吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1188-1196.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230719
基于正交试验法的悬索桥索夹螺杆紧固力损失影响因素
- 1.长安大学 公路大型结构安全教育部工程研究中心,西安 710064
2.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
3.广西欣港交通投资有限公司 广西 钦州 535000
4.陕西省交通规划设计研究院有限公司,西安 710065
Influence factors of preload loss in cable clamp bolt of suspension bridge based on orthogonal experiment method
Yong-jun ZHOU1,2( ),Feng-rui MU2,Cheng CAI3,Fan YANG4
),Feng-rui MU2,Cheng CAI3,Fan YANG4
- 1.Large Structures Highway Safety Engineering Research Center of the Ministry of Education,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
3.Guangxi Xingang Transportation Investment Co. ,Ltd. ,Qinzhou 535000,China
4.Shaanxi Provincial Transport Planning Design and Reaseach Institute Co. ,Ltd. ,Xi'an 710065,China
摘要:
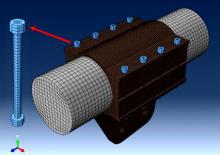
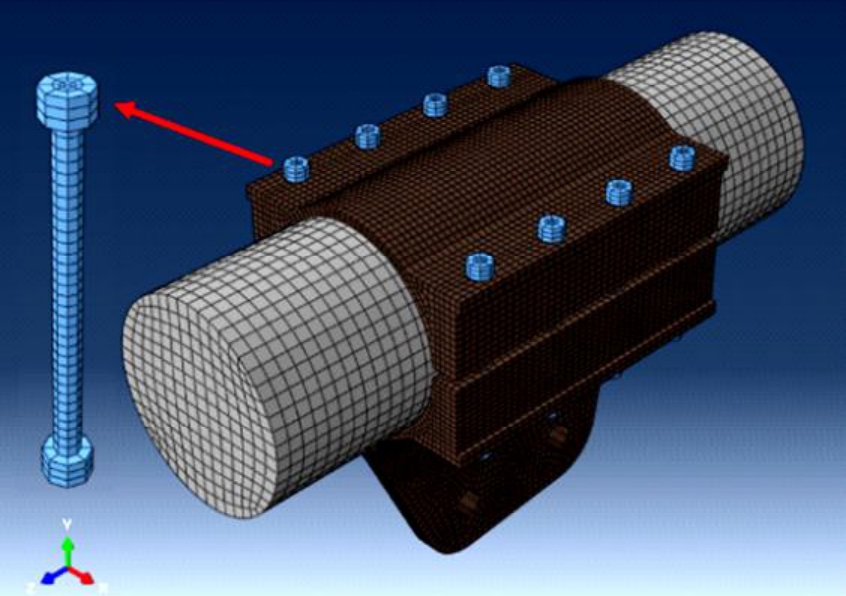
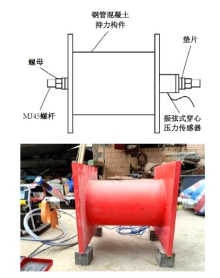
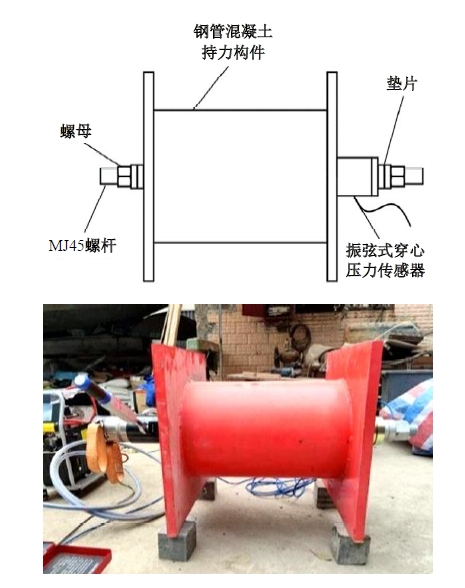
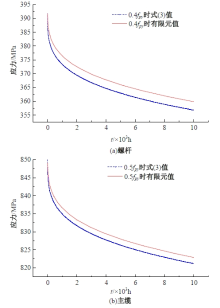
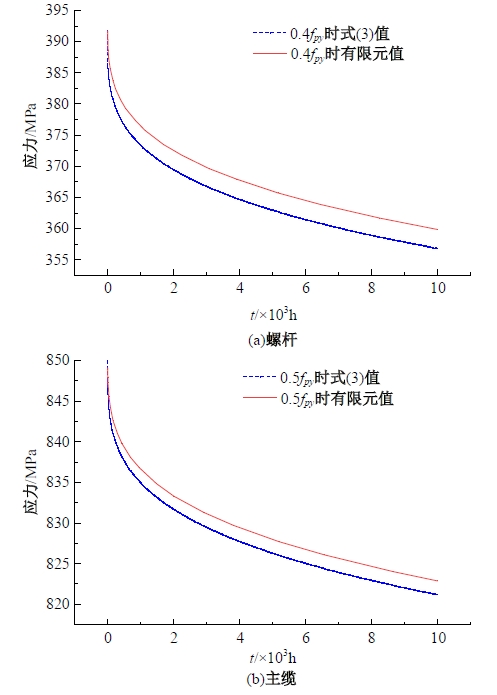
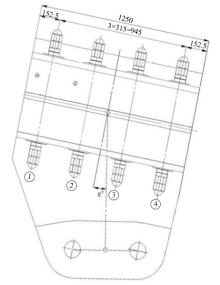
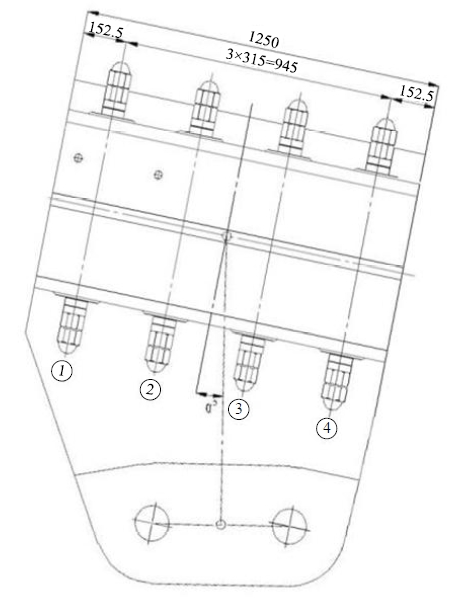
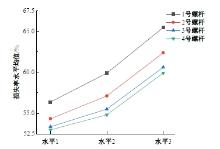
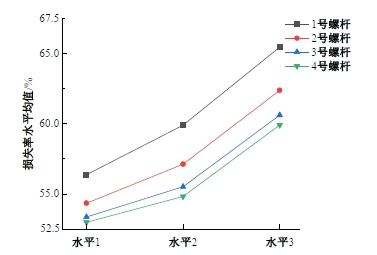
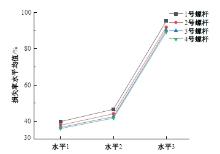
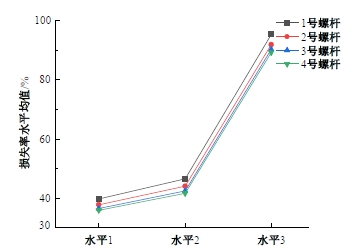
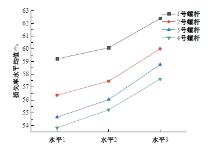
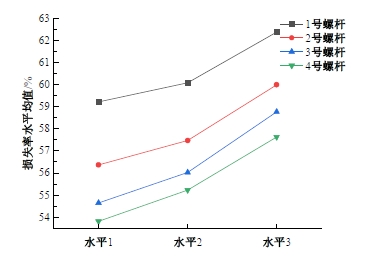
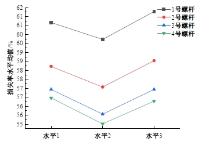
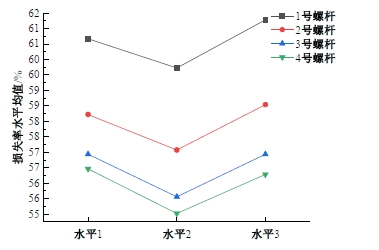
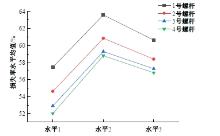
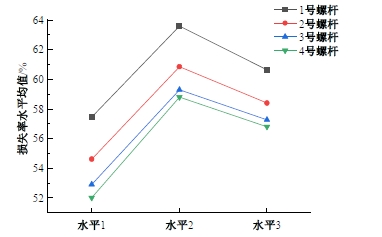
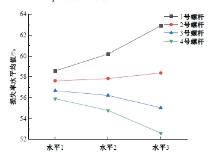
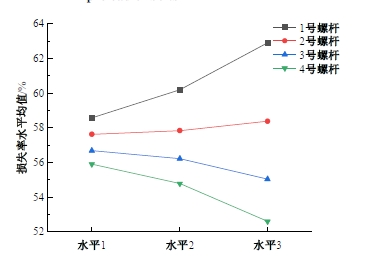
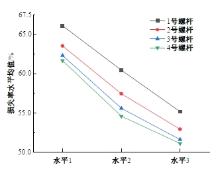
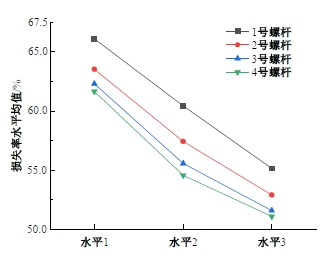
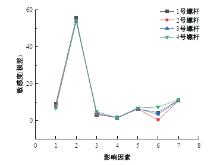
