吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 408-416.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181240
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于排气热管理的柴油机氧化催化器升温特性
- 1.江苏大学 汽车与交通工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
2.无锡伟博汽车科技有限公司,江苏 无锡 214000
Heating characteristics of DOC based on exhaust thermal management of diesel engine
Jian WANG1( ),Xin XU1,Han GU1,Duo-jun ZHANG2,Sheng-ji LIU1
),Xin XU1,Han GU1,Duo-jun ZHANG2,Sheng-ji LIU1
- 1.School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013,China
2.Wuxi Wabertec Automobile Technology Co. , Ltd. ,Wuxi 214000,China
摘要:
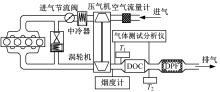
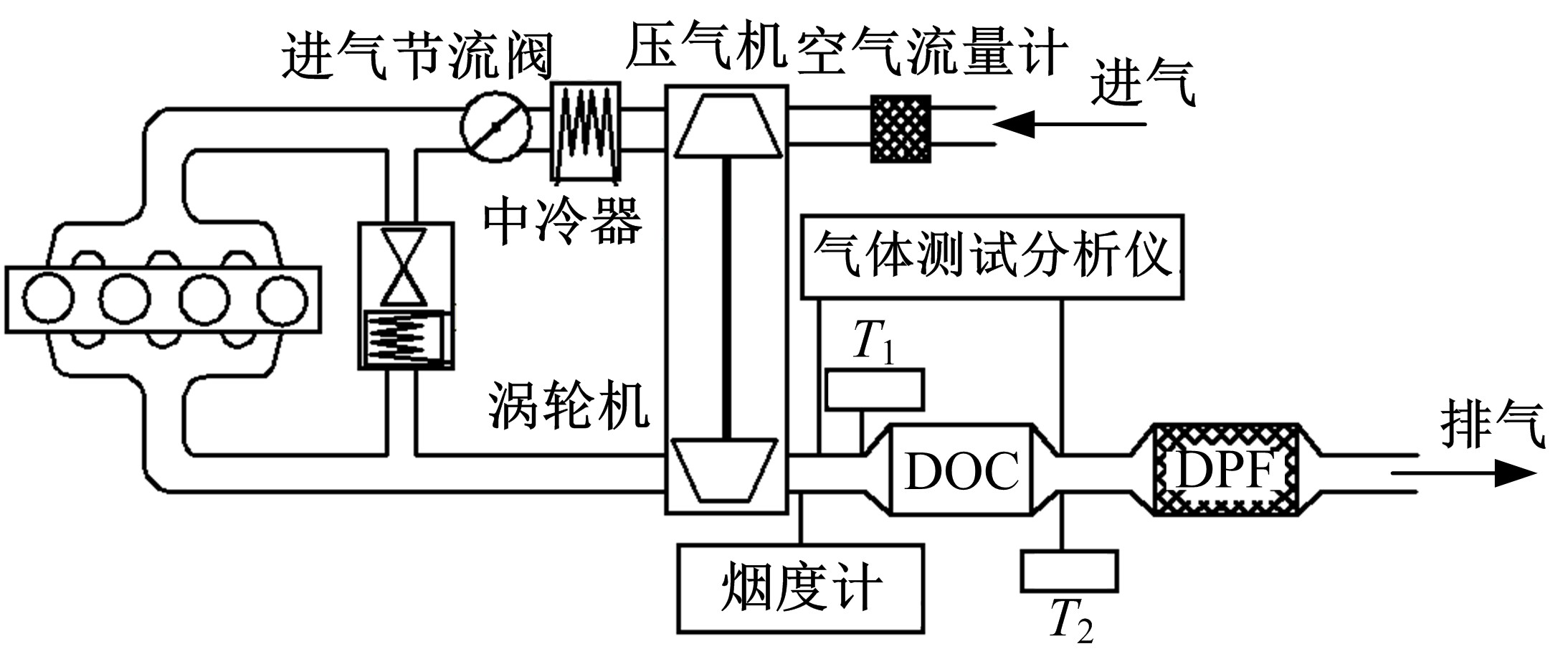
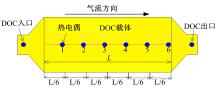
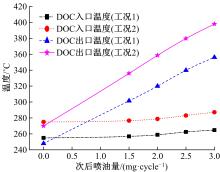
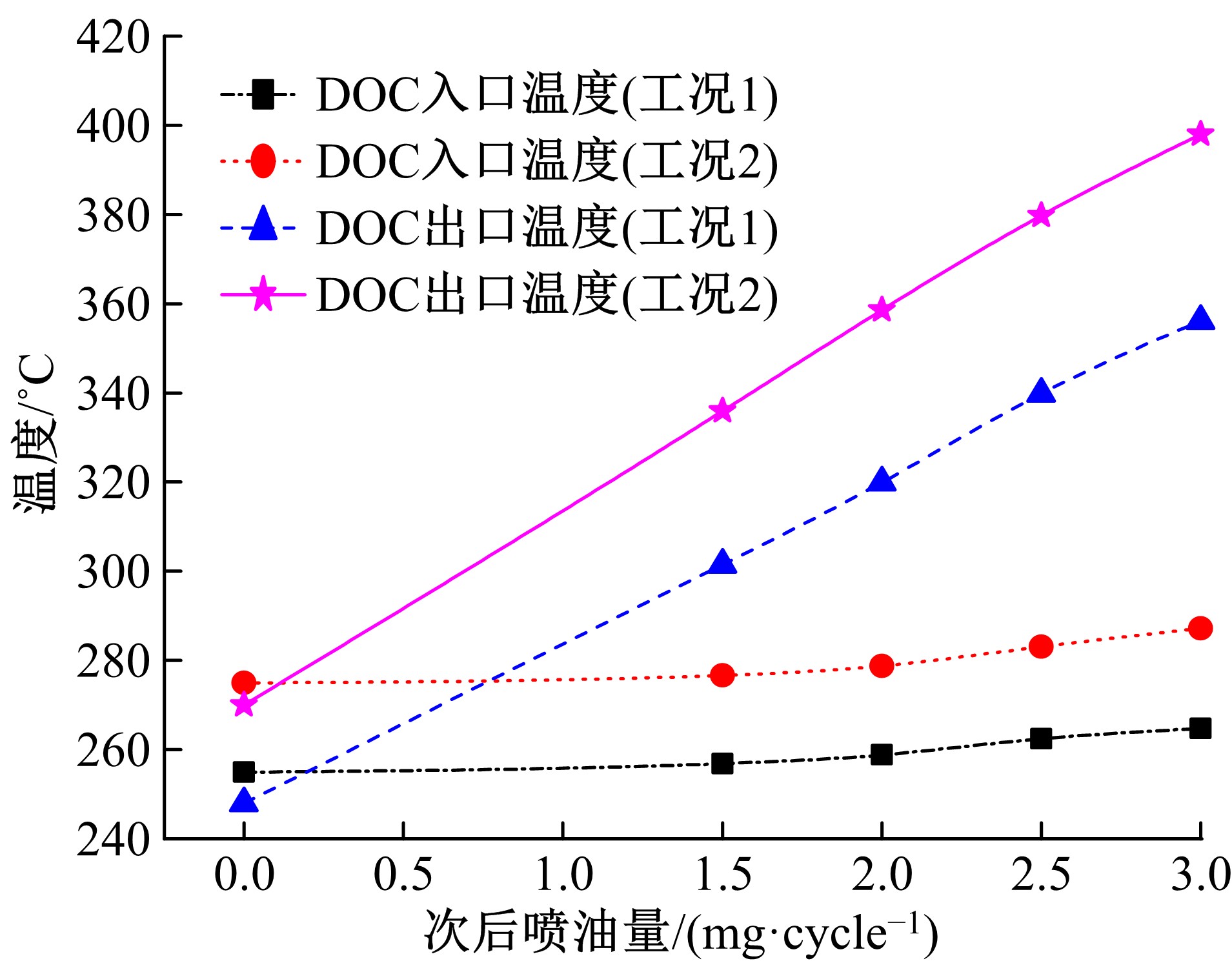
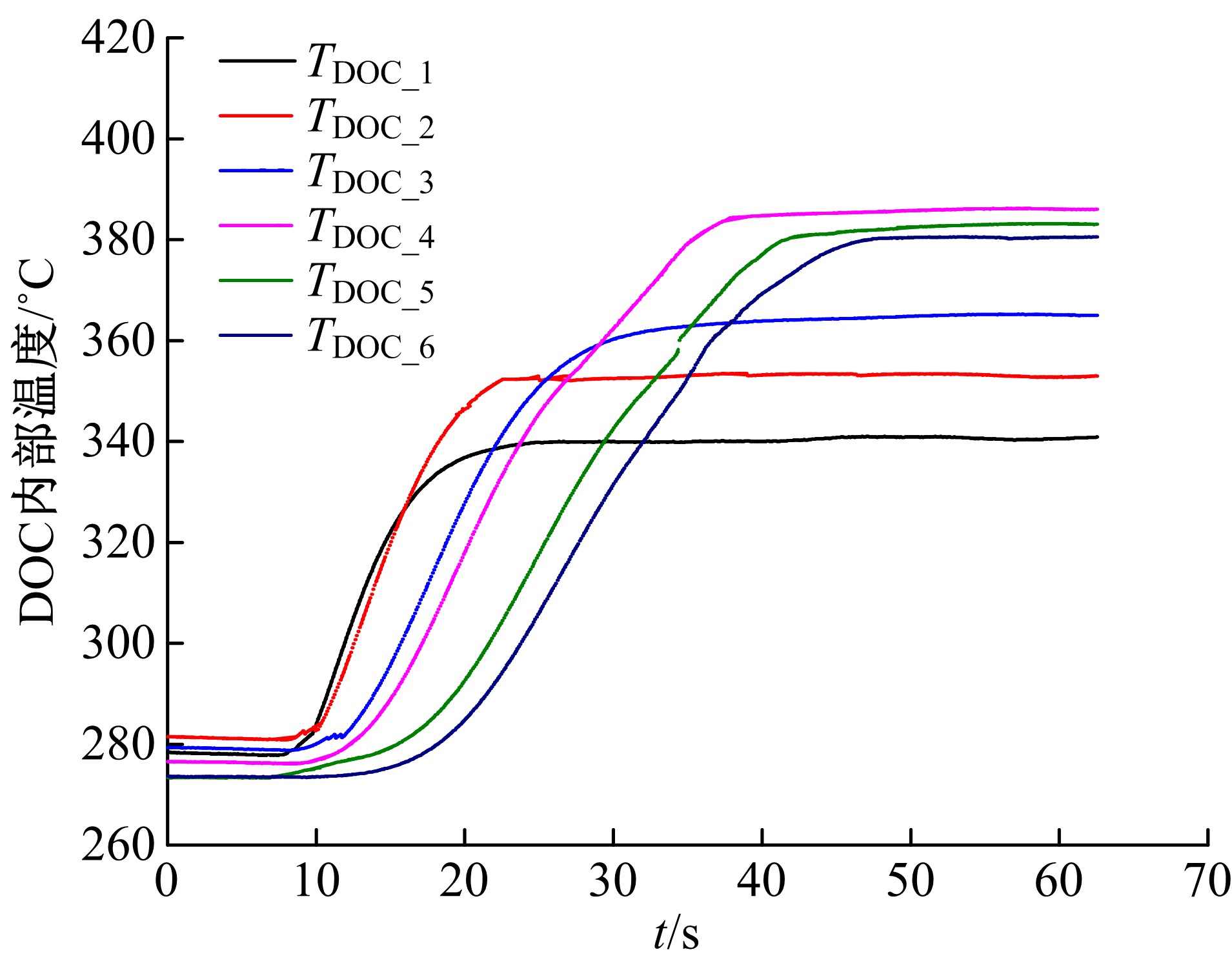
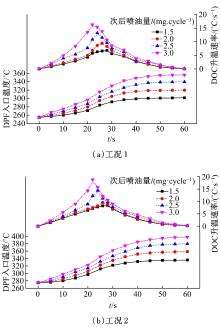
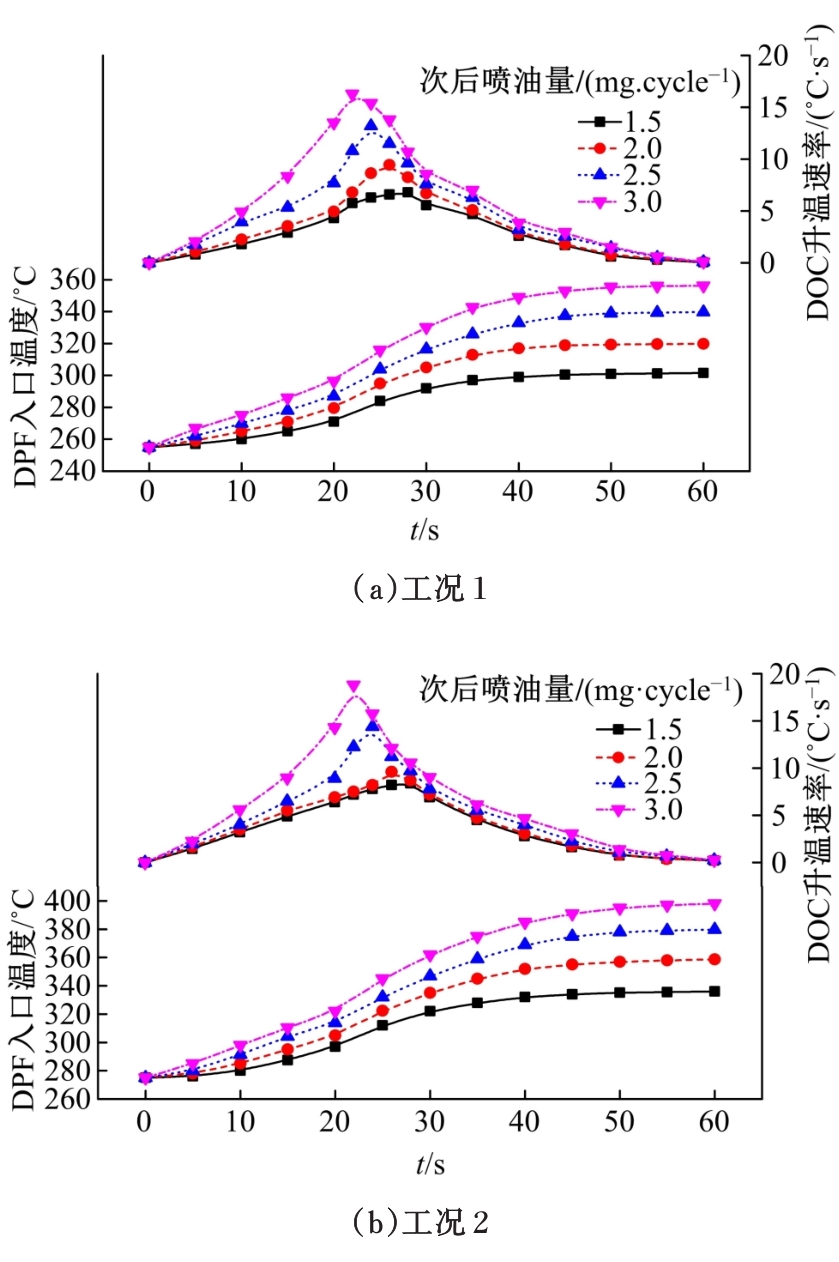
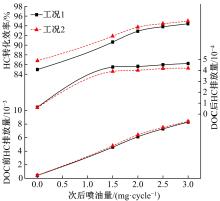
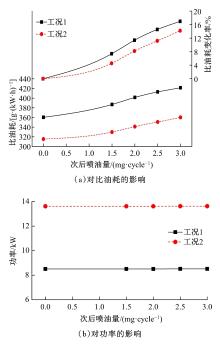
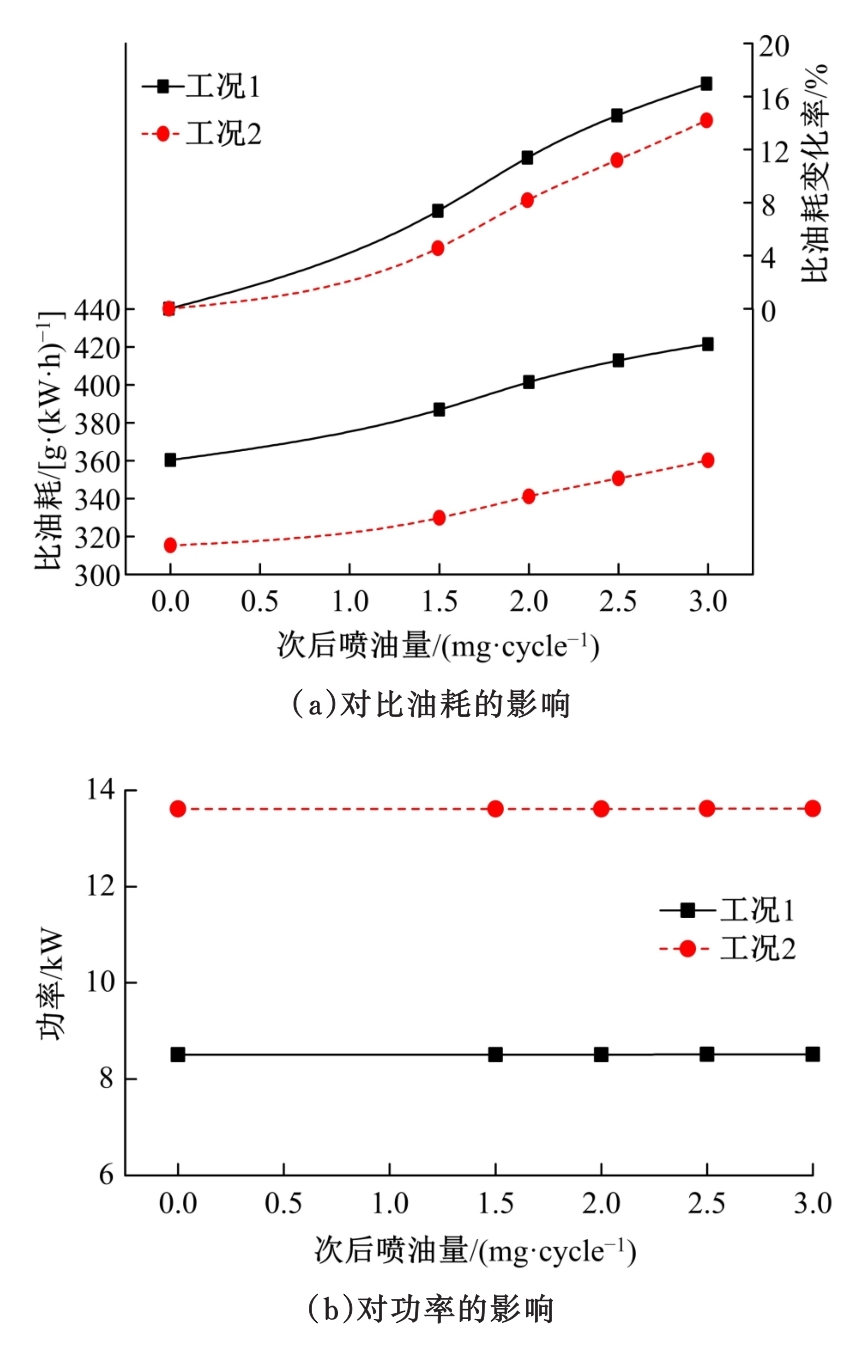
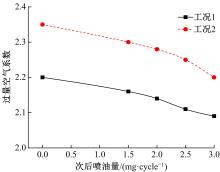
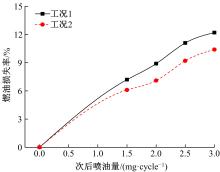
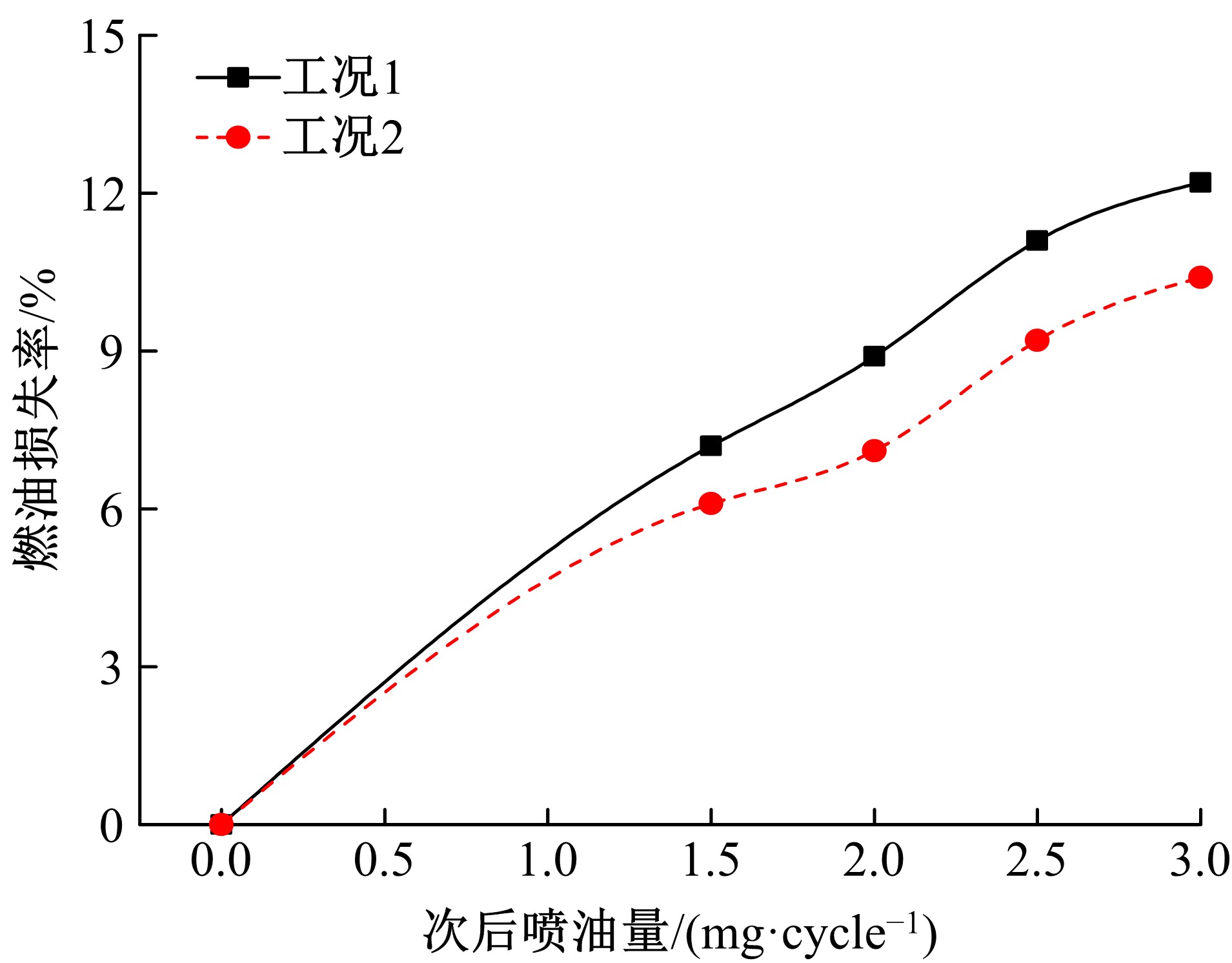
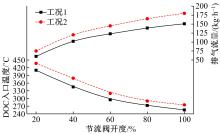
