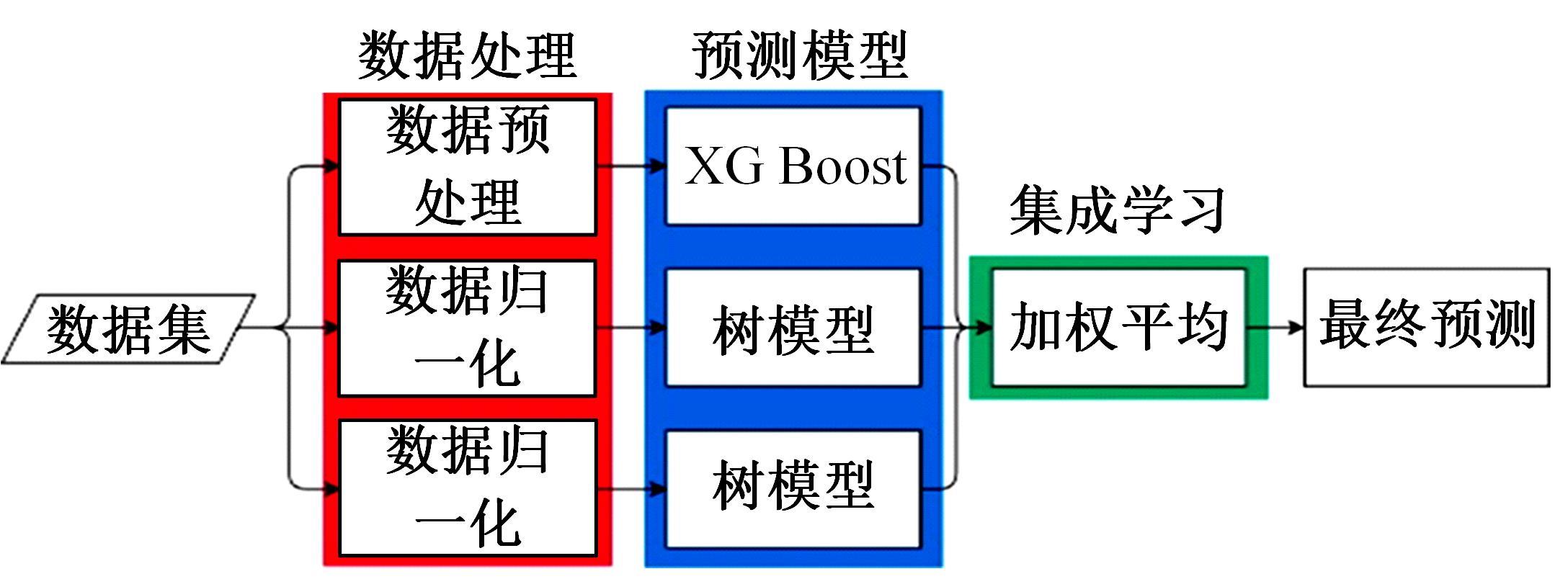
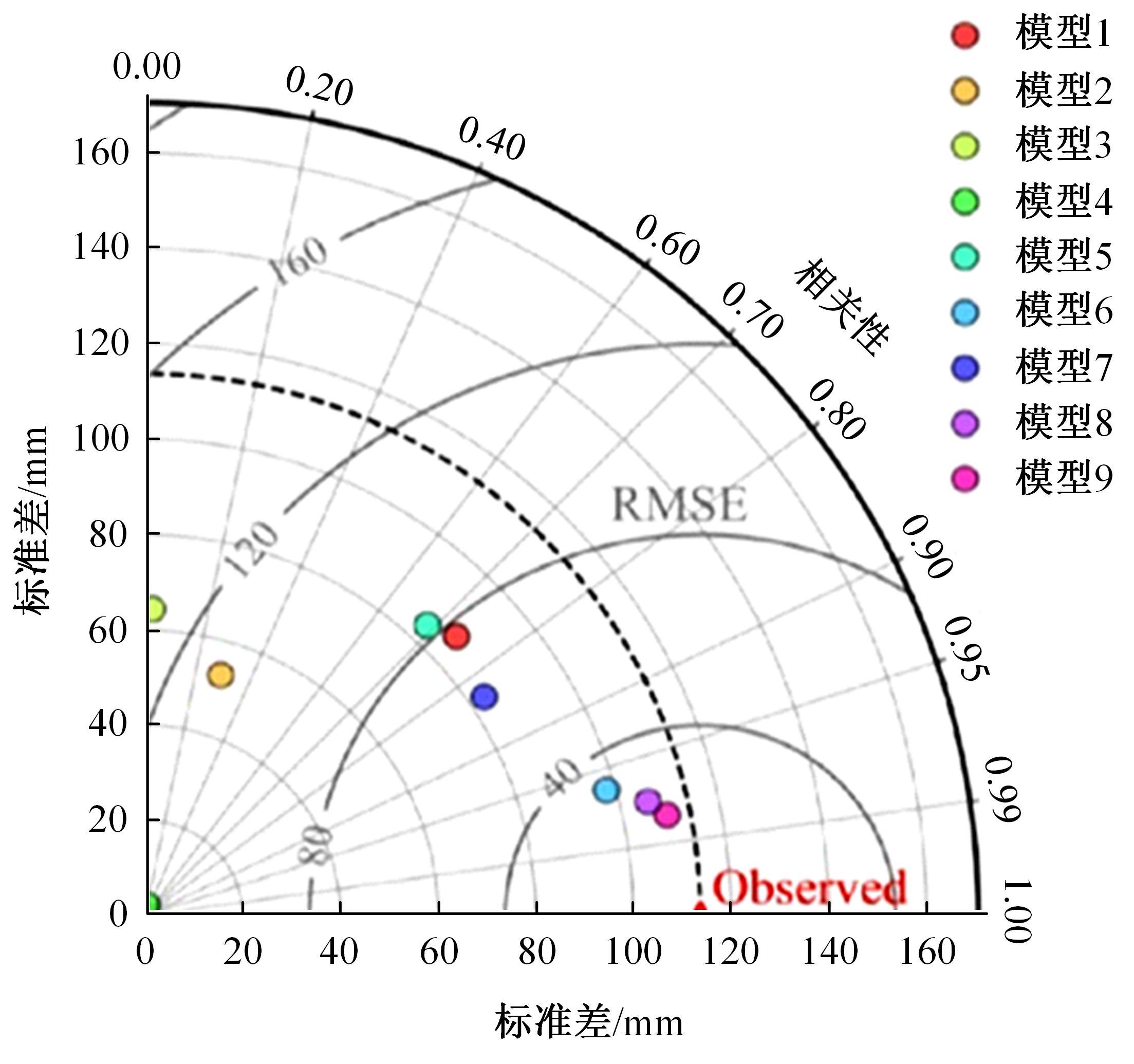
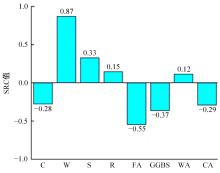
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (3): 771-789.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240056
人工智能在超高性能混凝土中的应用研究进展
- 哈尔滨工业大学 交通科学与工程学院,哈尔滨 150090
Research progress on application of artificial intelligence in ultra⁃high performance concrete
Jie YUAN( ),Jun-bo WANG,Xin CHEN(
),Jun-bo WANG,Xin CHEN( ),Xin HUANG,Ao-xiang ZHANG,An-qi CUI
),Xin HUANG,Ao-xiang ZHANG,An-qi CUI
- School of Transportation Science and Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150090,China
摘要:
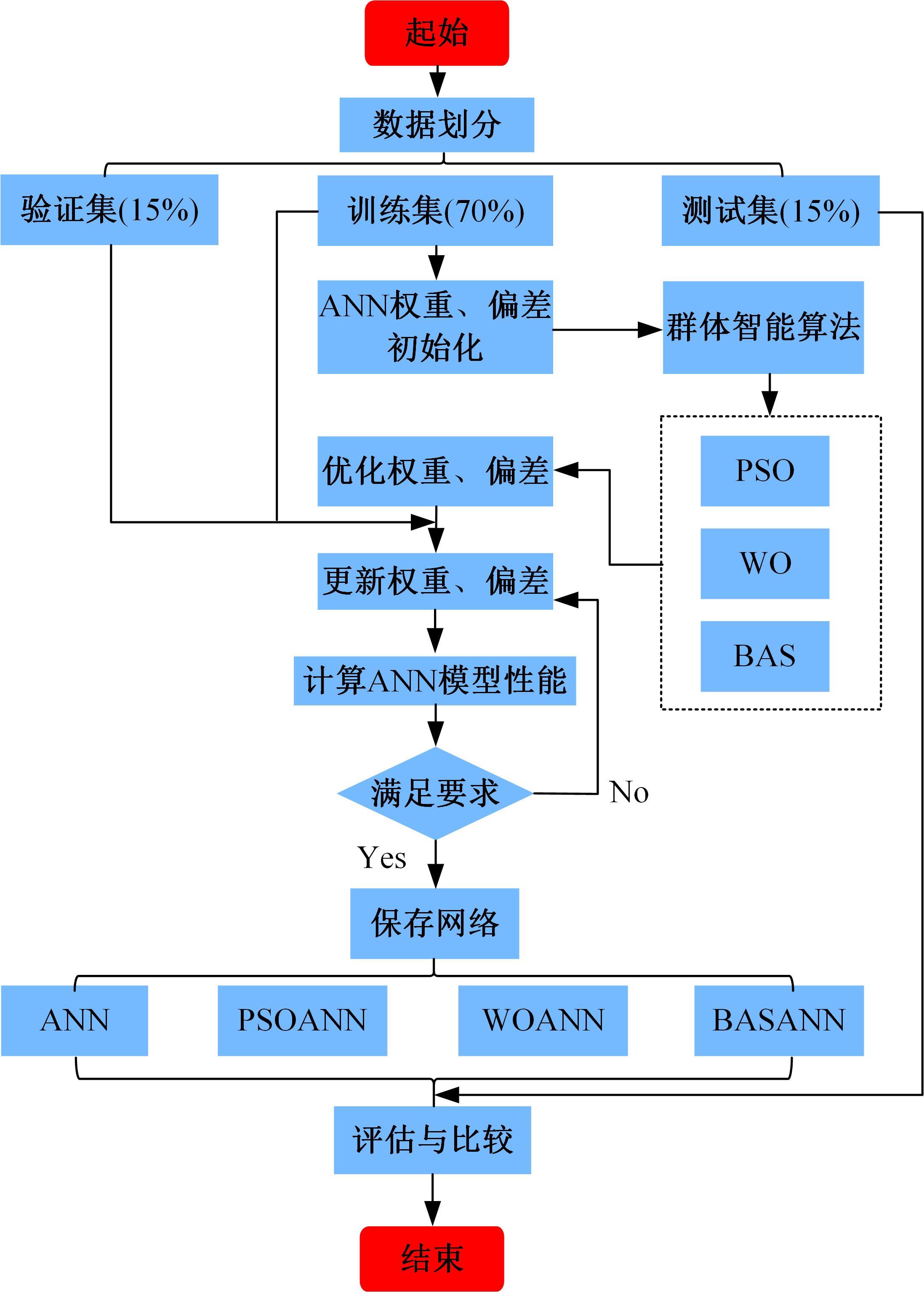
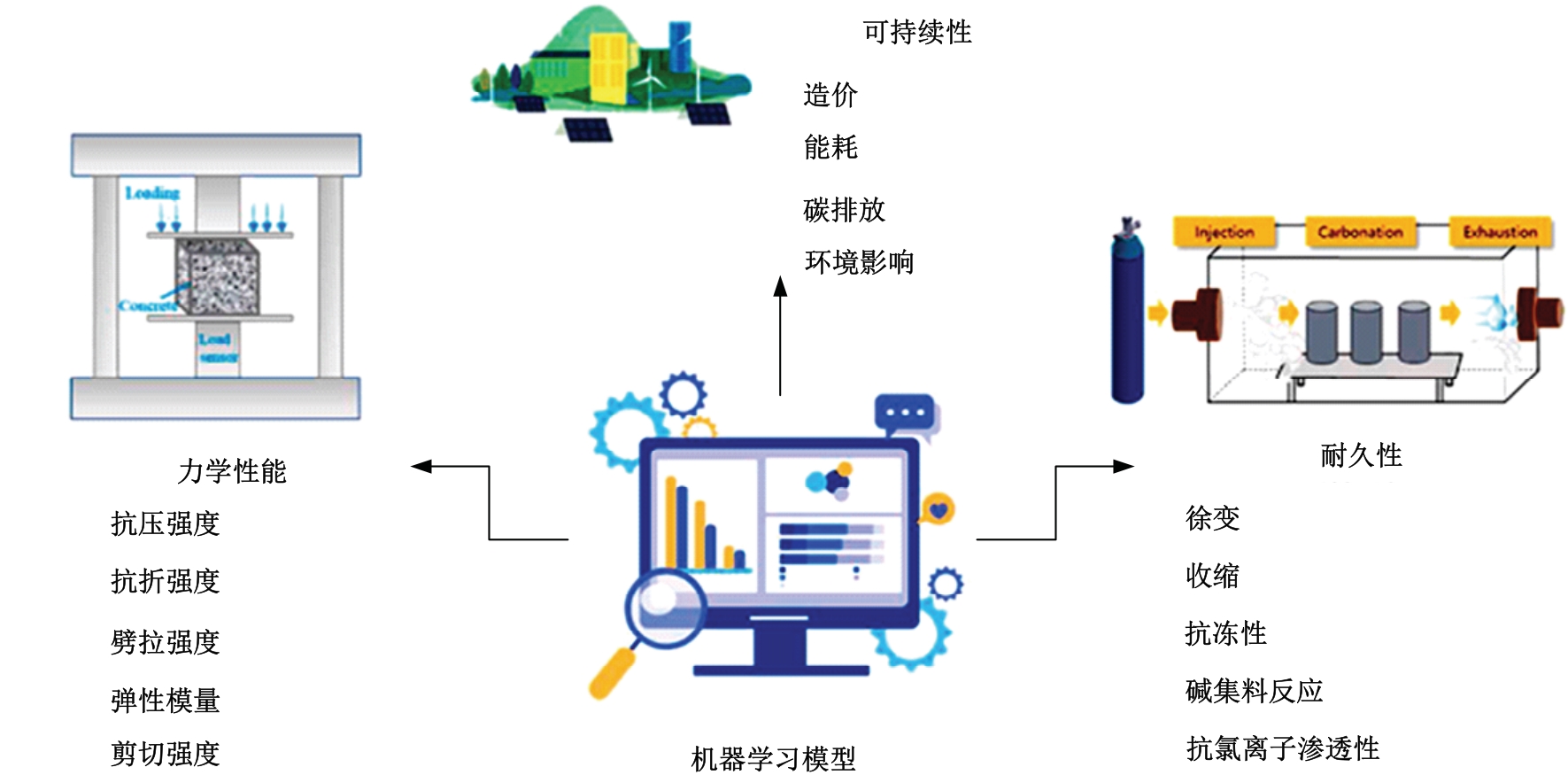
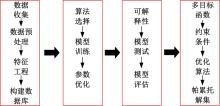
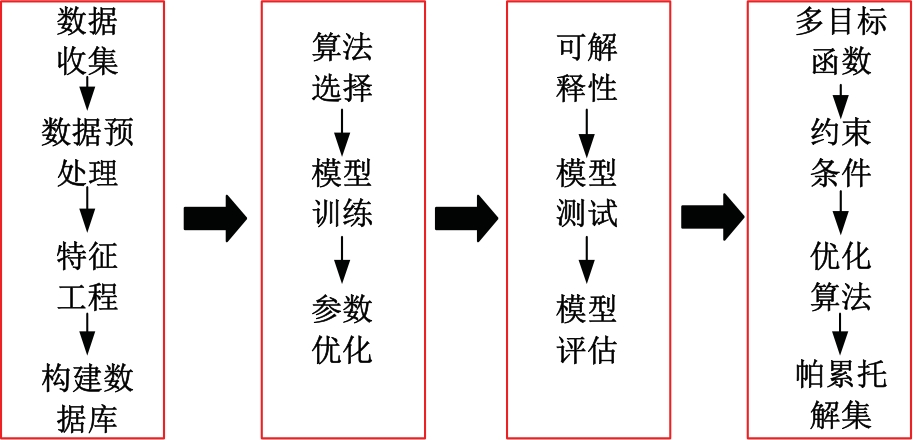
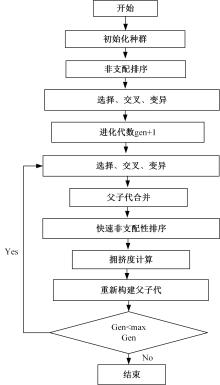
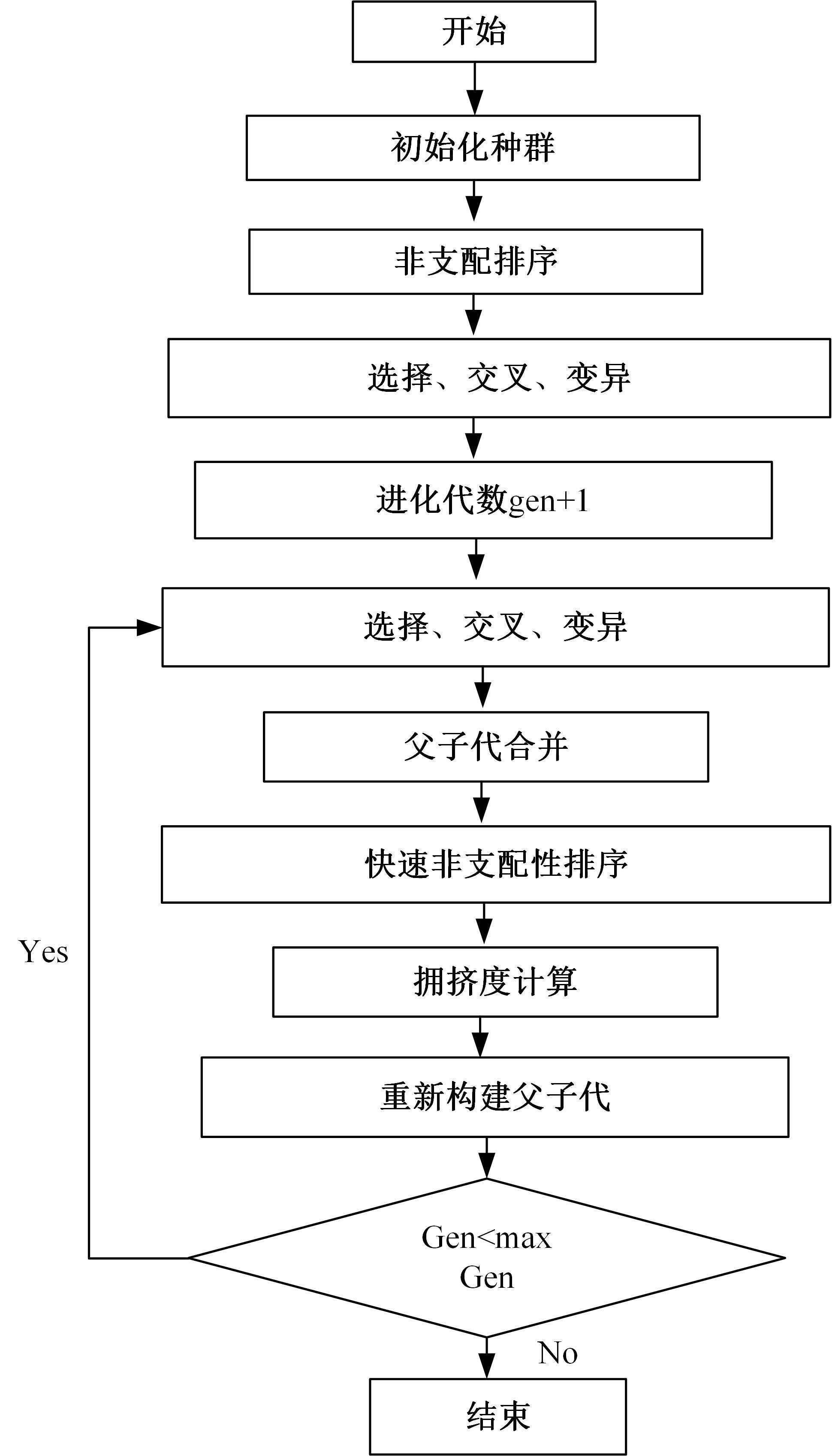
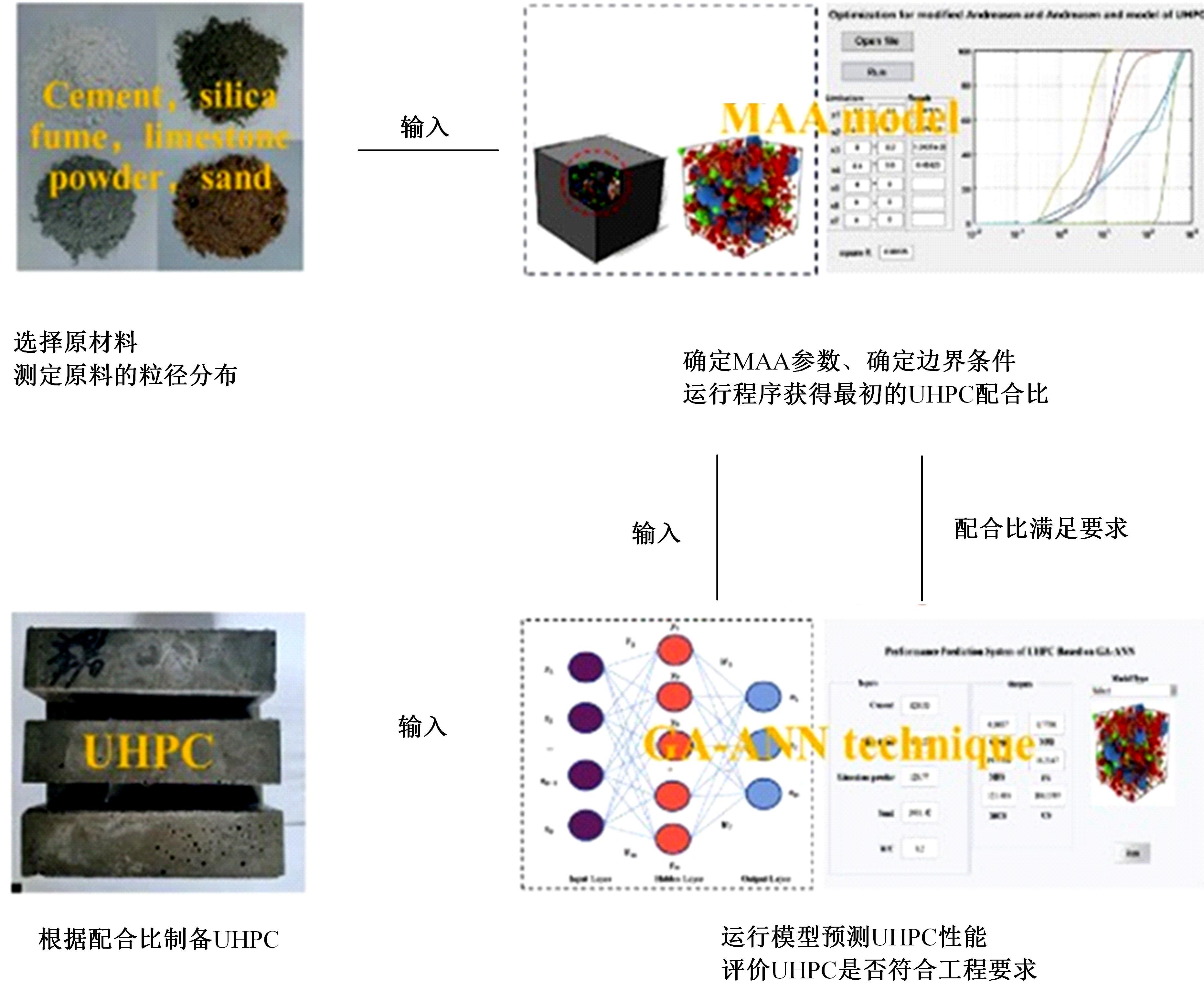
传统的超高性能混凝土配合比设计存在成本高、效率低、整体过程复杂等问题。人工智能技术的应用可以相对快速度且准确地预测超高性能混凝土的各项性能,实现超高性能混凝土配合比设计的智能化和绿色化。通过梳理人工智能技术在超高性能混凝土性能预测和配合比设计方面的研究进展,剖析了该领域目前主流技术尚存在的一系列问题,包括数据质量、模型验证、模型可解释性、多目标优化等问题。结合人工智能技术和学科理论,提出了针对相关问题的解决方案。
中图分类号:
- TU528
| 1 | Shi C, Wu Z, Xiao J, et al. A review on ultra high performance concrete: part I. raw materials and mixture design[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 101: 741-751. |
| 2 | 张超慧. 超高性能混凝土精细化模拟及其力学行为分析[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学土木工程学院, 2021. |
| Zhang Chao-hui. Elaborate simulations and analysis of mechanical behavior of ultra-high-performance concrete[D]. Changsha: College of Civil Engineering, Hunan University, 2021. | |
| 3 | Wang H, Zhang Z, Zhou Z, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on shear behavior of prefabricated bridge deck slabs with compact UHPC wet joint[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2023, 19: No.e02362. |
| 4 | Ashraf M H, Mohamed A, Hassan Y, et al. Effect of nano ferrosilicon and heavyweight fine aggregates on the properties and radiation shielding of ultra-high performance heavyweight concrete[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 17: No.e01543. |
| 5 | Furnas C. Grading aggregates I-mathematical relations for beds of broken solids of maximum density[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 1931, 23(9): 1052-1058. |
| 6 | Roy D M, Scheetz B E, Silsbee M R. Processing of optimized cements and concretes via particle packing[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1993, 18(3): 45-49. |
| 7 | Goltermann P, Johansen V, Palblo L. Packing of aggregates: an alternative tool to determine the optimal aggregate mix[J]. ACI Materials Journal, 1997, 94(5): 435-443. |
| 8 | Wong H H C, Kwan A K H. Packing density of cementitious materials: part 1—measurement using a wet packing method[J]. Materials and Structures, 2008, 41(4): 689-701. |
