吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1617-1628.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230788
干湿和冻融循环作用下固化淤泥的动力特性及微观结构演化
- 1.武汉理工大学 土木工程与建筑学院,武汉 430070
2.武汉大学 土木建筑工程学院,武汉 430072
Dynamic characteristics and microstructural evolution of solidified sludge under wet-dry and freeze-thaw cycling
Xie-qun WANG1( ),Xiang-wei YU1,Wei-lie ZOU2(
),Xiang-wei YU1,Wei-lie ZOU2( ),Zhong HAN2
),Zhong HAN2
- 1.School of Civil Engineering & Architecture,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
2.School of Civil Engineering,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430072,China
摘要:
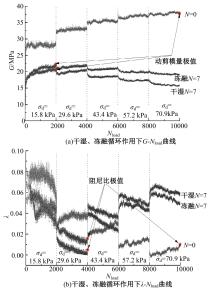
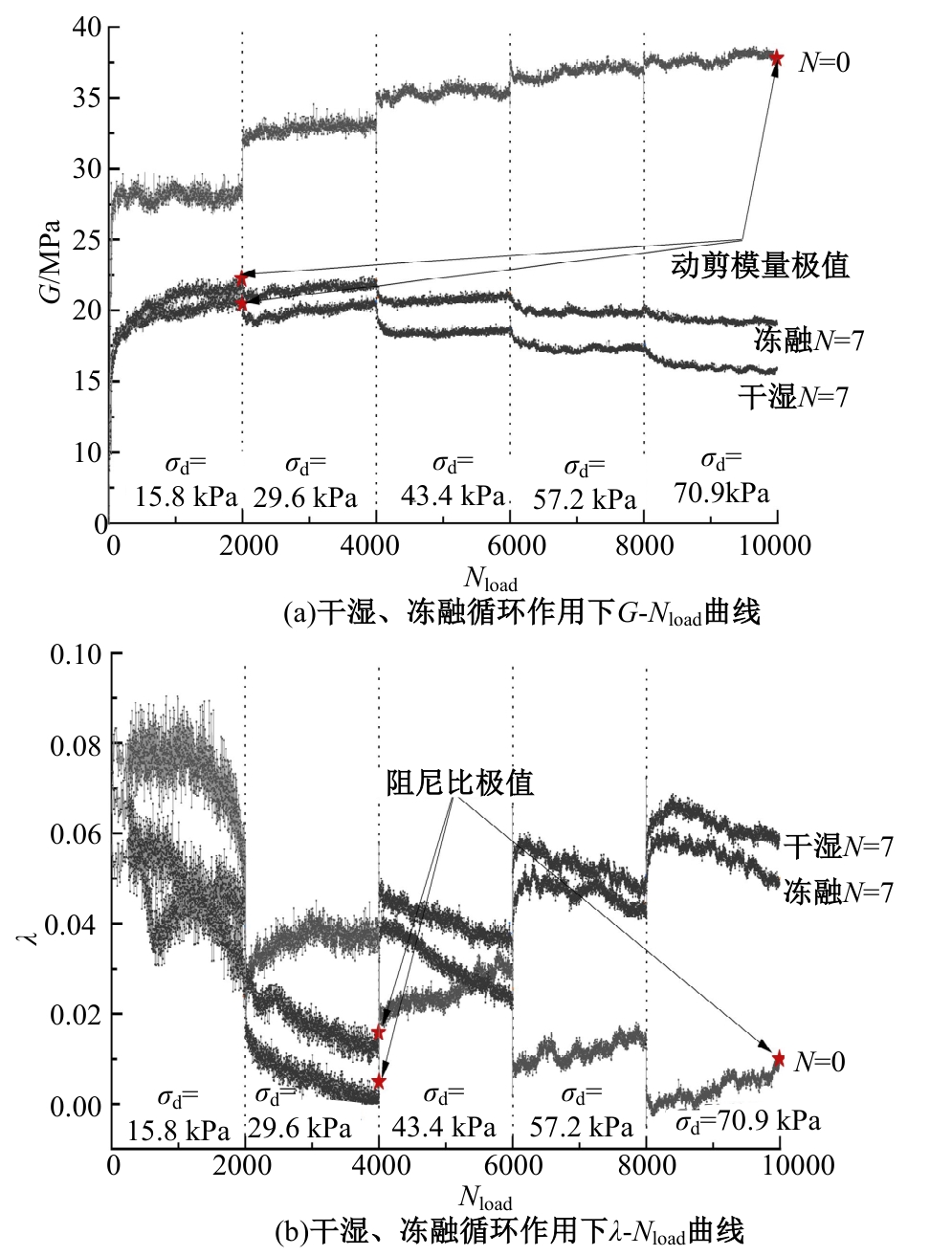
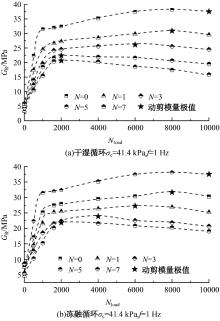
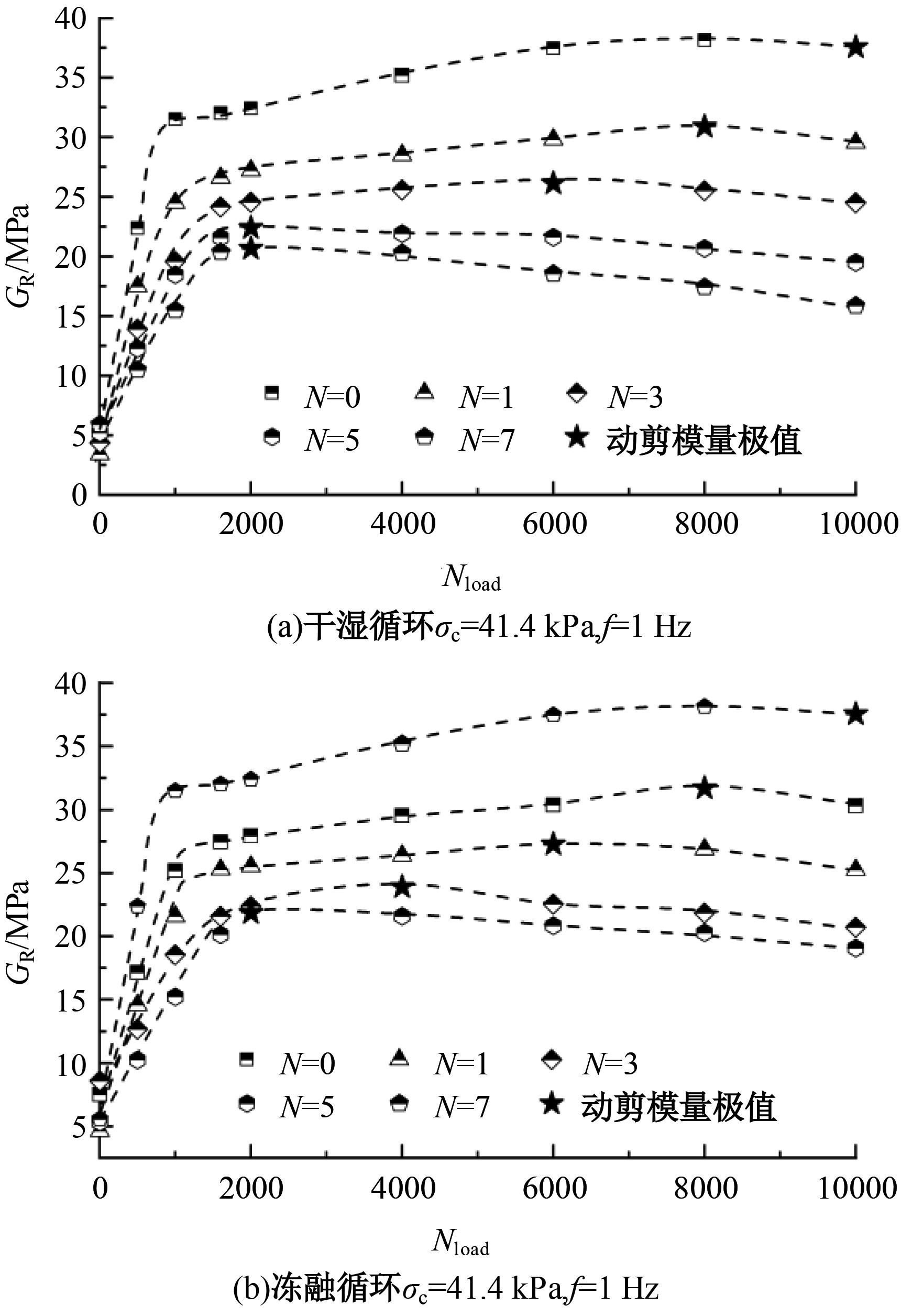
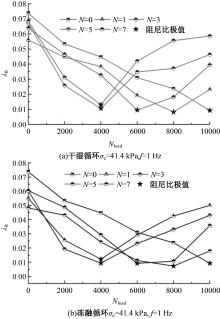
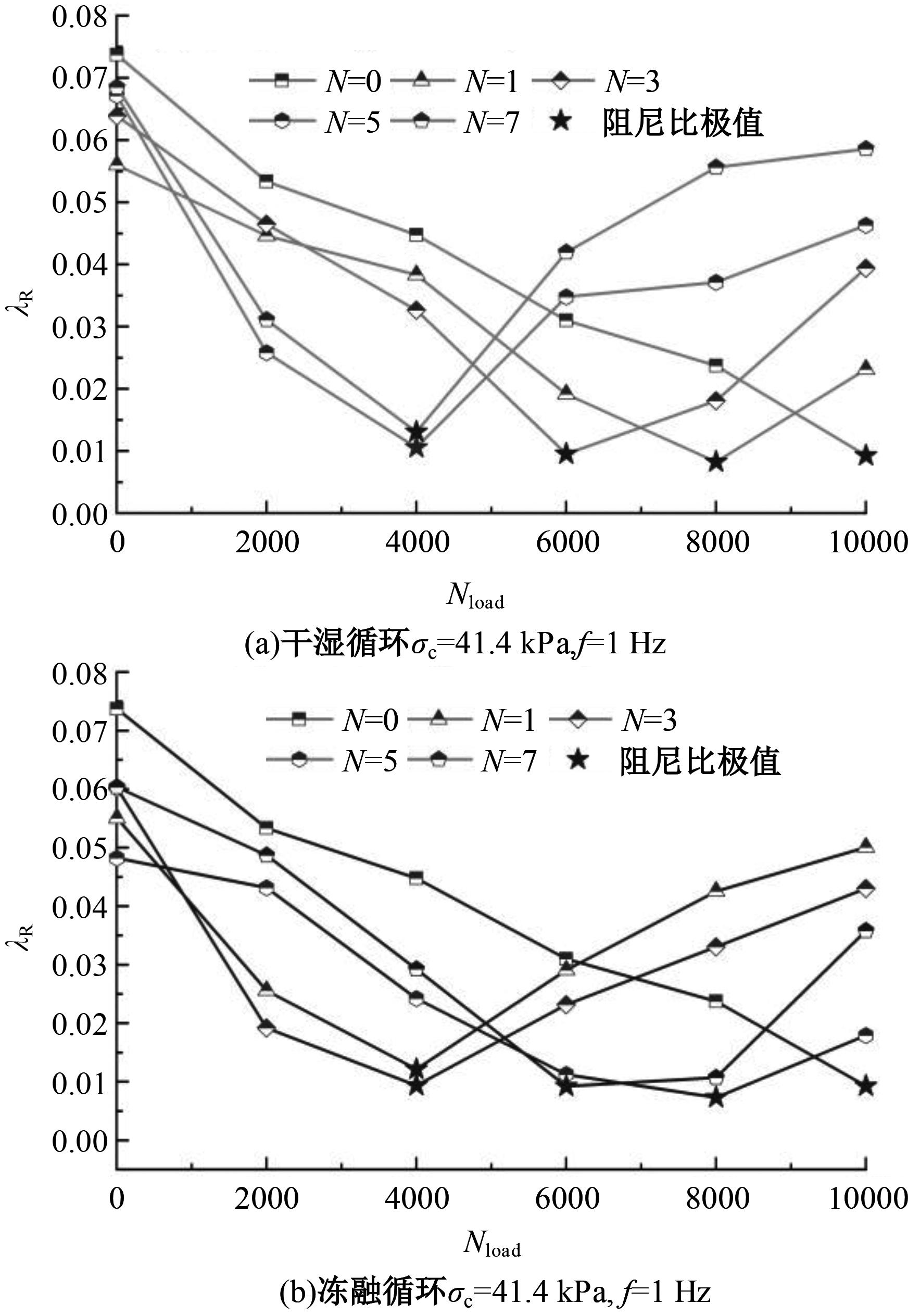
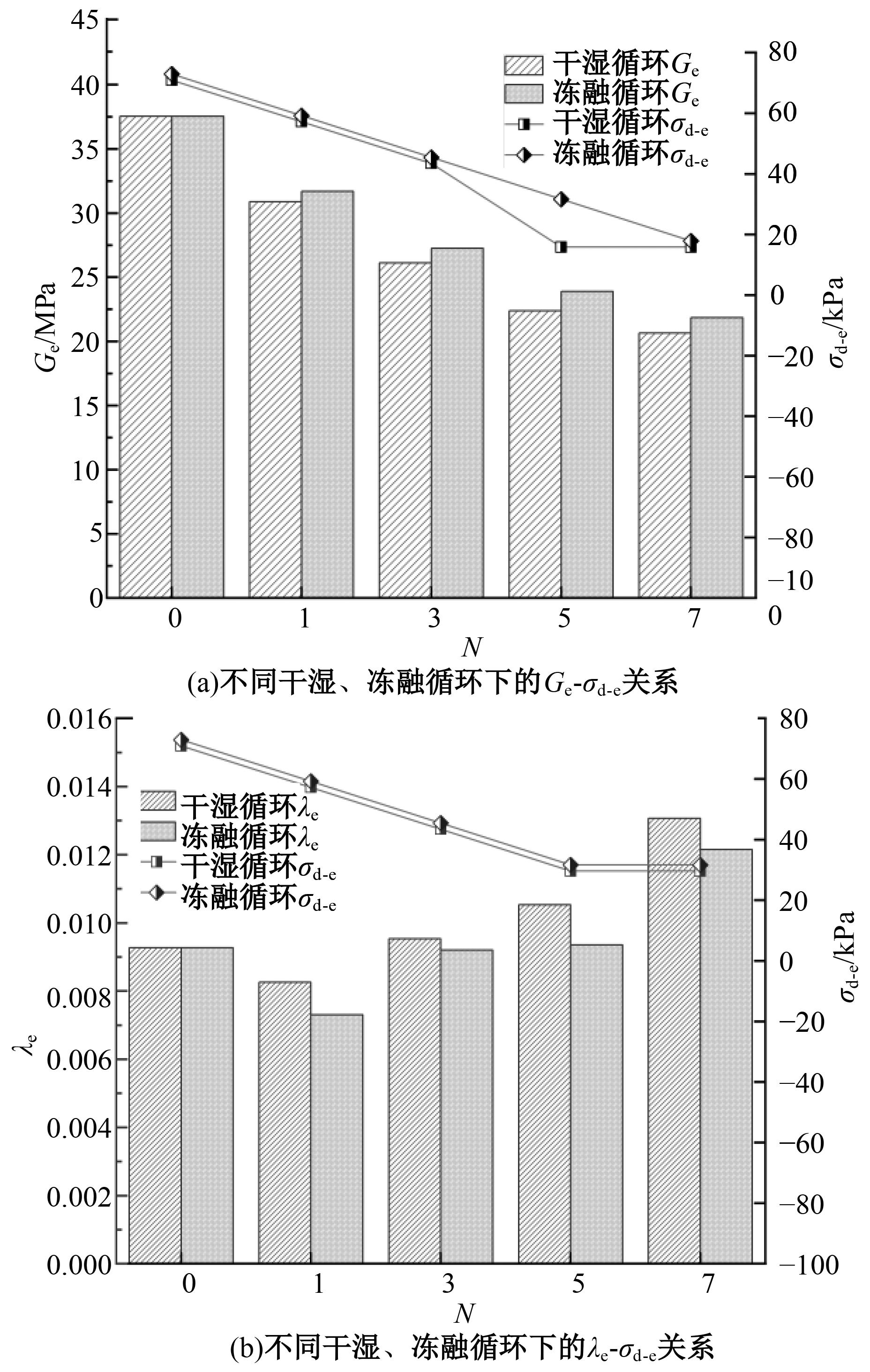
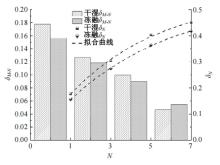
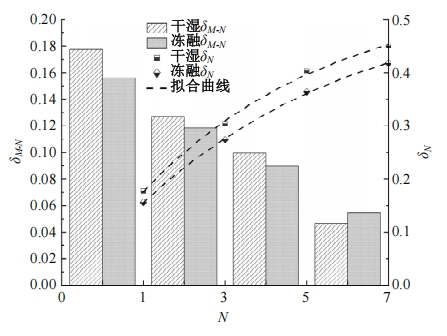
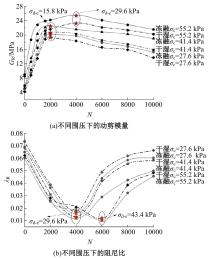
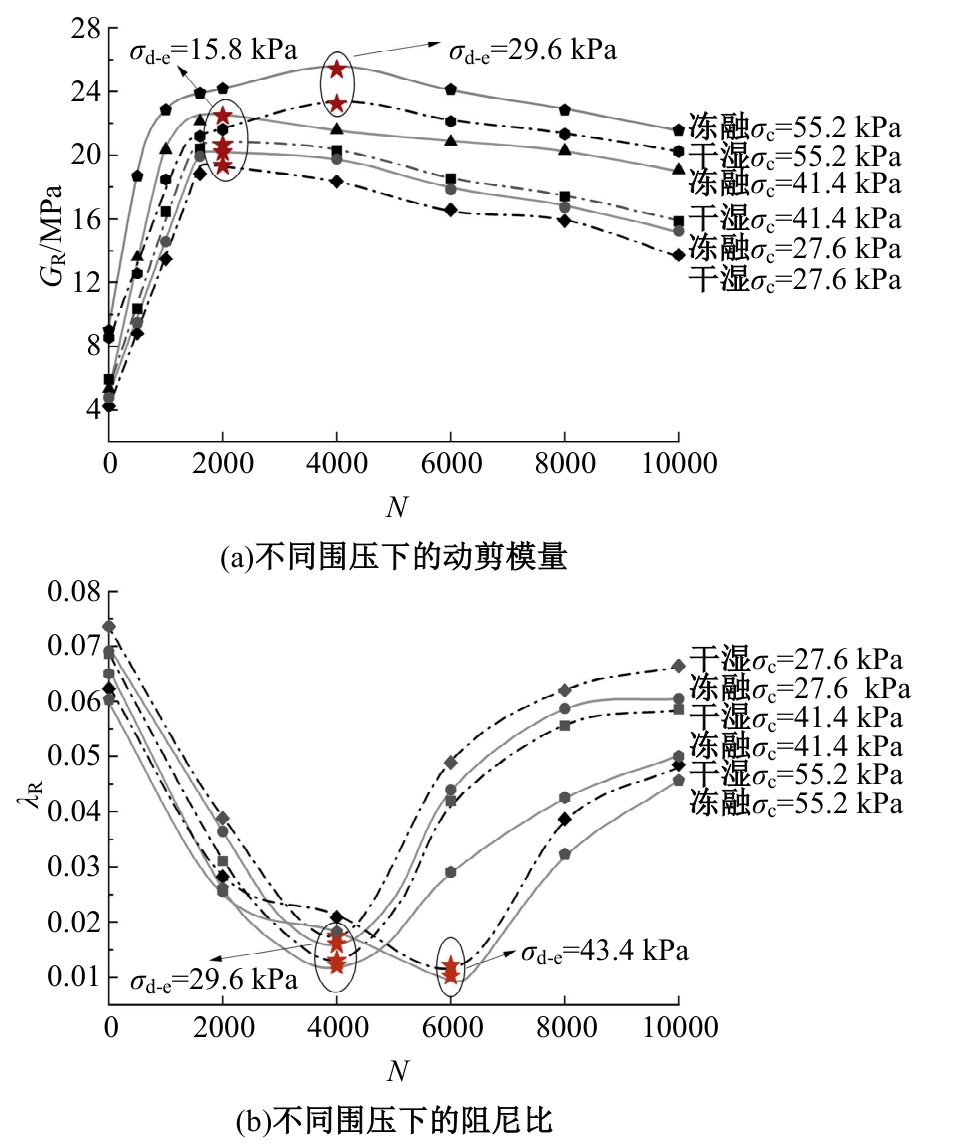
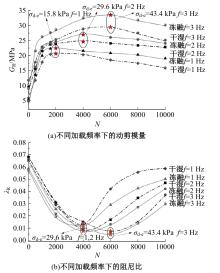
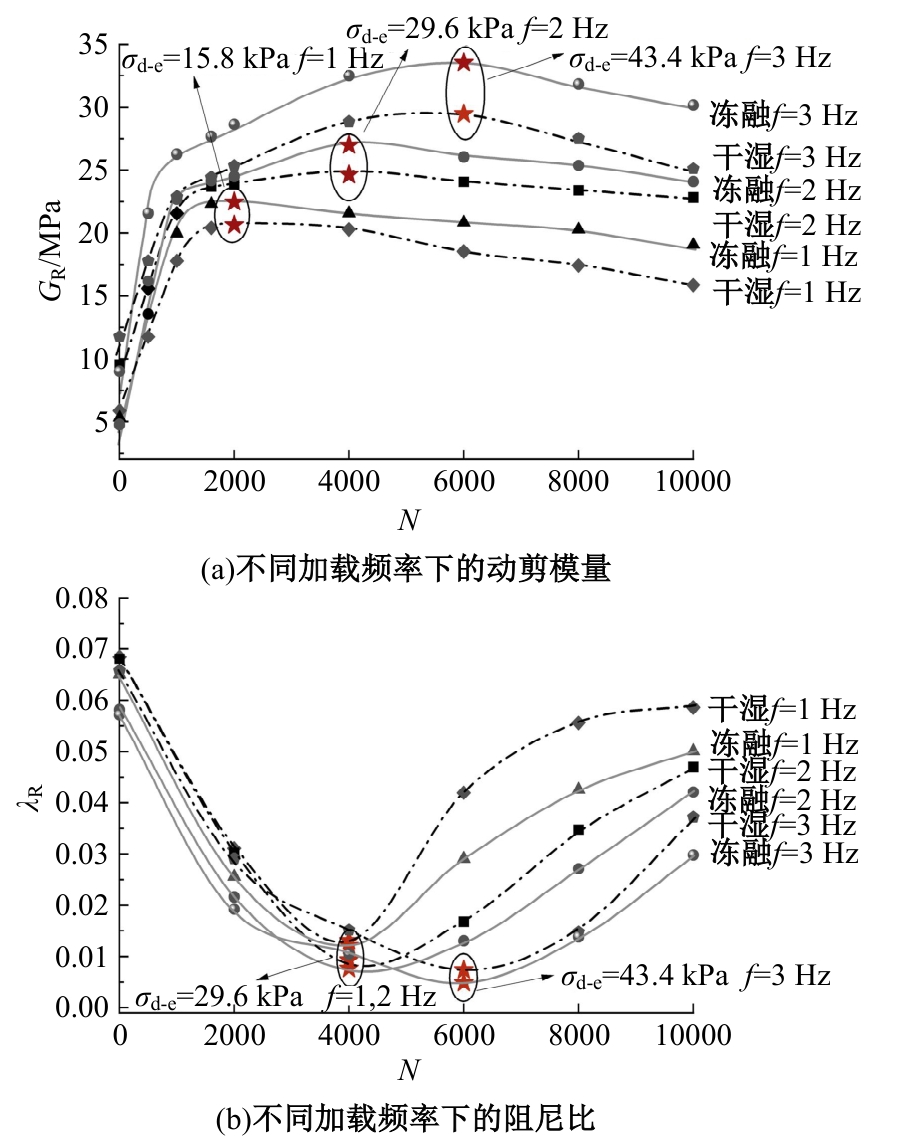
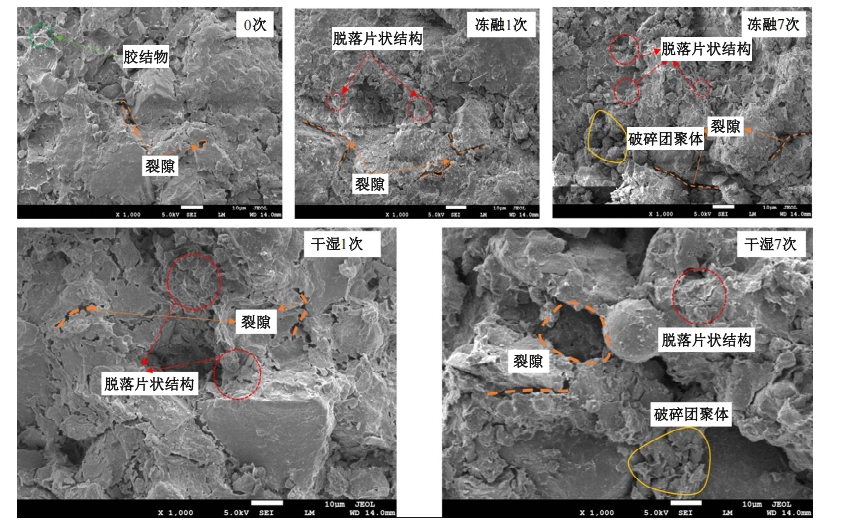
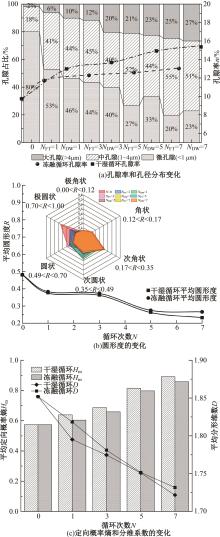
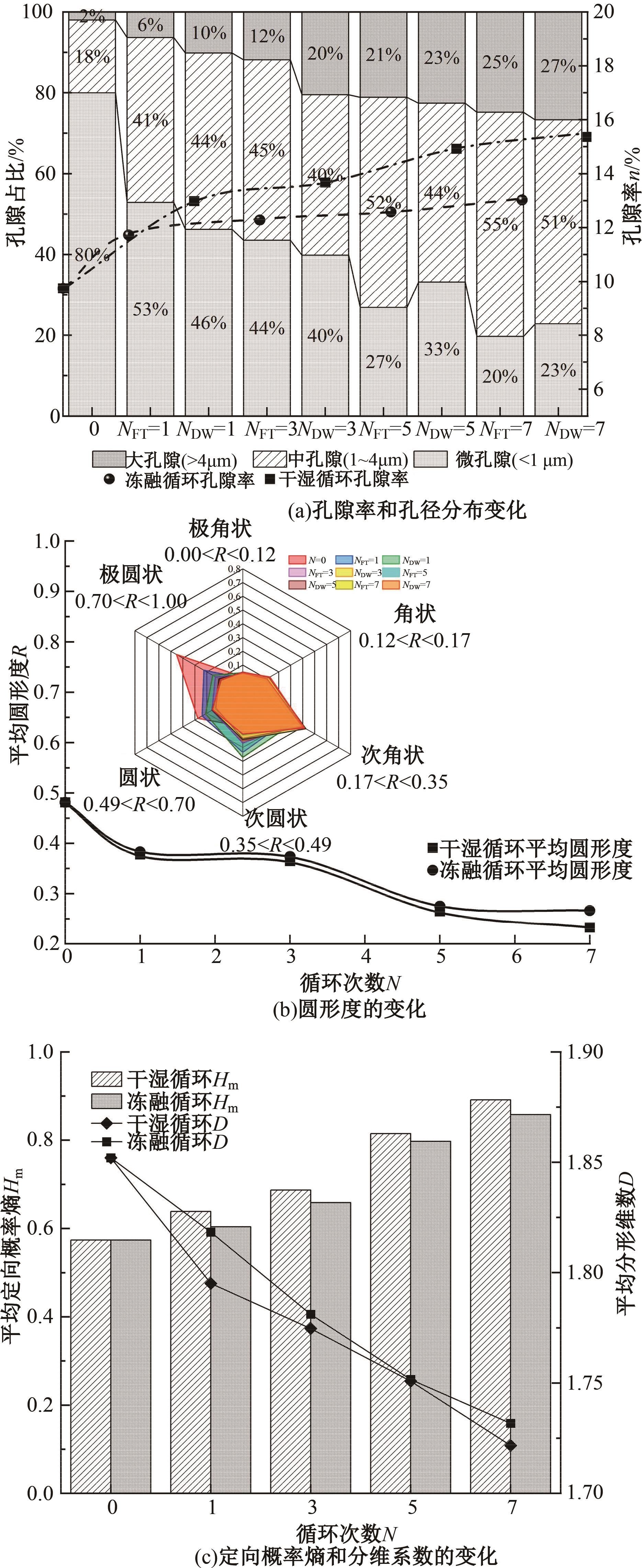
为探明镁质水泥基多相胶凝材料固化的淤泥用作路基土的可行性,对经历不同干湿、冻融循环及加载条件的固化淤泥进行了动三轴和微观结构试验。基于动剪切模量、阻尼比等参数,研究了围压、动应力及加载频率对固化淤泥动力特性的影响,并建立了考虑干湿和冻融循环次数的动剪切模量预估模型。通过定量分析微观孔隙参数,揭示了不同干湿、冻融循环次数后固化淤泥微观结构的演变规律,并进行了微观结构参数与宏观力学性能的关联性分析。结果显示,干湿、冻融循环作用后,试样的动剪模量减小,阻尼比增大,且干湿循环引起的刚度衰减大于冻融循环。随着围压和加载频率的增大,固化淤泥的动剪切模量增大而阻尼比减小。干湿和冻融循环作用使固化淤泥的孔隙率增加,大孔隙数量增多,孔隙形态逐渐转变为平滑的扁角状。循环次数和加载频率对固化淤泥动力特性的影响程度大于围压和动应力幅值;微观结构形态参数对固化淤泥动力特性的影响都较为显著,其中孔隙率的影响程度最大。