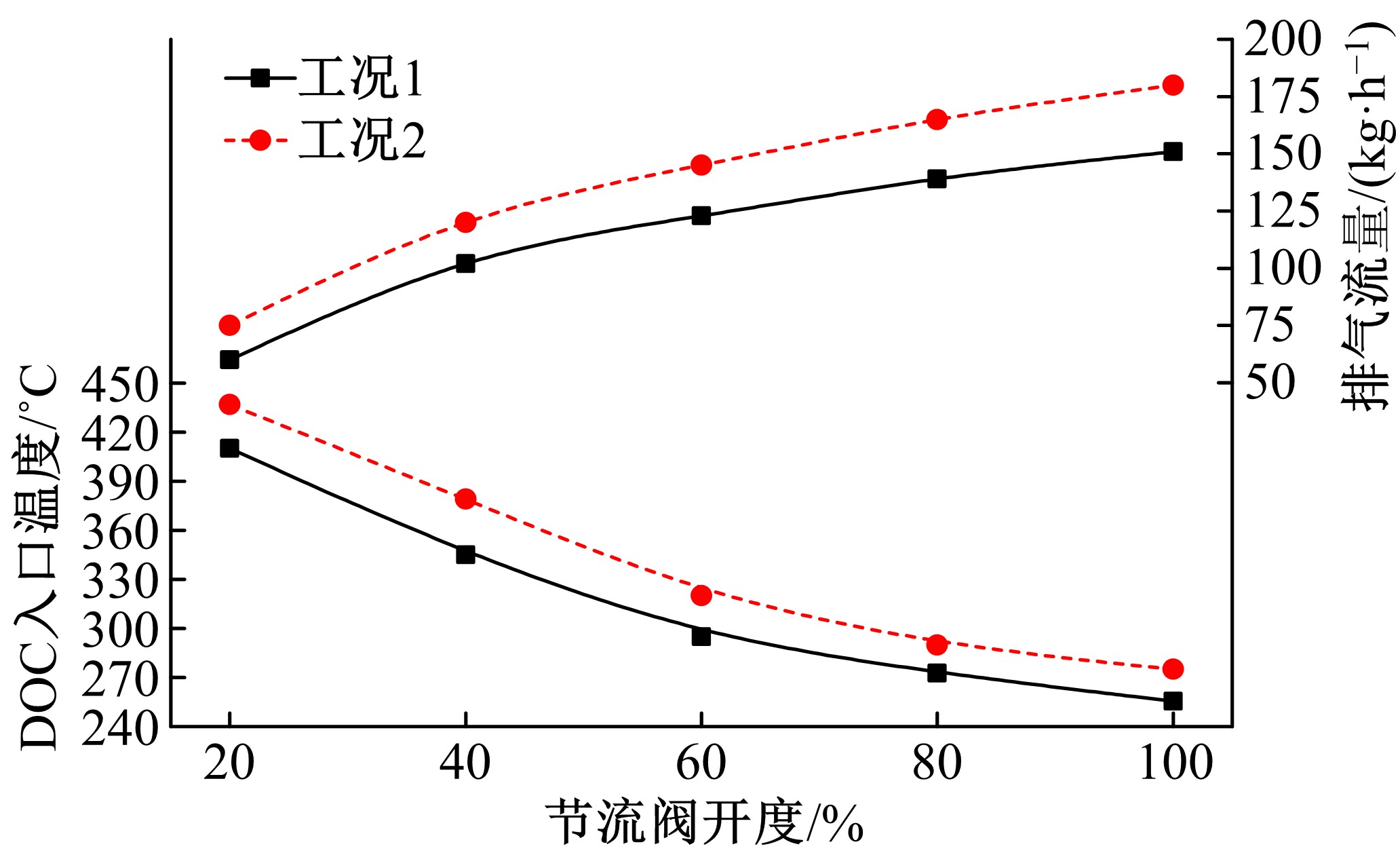
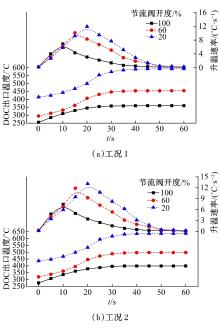
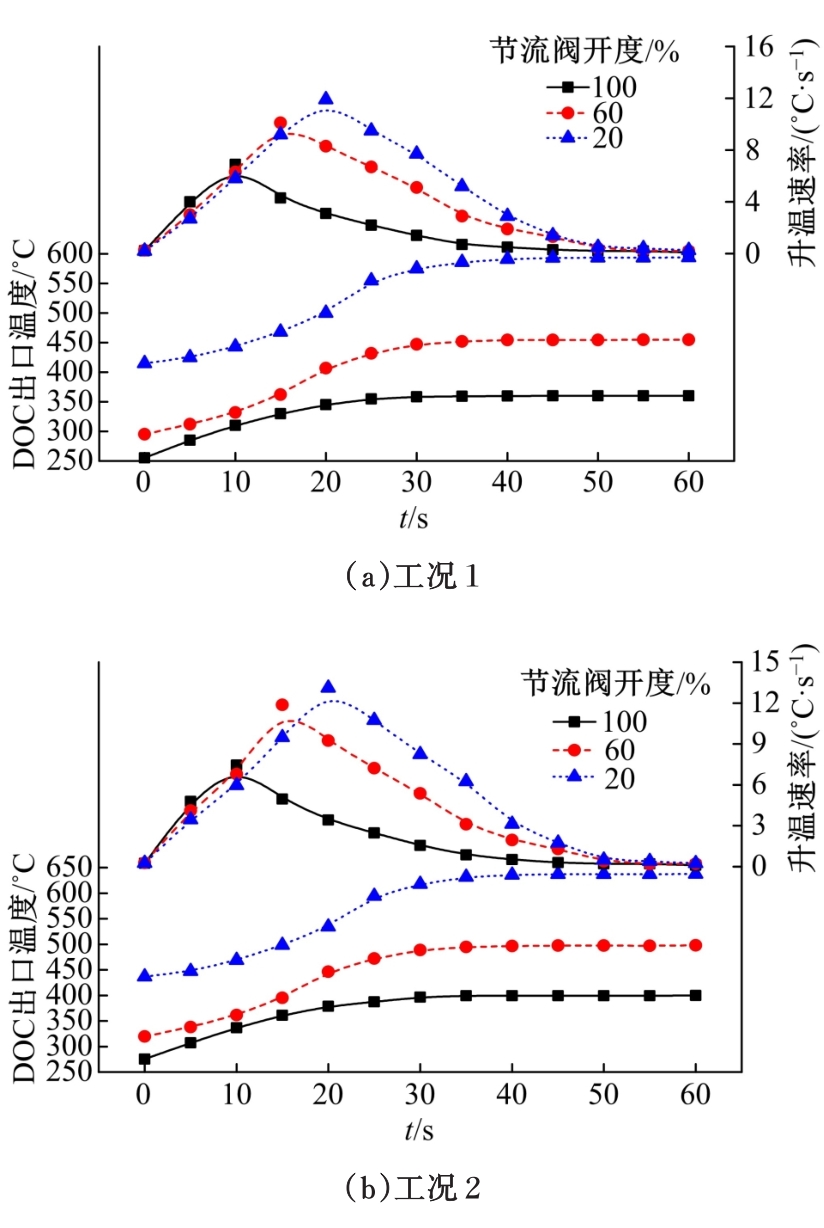
为研究柴油机颗粒捕集器(DPF)再生升温过程中所采用的排气热管理措施对柴油机氧化型催化器(DOC)升温特性及其他发动机性能的影响,选取低转速、中小负荷下的两个低排温的典型工况点进行试验研究。试验结果表明:增加次后喷油量对DOC入口排气温度影响较小,可提高DOC内部升温速率、缩短升温速率峰值到达时间,且负荷越大效果越明显;次后喷油量的增加能提高DOC对HC的转化效率,但由于HC基数的增多会导致DOC后的HC逃逸量增多;增加次后喷油量也会增加发动机的比油耗和加重发动机的机油稀释程度,需要合理控制次后喷油量;进气节流阀开度减小,节流作用增强,进气流量降低,DOC入口温度上升,DOC内部升温响应速度变缓但升温速率峰值增大。升温过程中,峰值温度出现在DOC中后部且温度梯度大。试验研究成果可为DPF主动再生方法及温升策略提供试验依据。
中图分类号:
- TK421
| 1 | 田径, 程义琳, 刘忠长, 等. 柴油机微粒捕集器降怠速再生过程载体温度的控制[J]. 内燃机学报, 2013, 31(2): 154-158. |
| Tian Jing, Cheng Yi-lin, Liu Zhong-chang, et al. Carrier temperature controlling strategies of diesel particulate filter during drop-to-idle regeneration process[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2013, 31(2): 154-158. | |
| 2 | 濮晓宇, 蔡忆昔, 施蕴曦,等. 排气余热辅助低温等离子体再生柴油机颗粒捕集器试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(14): 70-77. |
| Pu Xiao-yu, Cai Yi-xi, Shi Yun-xi, et al. Test on diesel particulate filter regeneration using non-thermal plasma technology aided by exhaust waste heat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(14): 70-77. | |
| 3 | Khair M K. A review of diesel particulate filter technologies[J]. SAE Paper, 2003-01-2303. |
