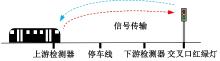
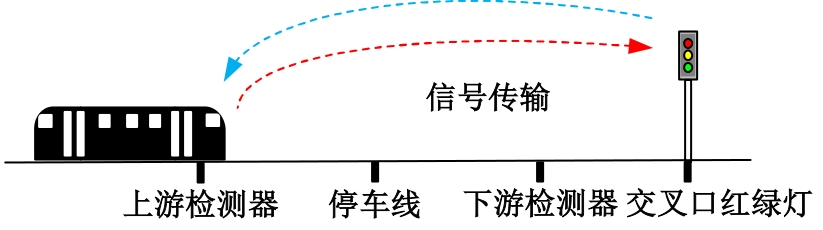
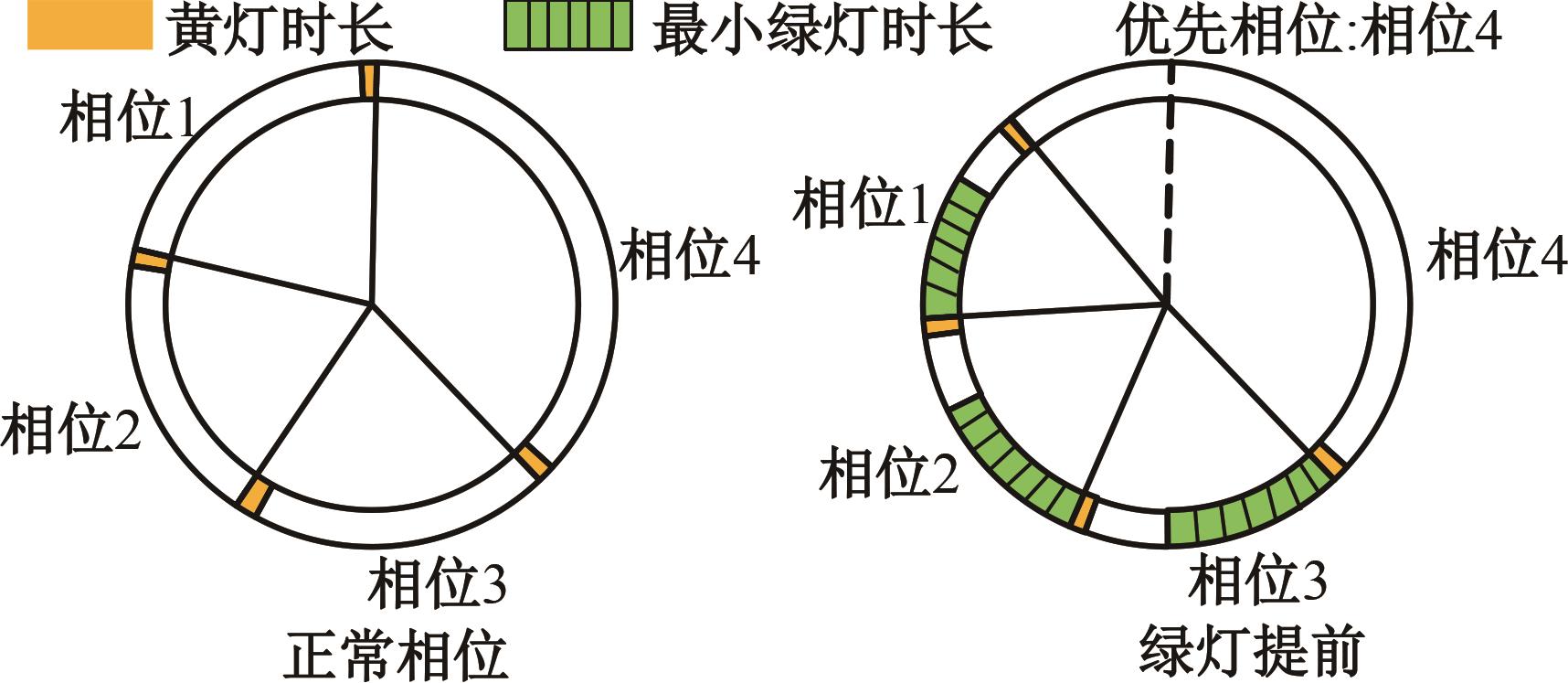
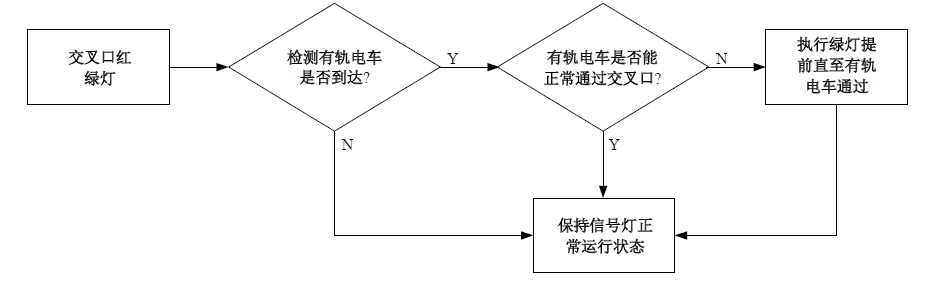
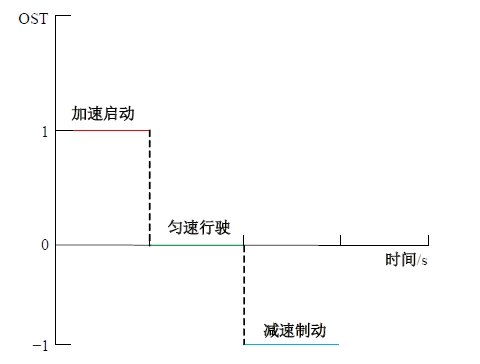
吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1176-1187.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230762
半独立路权下考虑锂电池SoC预测的有轨电车自适应能量管理策略
高锋阳1( ),高智山1,杨雨泽2,强雅昕1,徐昊1,史志龙1,张浩然3
),高智山1,杨雨泽2,强雅昕1,徐昊1,史志龙1,张浩然3
- 1.兰州交通大学 自动化与电气工程学院,兰州 730070
2.中车唐山机车车辆有限公司,河北 唐山 063035
3.铁科院(深圳)研究设计院有限公司,广东 深圳 518000
Adaptive energy management strategy for trams considering lithi-um battery SoC prediction under semi-independent right-of-way
Feng-yang GAO1( ),Zhi-shan GAO1,Yu-ze YANG2,Ya-xin QIANG1,Hao XU1,Zhi-long SHI1,Hao-ran ZHANG3
),Zhi-shan GAO1,Yu-ze YANG2,Ya-xin QIANG1,Hao XU1,Zhi-long SHI1,Hao-ran ZHANG3
- 1.Automation and Electrical Engineering,Lanzhou Jiaotong University,Lanzhou 730070,China
2.CRRC Tangshan Co. ,Ltd. ,Tangshan 063035,China
3.China Academy of Railway Sciences (Shenzhen) Research and Design Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Shenzhen 518000,China
摘要:
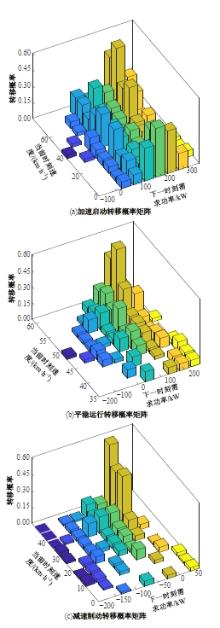
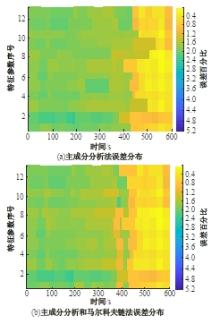
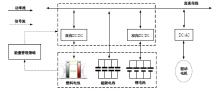
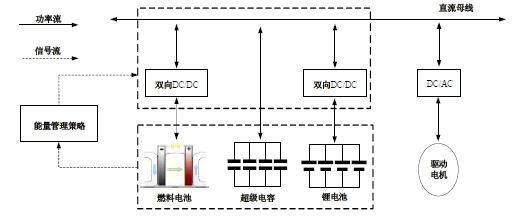
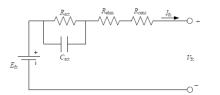
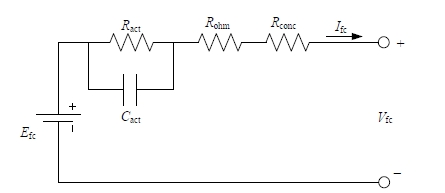
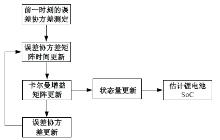
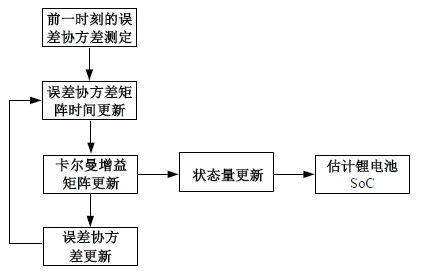
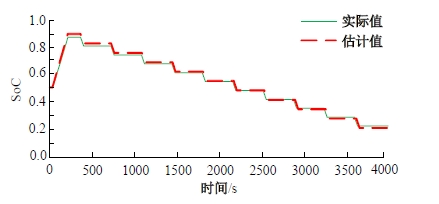
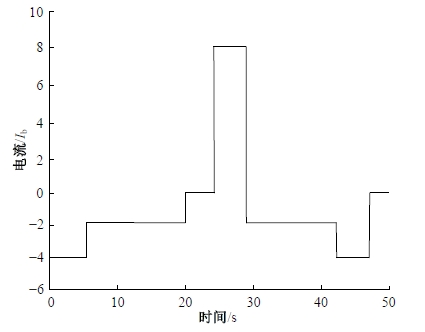
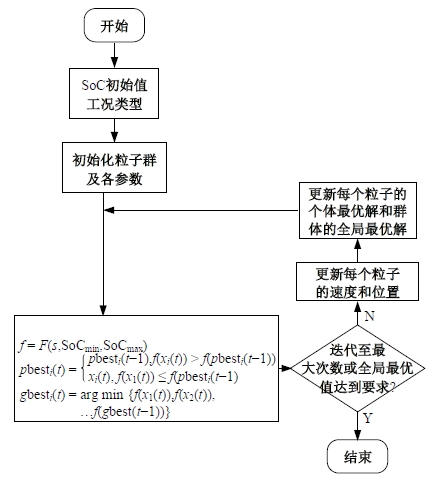
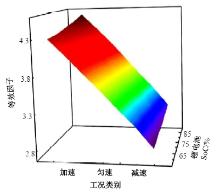
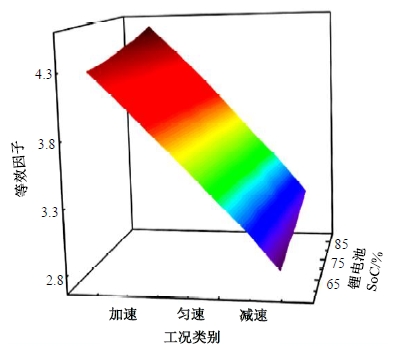
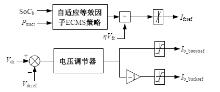
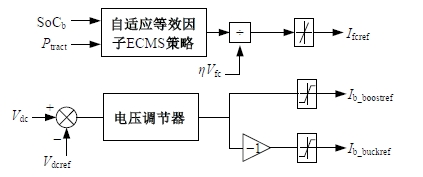
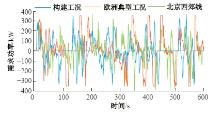