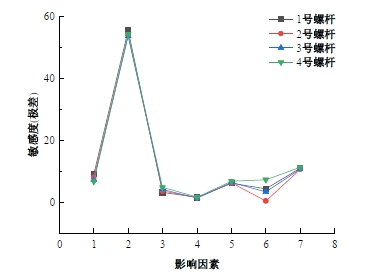
为研究悬索桥索夹螺杆紧固力损失的影响因素及敏感度,建立了广西某大桥索夹局部有限元模型,并利用蠕变试验结果对有限元模型进行验证。在此基础上,分别考虑螺杆的应力松弛速率、主缆蠕变速率、主缆空隙率、吊索力大小、螺杆的初始紧固力、索夹倾角和主缆与索夹温差等因素,利用正交试验法设计27种索夹螺杆紧固力损失的有限元分析工况,研究它们对螺杆紧固力的影响。研究结果表明:索夹螺杆紧固力损失随螺杆自身应力松弛速率的增大而增大;主缆蠕变速率对索夹螺杆紧固力损失的影响极其显著,索夹螺杆紧固力损失随主缆蠕变速率的增大而显著增大;索夹与主缆的温差对索夹螺杆紧固力损失的影响显著,螺杆紧固力损失随主缆与索夹温差的增大而减小;常见的主缆空隙率对索夹螺杆紧固力损失的影响相对较小;吊索力大小对索夹螺杆紧固力损失的影响可以忽略不计;螺杆紧固力损失随螺杆初始紧固力增大呈现先增大后减小的规律;索夹倾角对同一索夹不同位置的螺杆紧固力损失的影响有所差异;本文研究结论可为悬索桥的设计及养护提供参考。
中图分类号:
- U44
| [1] | 王俊, 李加武, 王峰, 等. 简化U形峡谷风速分布及其对悬索桥抖振响应的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2023, 53(6): 1658-1668. |
| Wang Jun, Li Jia-wu, Wang Feng, et al. Wind speed distribution in simplified U⁃shaped valley and its effect on buffeting response of long⁃span suspension bridge[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1658-1668. | |
| [2] | Mayrbaurl R M, Camo S. Guidelines for Inspection and Strength Evaluation of Suspension Bridge Parallel-Wire Cables[M]. USA: Transportation Research Board, 2004. |
| [3] | 中国公路学会桥梁与结构工程学会. 日本本州-四国连络桥上部结构设计标准及解说[M]. 北京: 中国公路学会桥梁与结构工程学会, 1998. |
| [4] | 费卿, 梁锦润. 自锚式悬索桥索夹滑移分析及修复技术[C]∥中国公路学会桥梁和结构工程分会2017年全国桥梁学术会议论文集, 广州, 中国, 2017: 654-659. |
| [5] | Tendo M, Yamada K, Shimura Y. Stress relaxation behavior at high-tension bolted connections of stainless-steel plates[J]. Journal of Engineering Materials & Technology, 2001, 123(2): 198-202. |
| [6] | Alkelani A A, Housari A B, Nassar A S. A proposed model for creep relaxation of soft gaskets in bolted joints at room temperature[J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology(ASME), 2008, 13(1): No.011211-1-6. |
| [7] | 徐浩, 王崴, 马跃. 螺栓联接蠕变松弛有限元分析[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2013, 271(9): 39-41, 45. |