| 4 | 田径, 韩永强, 刘忠长, 等. 柴油机燃油催化微粒后处理器性能与再生[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(1): 18-23. |
| Tian Jing, Han Yong-qiang, Liu Zhong-chang, et al. Performance and regeneration of diesel particulate filter with fuel borne catalyst on diesel engine[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(1): 18-23. | |
| 5 | Johnson T. Vehicular emissions in review[J]. SAE International Journal of Engines, 2013, 6(2): 699-715. |
| 6 | Kuwahara T, Nishii S, Kuroki T, et al. Complete regenration characteristics of diesel particulate filter using ozone injection[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 111: 652-656. |
| 7 | Castellano J, Chaudhari A, Bromham J. Adaptive temperature control for diesel particulate filter regeneration[J]. SAE Paper, 2013-01-0517. |
| 8 | Stadlbauer S.Waschl H, Schilling A,et al. DOC temperature control for low temperature operating ranges with post and main injection actuation[J]. SAE Paper, 2013-01-1580. |
| 9 | Johnson T V. Review of diesel emissions and control[J]. International Journal of Engine Research, 2009, 10(5): 275-285. |
| 10 | Jiao P H, Li Z J, Shen B X, et al. Research of DPF regeneration with NOx-PM coupled chemical reaction[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 110: 737-745. |