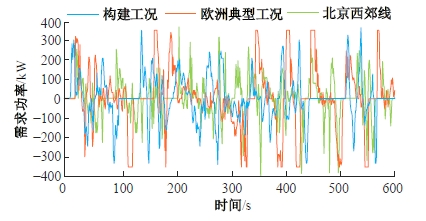
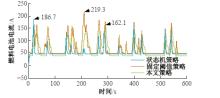
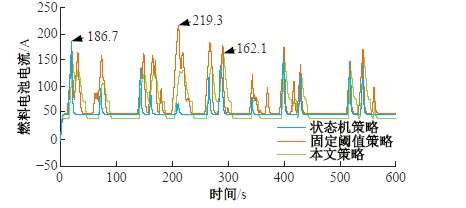
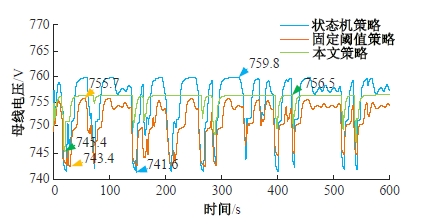
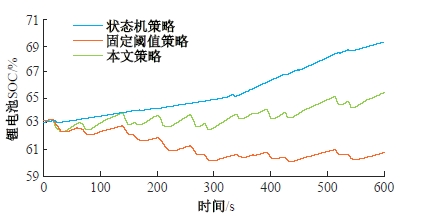
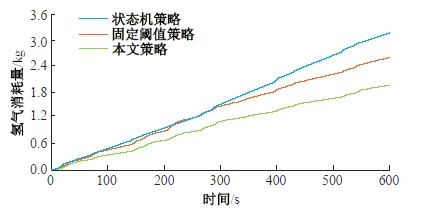
为改善传统等效氢耗最小化策略(ECMS)工况适应性差的缺陷,同时进一步提升混合储能系统燃料经济性,提出了一种考虑锂电池荷电状态(SoC)预测的自适应能量管理策略。首先,以国内有轨电车线路及行驶数据为基础,利用马尔科夫链构建半独立路权下有轨电车典型行驶工况。其次,通过自适应卡尔曼滤波法预测锂电池SoC,优化锂电池充、放电过程,增强锂电池可靠性,并以混合储能系统等效能耗最小为优化目标,同时结合粒子群算法优化传统ECMS等效因子,实现负载功率在燃料电池和锂电池间的合理有效分配。最后,在所构建半独立路权下有轨电车典型工况中进行对比分析。结果表明:在所构建典型工况中,本文策略相较于固定阈值策略氢气消耗降低0.63 kg,燃料电池峰值电流降低57.2 A;相较于状态机策略氢气消耗降低1.21 kg,燃料电池峰值电流降低24.6 A,且母线电压及锂电池SoC波动范围均有所改善。
中图分类号:
- U482.1
| [1] | 高锋阳, 强雅昕, 高智山, 等. 在线和离线控制相结合的燃料电池有轨电车能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024, 54(10): 3064-3076. |
| Gao Feng-yang, Qiang Ya-xin, Gao Zhi-shan, et al. Combined online and offline control for fuel cell tram energy management strategy[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition) 2024, 54(10): 3064-3076. | |
| [2] | Olatomiwa L, Mekhilef S, Ismail M S, et al. Energy management strategies in hybrid renewable energy systems: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 62: 821-835. |
| [3] | Alla J, Streit L, Peroutka Z, et al. Position based T-S fuzzy power management for tram withenergy storage system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(5): 3061-3071. |
| [4] | 刘炳姣, 石琴, 仇多洋, 等. 基于改进蚁群算法的行驶工况构建及精度分析[J]. 合肥工业大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 40(10): 1297-1302. |
| Liu Bing-jiao, Shi Qin, Qiu Duo-yang, et al. Drivingcycle construction based on improved ant colony optimization algorithm and precision analysis[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology(Natural Science), 2017, 40(10): 1297-1302. | |