中图分类号:
- TU414
| [1] | 李丽华, 韩琦培, 杨星, 等. 稻壳灰-水泥固化淤泥土力学特性及微观机理研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2023, 56 (12): 166-176. |
| Li Li-hua, Han Qi-pei, Yang Xing, et al. Mechanical properties and micro-mechanisms of RHA-cement solidified sludge[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2023, 56 (12): 166-176. | |
| [2] | Jin F, Wang F, Altabbaa A. Three-year performance of in-situ solidified/stabilised soil using novel MgO-bearing binders[J]. Chemosphere, 2016, 144:681-688. |
| [3] | Viani A, Lanzafame G, Chateigner D, et al. Microstructural evolution and texture analysis of magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2020, 103(2): 1414-1424. |
| [4] | 刘维正, 徐阳, 蔡雨, 等. 湿化作用下重载铁路改良膨胀土动力响应与累积变形试验研究[J]. 铁道学报, 2023, 45(2): 127-138. |
| Liu Wei-zheng, Xu Yang, Cai Yu, et al. Dynamic response accumulative deformation of modified expansive soil of heavy-haul railway under wetting action[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2023, 45(2): 127-138. | |
| [5] | 王协群, 张伊, 彭琛, 等. 废旧橡胶轮胎颗粒-水泥改性强膨胀土的长期路用性能研究[J]. 公路, 2023, 68(6): 362-370. |
| Wang Xie-qun, Zhang Yi, Peng Chen, et al. Road performance of highly expansive soil modified with waste rubber tire particles and cement[J]. Highway, 2023, 68(6): 362-370. | |
| [6] | Zhao G T, Han Z, Zou W L, et al. Evolution of mechanical behaviours of an expansive soil during drying-wetting, freeze-thaw, and drying-wetting-freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80: 8109-8121. |
