吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1773-1781.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230069
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
泥石流作用下道路结构韧性分析及提升
薛志佳1( ),王召阳1,张久鹏1(
),王召阳1,张久鹏1( ),晏长根1,许子凯1,张英立1,黄晓明2,马涛2
),晏长根1,许子凯1,张英立1,黄晓明2,马涛2
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211189
Toughness analysis and improvement of road structure under action of debris flow
Zhi-jia XUE1( ),Zhao-yang WANG1,Jiu-peng ZHANG1(
),Zhao-yang WANG1,Jiu-peng ZHANG1( ),Chang-gen YAN1,Zi-kai XU1,Ying-li ZHANG1,Xiao-ming Huang2,Tao Ma2
),Chang-gen YAN1,Zi-kai XU1,Ying-li ZHANG1,Xiao-ming Huang2,Tao Ma2
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
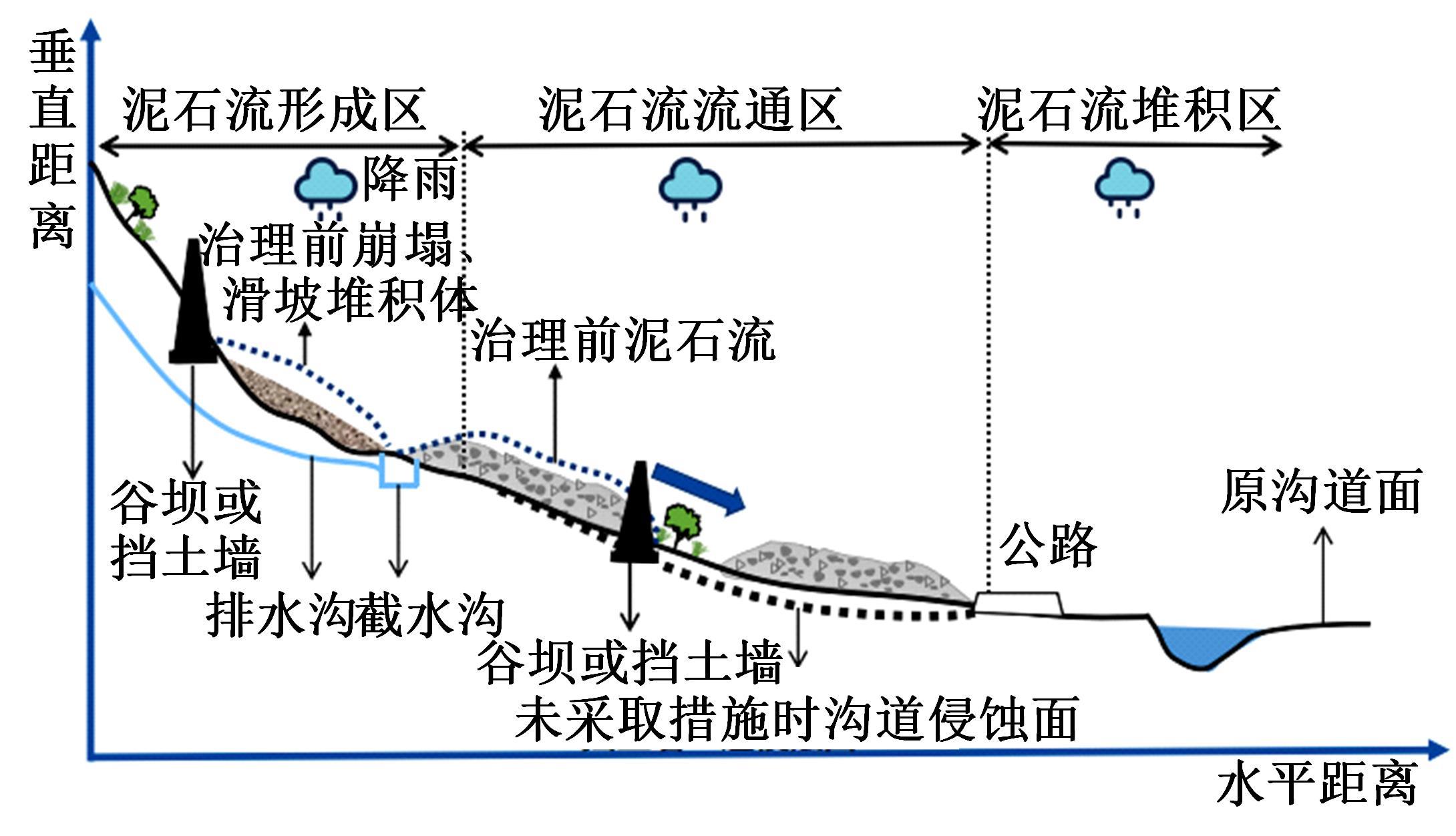
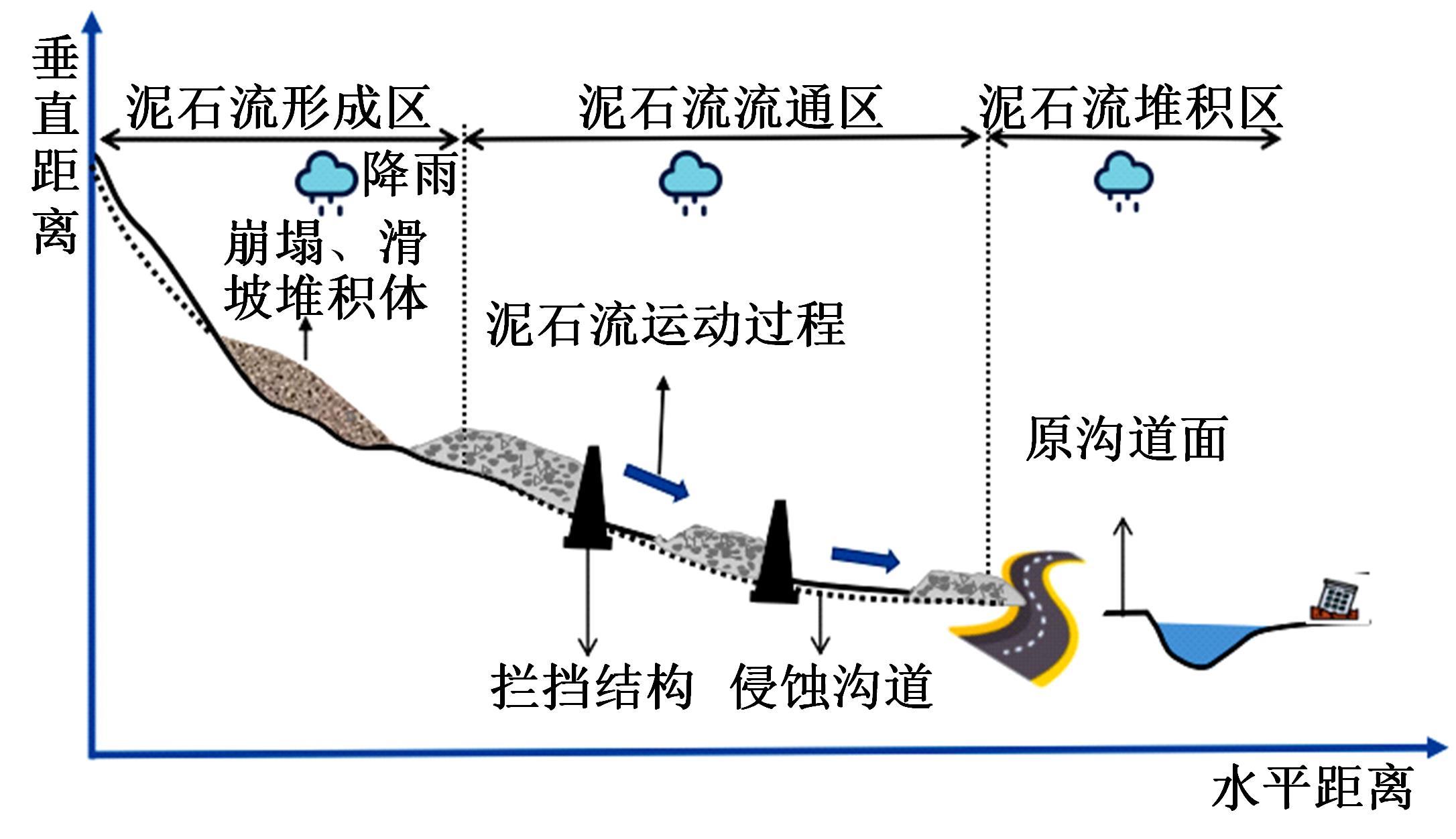
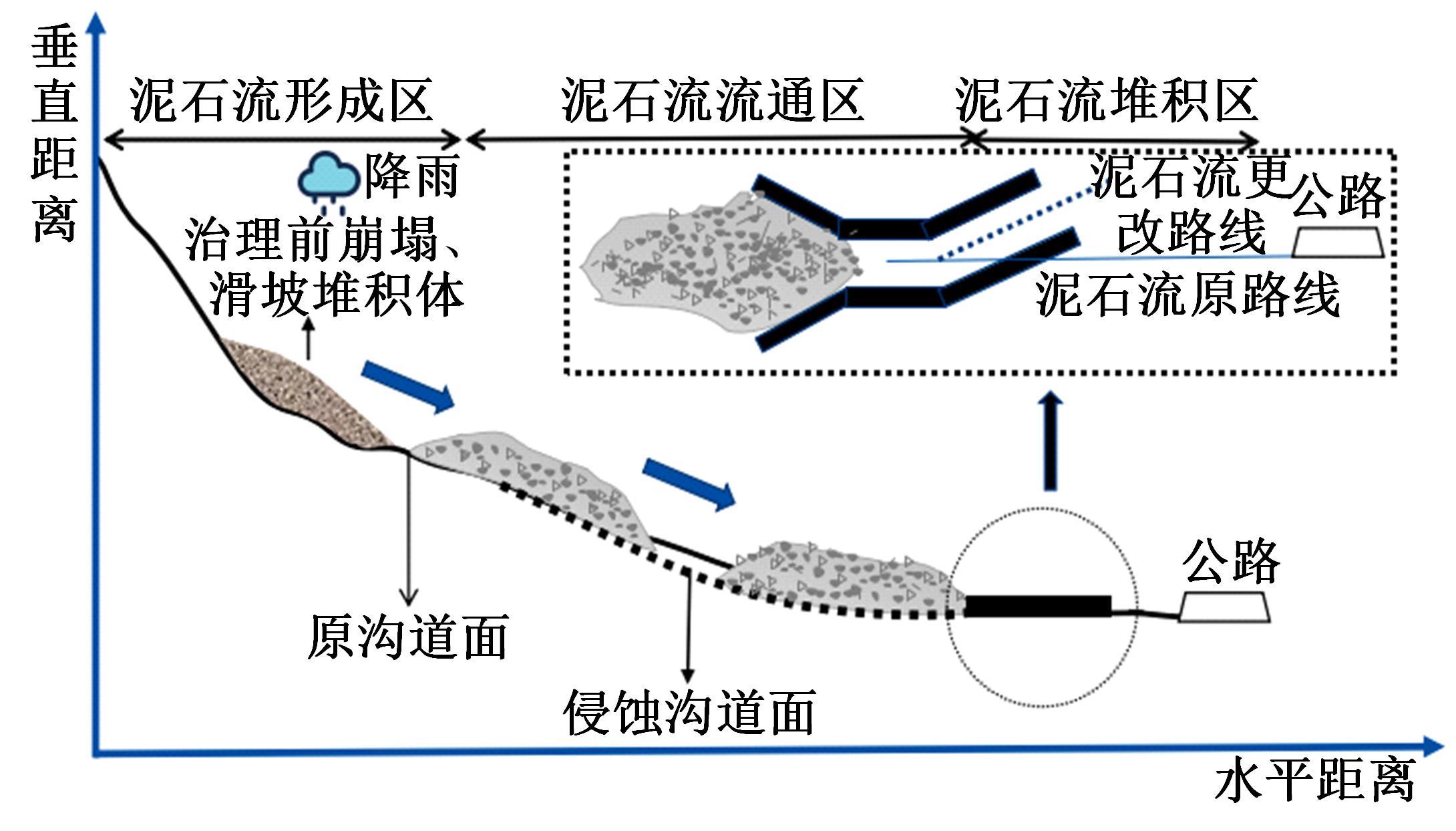
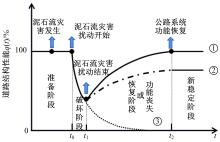
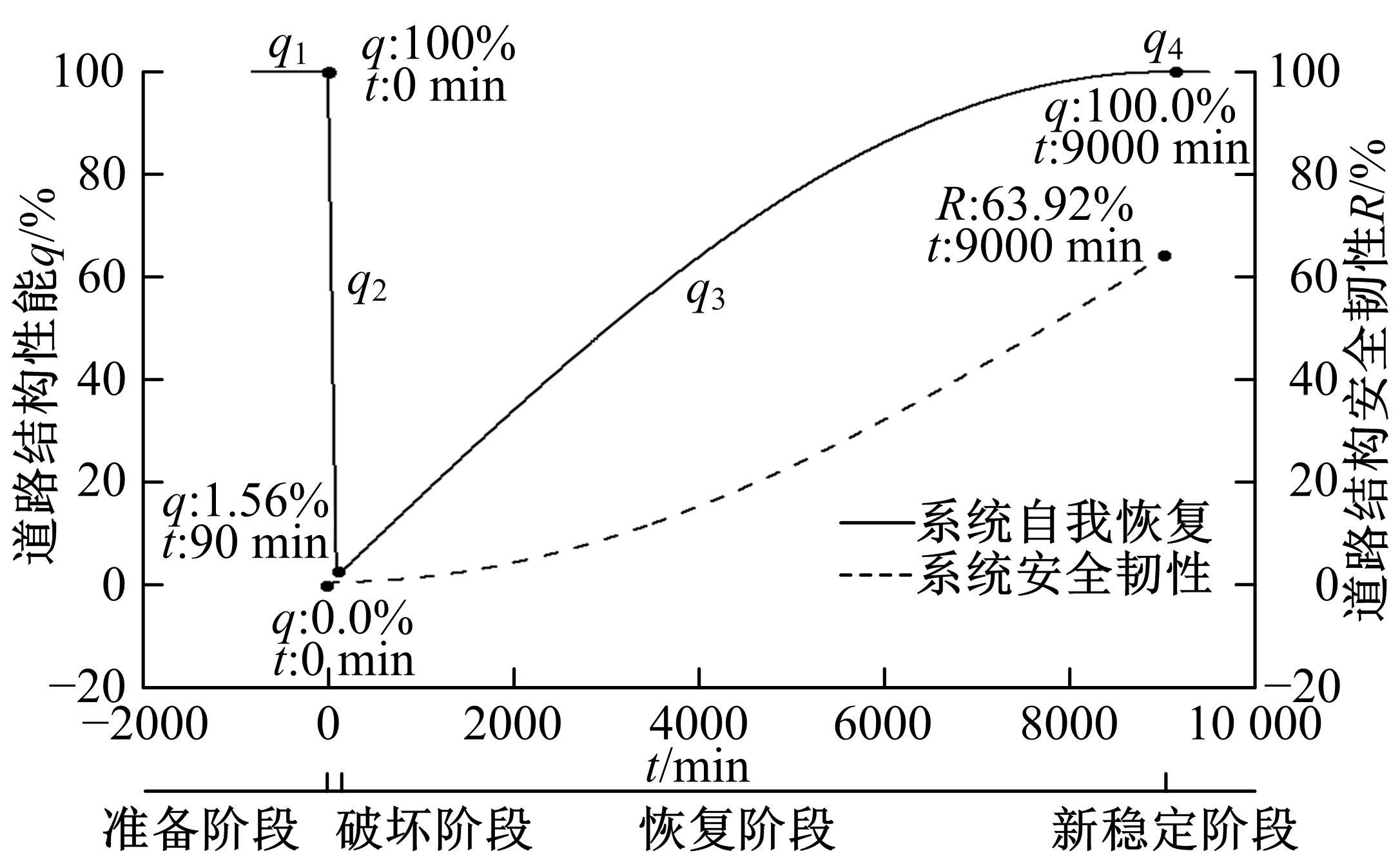
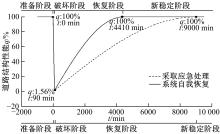
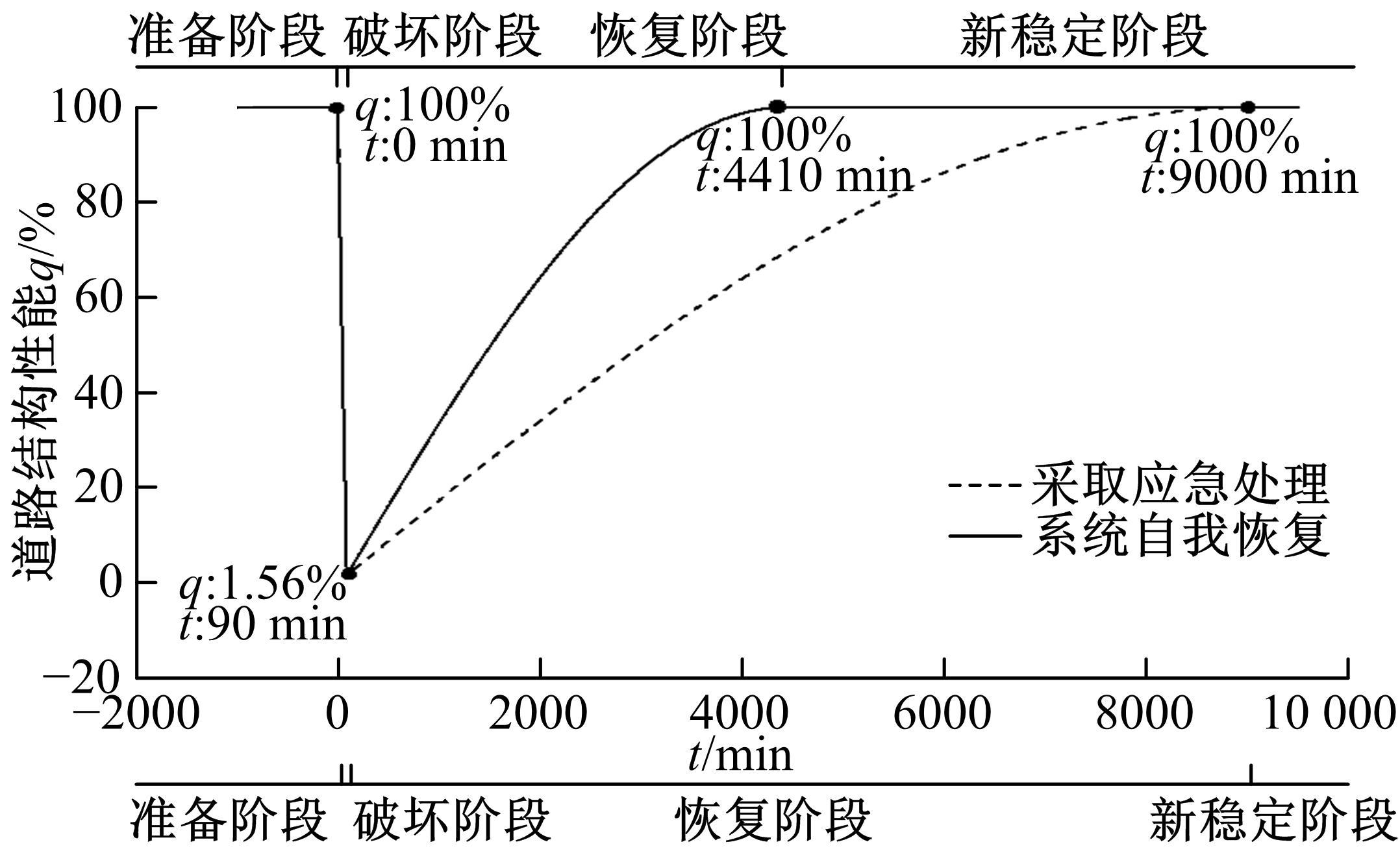
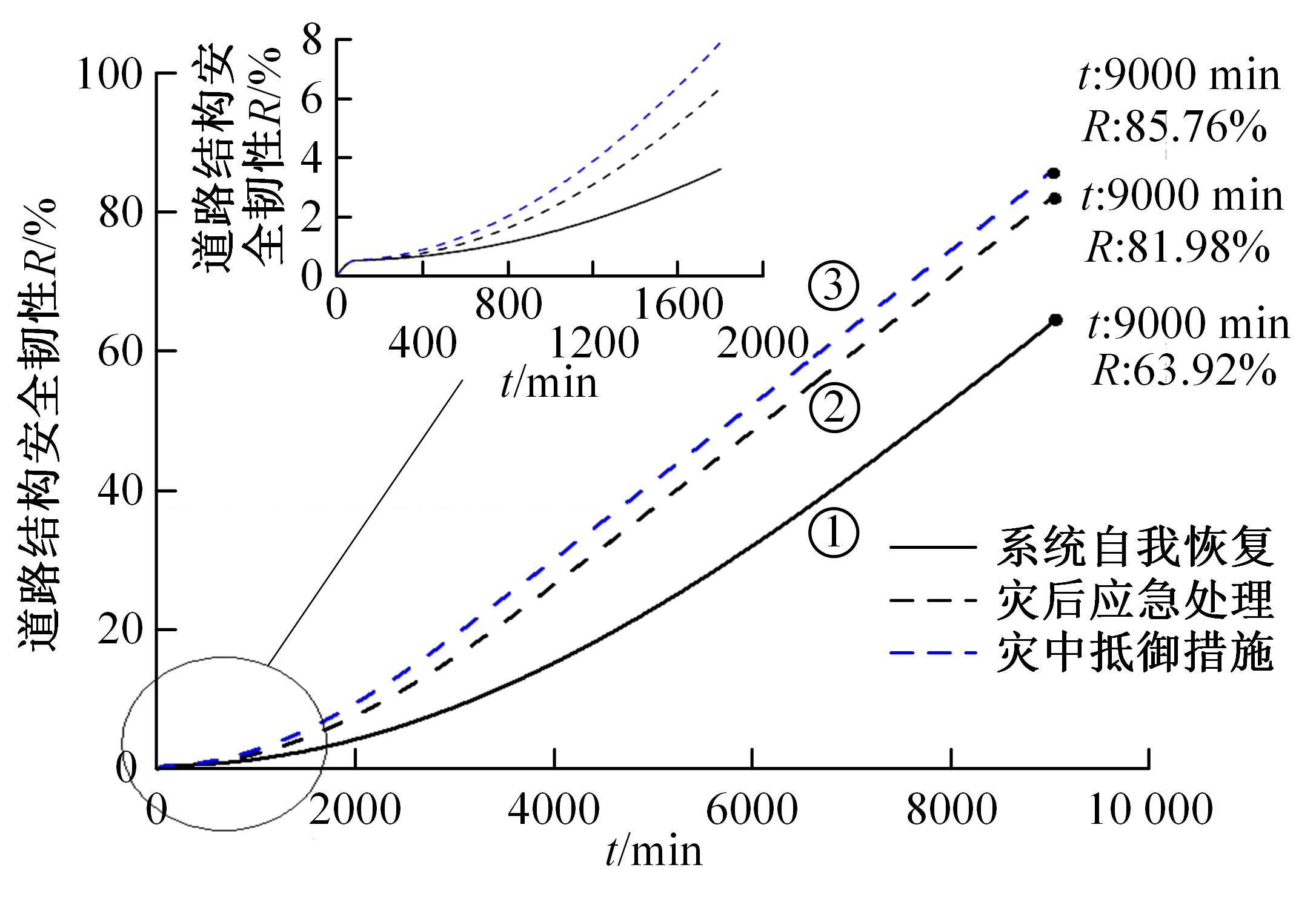
针对道路结构抗灾韧性研究的不足,提出了泥石流冲击和淤埋作用下的道路结构性能响应函数,通过分析泥石流防治特征和道路结构韧性特征对其进行求解,并用泥石流作用后道路结构性能的累积损失程度表征其安全韧性,构建了道路结构安全韧性理论模型。以甘肃省沙湾镇水峪沟泥石流为例,分析了水峪沟国道394 km+800 m处道路结构在自我恢复、灾中采取抵御措施、灾后应急处理3种情况下的韧性曲线和安全韧性。