| 9 | Kwan A K H, Wong H H C. Packing density of cementitious materials: part 2—packing and flow of OPC+PFA+CSF[J]. Materials and Structures, 2008, 41(4): 773-784. |
| 10 | Wang R, Gao X, Huang H, et al. Influence of rheological properties of cement mortar on steel fiber distribution in UHPC[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 144: 65-73. |
| 11 | Mehdipour I, Khayat K H. Effect of particle-size distribution and specific surface area of different binder systems on packing density and flow characteristics of cement paste[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2017, 78: 120-131. |
| 12 | Wu Q, An X. Development of a mix design method for SCC based on the rheological characteristics of paste[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 53: 642-651. |
| 13 | Meng W, Valipour M, Khayat K H. Optimization and performance of cost effective ultra-high performance concrete[J]. Materials and Structures, 2017, 50: No.29. |
| 14 | Teng L, Meng W, Khayat K H. Rheology control of ultra-high-performance concrete made with different fiber contents[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2020, 138: No.106222. |
| 15 | Zhou M, Wu Z, Ouyang X, et al. Mixture design methods for ultra-high-performance concrete—a review[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2021, 124: No.104242. |
| 16 | Ghafari E, Costa H, Julio E. RSM-based model to predict the performance of self-compacting UHPC reinforced with hybrid steel micro-fibers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2014, 66: 375-383. |
| 17 | Ghafari E, Costa H, Julio E. Statistical mixture design approach for eco-efficient UHPC[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2015, 55: 17-25. |
| 18 | Li Z, Lu D, Gao X. Optimization of mixture proportions by statistical experimental design using response surface method-a review[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2021, 36: No.102101. |
| 19 | Mosaberpanah M A, Eren O. Statistical models for mechanical properties of UHPC using response surface methodology[J]. Computers and Concrete, 2017, 19(6): 667-675. |
| 20 | Ferdosian I, Camoes A. Eco-efficient ultra-high performance concrete development by means of response surface methodology[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2017, 84: 146-156. |
| 21 | Roya S, Salehi H, Kodur V, et al. Machine learning framework for predicting failure mode and shear capacity of ultra high performance concrete beams[J]. Engineering Structures, 2020, 224: No.111221. |
| 22 | Abuodeh O R, Abdalla J, Hawileh R A. Assessment of compressive strength of ultra-high performance concrete using deep machine learning techniques[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 95: No.106552. |
| 23 | 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016. |