| [7] | 李甜果, 孔令伟, 周振华. 原状膨胀土脱湿过程中多层次微细观结构演化特征与概化模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(): 35-39. |
| Li Tian-guo, Kong Ling-wei, Zhou Zhen-hua. Evolution characteristics and generalized model of multilevel microstructure of undisturbed expansive soils during dehumidification[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(Sup.1): 35-39. | |
| [8] | 安然, 孔令伟, 张先伟, 等. 干湿循环效应下花岗岩残积土结构损伤的多尺度研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(3): 758-767. |
| An Ran, Kong Ling-wei, Zhang Xian-wei, et al. A multi-scale study on structure damage of granite residual soil under wetting-drying environments[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(3): 758-767. | |
| [9] | 张建新, 马昌虎, 郎瑞卿, 等. 不同冻融模式下淤泥质土力学及微观结构特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(): 3801-3811. |
| Zhang Jian-xin, Ma Chang-hu, Lang Rui-qing, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties and microstructure of muddy soil under different freeze-thaw modes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(Sup.1): 3801-3811. | |
| [10] | 刘文化, 杨庆, 唐小微, 等. 干湿循环条件下粉质黏土在循环荷载作用下的动力特性试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2015, 46(4): 425-432. |
| Liu Wen-hua, Yang Qing, Tang Xiao-wei, et al. Experimental study on the dynamic characteristics of silt clay subjected to drying-wetting cycles under cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2015, 46(4): 425-432. | |