结果表明:未采取任何措施时,道路结构安全韧性值仅为63.92%;而对泥石流灾害采取应急处理后,道路结构应对灾害的能力提升至81.98%;对泥石流采取抵御措施后,道路结构应对灾害的能力进一步提升至85.76%,韧性得到了明显提升。本文研究成果量化了泥石流作用下道路结构的抵抗力和恢复力,可为提升泥石流作用下的道路结构韧性提供决策依据。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 刘坤. 我国基础设施整体水平跨越式提升[N]. 光明日报, 2022-09-27. |
| 2 | 黄琦, 谢涛, 陈欢欢, 等. 2020年8月甘肃武都群发泥石流基本特征及减灾建议[J]. 公路, 2022, 67(9): 30-37. |
| Huang Qi, Xie Tao, Chen Huan-huan, et al. Basic characteristics of mass debris flows in wudu, gansu province in august 2020 and suggestions for disaster reduction[J]. Highway, 2022, 67(9): 30-37. | |
| 3 | 马敏, 胡大伟, 舒兰, 等. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| Ma Min, Hu Da-wei, Shu Lan, et al. Resilience assessment and recovery strategy analysis of urban rail transit network[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. | |
| 4 | 殷凯. 城市交通网络韧性综合评估研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输工程学院, 2021. |
| Yin Kai. Research on comprehensive assessment of urban transport network resilience [D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2021. | |
| 5 | Bruneau M, Chang S E, Eguchi R T. A framework to quantitatively assess and enhance the seismic resilience of communities[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 2003, 19(4): 733-752. |
| 6 | 唐少虎, 朱伟, 程光, 等. 暴雨内涝下城市道路交通系统安全韧性评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7): 143-150. |