| 24 | 李航. 机器学习方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2022. |
| 25 | Wang S, Xia P, Chen K, et al. Prediction and optimization model of sustainable concrete properties using machine learning, deep learning and swarm intelligence: a review[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2023, 80: No.108065. |
| 26 | 叶永锋. 基于机器学习的注塑制品克重预测及模型可解释性研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学机械与汽车工程学院, 2022. |
| Ye Yong-feng. Research on gram weight prediction of injection molding products based on machine learning and model interpretability[D]. Guangzhou: School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering, South China University of Technology, 2022. | |
| 27 | 于玲, 吴铁军. 集成学习: Boosting算法综述[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2004, 17(1): 52-59. |
| Yu Ling, Wu Tie-jun. Ensemble learning: a review of boosting algorithms[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2004, 17(1): 52-59. | |
| 28 | Tran V Q, Dang V Q, Ho L S. Evaluating compressive strength of concrete made with recycled concrete aggregates using machine learning approach[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 323: No.126578. |
| 29 | Finotti R P, Barbosa F D S, Cury A A, et al. Numerical and experimental evaluation of structural changes using sparse auto-encoders and SVM applied to dynamic responses[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(24): No.11965. |
| 30 | Cho H U, Nam Y J, Choi E J, et al. Comparative analysis of the optimized ANN, SVM, and tree ensemble models using Bayesian optimization for predicting GSHP COP[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2021, 44: No. 103411. |
| 31 | Tran V L, Kim J K. Innovative formulas for reinforcing bar bonding failure stress of tension lap splice using ANN and TLBO[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 369: No.130500. |
| 32 | Zeng Z, Zhu Z, Yao W, et al. Accurate prediction of concrete compressive strength based on explainable features using deep learning[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 339: No. 127082. |
| 33 | Yang G, Wang K C P, Li J Q, et al. Automatic pavement type recognition for image-based pavement condition survey using convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2021, 35(1): No.0402006. |
| 34 | Han T, Bhat R, Ponduru S A, et al. Deep learning to predict the hydration and performance of fly ash-containing cementitious binders[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2023, 165: No.107093. |
| 35 | Song H, Ahmad A, Farooq F, et al. Predicting the compressive strength of concrete with fly ash admixture using machine learning algorithms[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 308: No. 125021. |