| [11] | Wu H, Shao S, Shao S, et al. Variations in dynamic shear modulus of loess exposed to dry-wet cycles from Xi'an area, China[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2023, 173: No.108126. |
| [12] | 胡再强, 黄帅, 周衡立, 等. 干湿循环条件下人工制备遗址土动力特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(): 3499-3507. |
| Hu Zai-qiang, Huang Shuai, Zhou Heng-li, et al. Experimental study on dynamic characteristics of artificial ruins under drying-wetting cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(Sup.2): 3499-3507. | |
| [13] | 魏新江, 庄家煌, 丁智, 等. 地铁循环荷载作用下冻融土滞回曲线及阻尼比特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(10): 2092-2102. |
| Wei Xin-jiang, Zhuang Jia-huang, Ding Zhi, et al. Research on the characteristics of hysteretic curves and damping ratio of frozen-thawed soils under cyclic subway loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(10): 2092-2102. | |
| [14] | 徐永丽, 董子建, 周吉森, 等. 冻融及不同温度下石灰改良盐渍土动力参数研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(1): 90-97. |
| Xu Yong-li, Dong Zi-jian, Zhou Ji-sen, et al. Dynamic parameters of lime-improved saline soil under freeze-thaw and different temperatures[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(1): 90-97. | |
| [15] | Lin B, Zhang F, Feng D, et al. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of thawed saturated clay under long-term cyclic loading[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2018, 145: 93-105. |
| [16] | Tang S, Hu Y, Ren W, et al. Modeling on the hydration and leaching of eco-friendly magnesium oxychloride cement paste at the micro-scale[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 204: 684-690. |