| Tang Shao-hu, Zhu Wei, Cheng Guang, et al. Assessment of urban road traffic system safety resilience under rainstorm and water logging[J]. Chinese Journal of Safety Science, 2022, 32(7): 143-150. | |
| 7 | Cimellaro G P, Reinhorn A M, Bruneau M. Seismic resilience of a hospital system[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering, 2010, 6(1/2): 127-144. |
| 8 | 刘杰. 泥石流路基破坏机理与拦挡结构设计研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学交通运输工程学院, 2018. |
| Liu Jie. Research on damage mechanism of debris flow subgrade and design of retaining structure[D]. Chongqing: College of Transportation Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2018. | |
| 9 | 王林峰, 唐红梅, 陈洪凯. 泥石流冲击作用下路基的毁损机制研究[J]. 公路, 2011(11): 31-35. |
| Wang Lin-feng, Tang Hong-mei, Chen Hong-kai. Research on damage mechanism of subgrade under debris flow impact[J]. Highway, 2011(11): 31-35. | |
| 10 | 沈志红. 泥石流堆积区对公路工程的影响[D]. 西安:长安大学公路学院, 2010. |
| Shen Zhi-hong. Impact of debris flow accumulation area on highway engineering[D]. Xi'an: College of Highway, Chang'an University, 2010. | |
| 11 | 胡涛. 汶川震区震后大型泥石流致灾机理及防治对策研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学地质勘察学院, 2017. |
