吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (11): 3309-3317.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20240916
适用于无监督行人重识别的反向骨干网
- 长春理工大学 电子信息工程学院,长春 130022
Reverse backbone net for unsupervised person re-identification
- School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
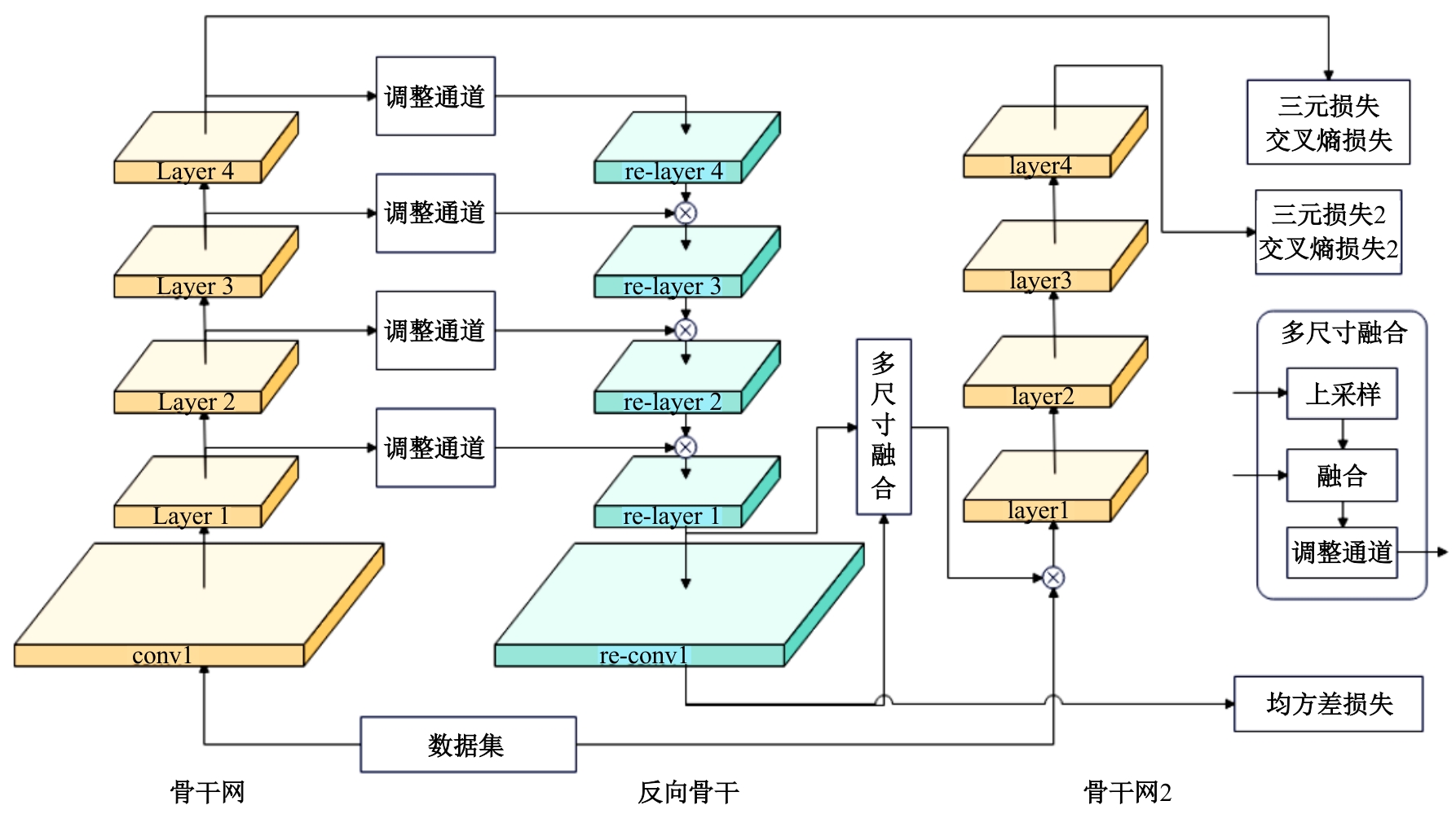
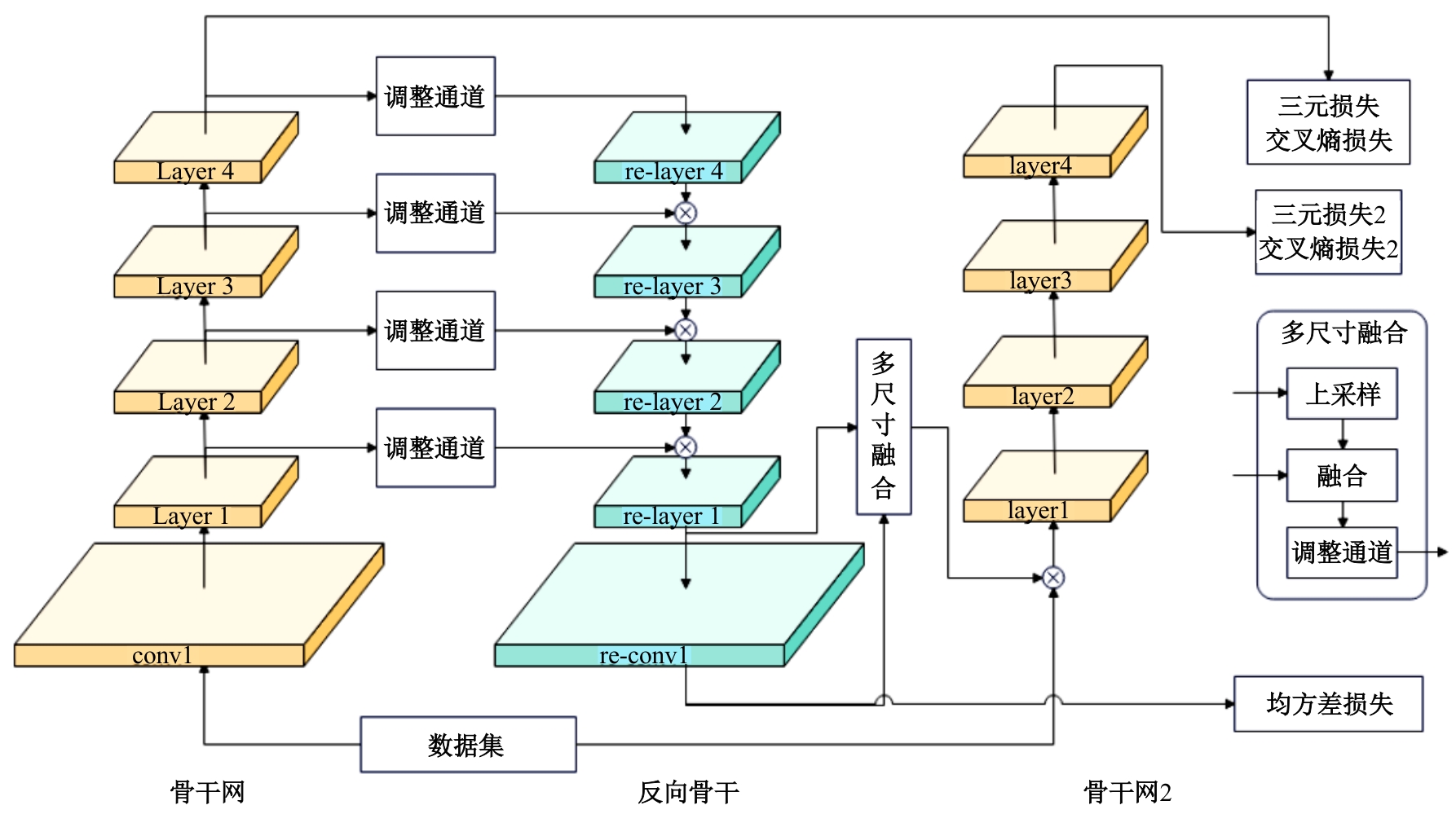
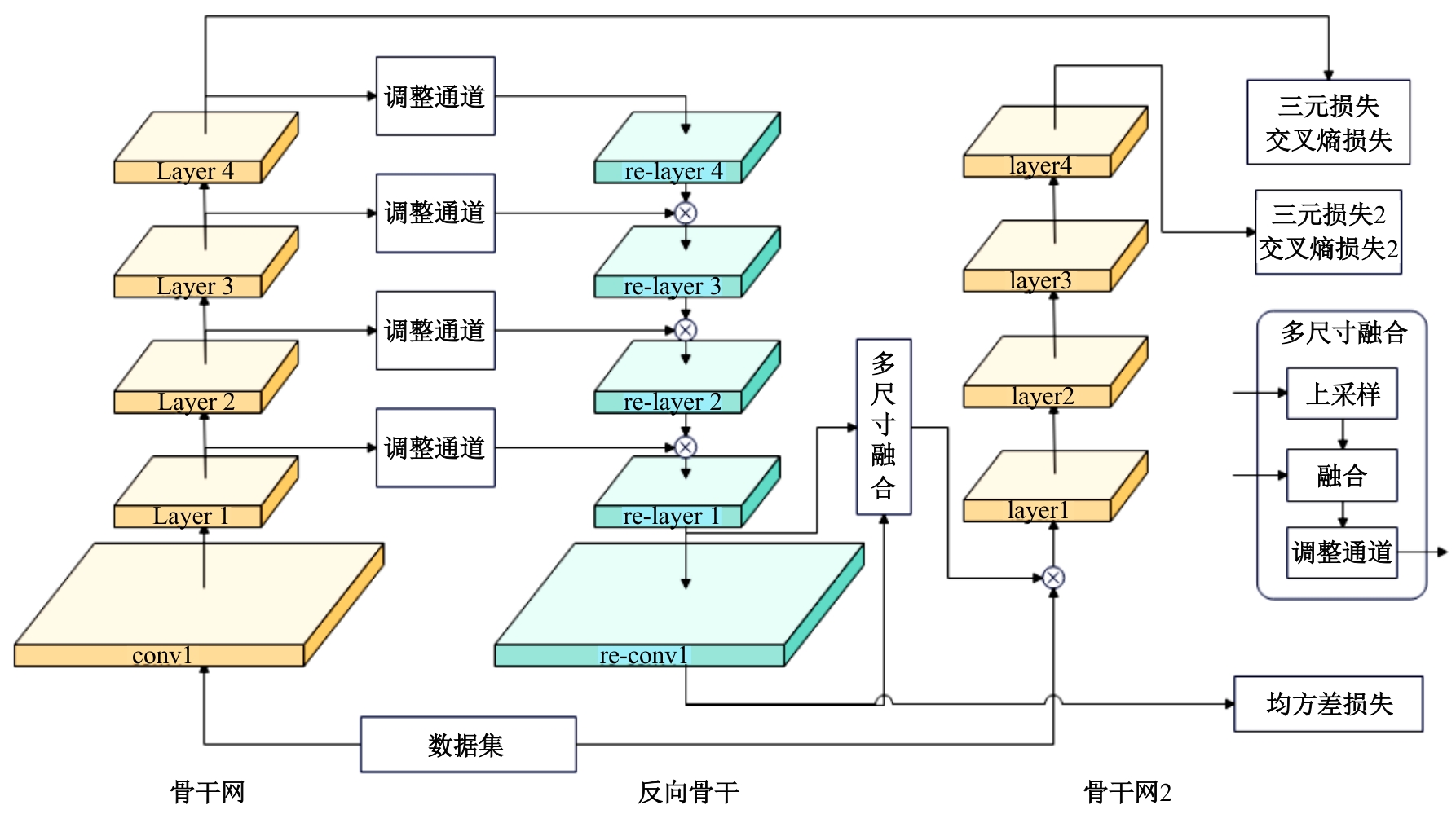
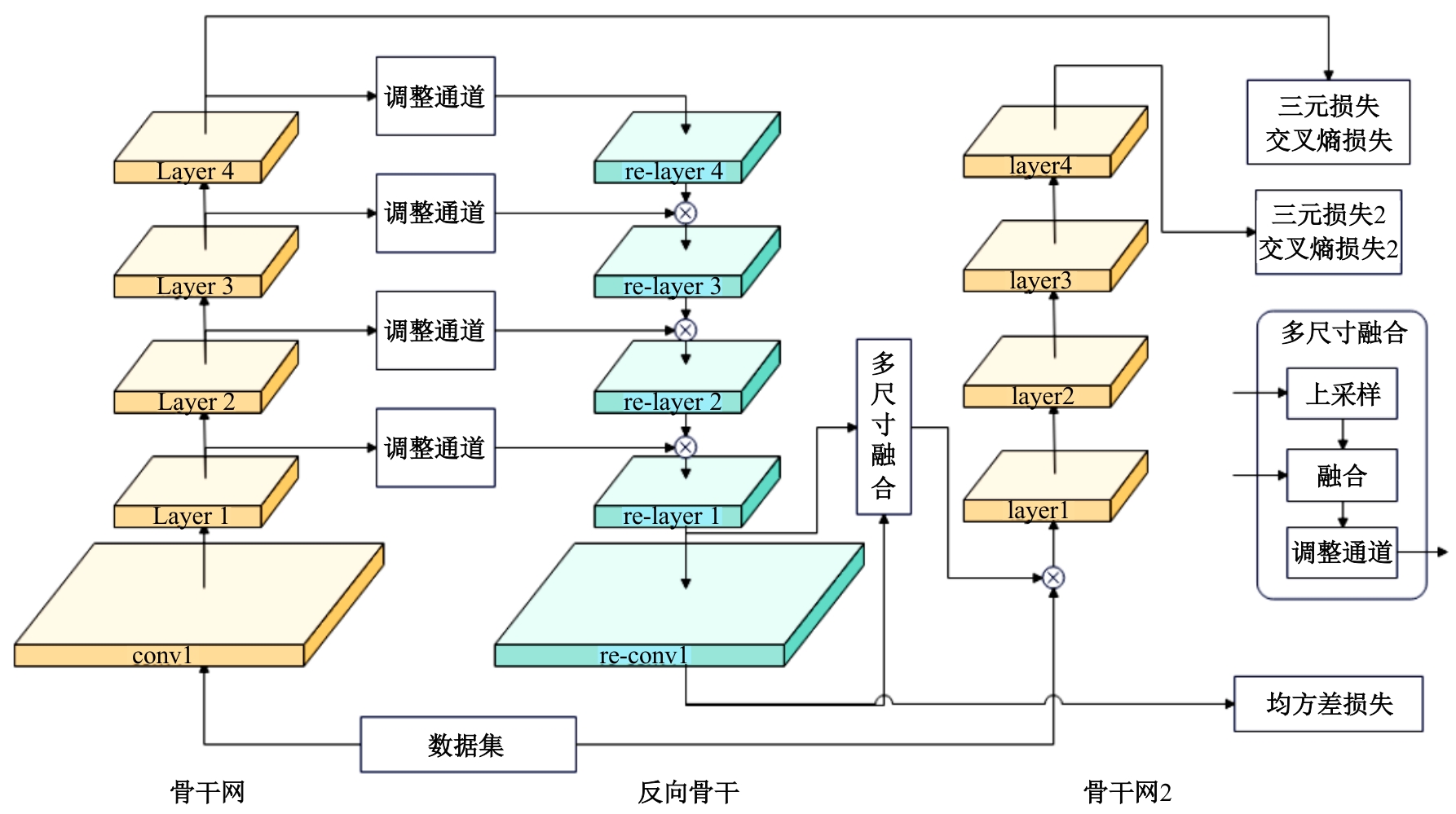
行人重识别(re-id)的目的是在不同的摄像机上识别同一个人的图像。虽然无监督模型比有监督模型有更好的泛用性,但无监督的聚类会更容易受到噪声干扰。针对这一问题,本文提出了一个可以减少噪声干扰的模型反向骨干网(RBNet),利用反向骨干网学习姿态检测模型输出的人体关键点,调整局部空间信息并生成掩码,用生成掩码增强指定位置注意力。实验结果表明:对比baseline在Market-1501到DukeMTMC-reID的跨域实验结果,mAP提升了7.0%,Rank-1提升了6.4%。强化对不同局部信息的注意力,可有效提升模型准确率。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| 1 | Chiat P T, Sharmili R, Kim H Y. AANet: attribute attention network for person re-identifications[C]∥32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7127-7136. |
| 2 | Lin Y T, Zheng L, Zheng Z D, et al. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 95: 151-161. |
| 3 | Sun Y F, Zheng L, Yang Y, et al. Beyond part models: person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline)[C]∥15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 501-518. |
| 4 | Miao J X, Wu Y, Yang Y. Identifying visible parts via pose estimation for occluded person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(9): 4624-4634. |
| 5 | Cai H L, Wang Z G, Cheng J X. Multi-scale body-part mask guided attention for person re-identification[C]∥32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1555-1564. |