| 36 | Ali B, Emadaldin M G. Predicting the compressive strength of silica fume concrete using hybrid artificial neural network with multi-objective grey wolves[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 202: 54-64. |
| 37 | 毛亚娜, 刘世忠, 杏剑, 等.超高性能玻璃砂混凝土-高强钢筋粘结滑移特性及其声发射参数表征[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(6): 1686-1694. |
| Mao Ya-na, Liu Shi-zhong, Xing Jian, et al. Bond⁃slip characterization between ultra-high performance glass sand concrete and high⁃strength reinforcement based on acoustic emission parameters[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1686-1694. | |
| 38 | Sadrossadat E, Basarir H, Karrech A, et al. Multi-objective mixture design and optimisation of steel fiber reinforced UHPC using machine learning algorithms and metaheuristics[J]. Engineering with Computers, 2022, 38(3): 2569-2582. |
| 39 | Ehsan G, Mojtaba B, Hugo C, et al. Prediction of fresh and hardened state properties of UHPC: comparative study of statistical mixture design and an artificial neural network model[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2015, 27(11): No. 4015017. |
| 40 | Qian Y F, Sufian M, Accouche O, et al. Advanced machine learning algorithms to evaluate the effects of the raw ingredients on flowability and compressive strength of ultra-high-performance concrete[J]. Public Library of Science, 2023, 17(12): No.e0278161 |
| 41 | Mahjoubi S, Meng W N, Yi B. Auto-tune learning framework for prediction of flowability, mechanical properties, and porosity of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC)[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 115: No.108182. |
| 42 | Mahjoubi S, Barhemat R, Meng W, et al. AI-guided auto-discovery of low-carbon cost-effective ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC)[J]. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 2023, 189: No.106741. |
| 43 | 赵筠, 路新瀛. 构建科学智能混凝土配制新技术体系的设想和建议(四)[J]. 混凝土世界, 2020(1): 56-70. |
| Zhao Yun, Lu Xin-ying. Ideas and suggestions for building a new technology system for scientific and intelligent concrete preparation(4)[J]. China Concrete, 2020(1): 56-70. | |
| 44 | Zhang J, Ma G, Huang Y, et al. Modelling uniaxial compressive strength of lightweight self-compacting concrete using random forest regression[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 210: 713-719. |
| 45 | 龙武剑, 罗盛禹, 程博远, 等. 机器学习算法用于自密实混凝土性能设计的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2024(11): 104-113 |
| Long Wu-jian, Luo Sheng-yu, Cheng Bo-yuan, et al. Research progress of machine learning algorithm for self-compacting concrete performance design[J]. Materials Reports, 2024(11): 104-113 . | |
| 46 | Ghafari E, Bandarabadi M, Costa H, et al. Design of UHPC using artificial neural networks[J]. Brittle Matrix Composites, 2012: 61-69. |