| Hu Tao. Research on the disaster mechanism and prevention countermeasures of large-scale debris flow after the Wenchuan earthquake[D]. Chengdu: College of Geological Exploration, Chengdu University of Technology, 2017. | |
| 12 | 冯明硕. 干旱半干旱地区暴雨型稀性泥石流运动学特征及防治研究[D]. 西安:长安大学水资源与环境学院, 2007. |
| Feng Ming-shuo. Study on the kinematic characteristics and prevention of rainstorm type rare debris flow in arid and semi arid areas[D]. Xi'an: College of Water Resources and Environment, Chang'an University, 2007. | |
| 13 | 罗恒. 云南省元谋县城泥石流治理工程效果评价[D]. 成都:成都理工大学地质勘察学院, 2018. |
| Luo Heng. Effect evaluation of debris flow control project in yuanmou county, yunnan province[D]. Chengdu: College of Geological Exploration, Chengdu University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 14 | 陈娱. 大箐泥石流对桥墩的冲击动力作用及灾害治理措施研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学国土资源学院, 2017. |
| Chen Yu. Research on impact dynamic effect of daqing debris flow on piers and disaster control measures[D]. Kunming: College of Land and Resources, Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2017. | |
| 15 | 瞿华南. 考虑坝后淤积作用下的泥石流冲击拦挡坝动力响应研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学地质勘查学院, 2021. |