| 6 | Qiao S Y, Chen L C, Alan Y. Detectors: detecting objects with recursive feature pyramid and switchable atrous convolution[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10208-10219. |
| 7 | Hou S Q, Yin K N, Liang J, et al. Gradient-supervised person re-identification based on dense feature pyramid network[J]. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2022, 8(6I): 5329-5342. |
| 8 | Zhang Z Z, Lan G L, Zeng W J, et al. Relation-aware global attention for person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 3183-3192. |
| 9 | Zhou K Y, Yang Y X, Cavallaro A, et al. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 3701-3711. |
| 10 | Divyansh G, Netra P, Thomas T, et al. Towards explainable person re-identification[C]∥IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence, Orlando, USA, 2021: 9660071. |
| 11 | Niki M, Gian L F, Christian M. Deep pyramidal pooling with attention for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 7306-7316. |
| 12 | Yang F X, Zhong Z, Luo Z M, et al. Joint noise-tolerant learning and meta camera shift adaptation for unsupervised person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 4853-4862. |
| 13 | Antti T, Harri V. Mean teachers are better role models: weight-averaged consistency targets improve semi-supervised deep learning results[C]∥31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 1195-1204. |
| 14 | Ge Y X, Chen D P, Li H S. Mutual mean-teaching: pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification[C]∥8th International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020: 200101526. |
| 15 | He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥ IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 16 | Sun K, Xiao B, Liu D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation[C]∥32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5686-5696. |
| 17 | Martin E, Hans P K, Jorg S, et al. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise[C]∥2nd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Portland, USA, 1996: 226-231. |
| 18 | Zheng L, Shen L Y, Tian L, et al. Scalable person re-identification: a benchmark[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, USA, 2015: 1116-1124. |
| 19 | Ergys R, Francesco S, Roger Z, et al. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking[C]∥14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 17-35. |
| 20 | Wei L H, Zhang S L, Gao W, et al. Person transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification[C]∥31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 79-88. |
| 21 | Park H J, Ham B. Relation network for person re-identification[C]∥34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 11839-11847. |
| 22 | He L X, Liao X Y, Liu W, et al. Fastreid: a pytorch toolbox for general instance re-identification[J]. Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2020, 10: 9662-9667. |