| Xu Hao, Wang Wei, Ma Yue. Finite element analysis of creep relaxation in bolted connections[J]. Mechanical Design and Manufacturing, 2013, 271(9): 39-41, 45. | |
| [8] | 刘海波, 吴嘉锟, 王永青. 地脚螺栓蠕变松弛对大型数控机床几何精度衰退的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2015, 49(9): 14-17, 140. |
| Liu Hai-bo, Wu Jia-kun, Wang Yong-qing. The effect of creep relaxation of anchor bolts on the geometric accuracy degradation of large CNC machine tools [J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2015, 49(9): 14-17, 140. | |
| [9] | Xu H, Wang F, Cheng X. Pullout creep properties of grouted soil anchors[J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2007, 14(1): 474-477. |
| [10] | Kim N. Performance of tension and compression anchors in weathered soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2003, 129(12): 1138-1150. |
| [11] | 沈锐利, 何恺, 苗如松. 基于多尺度模型的销接式索夹极限抗滑摩阻力分析[J]. 桥梁建设, 2018, 48(5): 16-20. |
| Shen Rui-li, He Kai, Miao Ru-song. Analysis of ultimate sliding friction resistance of pin connected cable clamps based on multi-scale models[J]. Bridge Construction, 2018, 48(5): 16-20. | |
| [12] | 周勇军, 贾利强, 杨帆, 等. 考虑主缆镀锌层蠕变的索夹螺杆紧固力损失预测[J]. 中国公路学报, 2024, 37(7): 157-167. |
| Zhou Yong-jun, Jia Li-qiang, Yang Fan, et al. Research on Preload Loss Prediction of Clamp Bolt Considering Cable Creep of Galvanized Layer[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2024, 37(7): 157-167. | |
| [13] | 何恺. 铁路悬索桥长索夹下主缆应力及索夹抗滑承载力研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. |
| He Kai. Research on stress of main cable under long cable clamp and anti sliding bearing capacity of cable clamp of railway suspension bridge[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017. | |
| [14] | 唐冕, 车天鑫, 宋旭明, 等. 基于蠕变理论的自锚式悬索桥索夹预紧力研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2022, 50(1): 59-68. |