| [5] | Brady J, O'mahony M. Development of a driving cycle to evaluate the energy economy of electric vehicles in urban areas[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 177: 165-178. |
| [6] | 林泓涛, 姜久春, 贾志东, 等. 权重系数自适应调整的混合储能系统多目标模型预测控制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(18): 5538-5547. |
| Lin Hong-tao, Jiang Jiu-chun, Jia Zhi-dong, et al. Multi-objective model predictive control for hybrid energy storage system with adaptive adjustment of weight coefficients[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2018, 38(18): 5538-5547. | |
| [7] | 高锋阳, 张国恒, 石岩, 等. 新型城轨电车混合动力系统能量管理策略[J]. 铁道学报, 2019, 41(4): 48-54. |
| Gao Feng-yang, Zhang Guo-heng, Shi Yan, et al. Energy management strategy of hybrid power system of new urban rail transit[J]. Railway Transaction, 2019, 41(4): 48-54. | |
| [8] | Xiong R, Cao J Y, Yu Q Q. Reinforcement learning-based real-time power management for hybrid energy storage system in the plug-in hybrid electric vehicle[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 211: 538-548. |
| [9] | Bhattacharyy A K, Maitra B, Boltze M. Implementation of bus priority with queue jump lane and pre-signal at urban intersections with mixed traffic operations: lessons learned?[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2019, 2673(3): 646-657. |
| [10] | 周洋帆, 贾顺平, 陈绍宽, 等. 有轨电车信号优先时长阈值优化模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2016, 16(5): 151-158. |
| Zhou Yang-fan, Jia Shun-ping, Chen Shao-kuan, et al. Optimization model signal priority time threshold of tram[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering and Development, 2016, 16(5): 151-158. | |
| [11] | 王云鹏, 郭戈. 基于深度强化学习的有轨电车信号优先控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2366-2377. |