| 47 | Zhang J, Zhao Y, Li H. Experimental investigation and prediction of compressive strength of ultra-high-performance concrete containing supplementary cementitious[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 2017: No.4563164. |
| 48 | Qu D, Cai X, Wei C. Evaluating the effects of steel fibers on mechanical properties of ultra-high performance concrete using artificial neural networks[J]. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(7): No.11202. |
| 49 | Joaquin A G. Four-layer perceptron approach for strength prediction of UHPC[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 256: No.119465. |
| 50 | Fan D, Yu R, Fu S, et al. Precise design and characteristics prediction of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) based on artificial intelligence techniques[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2021, 122:No. 104171. |
| 51 | Joaquin A G. Study of nonlinear relationships between dosage mixture design and the compressive strength of UHPC[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 17: No.e01228. |
| 52 | Joaquin A G, Jaime F G, Nancy T C. Properties prediction of environmentally friendly ultra-high-performance concrete using artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering, 2022, 26(6): 2319-2343. |
| 53 | Nguyen N, Abellan-García J, Lee S, et al. Efficient estimating compressive strength of ultra-high performance concrete using XG Boost model[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2022, 52: No.104302. |
| 54 | Shen Z, Deifalla A F, Kaminski P, et al. Compressive strength evaluation of ultra-high-strength concrete by machine learning[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(10): 3523. |
| 55 | Saleh E, Tarawneh A, Naser M Z, et al. You only design once (YODO): Gaussian process-batch Bayesian optimization framework for mixture design of ultra high performance concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 330: No.127270. |
| 56 | Alabduljabbar H, Khan M, Awan H H, et al. Predicting ultra-high-performance concrete compressive strength using gene expression programming method[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2023, 18: No.e02074. |
| 57 | Guo P, Mahjoubi S, Liu K J, et al. Self-updatable AI-assisted design of low-carbon cost-effective ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC)[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2023, 19: No.e2625. |
| 58 | Tavares C, Wang X, Saha S, et al. Machine learning-based mix design tools to minimize carbon footprint and cost of UHPC. part 1: efficient data collection and modeling[J]. Cleaner Materials, 2022, 4: No.100082. |
| 59 | Iqbal K M, Yassir M A. Intelligent data-driven compressive strength prediction and optimization of reactive powder concrete using multiple ensemble-based machine learning approach[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 404: No.133148. |