| Qu Hua-nan. Study on the dynamic response of debris flow impacting the retaining dam under the consideration of sedimentation behind the dam[D]. Chengdu: College of Geological Exploration, Chengdu University of Technology, 2021. | |
| 16 | 杨再智. 云南大盈江浑水沟泥石流防治工程效益分析[D]. 昆明: 云南大学生态与环境学院, 2021. |
| Yang Zai-zhi. Benefit analysis of debris flow control project in Hunshui gully of Daying River in Yunnan[D]. Yunnan: School of Ecology and Environment, Yunnan University, 2021. | |
| 17 | 张文涛. 泥石流防治岩土-生态工程综合治理效果分析与评价[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学建筑与土木工程学院, 2021. |
| Zhang Wen-tao. Analysis and evaluation of comprehensive control effect of geotechnical ecological engineering for debris flow control[D]. Beijing: School of Architecture and Civil Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021. | |
| 18 | 熊木齐, 郭富赟, 崔志杰, 等. 甘肃省武都区马槽沟泥石流特征及其治理工程效应[J]. 兰州大学学报, 2015, 51(6): 831-836. |
| Xiong Mu-qi, Guo Fu-yun, Cui Zhi-jie, et al. Characteristics of debris flow in Machao valley, Wudu district, Gansu province and its control engineering effects[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University, 2015, 51(6): 831-836. | |
| 19 | 周海波, 陈宁生, 卢阳, 等. 泥石流沟谷坊坝群治理效应——以地震极重灾区北川县化石板沟为例[J]. 山地学报, 2012, 30(3): 347-354. |