| Wang Yun-peng, Guo Ge. Signal priority control for trams using deep reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2366-2377. | |
| [12] | Sermpis D, Papadakos P, Fousekis K. Tram priority atsignal-controlled junctions[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers Transport, 2012, 165(2):87-96. |
| [13] | Xu Q, Zhang C, Xu Z, et al. A composite finite-time controller for decentralized power sharing and stabilization of hybrid fuel cell/supercapacitor system with constant power load[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(2): 88-100. |
| [14] | Bishop J D K, Axon C J, Mcculloch M D. A robust, data-driven methodology for real-world driving cycle development[J]. Transportation Research, part D: Transport and Environment, 2012, 17(5):389-397. |
| [15] | 高锋阳, 高翾宇, 张浩然, 等. 全局与瞬时特性兼优的燃料电池有轨电车能量管理策略[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023(21):5923-5938. |
| Gao Feng-yang, Gao Xuan-yu, Zhang Hao-ran, et al. Management strategy for fuel cell trams with both global and transient characteristics[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society,2023(21):5923-5938. | |
| [16] | 周娟, 孙啸, 刘凯, 等. 联合扩展卡尔曼滤波的滑模观测器SoC估算算法研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41(2): 692-703. |
| Zhou Juan, Sun Xiao, Liu Kai, et al. Research on the SoC estimation algorithm of combining sliding mode observer with extended Kalman filter[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2021, 41(2): 692-703. | |
| [17] | 张国瑞, 李奇, 韩莹, 等. 基于运行模式和动态混合度的燃料电池混合动力有轨电车等效氢耗最小化能量管理方法研究[J].中国电机工程学报, 2018, 38(23): 6905-6914, 7124. |
| Zhang Guo-rui, Li Qi, Han Ying, et al. Study on equivalent consumption minimization strategy based on operation mode and DDOH for fuel cell hybrid tramway [J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2018, 38(23): 6905-6914, 7124. |
