吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 1911-1919.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180922
重型增压柴油机燃烧过程中的缸内㶲损失
- 吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
In⁃cylinder exergy destruction during combustion process ofheavy⁃duty turbocharged diesel engine
Chang-cheng LIU( ),Zhong-chang LIU,Jing TIAN(
),Zhong-chang LIU,Jing TIAN( ),Yun XU,Ze-yu YANG
),Yun XU,Ze-yu YANG
- State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
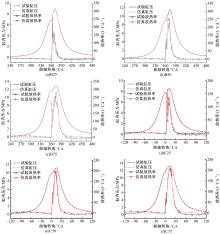
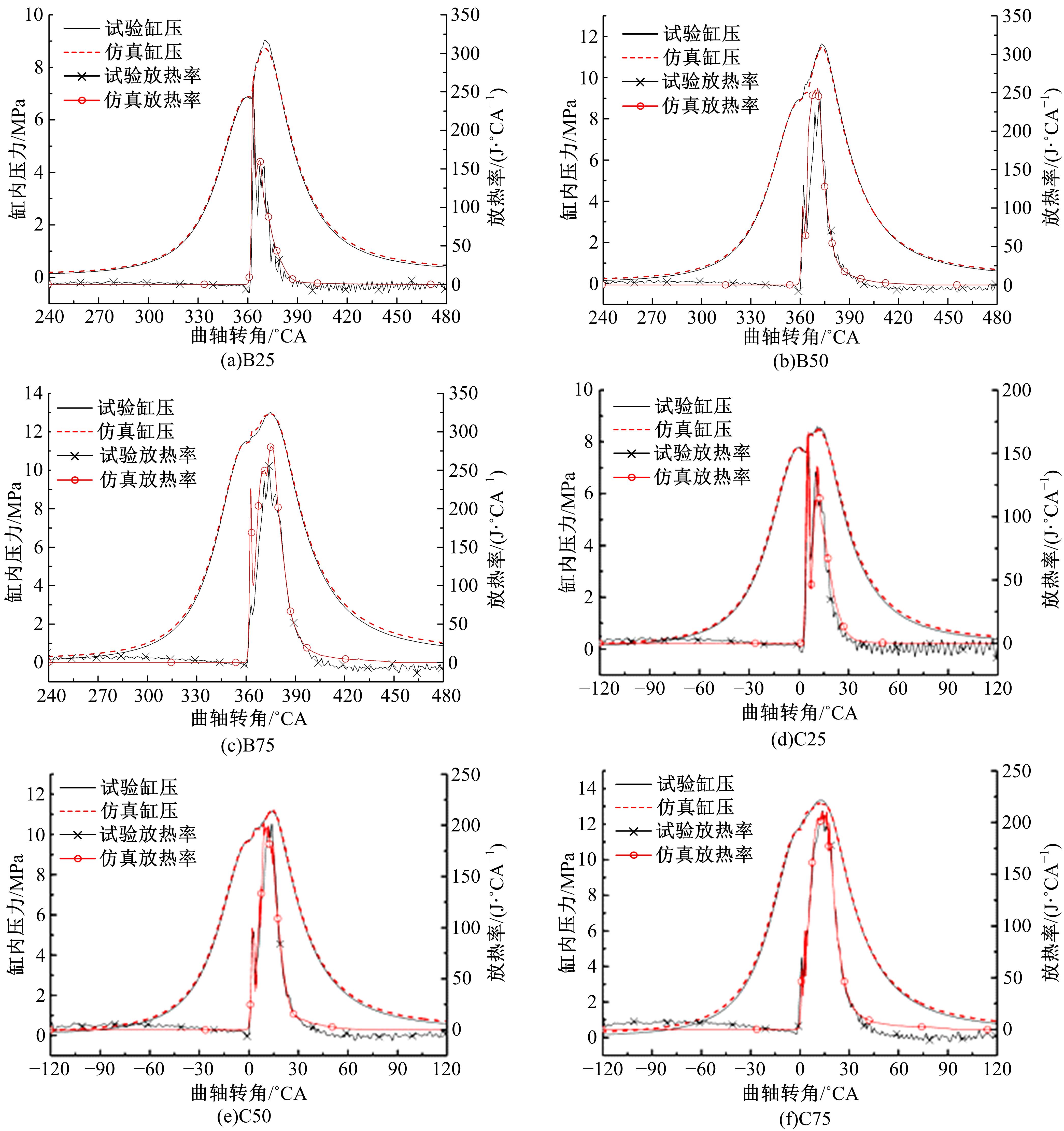
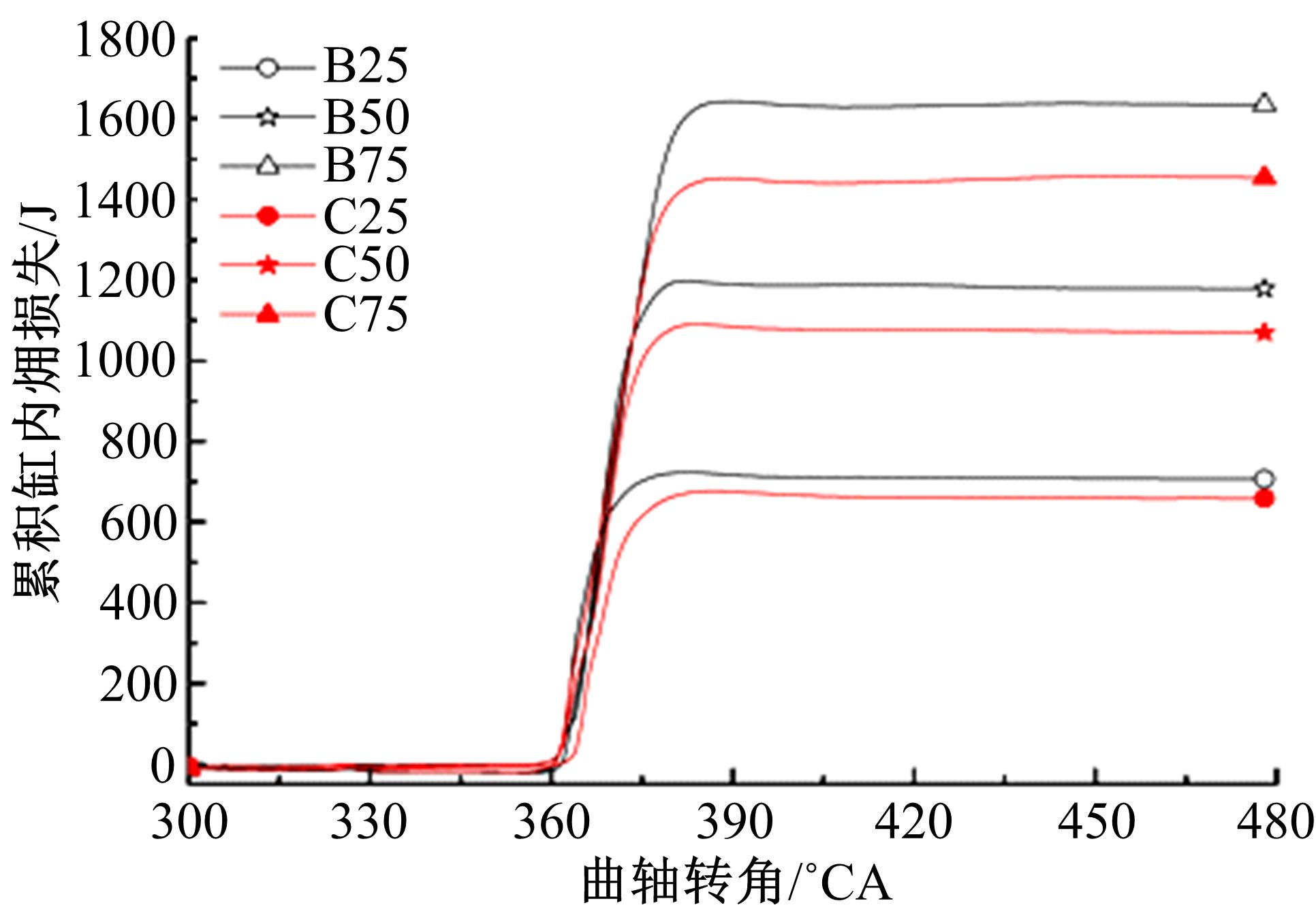
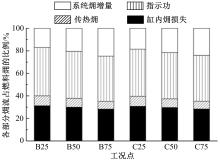
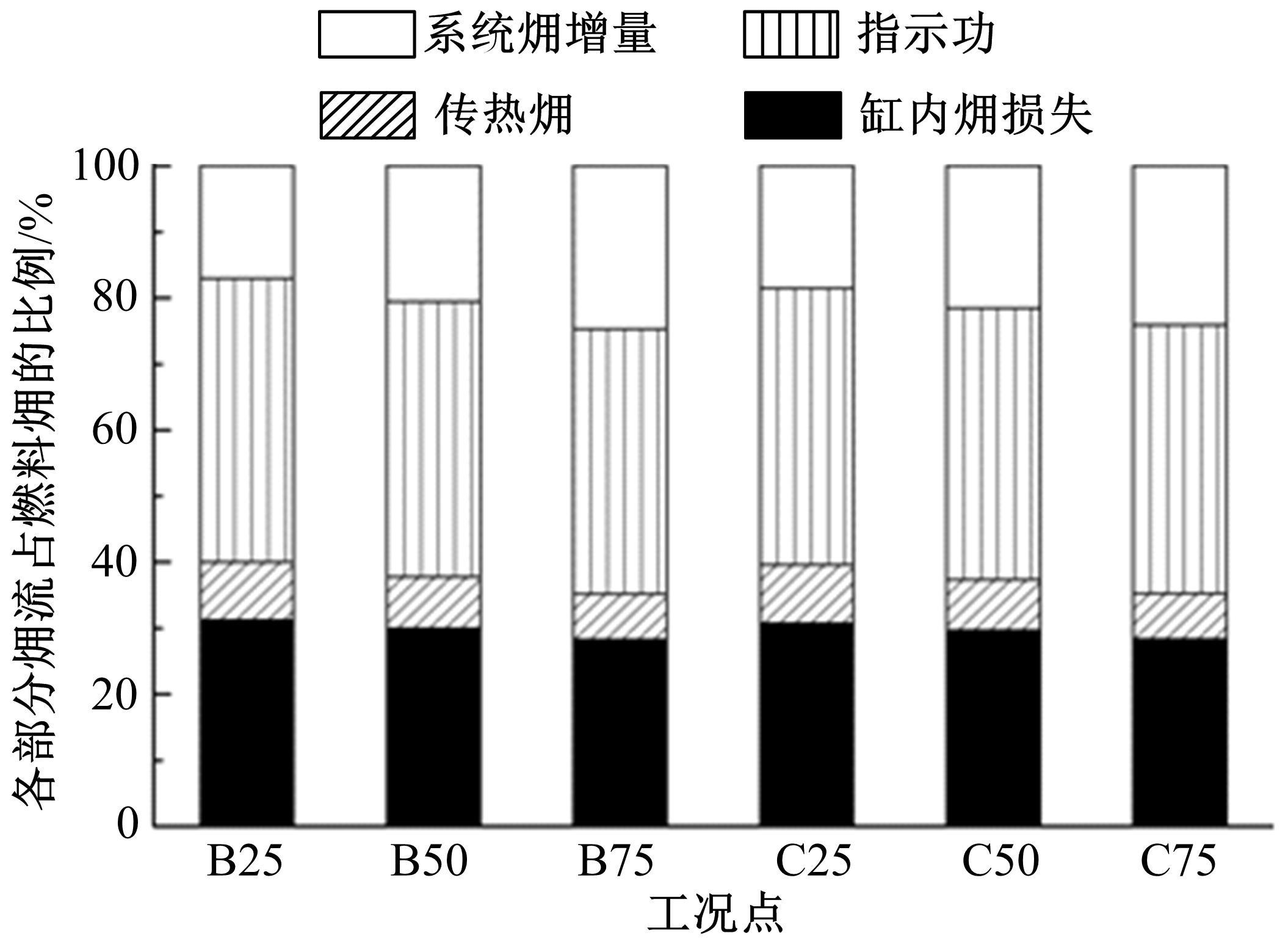
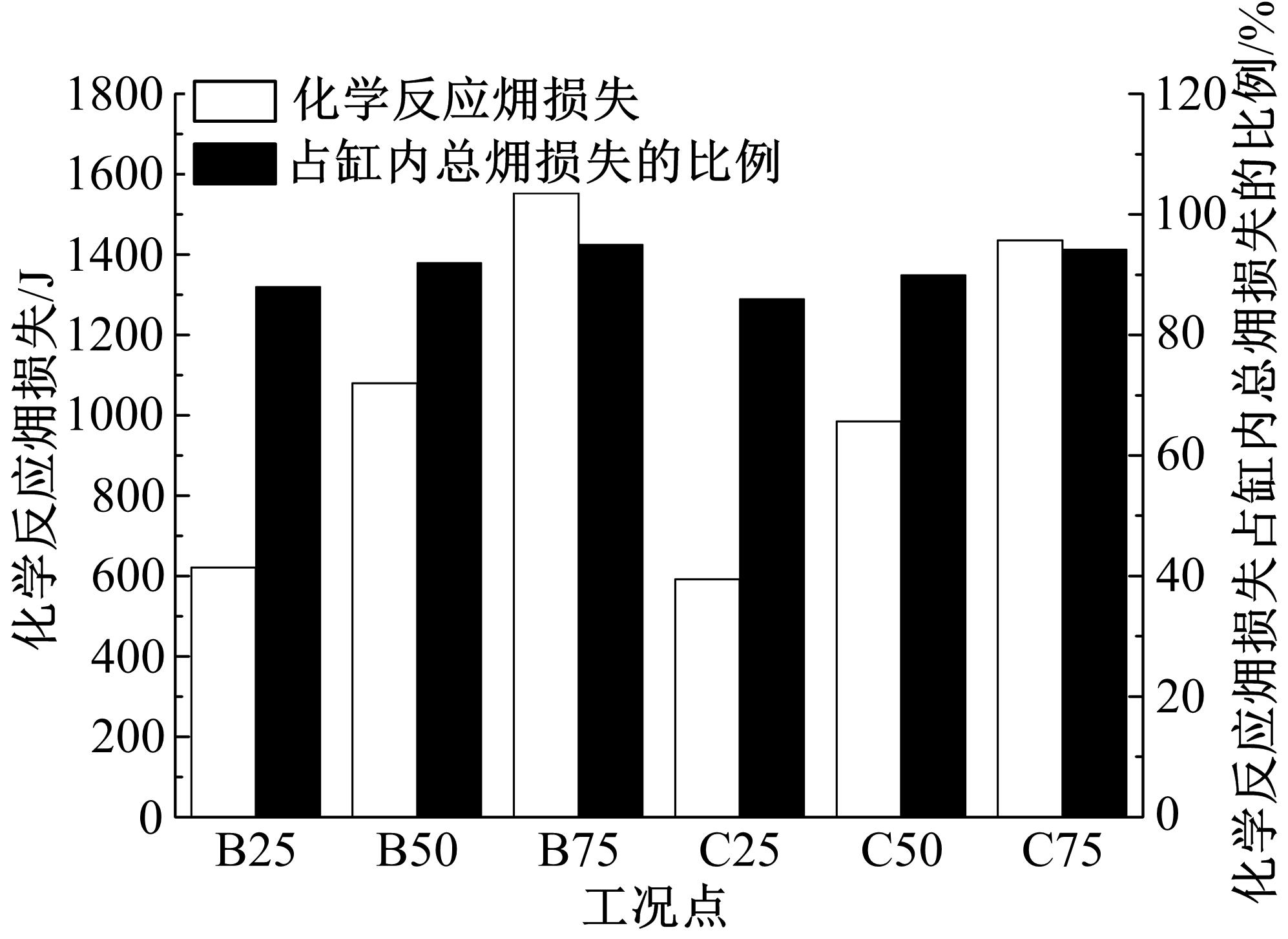
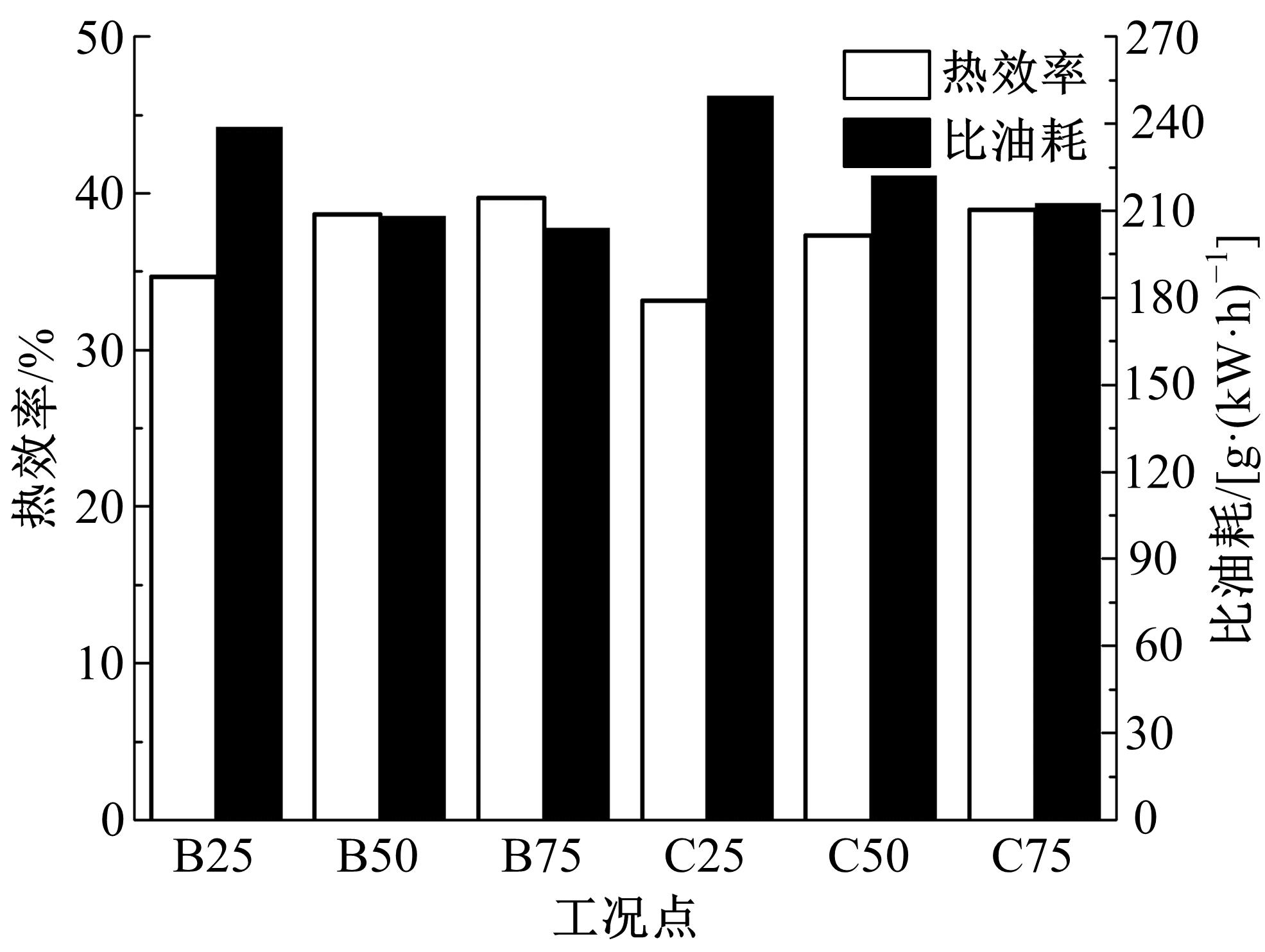
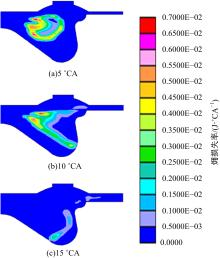