| Zhou Hai-bo, Chen Ning-sheng, Lu Yang, et al. The harnessing effect of debris flow gullies and gufang dams—taking Huashiban Gully in Beichuan County, a severely earthquake stricken area, as an example[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2012, 30(3): 347-354. | |
| 20 | 李彪. G310线牛背至麦积公路泥石流灾害处治设计研[J]. 甘肃科技, 2018, 34(16): 39-40. |
| Li Biao. Research on design of debris flow disaster treatment for Niubei Maiji Highway of G310 Line[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2018, 34 (16): 39-40. | |
| 21 | 王天健, 胡桂胜, 陈宁生, 等. 泥石流单双边防护堤防治效果对比——以曾达沟为例[J]. 防灾减灾学报, 2022, 38(1): 1-8. |
| Wang Tian-jian, Hu Gui-sheng, Chen Ning-sheng, et al. Comparison of prevention and control effects of single and bilateral protective dikes for debris flow—taking Zengda valley as an example[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Reduction, 2022, 38(1): 1-8. | |
| 22 | Nipa T J, Kermanshachi S. Resilience measurement in highway and roadway infrastructures: experts' perspectives[J]. Progress in Disaster Science, 2022, 14: No.100230. |
| 23 | Ouyang M, Dueñas-Osorio L, Min X. A three-stage resilience analysis framework for urban infrastructure systems[J]. Structural Safety, 2012, 36/37: 23-31. |
| 24 | 黄弘, 李瑞奇, 秦挺鑫, 等. 安全韧性城市评价模型与方法研究[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2021. |
| 25 | 陈洪凯, 唐红梅. 泥石流两相冲击力及冲击时间计算方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2006, 19(3): 19-23. |
