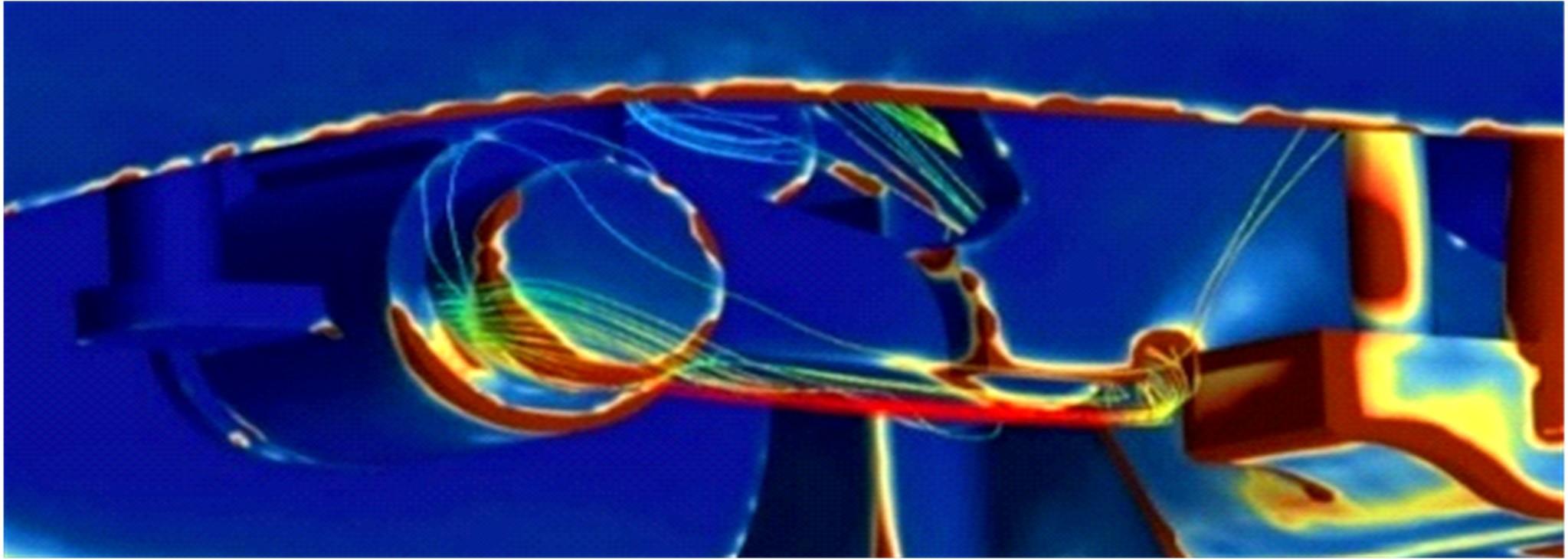
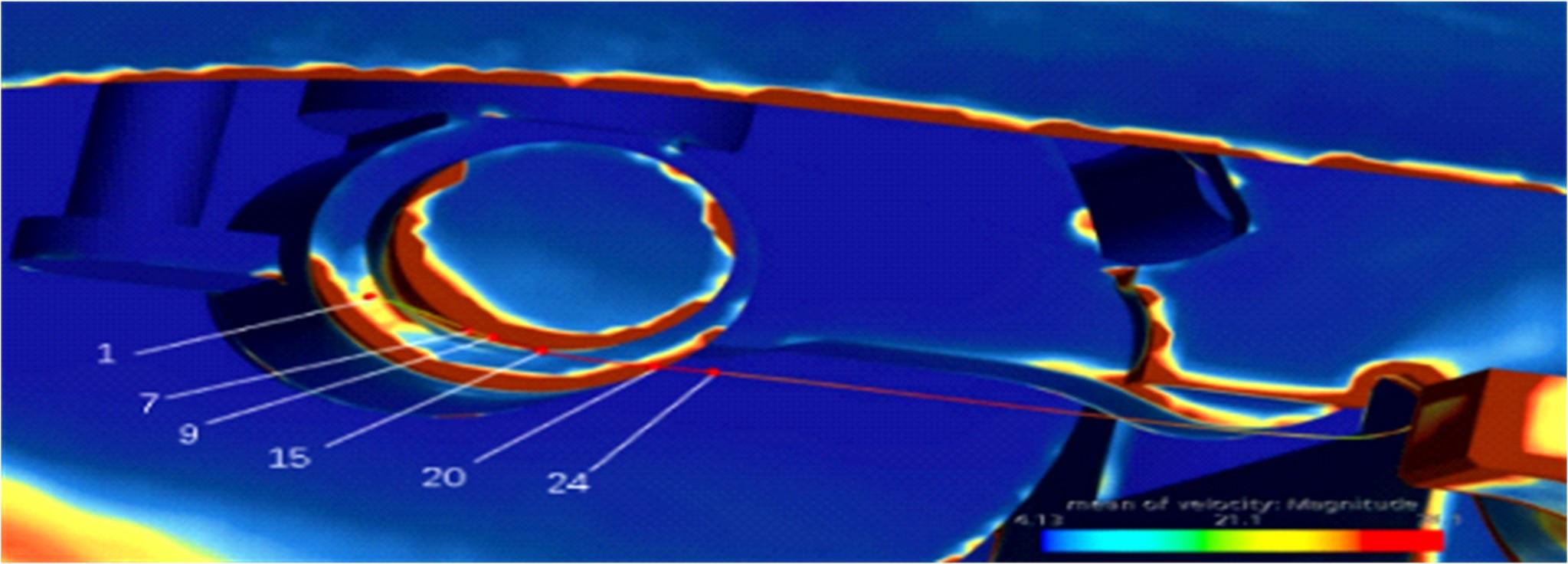
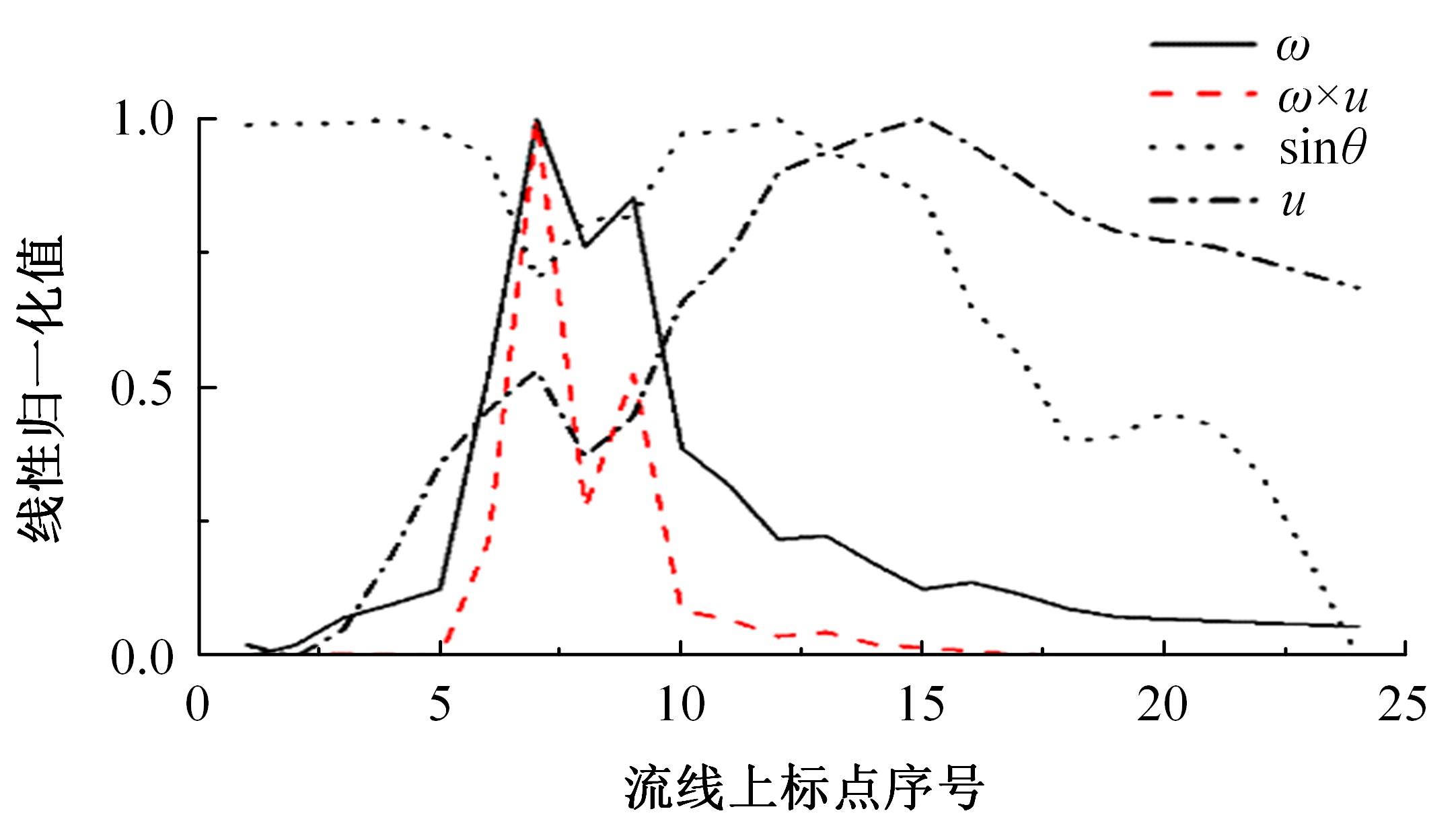
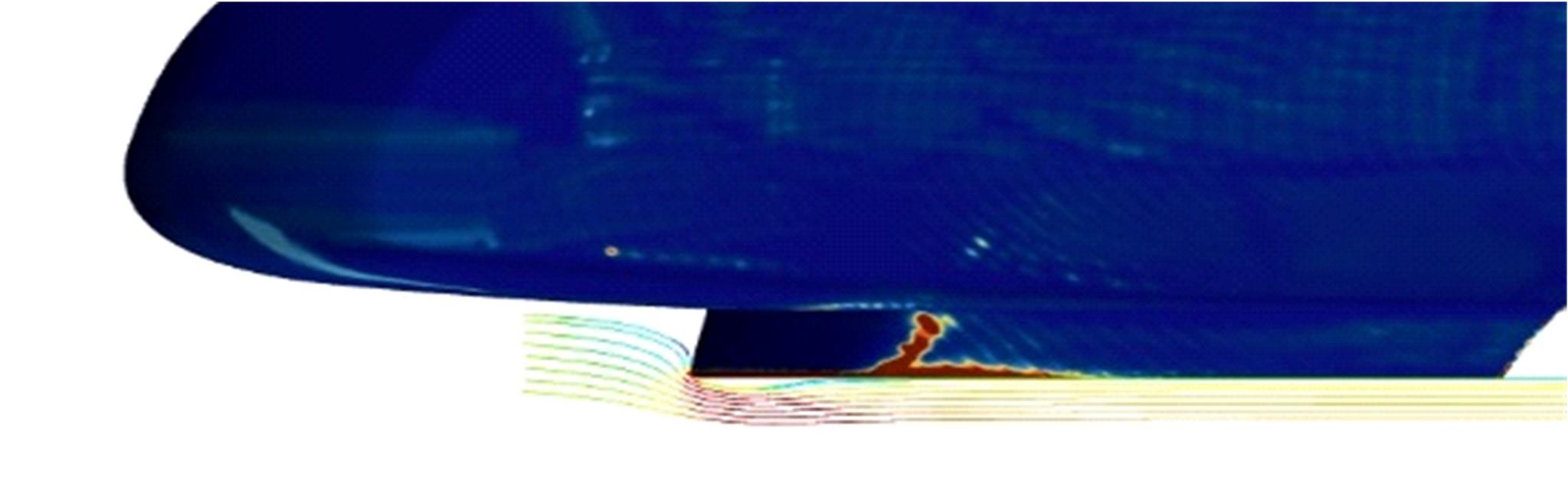
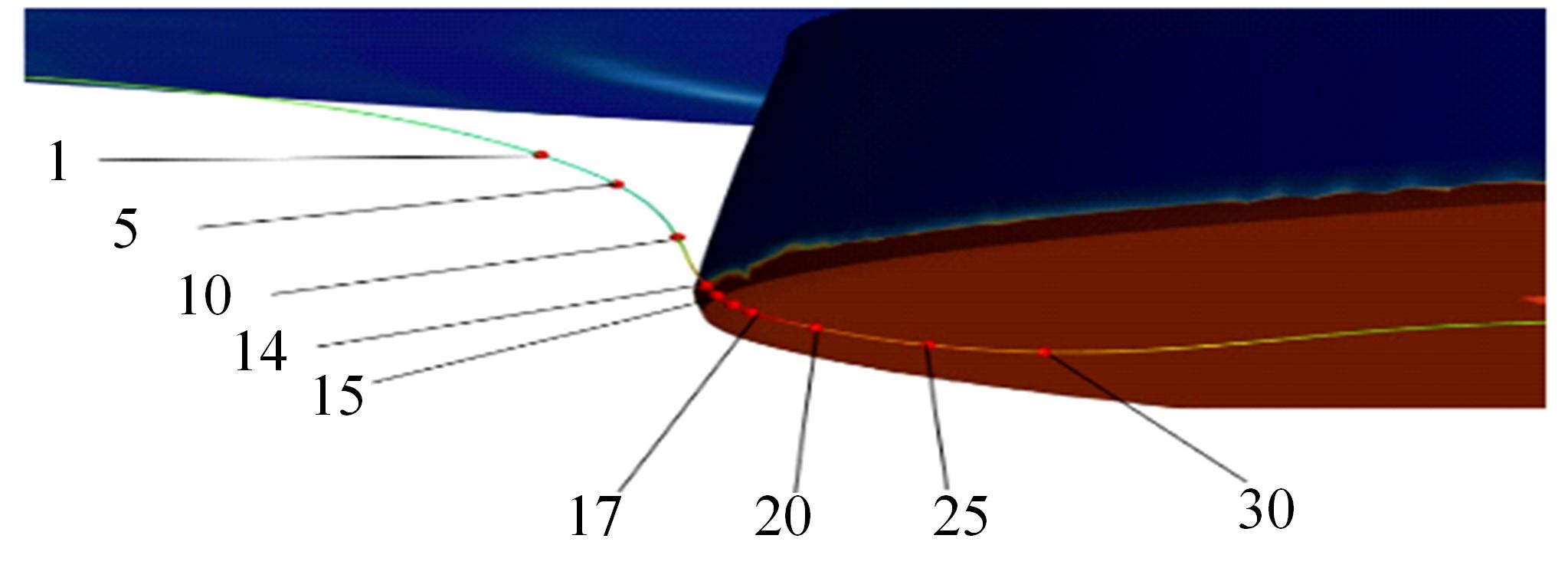
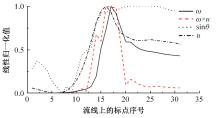
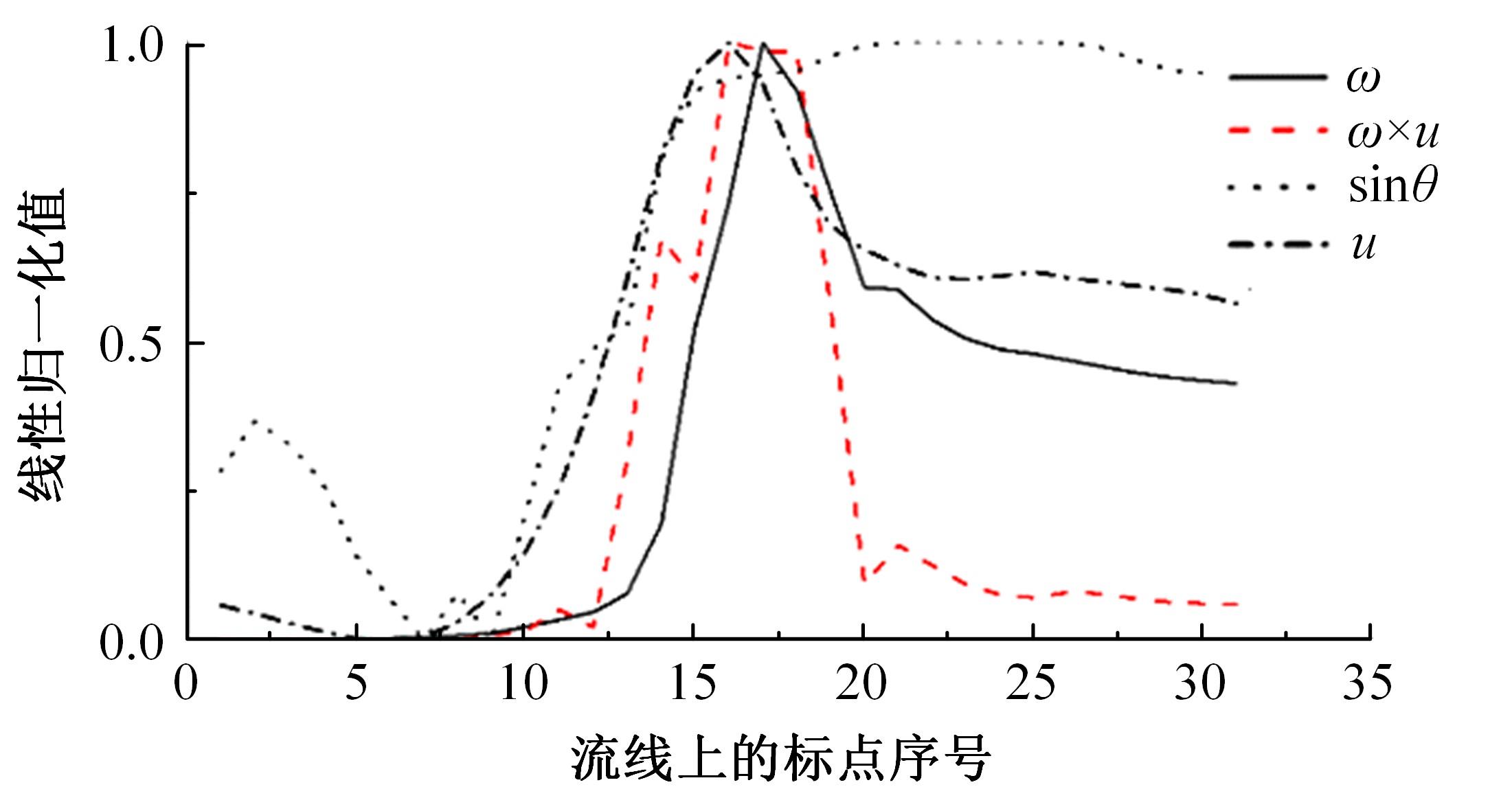
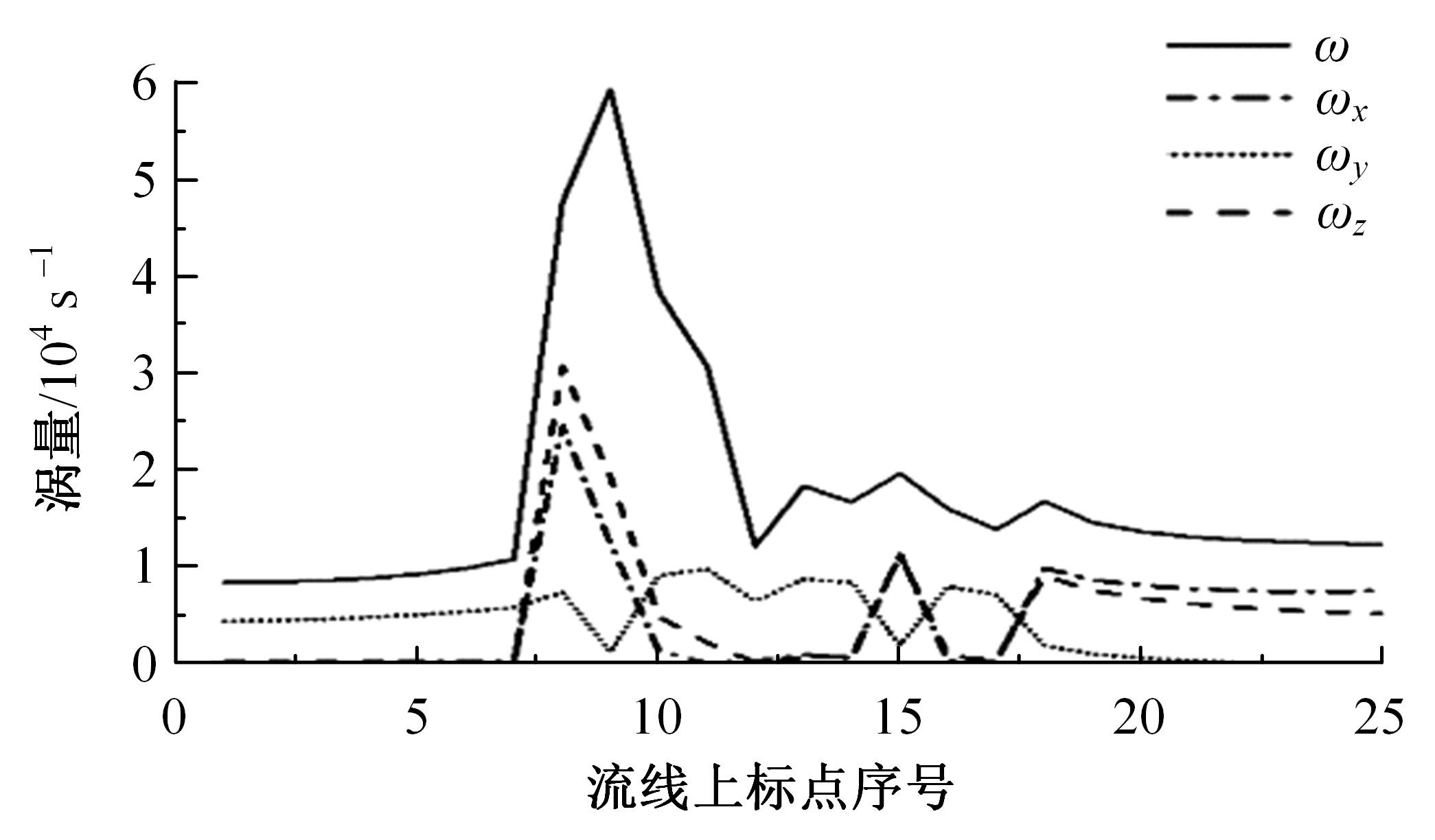
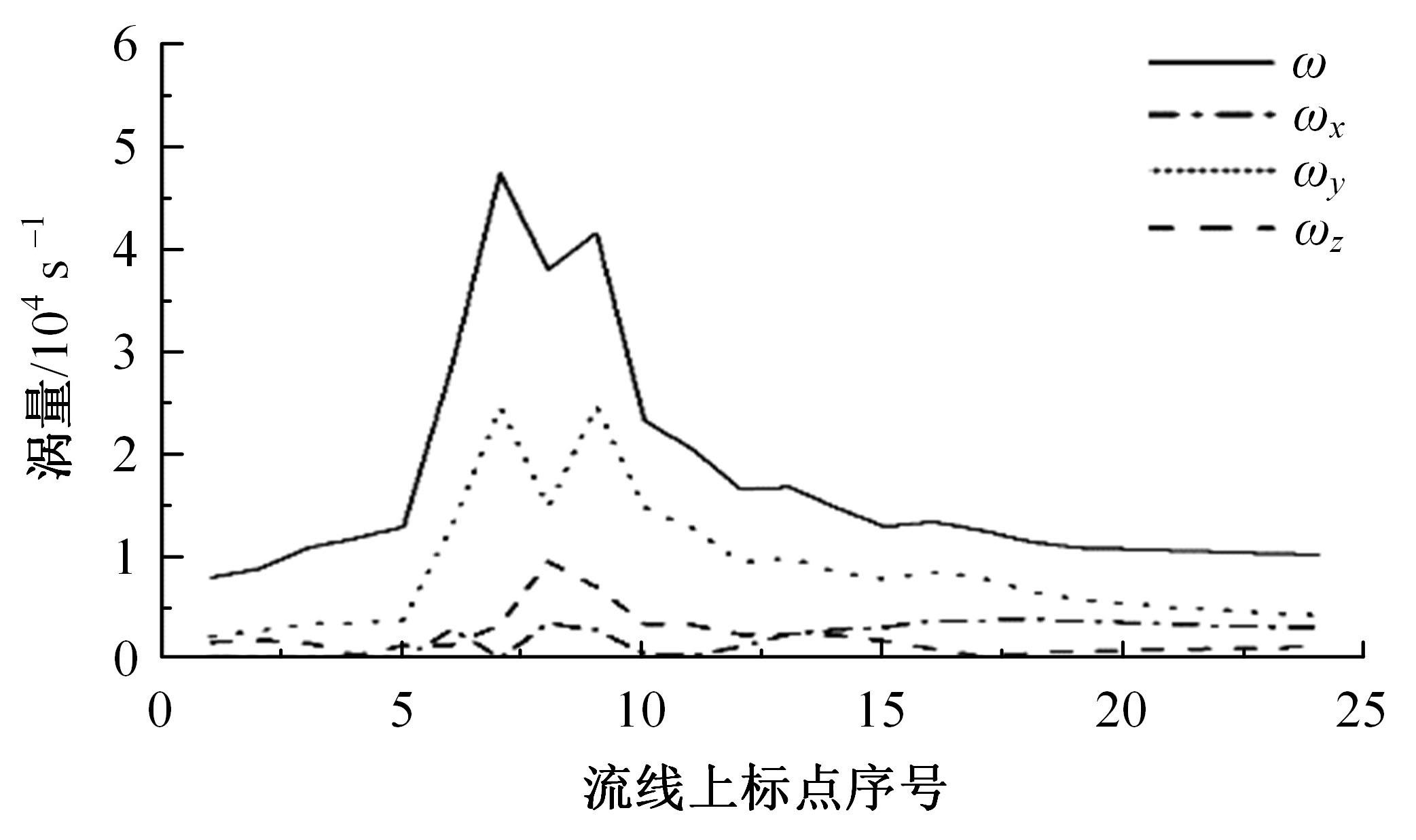
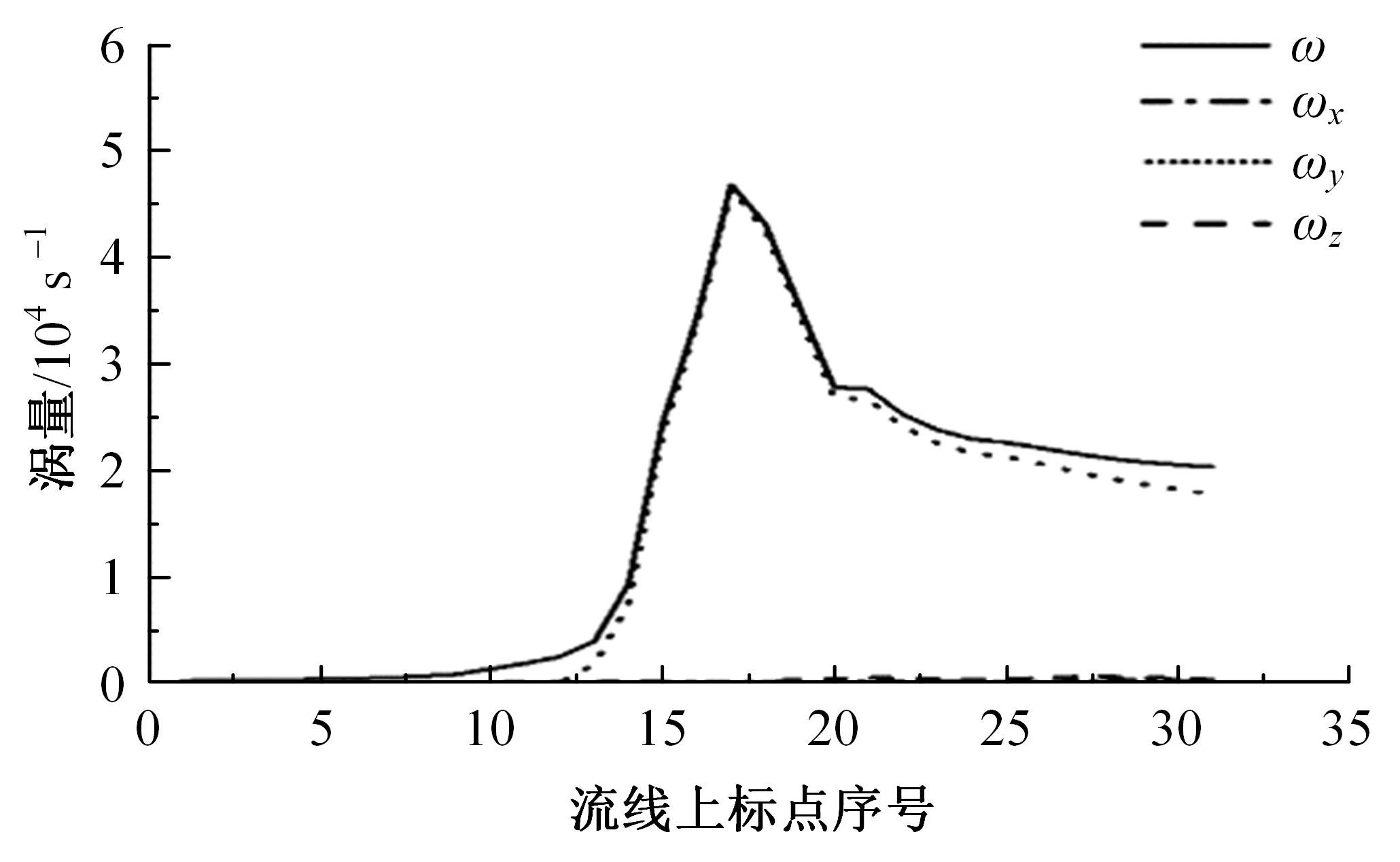
高速列车转向架区域为其主要气动噪声源之一,迄今为止较难描述高速列车气动噪声源特征,鲜有有效的声源识别方法。利用高速列车转向架区域以偶极子声源为主的声源特征,将气动声源等效为无数个球形声源的集合,基于声辐射与声源,声源与流场物理量之间的关系,结合流体数值仿真,建立高速列车偶极子声源识别方法,并聚焦头车转向架区域进行声源识别。同时,以涡声理论为基础,建立偶极子声源强度和流场多物理量的关系,分析流场产生声源的本质。研究表明,偶极子声源集中的位置多为迎风侧气流与壁面发生激烈作用的位置,气流与壁面发生撞击与分离是产生偶极子声源的主要原因,且在该区域涡量的变化对偶极声源强度影响最大,在不同区域,不同方向的涡量分量在起主导作用。