| 23 | Tan H C, Liu X P, Bian Y H, et al. Incomplete descriptor mining with elastic loss for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(1): 160-171. |
| 24 | Li Y L, He J F, Zhang T Z, et al. Diverse part discovery: occluded person re-identification with part-aware transformer[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2897-2906. |
| 25 | Li H J, Wu G J, Zheng W S. Combined depth space based architecture search for person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 6725-6734. |
| 26 | Zheng K C, Liu W, He L X, et al. Group-aware label transfer for domain adaptive person re-identification[C]∥IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 5306-5315. |
| 27 | Wang D K, Zhang S L. Unsupervised person re-identification via multi-label classification[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2022, 130(12): 2924-2939. |
| 28 | Zou Y, Yang X D, Yu Z D, et al. Joint disentangling and adaptation for cross-domain person re-identification[C]∥16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 87-104. |
| 29 | Jin X, Lan C L, Zeng W J, et al. Global distance-distributions separation for unsupervised person re-identification[C]∥16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 735-751. |
| 30 | Zhong Z, Zheng L, Luo Z M, et al. Learning to adapt invariance in memory for person re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(8): 2723-2738. |
| 31 | Chen G Y, Gu T P, Lu J W, et al. Person re-identification via attention pyramid[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 7663-7676. |