| 11 | Wang D, Liu Z C, Han Y Q, et al. Experimental studies on pressure drop performance and regeneration safety of diesel particulate filter[C]∥International Conference on Electric Information and Control Engineering, Wuhan, China, 2011: 2175-2178. |
| 12 | Nigro A, Algieri A, Bartolo C D, et al. Fluid dynamic investigation of innovative intake strategies for multivalve internal combustion engines[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2017, 123: 297-310. |
| 13 | 韦雄, 冒晓建, 祝轲卿, 等. 基于机内技术的DPF再生控制策略研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013, 44(11): 1-5, 11. |
| Wei Xiong, Mao Xiao-jian, Zhu Ke-qing, et al. Control strategy of DPF regeneration based on machine technology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(11): 1-5, 11. | |
| 14 | Suresh A, Yezerets A, Currier N, et al. Diesel particulate filter system-effect of critical variables on the regeneration strategy development and optimization[J]. SAE Paper, 2008-01-0329. |
| 15 | 吴风英, 王站成, 徐斌, 等. 柴油机颗粒捕集器(DPF)再生技术分析[J]. 环境工程, 2015,33(6): 67-70, 18. |
| Wu Feng-ying, Wang Zhan-cheng, Xu Bin, et al. Analysis of the regeneration technologies for diesel particulate filter[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2015, 33(6): 67-70, 18. | |