| [17] | Chang C, Dong J, Xiao X, et al. Long-term mechanical properties and micro mechanism of magnesium oxychloride cement concrete[J]. Advances in Cement Research, 2020, 32(8): 371-378. |
| [18] | 李颖, 余红发, 董金美, 等. 氯氧镁水泥的水化产物、相转变规律和抗水性评价方法的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2013, 41(11): 1465-1473. |
| Li Ying, Yu Hong-fa, Dong Jin-mei, et al. Reseach development on hydration product, phase transformation and water resistance evaluation method of magnesium oxychloride cement[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2013, 41(11): 1465-1473. | |
| [19] | Yao K, Wang W, Li N, et al. Investigation on strength and microstructure characteristics of nano-MgO admixed with cemented soft soil[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 206: 160-168. |
| [20] | Wang D, Di S, Gao X, et al. Strength properties and associated mechanisms of magnesium oxychloride cement-solidified urban river sludge[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 250: No.118933. |
| [21] | Wang D, Gao X, Liu X, et al. Strength, durability and microstructure of granulated blast furnace slag-modified magnesium oxychloride cement solidified waste sludge[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 292: No.126072. |
| [22] | . 公路土工试验规程 : [S]. |
| [23] | 刘宁. 氯氧镁水泥基多相胶凝材料改性固化淤泥的路用性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学土木工程与建筑学院, 2022. |
