吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1510-1517.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220617
不同部位孤立性纤维性肿瘤患者临床病理特征和预后影响因素分析
- 吉林大学第二医院病理科, 吉林 长春 130041
Clinicopathological characteristics and analysis on prognostic factors of patients with solitary fibrous tumors in different sites
Yunhe GAO,Jianan YAO,Lanqing CAO,Chuanjie XU( )
)
- Department of Pathology,Second Hospital,JilinUniversity,Changchun 130041,China
摘要:
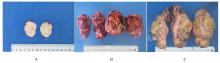
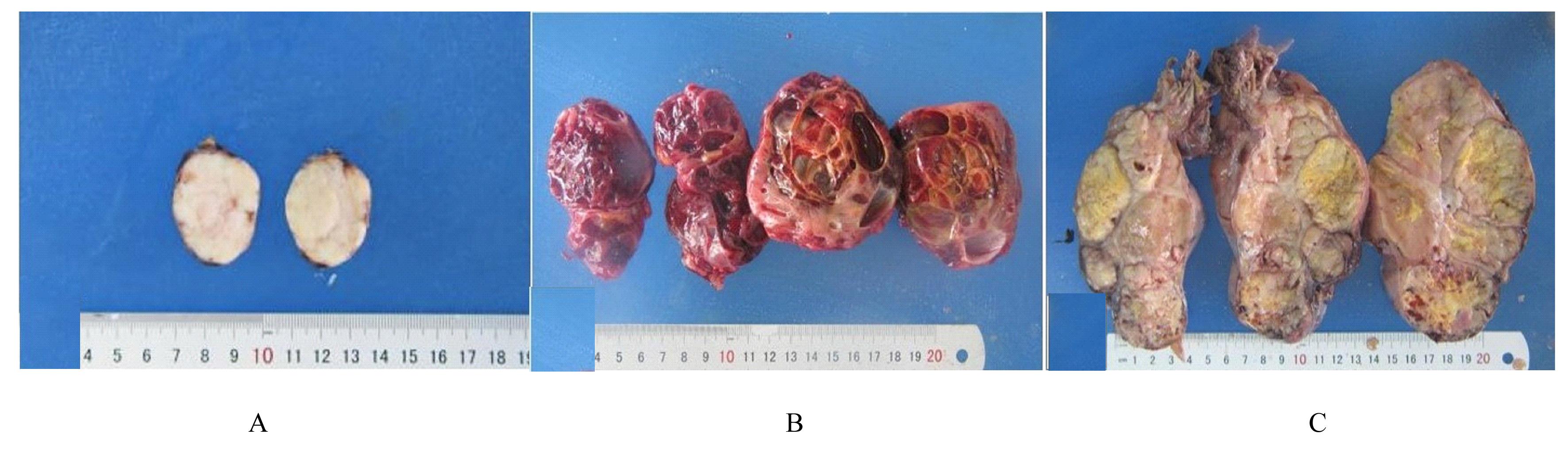
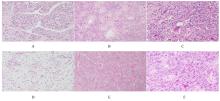
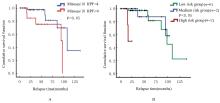
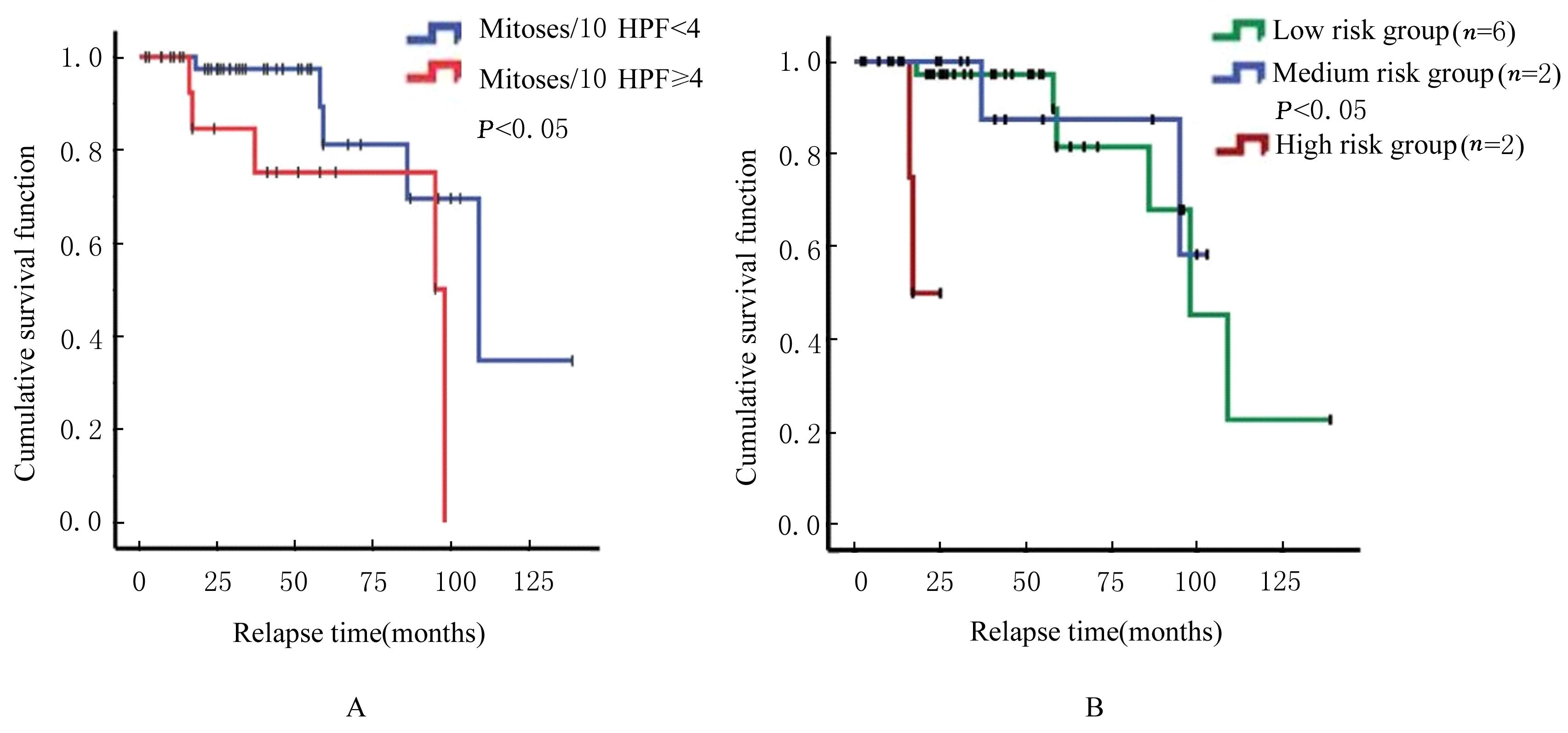
目的 探讨孤立性纤维性肿瘤(SFT)患者的临床病理特征和预后相关影响因素,为该病病理诊断、临床治疗及患者预后判断提供依据。 方法 收集经手术切除原发于不同系统的86例SFT患者临床病理资料,根据危险度分级标准分为低(n=65)、中(n=14)和高危险组(n=7)。观察肿瘤大体形态表现、HE染色和免疫组织化学染色检测SFT形态表现,获取患者随访资料行预后相关分析。采用Kaplan-Meier生存曲线法分析不同部位的单一临床病理因素与患者无进展生存期的关系,多因素Cox回归分析法进行多因素与患者无进展生存期关系的分析。 