| 60 | Nguyen M H, Nguyen T A, Hai-Bang LY. Ensemble XGBoost schemes for improved compressive strength prediction of UHPC[J]. Structures, 2023, 57: No.105062. |
| 61 | Naseri H, Jahanbakhsh H, Hosseini P, et al. Designing sustainable concrete mixture by developing a new machine learning technique[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 258:No. 120578. |
| 62 | Erdal H I, Karakurt O, Namli E. High performance concrete compressive strength forecasting using ensemble models based on discrete wavelet transforms engineering[J]. Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 26: 1246-1254. |
| 63 | Cai R, Han T, Liao W, et al. Prediction of surface chloride concentration of marine concrete using ensemble machine learning[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2020, 136: No.106164. |
| 64 | Kang M C, Yoo D Y, Gupta R. Machine learning-based prediction for compressive and flexural strengths of steel fiber-reinforced concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 266: No.121117. |
| 65 | Li Q, Song Z. High-performance concrete strength prediction based on ensemble learning[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 324: No.126694. |
| 66 | Wang Q C, Hussain A, Farooqi M U, et al. Artificial intelligence-based estimation of ultra-high-strength concrete's flexural property[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 17: No.e01243. |
| 67 | Das P, Kashem A. Hybrid machine learning approach to prediction of the compressive and flexural strengths of UHPC and parametric analysis with shapley additive explanations[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2024, 20: No.e2723. |
| 68 | Dong W, Huang Y, Cui A, et al. Mix design optimization for fly ash-based geopolymer with mechanical, environmental, and economic objectives using soft computing technology[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2023, 72: No.106577. |
| 69 | 陈权, 李莉, 陈永乐, 等. 面向深度学习可解释性的对抗攻击算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(2): 510-518. |
| Chen Quan, Li Li, Chen Yong-le, et al. Adversarial attack algorithm for deep learning interpretability[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(2): 510-518. | |
| 70 | 李扬. 基于随机森林模型解释的越野路面识别算法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学交通学院, 2022. |
| Li Yang. Research on off-road pavement recognition algorithm based on random forest model interpretation[D]. Changchun: College of Transportation, Jilin University, 2022. | |
| 71 | Wu Y, Zhou Y. Hybrid machine learning model and Shapley additive explanations for compressive strength of sustainable concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 330: No.127298. |
| 72 | Kina C, Turk K, Tanyildizi H. Deep learning and machine learning-based prediction of capillary water absorption of hybrid fiber reinforced self-compacting concrete[J]. Structural Concrete, 2022, 23(5): 3331-3358. |