| Tang Mian, Che Tian-xin, Song Xu-ming, et al. Study on pretension force of cable clamp of self anchored suspension bridge based on creep theory[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(1): 59-68. | |
| [15] | 梅葵花, 经德良, 黄平明, 等. 悬索桥主缆温度效应的分析研究[C]∥中国公路学会桥梁和结构工程学会2001年桥梁学术研讨会论文集, 重庆,中国,2001. |
| [16] | 吕佳欣, 肖毅. 复合材料螺栓连接预紧力松弛的改进预测模型[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(10): 229-237. |
| Jia-xin Lyu, Xiao Yi. Improved approach to modelling preload relaxation in bolted composite joints[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018,35 (10): 229-237. | |
| [17] | 陆光闾. 预应力高强钢丝松弛性能研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 1997, 44(6): 41-46. |
| Lu Guang-lyu. Research on relaxation performance of prestressed high strength steel wire[J]. Journal of Civil Engineering, 1997,44(6): 41-46. | |
| [18] | 周勇军, 全伟, 贺拴海. 基于正交试验的连续刚构桥地震响应敏感性参数分析[J]. 地震研究, 2006, 29(2): 176-181, 216. |
| Zhou Yong-jun, Quan Wei, He Shuan-hai. Analysis of seismic response sensitivity parameters of continuous rigid frame bridges based on orthogonal tests[J]. Earthquake Research, 2006, 29(2): 176-181, 216. | |
| [19] | 蒋树勤, 周勇军, 曹资源, 等. 基于拉拔法的索夹螺杆紧固力检测试验[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版, 2024, 44(6): 72-80. |
| Jiang Shu-qin, Zhou Yong-jun, Cao Zi-yuan, et al. Experiment on detection of preload force in bolt clamp by pulling method[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 44(6): 72-80. | |
| [20] | 黄铁生. 大岛大桥主缆施工[J]. 国外桥梁, 1993, 21(3): 175-180. |
| Huang Tie-sheng. Construction of the main cable of the Oshima Bridge[J]. Foreign Bridges, 1993, 21(3): 175-180. | |
| [21] | 《中国公路学报》编辑部. 中国桥梁工程学术研究综述·2024[J]. 中国公路学报, 2024, 37(12): 1-160. |