结果 86例SFT中,男性37例, 女性49例, 不同部位SFT的患者性别构成比比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。不同部位SFT的患者年龄比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。不同部位SFT在低、中、高危险组的分布情况比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。不同部位肿瘤直径比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。光镜下,肿瘤细胞形态及排列多样,呈梭形或卵圆形细胞疏密不等地无结构排列,常见特征性鹿角样分枝状血管和粗细不等的胶原纤维,大部分肿瘤细胞形态温和、异型性和核分裂象不明显。免疫组织化学染色,STAT-6核弥漫强阳性;CD34、Bcl-2及CD99不同程度阳性表达。61例患者获随访信息,随访时间为2~139个月。其中10例患者出现复发,各组患者复发率分别为低危险组9%、中危险组14%、高危险组28%。单因素分析, 核分裂象<4个/10HPF与≥4个/10HPF患者无进展生存期比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);高危险组与低、中危险组患者无进展生存期比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。多因素分析,性别、年龄、肿瘤直径和核分裂象计数均非患者无进展生存期的独立预测因素(P>0.05)。 结论 SFT可发生于人体多种器官和系统, 形态学表现多样。发生在中枢神经系统、上呼吸道及眼眶的肿瘤直径明显小于女性生殖道、腹腔、皮下软组织、肺及胸膜。STAT-6是SFT诊断特异且敏感指标;核分裂象≥4个/10HPF和高危险分级是患者无进展生存期缩短的危险因素;多因素综合分析肿瘤危险度分级不能完全反映患者预后。
中图分类号:
- R73