| Liu Ning. Study on road performance of modified solidified mud by magnesium oxychloride cement-based multiphase cementing material[D]. Wuhan: School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Wuhan University of Technology, 2022. | |
| [24] | 王协群, 刘宁, 李智奇, 等. 干湿循环作用下氯氧镁水泥基多相胶凝材料改性固化淤泥的水力-力学特性[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2023, 45(10): 2004-2013. |
| Wang Xie-qun, Liu Ning, Li Zhi-qi, et al. Hydro-mechanical behaviors of sludge stabilized with magnesium oxychloride cement-based multi-cementitious materials under influence of drying-wetting cycles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(10): 2004-2013. | |
| [25] | 赵贵涛, 韩仲, 邹维列, 等. 干湿、冻融循环对膨胀土土-水及收缩特征的影响[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(6):1139-1146. |
| Zhao Gui-tao, Han Zhong, Zou Wei-lie, et al. Influences of drying-wetting-freeze-thaw cycles on soil-water and shrinkage characteristics of expansive soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021,43(6):1139-1146. | |
| [26] | 刘维正, 徐阳, 石志国, 等. 湿化作用下改良膨胀土永久变形特性多级加载试验研究[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2022, 53(1): 296-305. |
| Liu Wei-zheng, Xu Yang, Shi Zhi-guo, et al. Characterization of permanent deformation of modified expansive soil under wetting effect using multi-stage dynamic triaxial test[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2022, 53(1): 296-305. | |
| [27] | Ren J, Vanapalli S K, Han Z, et al. The resilient moduli of five Canadian soils under wetting and freeze-thaw conditions and their estimation by using an artificial neural network model[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2019, 168: No.102894. |