中图分类号:
- V221.3
| 1 | Lighthill M J. On sound generated aerodynamically. I. General theory[J]. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1952, 211: 564-587. |
| 2 | Lighthill M J. On sound generated aerodynamically. II. Turbulence as a source of sound[J]. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1954, 222: 1-32. |
| 3 | Curle N. The Influence of solid boundaries upon aerodynamic sound[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A, 1955, 231:505-514. |
| 4 | Williams J E F. Hawkings D L. Sound generation by turbulence and surfaces in arbitrary motion[J]. Philosophical Transcations of the Roval Society A, 1969, 264: 321342. |
| 5 | Williams J E F, Hawkings D L. Sound generation by turbulence and surfaces in arbitrary motion[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1969, 264:321-342. |
| 6 | Powell A. Theory of vortex sound[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1964, 36(1):177. |
| 7 | Howe M S. Theory of Vortex Sound[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2003. |
| 8 | 张曙光.350 km/h高速列车噪声机理、声源识别及控制[J].中国铁道科学,2009,30(1):86-90. |
| Zhang Shu-guang. Noise mechanism, sound source identification and control of 350 km/h high-speed trains[J]. China Railway Science, 2009,30(1):86-90. | |
| 9 | Mellet C, Létourneaux F, Poisson F, et al. High speed train noise emission: latest investigation of the aerodynamic/rolling noise contribution[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 2006, 293(3-5):535-546. |
| 10 | 张卫华. 高速列车顶层设计指标研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2012(9):15-19. |
| Zhang Wei-hua. Research on top-level design index of high-speed train[J]. Journal of Railways, 2012(9):15-19. | |
| 11 | 高阳,王毅刚,王金田,等.声学风洞中的高速列车模型气动噪声试验研究[J].声学技术, 2013,32(6):506-510. |
| Gao Yang, Wang Yi-gang, Wang Jin-tian, et al. Experimental study on aerodynamic noise of high-speed train model in acoustic wind tunnel[J]. Acoustic Technology, 2013, 32(6): 506-510. | |