| 73 | Liu K, Zheng J, Zhao X, et al. Innovative modeling framework of chloride resistance of recycled aggregate concrete using ensemble-machine-learning methods[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 337: No.127613. |
| 74 | Biswas R, Li E, Zhang N, et al. Development of hybrid models using metaheuristic optimization techniques to predict the carbonation depth of fly ash concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 346: No.128483. |
| 75 | Liu K, Alams M S, Zhu J, et al. Prediction of carbonation depth for recycled aggregate concrete using ANN hybridized with swarm intelligence algorithms[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 301:No. 124382. |
| 76 | 吴贤国, 陈彬, 杨赛, 等. 基于RF-NSGA-Ⅱ算法的高耐久性混凝土配合比优化研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2021, 5(17): 156-161. |
| Wu Xian-guo, Chen Bin, Yang Sai, et al. Study on optimization of high durability concrete mix ratio based on RF-NSGA-Ⅱ algorithm[J]. Industrial Construction, 2021, 5(17): 156-161. | |
| 77 | Selim C, Enes G, Onur O, et al. A novel prediction model for durability properties of concrete modified with steel fiber and silica fume by using Hybridized GRELM[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 341: No.127856. |
| 78 | Sahoo S, Mahapatra T R. ANN modeling to study strength loss of fly ash concrete against long term sulphate attack[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5(11): 24595-24604. |
| 79 | Liu K, Dai Z, Zhang R, et al. Prediction of the sulfate resistance for recycled aggregate concrete based on ensemble learning algorithms[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 317: No.125917. |
| 80 | Wang S, Peng X, Chen K, et al. Prediction and optimization model of sustainable concrete properties using machine learning, deep learning and swarm intelligence: a review[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2023, 80: No.108065. |
| 81 | 曹鑫. 超高性能混凝土的制备及其性能研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽建筑大学土木工程学院, 2022. |
| Cao Xin. Study on preparation and properties of ultra-high-performance concrete[D]. Hefei: College of Civil Engineering, Anhui Jian Zhu University, 2022. | |
| 82 | 刘艳彪, 乔建质, 尤世界. 机器学习在碳基环境功能材料领域的应用研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2022, 40(6): 182-187. |
| Liu Yan-biao, Qiao Jian-zhi, You Shi-jie. Research progress on application of machine learning in the field of carbon-based environmental functional materials[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2022, 40(6): 182-187. | |
| 83 | Tipu R K, Panchal V R, Pandya K S. Multi-objective optimized high-strength concrete mix design using a hybrid machine learning and metaheuristic algorithm[J]. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2023, 24: 849-867. |