| [28] | T307-99. Standard method of test for determining the resilient modulus of soils and aggregate materials [S]. Washington, DC: American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials, 1999. |
| [29] | 蔡袁强, 赵莉, 曹志刚, 等. 不同频率循环荷载下公路路基粗粒填料长期动力特性试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(5): 1238-1246. |
| Cai Yuan-qiang, Zhao Li, Cao Zhi-gang, et al. Experimental study on dynamic characteristics of unbound granular materials under cyclic loading with different frequencies[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(5): 1238-1246. | |
| [30] | 彭瑞东, 谢和平, 鞠杨. 二维数字图像分形维数的计算方法[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2004, 50(1): 22-27. |
| Peng Rui-dong, Xie He-ping, Ju Yang. Computation method of fractal dimension for 2-D digital image [J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2004, 50(1): 22-27. | |
| [31] | 谭学瑞, 邓聚龙. 灰色关联分析:多因素统计分析新方法[J]. 统计研究, 1995, 12(3): 46-48. |
| Tan Xue-rui, Deng Ju-long. Grey relational analysis: a new method for multifactor statistical analysis[J]. Statistical Research, 1995, 12(3): 46-48. | |
| [32] | Delage P, Audiguier M, Cui Y-J, et al. Microstructure of a compacted silt[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1996, 33(1): 150-158. |
| [1] | 俞靖洋,李东钊,张志清,王真,孙海林,布海玲,李明春. 环保型蓄盐沥青混合料性能损伤演变[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(3): 888-898. |
| [2] | 李义,刘天宝,王绍强,梁继才. 软质炭黑对天然橡胶基磁流变弹性体性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1548-1554. |