| Editorial Department of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review on China's pavement engineering research:2024[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2024, 37(12): 1-160. |
| [1] | 孙永新,蔺鹏臻,杨子江,冀伟. 考虑黏结-滑移效应的UHPC梁裂缝宽度计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2600-2608. |
| [2] | 谢朋书,崔达,王国强,李凯. 基于离散元方法的立式螺旋搅拌磨机工作性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2423-2431. |
| [3] | 薛宇欣,周勇军,王业路,范凯翔,赵煜. 基于悬锤系统的简支梁桥冲击系数测试方法适用性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2557-2567. |
| [4] | 郭雪莲,韩万水,王涛,周恺,张修石,张书颖. 大件车通行弯桥抗倾覆稳定安全系数评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2229-2237. |
| [5] | 肖林,魏欢博,卫星,康志锐. 钢混组合梁栓钉锈胀下混凝土板开裂行为数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1958-1965. |
| [6] | 刘昕晖,相志霖,谭鹏,陈伟,冯吉宇. 基于Fluent的散热系统扩流结构内部流场分析及优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1831-1843. |
| [7] | 张春雷,邵长宇,苏庆田,戴昌源. 球扁钢肋钢纤维混凝土组合桥面板正弯矩受力性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1634-1642. |
| [8] | 张彦玲,贾云飞,贾晓远,郑旺,李运生. 装配式小箱梁桥内力横向分布系数建议公式[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1688-1700. |
| [9] | 黄汉辉,陈康明,吴庆雄. 钢管混凝土桁式弦杆组合连续梁抗弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1665-1676. |
| [10] | 李光保,高栋,路勇,平昊,周愿愿. 基于改进神经网络和Fluent的气液固技术的内表面处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1537-1547. |
| [11] | 邵长江,崔皓蒙,漆启明,庄卫林. 近断层大跨RC轻柔拱桥纵向阻尼器减震研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1355-1367. |
| [12] | 赵秋,陈鹏,赵煜炜,余澳. 台后设置拱形结构的无缝桥梁整体受力性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1016-1027. |
| [13] | 刘元义,于圣洁,胥备,王宪良,宋发成. 基于离散元的设施农业就地翻土犁的研究与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1153-1165. |
| [14] | 张洪,朱志伟,胡天宇,龚燕峰,周建庭. 基于改进YOLOv5s的桥梁螺栓缺陷识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 749-760. |
| [15] | 韩智强,谢刚,卓亚娟,骆佐龙,李华腾. 基于车轮-桥面相干激励的大跨连续梁桥振动响应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 436-444. |
|