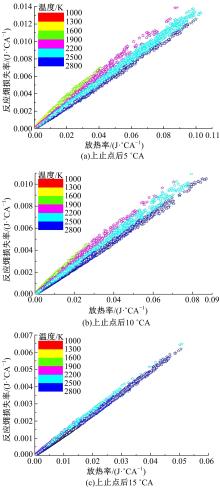
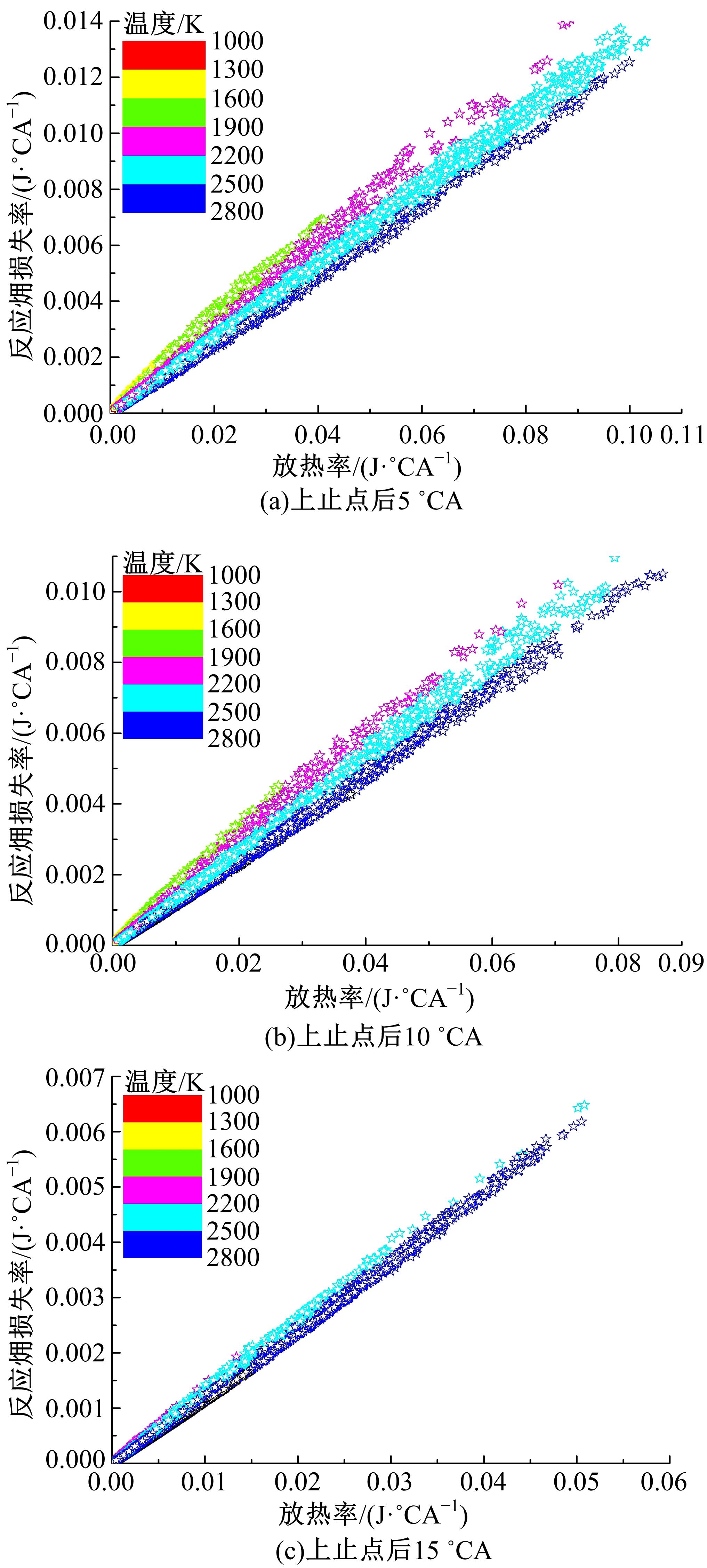
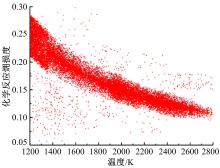
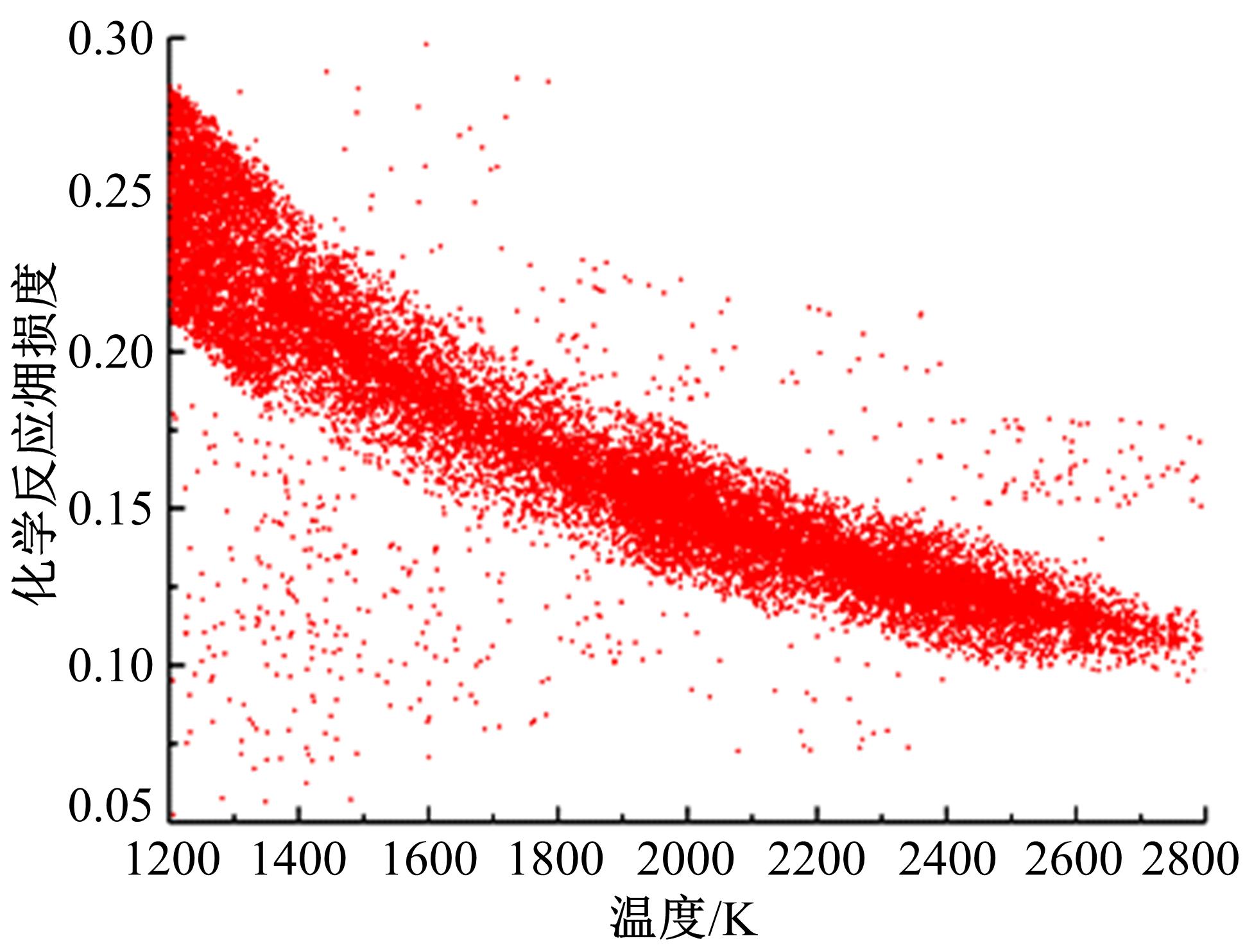
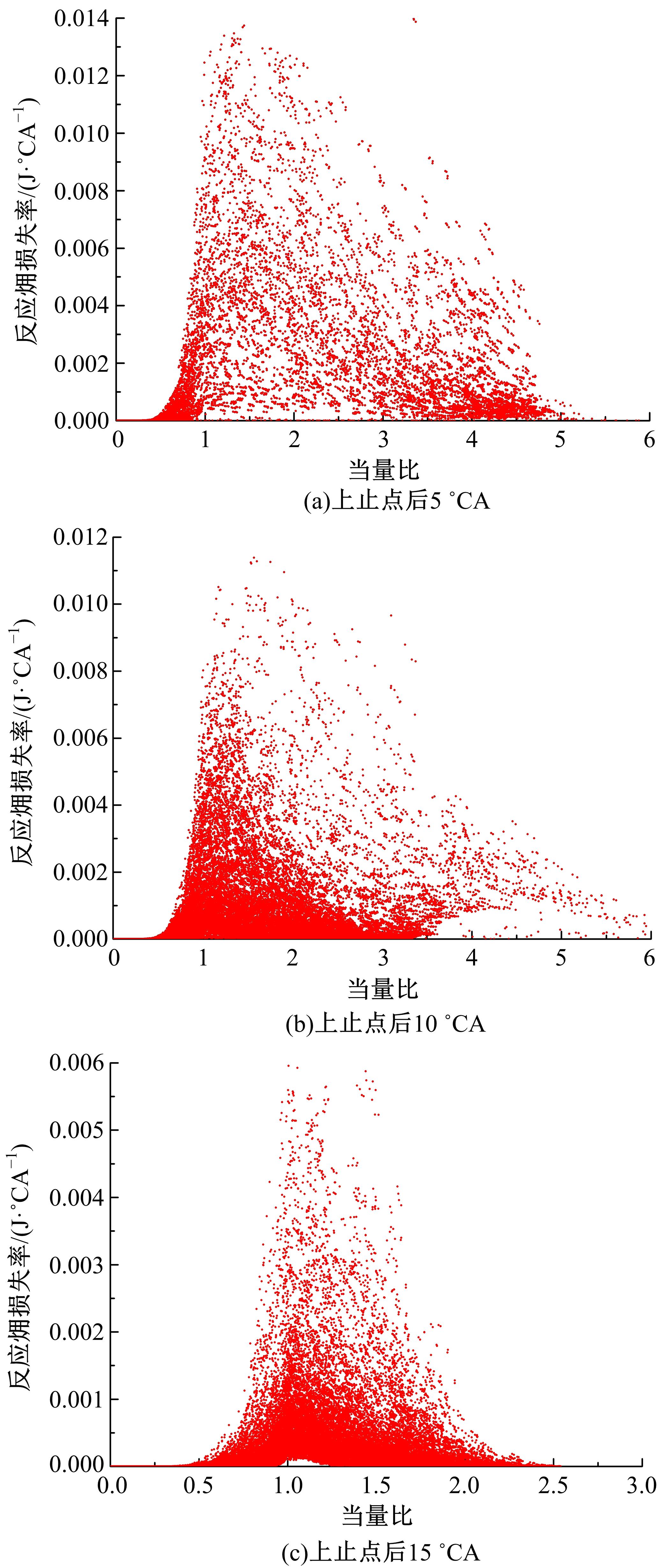
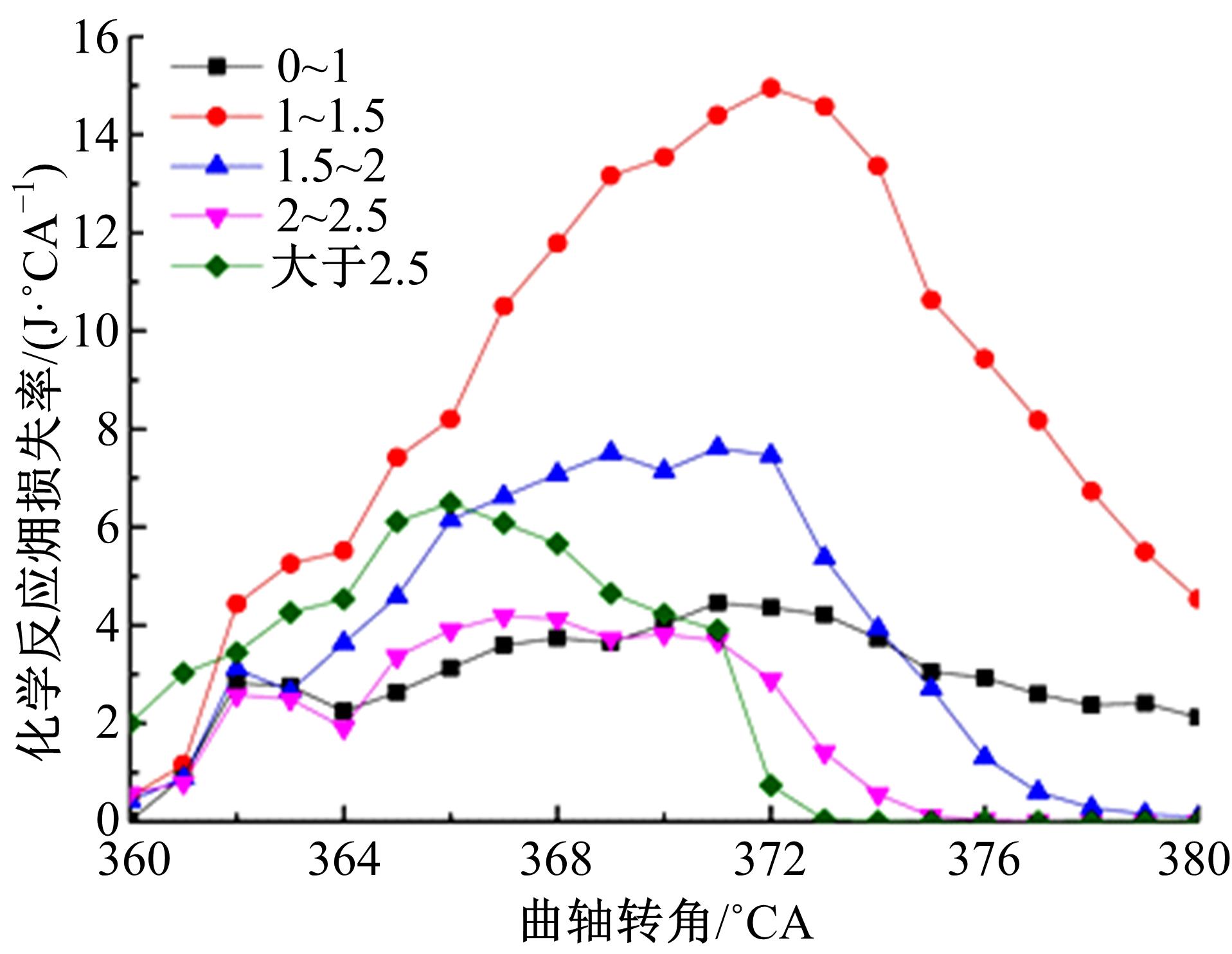
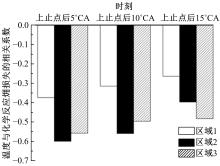
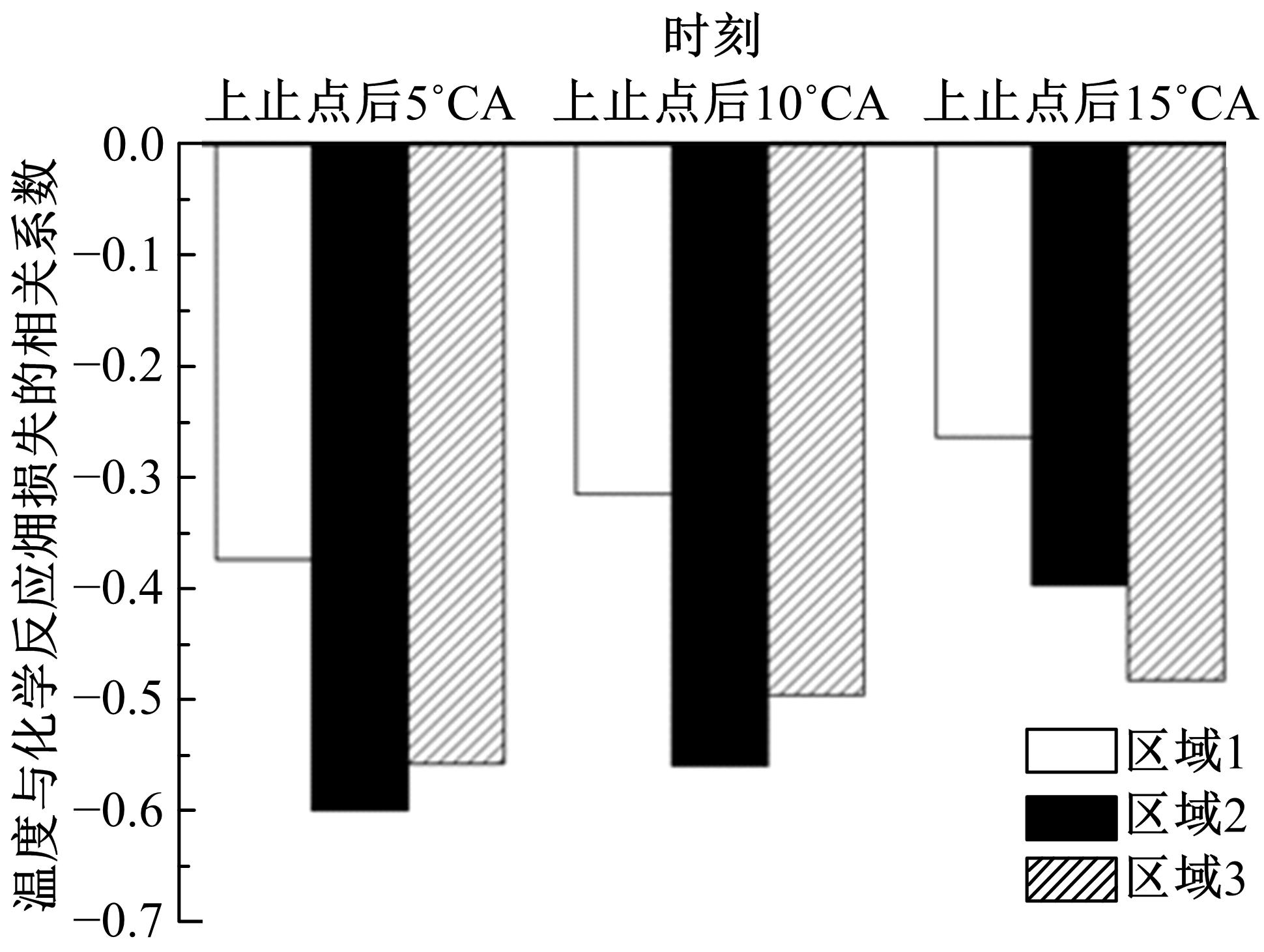
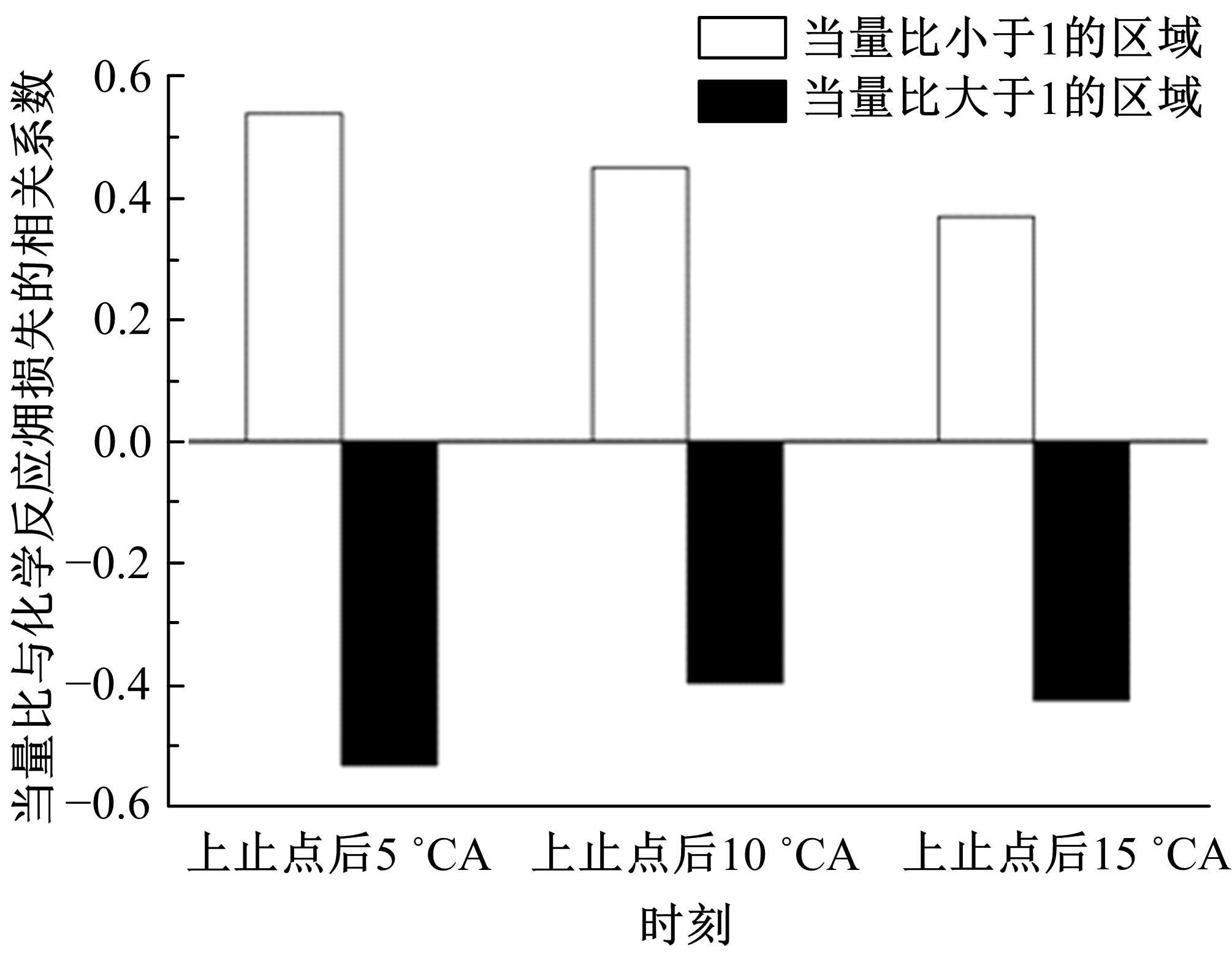