| [3] | 李丽华,李孜健,肖衡林,曹文哲,周鑫隆,黄少平. 土工格栅加筋建筑垃圾土循环剪切试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1612-1623. |
| [4] | 何华飞,李兆平,符瑞安,马绍麟,黄明利. 考虑地层约束效应的预制侧墙节点抗震性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1601-1611. |
| [5] | 宫亚峰,刘佰鑫,杨建星,何锋,孙亮,田立华. 基于深基坑施工的概率有限元基准模型参数修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3534-3544. |
| [6] | 李林,沈珂任,何世玉,陈镇旺. 基于3D-DIC技术和摄影测量原理的无侧限试样体积与变形测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(11): 3255-3264. |
| [7] | 于本田,李彦宵,张占旭,苏俊辉,谢超,张凯. 不同石粉及掺量对高延性工程水泥基复合材料的性能影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2908-2921. |
| [8] | 李丽华,康浩然,张鑫,肖衡林,刘一鸣,周鑫隆. 加筋土石混合体动力特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2897-2907. |
| [9] | 刘方成,王将,吴孟桃,补国斌,何杰. 土工格栅加筋橡胶砂应力-应变特性试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2542-2553. |
| [10] | 宫亚峰,吴树正,毕海鹏,谭国金. 基于现场监测技术的装配式箱涵温度场及冻胀分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2321-2331. |
| [11] | 惠迎新,陈嘉伟. 基于改进遗传算法的挤扩支盘群桩优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2089-2098. |
| [12] | 宫亚峰,吴树正,毕海鹏,周冬明,谭国金,黄晓明. 玄武岩纤维活性粉末混凝土与钢绞线粘结滑移过程声学特性表征[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1819-1832. |
| [13] | 姜屏,陈业文,陈先华,张伟清,李娜,王伟. 改性石灰土在干湿和冻融循环下的无侧限抗压性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1809-1818. |
| [14] | 张哲,付伟,张军辉,黄超. 循环荷载下冻融路基黏土长期塑性行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1790-1798. |
| [15] | 于贵申,陈鑫,武子涛,陈轶雄,张冠宸. AA6061⁃T6铝薄板无针搅拌摩擦点焊接头结构及性能分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1338-1344. |
|