| 16 | Bari S. Diesel Engine-Combustion, Emissions and Condition Monitoring[M].Australia: Tailieu Vn, 2013. |
| 17 | Park D S,Kim J U,Kim E S. A burner-type trap for particulate matter from a diesel engine[J]. Combustion and Flame, 1998, 114(3/4): 585-590. |
| 18 | Mayer A, Lutz T, Lammle C, et al. Engine intake throttling for active regeneration of diesel engine[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 2003-01-0381. |
| 19 | 张德满, 汪正清, 马士虎, 等. 怠速工况下氧化型催化转换器辅助DPF再生方法[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013, 44(3): 24-27. |
| Zhang De-man, Wang Zheng-qing, Ma Shi-hu, et al. DOC assisted DPF regeneration under idle condition[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(3): 24-27. | |
| 20 | 王丹, 刘忠长, 王忠恕, 等. 柴油机微粒捕集器缸内次后喷主动再生方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 42(3): 551-556. |
| Wang Dan, Liu Zhong-chang, Wang Zhong-shu, et al. Diesel particulate filter active regeneration by in-cylinder late post injection[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42(3): 551-556. | |
| 21 | Osman A K, Hikmet A, Alper T C. Methods to improve efficiency of four stroke,spark ignition engines at part load[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2005, 46(20): 3202-3220. |