为了探索增压柴油机燃烧过程中缸内?损失分布特征及其影响因素,以某车用重型增压柴油机为研究对象,基于试验平台、STAR-CD计算流体力学软件及其理论,计算分析了特定工况下燃烧过程中的缸内?损失变化规律、分布特征、影响因素及其相关性。结果表明:缸内?损失主要发生在燃烧过程,且化学反应?损失及其所占缸内总?损失的比例正相关于柴油机负荷;柴油机缸内?损失主要由化学反应的不可逆性引起,化学反应引起的?损失多发生在油束边缘附近;最大的化学反应?损失率发生在当量比为1~1.5的区域,而在当量比为0~1的稀混合区及大于1.5的过浓混合区相对偏低;在一定温度范围内化学反应?损失率与燃油放热率基本呈正比关系,在特定放热率区域内,随缸内局部温度的升高,化学反应?损失及化学反应?损度逐渐减少;随燃烧过程的进行,当量比、温度与化学反应?损失的相关强度均逐渐减小。
中图分类号:
- TK421
|
| [1] | 何仁,涂琨. 基于温度补偿气隙宽度的电磁制动器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1777-1785. |
| [2] | 宋昌庆,陈文淼,李君,曲大为,崔昊. 不同当量比下单双点火对天然气燃烧特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1929-1935. |
| [3] | 朱一骁,何小民,金义. 联焰板宽度对单凹腔驻涡燃烧室流线形态的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1936-1944. |
| [4] | 胡潇宇,李国祥,白书战,孙柯,李思远. 考虑加热面粗糙度和材料的沸腾换热修正模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1945-1950. |
| [5] | 段春争,张方圆,寇文能,魏斌. 高速硬切削表面白层马氏体相变[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1575-1583. |