| 84 | Fann D, Zhu J, Fan M, et al. Intelligent design and manufacturing of ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC)-a review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 385:No. 131495. |
| 85 | Sun G, Du M, Shan B, et al. Ultra-high performance concrete design method based on machine learning model and steel slag powder[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials, 2022, 17: No.e1682. |
| 86 | Dua D, Graff C. UCI Machine learning repository[EB/OL]. [2024-01-12]. |
| 87 | Jain N, Shyue P O, Hautier G, et al. Commentary: the materials project: a materials genome approach to accelerating materials innovation[J]. APL Materials, 2013, 1(1): No.11002. |
| 88 | Young B A, Hall A, Pilon L, et al. Can the compressive strength of concrete be estimated from knowledge of the mixture proportions?: New insights from statistical analysis and machine learning methods[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2019, 115: 379-388. |
| 89 | DeRousseau M A, Laftchiev J R E., Kasprzyk, et al. A comparison of machine learning methods for predicting the compressive strength of field-placed concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 228: No.116661. |
| [1] | 曲俊龙,史文库,玄圣夷,陈志勇. 面向汽车传动系统多挡共振的多级吸振器参数设计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 444-455. |
| [2] | 曹毅,夏宇,高清源,叶培涛,叶凡. 基于超连接图卷积网络的骨架行为识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 731-740. |
| [3] | 朱劲松,佟欣瑶,刘晓旭. 装配式小箱梁桥超高性能混凝土免支模湿接缝抗弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2568-2580. |
| [4] | 孙永新,蔺鹏臻,杨子江,冀伟. 考虑黏结-滑移效应的UHPC梁裂缝宽度计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2600-2608. |
| [5] | 井佩光,田雨豆,汪少初,李云,苏育挺. 基于动态扩散图卷积的交通流量预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1582-1592. |
| [6] | 陈涛,周志刚,雷楠南. 粒子群算法下汽车机械式自动变速系统参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1214-1220. |
| [7] | 曲福恒,潘曰涛,杨勇,胡雅婷,宋剑飞,魏成宇. 基于加权空间划分的高效全局K-means聚类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1393-1400. |
| [8] | 孙帅帅,冯春晓,张良. 基于离散采样的多模态四足机器人路径规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1120-1128. |
| [9] | 金志刚,苏仁鋆,赵晓芳. 基于异质图网络的心理评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1078-1085. |
| [10] | 杨欣,王阳,宋家锋,朱勇,黄彬兵,许述财. 基于虾螯结构的仿生夹层板设计及数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 842-851. |
| [11] | 高敬鹏,王国轩,高路. 基于异步合作更新的LSTM-MADDPG多智能体协同决策算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 797-806. |
| [12] | 冯琼,田浩正,乔宏霞,念腾飞,韩文文. 自然暴露与盐雾加速环境下钢筋混凝土劣化规律及等效关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 494-505. |
| [13] | 刘浏,丁鲲,刘姗姗,刘茗. 基于机器阅读理解的事件检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
| [14] | 于鹏,朴燕. 适用于无监督行人重识别的反向骨干网[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(11): 3309-3317. |
| [15] | 于跟社,邓宗才. 钢纤维与细非金属纤维混杂UHPC双向板弯曲特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(11): 3265-3273. |
|
||