| Chen Hong-kai, Tang Hong-mei. Mud-rock flow of two phase impact force and impact time calculation method[J]. China Journal of Highway, 2006, 19(3): 19-23. | |
| 26 | 陇南发布. 陇南交通路况信息[DB/OL]. [2023-01-15]. |
| 27 | 梁梦辉, 向灵芝, 沈娜, 等. 白龙江流域水峪沟泥石流危险性分析[J]. 路基工程, 2022(6): 214-219. |
| Liang Meng-hui, Xiang Ling-zhi, Shen Na, et al. Hazard analysis of debris flow in Shuiyu valley of Bailong river basin[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2022(6): 214-219. | |
| 28 | 高路. 四川省九寨沟县牙屯沟泥石流灾害防治研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学地质勘查学院, 2011. |
| Gao Lu. Research on the prevention and control of debris flow in Yatun gully, Jiuzhaigou county, Sichuan province[D]. Chengdu: College of Geological Exploration, Chengdu University of Technology, 2011. | |
| 29 | 刘传正, 苗天宝, 陈红旗, 等. 甘肃舟曲2010年8月8日特大山洪泥石流灾害的基本特征及成因[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(1): 141-150. |
| Liu Chuan-zheng, Miao Tian-bao, Chen Hong-qi, et al. Basic characteristics and causes of the catastrophic mountain torrents and debris flows on August 8, 2010 in Zhouqu, Gansu[J]. Bulletin Geological, 2011, 30(1): 141-150. |
| [1] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [2] | 程国柱,盛林,赵浩,冯天军. 基于危险度分析的信号交叉口专用相位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1962-1969. |