| [1] | 曹毅,夏宇,高清源,叶培涛,叶凡. 基于超连接图卷积网络的骨架行为识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 731-740. |
| [2] | 井佩光,田雨豆,汪少初,李云,苏育挺. 基于动态扩散图卷积的交通流量预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1582-1592. |
| [3] | 曲福恒,潘曰涛,杨勇,胡雅婷,宋剑飞,魏成宇. 基于加权空间划分的高效全局K-means聚类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1393-1400. |
| [4] | 孙帅帅,冯春晓,张良. 基于离散采样的多模态四足机器人路径规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1120-1128. |
| [5] | 金志刚,苏仁鋆,赵晓芳. 基于异质图网络的心理评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1078-1085. |
| [6] | 高敬鹏,王国轩,高路. 基于异步合作更新的LSTM-MADDPG多智能体协同决策算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 797-806. |
| [7] | 刘浏,丁鲲,刘姗姗,刘茗. 基于机器阅读理解的事件检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
| [8] | 李健,熊琦,胡雅婷,刘孔宇. 基于Transformer和隐马尔科夫模型的中文命名实体识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1427-1434. |
| [9] | 于鹏,朴燕. 基于多尺度特征的行人重识别属性提取新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1155-1162. |
| [10] | 刘春晖,王思长,郑策,陈秀连,郝春蕾. 基于深度学习的室内导航机器人避障规划算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3558-3564. |
| [11] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [12] | 王生生,姜林延,杨永波. 基于最优传输特征选择的医学图像分割迁移学习[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1626-1638. |
| [13] | 田皓宇,马昕,李贻斌. 基于骨架信息的异常步态识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 725-737. |
| [14] | 刘勇,徐雷,张楚晗. 面向文本游戏的深度强化学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [15] | 侯春萍,杨庆元,黄美艳,王致芃. 基于语义耦合和身份一致性的跨模态行人重识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2954-2963. |
|
||