| 22 | Cleary D,Silvas G. Unthrottled engine operation with variable intake[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 2007-01-1282. |
| 23 | Mohsen G, Mohammad E F, Omid M, et al. Effects of altitude on the soot emission and fuel consumption of a light-duty diesel engine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013, 28(2): 130-139. |
| 24 | Surenhalli H S, Premchand K, Johnson J H, et al. Modeling study of active regeneration of a catalyzed particulate filter using one-dimensional DOC and CPF models[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 2011-01-1242. |
| 25 | Budde M, Ehrly M, Jakob M, et al. Simulation and optical analysis of oil dilution in diesel regeneration operation[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 2011-01-1844. |
| 26 | 王建, 曹政, 张多军, 等. 基于DPF主动再生温度需求的柴油机进气节流控制策略[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(2): 32-39. |
| Wang Jian, Cao Zheng, Zhang Duo-jun, et al. Intake throttling control strategy based on DPF active regeneration temperature for diesel[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(2): 32-39. | |
| 27 | 王建, 曹政, 张多军, 等. 基于柴油机排气热管理的喷油策略控制试验研究[J]. 车用发动机, 2018(2): 79-86. |
| Wang Jian, Cao Zheng, Zhang Duo-jun, et al. Fuel injection control strategy based on exhaust thermal management of diesel engine[J]. Vehical Engine, 2018(2): 79-86. | |
| 28 | Hannibal W, Flied R, Stiegler L, et al. Overview of current continuously variable valve lift system for four-stroke spark-ignition engines and the criteria for their design ratings[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 2004-01-0263. |
| 29 | 姚广涛, 赵国斌, 邓成林, 等. 进气节流对柴油机性能影响的试验研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2016, 38(5): 521-525. |
| Yao Guang-tao, Zhao Guo-bin, Deng Cheng-lin, et al. An experimental study on the effects of intake throttling on diesel engine performance[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2016, 38(5): 521-525. |
| [1] | 刘长铖,刘忠长,田径,许允,杨泽宇. 重型增压柴油机燃烧过程中的缸内㶲损失[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1911-1919. |
| [2] | 胡潇宇,李国祥,白书战,孙柯,李思远. 考虑加热面粗糙度和材料的沸腾换热修正模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1945-1950. |
| [3] | 宋昌庆,陈文淼,李君,曲大为,崔昊. 不同当量比下单双点火对天然气燃烧特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1929-1935. |
| [4] | 朱一骁,何小民,金义. 联焰板宽度对单凹腔驻涡燃烧室流线形态的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1936-1944. |