| 12 | 黄莎. 高速列车车外气动噪声数值模拟研究[D]. 湖南: 中南大学交通运输工程学院,2009. |
| Huang Sha. Research on numerical simulation of outside aerodynamic noise of high-speed train[D]. Hunan: School of Traffic & Transportation Engineering, Central South University, 2009. | |
| 13 | 张亚东, 张继业, 张亮, 等 高速列车动车转向 架气动噪声数值分析 [J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016, 51(5):870-877. |
| Zhang Ya-dong, Zhang Ji-ye, Zhang Liang, et al. Numerical analysis of aerodynamic noise of high-speed train bogies[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 870-877. | |
| 14 | 李辉,肖新标,金学松.基于简化模型的头车转向架气动噪声特性研究 [J].机械工程学报,2016,52(8):152-161. |
| Li Hui, Xiao Xin-biao, Jin Xue-song. Research on the aerodynamic noise characteristics of the lead car bogie based on a simplified model[J].Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2016,52(8):152-161. | |
| 15 | 张强. 气动声学基础[M]. 北京:国防工业出版社, 2012. |
| [1] | 邓小林,杨馥模,覃善甘. 新型仿竹六边形梯度层级多胞管耐撞性对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 333-345. |
| [2] | 李旭东,王新宇,田程,张新峰,牛治慧,赵志强. 基于用户关联的车辆耐久性载荷谱编制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 66-75. |
| [3] | 王铁,李旭东,田程,赵宏伟. 基于多轴载荷投影构建轮辋双轴疲劳损伤模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 99-104. |