| [1] | 王玉海,李晓之,李兴坤. 面向高速工况的混合动力卡车预见性节能算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2121-2129. |
| [2] | 赵靖华,张雨彤,曹派,王忠恕,李小平,孙亚南,解方喜. 压缩天然气发动机增程式电动汽车能量管理优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 600-609. |
| [3] | 高锋阳,强雅昕,高智山,徐昊,史志龙. 在线和离线控制相结合的燃料电池有轨电车能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 3064-3076. |
| [4] | 隗海林,王泽钊,张家祯,刘洋. 基于Avl-Cruise的燃料电池汽车传动比及能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [5] | 孙闫,夏长高,尹必峰,韩江义,高海宇,刘静. 燃料电池电动汽车的能量管理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2130-2138. |
| [6] | 武小花,余忠伟,朱张玲,高新梅. 燃料电池公交车模糊能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2077-2084. |
| [7] | 陈凤祥,伍琪,李元松,莫天德,李煜,黄李平,苏建红,张卫东. 2.5吨燃料电池混合动力叉车匹配、仿真及优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
| [8] | 刘汉武,雷雨龙,阴晓峰,付尧,李兴忠. 增程式电动汽车增程器多点控制策略优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1741-1750. |
| [9] | 王哲,谢怡,臧鹏飞,王耀. 基于极小值原理的燃料电池客车能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 36-43. |
| [10] | 席利贺,张欣,孙传扬,王泽兴,姜涛. 增程式电动汽车自适应能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1636-1644. |
| [11] | 夏超英, 杜智明. 丰田PRIUS混合动力汽车能量优化管理策略仿真分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 373-383. |
| [12] | 宋传学, 周放, 肖峰. 基于动态规划的复合电源能量管理优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 8-14. |
| [13] | 秦大同, 杨官龙, 胡明辉, 刘永刚, 林毓培. 基于驾驶意图的插电式混合动力汽车能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(6): 1743-1750. |
| [14] | 董冰,田彦涛,周长久. 基于模糊逻辑的纯电动汽车能量管理优化控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 516-525. |
| [15] | 孙强,白书战,韩尔樑,郭春艳,李国祥. 基于试验测量的瞬时行驶工况构建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 364-370. |
|