| [6] | 闫光,卢建中,张开宇,孟凡勇,祝连庆. 温度解耦大量程光纤光栅应变传感器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1682-1688. |
| [7] | 王德军,吕志超,王启明,张建瑞,丁建楠. 基于EKF及调制傅式级数的缸压辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1174-1185. |
| [8] | 张艳芹,冯雅楠,孔鹏睿,于晓东,孔祥滨. 基于热油携带的静压支承油膜温度场及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1203-1211. |
| [9] | 臧鹏飞,王哲,高洋,孙晨乐. 直线电机/发动机系统稳态运行综合控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 798-804. |
| [10] | 李于朋,孙大千,宫文彪. 6082⁃T6铝合金薄板双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊温度场[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 836-841. |
| [11] | 李伊,刘黎萍,孙立军. 沥青面层不同深度车辙等效温度预估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1703-1711. |
| [12] | 董伟,宋佰达,邱立涛,孙昊天,孙平,蒲超杰. 直喷汽油机暖机过程中两次喷射比例对燃烧和排放的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1755-1761. |
| [13] | 林学东, 江涛, 许涛, 李德刚, 郭亮. 高压共轨柴油机起动工况高压泵控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1436-1443. |
| [14] | 李志军, 汪昊, 何丽, 曹丽娟, 张玉池, 赵新顺. 催化型微粒捕集器碳烟分布及其影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1466-1474. |
| [15] | 秦静, 徐鹤, 裴毅强, 左子农, 卢莉莉. 初始温度和初始压力对甲烷-甲醇裂解气预混层流燃烧特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1475-1482. |
|