| [4] | 吴骁,史文库,郭年程,赵燕燕,陈志勇,李鑫鹏,孙卓,刘健. 基于Ease off的准双曲面齿轮多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 76-85. |
| [5] | 陈兆玮,蒲前华. 弹性车轮对大跨斜拉桥车桥耦合振动的抑制特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2519-2532. |
| [6] | 刘平义,李晓婷,高偌霖,李海涛,魏文军,王亚. 车辆侧倾驱动机构设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2185-2192. |
| [7] | 黄学劲,钟锦星,路京雨,赵霁,肖伟,袁新枚. 基于用户画像的电动汽车充电负荷预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2193-2200. |
| [8] | 张树培,夏明悦,张玮,陈钊,陈义祥. 考虑非线性刚度的间隙球铰碰撞动力学建模与仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2227-2235. |
| [9] | 陈辉,邵亚军. 基于惯性基准多传感器耦合的路面谱测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2254-2262. |
| [10] | 吴春利,黄诗茗,李魁,顾正伟,黄晓明,张炳涛,杨润超. 基于数值仿真和统计分析的洪水作用下桥墩作用效应分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1612-1620. |
| [11] | 陈鑫,张冠宸,赵康明,王佳宁,杨立飞,司徒德蓉. 搭接焊缝对铝合金焊接结构轻量化设计的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1282-1288. |
| [12] | 张勇,毛凤朝,刘水长,王青妤,潘神功,曾广胜. 基于Laplacian算法的汽车外流场畸变网格优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1289-1296. |
| [13] | 汪少华,储堃,施德华,殷春芳,李春. 基于有限时间扩张状态观测的HEV鲁棒复合协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [14] | 陈磊,王杨,董志圣,宋亚奇. 一种基于转向意图的车辆敏捷性控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1257-1263. |
| [15] | 于贵申,陈鑫,武子涛,陈轶雄,张冠宸. AA6061⁃T6铝薄板无针搅拌摩擦点焊接头结构及性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
|
||