| [3] | 何永明,陈世升,冯佳,万亚楠. 基于高精地图的超高速公路虚拟轨道系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2016-2028. |
| [4] | 黄晓明,赵润民. 道路交通基础设施韧性研究现状及展望[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1529-1549. |
| [5] | 刘振亮,赵存宝,吴云鹏,马迷娜,马龙双. 数据驱动的公路桥梁网络全寿命抗震韧性评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1695-1701. |
| [6] | 贾洪飞,徐英俊,杨丽丽,王楠. 商品车多式联运联盟成员选择及利益分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [7] | 常玉林,徐文倩,孙超,张鹏. 车联网环境下考虑遵从程度的混合流量逐日均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1085-1093. |
| [8] | 孙超,尹浩为,汤文蕴,褚昭明. 交通需求估计下的检测器布局和手机数据扩样推断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1070-1077. |
| [9] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [10] | 肖雪,李克平,彭博,昌满玮. 基于决策-规划迭代框架的智驾车换道行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 746-757. |
| [11] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [12] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [13] | 黄文博,陈艳艳,柴树山. 手机信息干预下寒冷赛区行人候车决策行为[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 132-140. |
| [14] | 卢辉遒,赵枫,谢波,田彦涛. 冰雪环境下基于神经网络的驾驶人换道意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 273-284. |
| [15] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
|
||