| [5] | 王德军,吕志超,王启明,张建瑞,丁建楠. 基于EKF及调制傅式级数的缸压辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1174-1185. |
| [6] | 臧鹏飞,王哲,高洋,孙晨乐. 直线电机/发动机系统稳态运行综合控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 798-804. |
| [7] | 董伟,宋佰达,邱立涛,孙昊天,孙平,蒲超杰. 直喷汽油机暖机过程中两次喷射比例对燃烧和排放的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1755-1761. |
| [8] | 李志军, 汪昊, 何丽, 曹丽娟, 张玉池, 赵新顺. 催化型微粒捕集器碳烟分布及其影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1466-1474. |
| [9] | 林学东, 江涛, 许涛, 李德刚, 郭亮. 高压共轨柴油机起动工况高压泵控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1436-1443. |
| [10] | 秦静, 徐鹤, 裴毅强, 左子农, 卢莉莉. 初始温度和初始压力对甲烷-甲醇裂解气预混层流燃烧特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1475-1482. |
| [11] | 宫洵, 蒋冰晶, 胡云峰, 曲婷, 陈虹. 柴油机主-从双微元Urea-SCR系统非线性状态观测器设计与分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1055-1062. |
| [12] | 席雷, 徐亮, 高建民, 赵振, 王明森. 厚壁矩形带肋通道内蒸汽流动及传热特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 752-759. |
| [13] | 钟兵, 洪伟, 金兆辉, 苏岩, 解方喜, 张富伟. 进气门早关液压可变气门机构运动特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 727-734. |
| [14] | 李龙, 张幽彤, 左正兴. 变负载控制在自由活塞内燃发电机的缸压控制中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 473-479. |
| [15] | 卫海桥, 裴自刚, 冯登全, 潘家营, 潘明章. 压电喷油器多次喷射对GDI汽油机颗粒物排放的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 166-173. |
|
||