吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1035-1043.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240418
PLOD1在口腔鳞状细胞癌组织和细胞中的表达及其意义
郭超杰,张佳佳,曾洁,王晖予,艾尔法提·艾麦尔null,徐江( )
)
- 石河子大学第一附属医院口腔科,新疆 石河子 832000
Expressions of PLOD1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma tissue and cells and their significances
Chaojie GUO,Jiajia ZHANG,Jie ZENG,Huiyu WANG, AIERFATI·Aimaier,Jiang XU( )
)
- Department of Stomatology,First Affiliated Hospital,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832000,China
摘要:
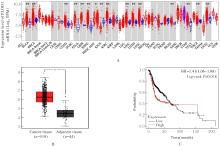
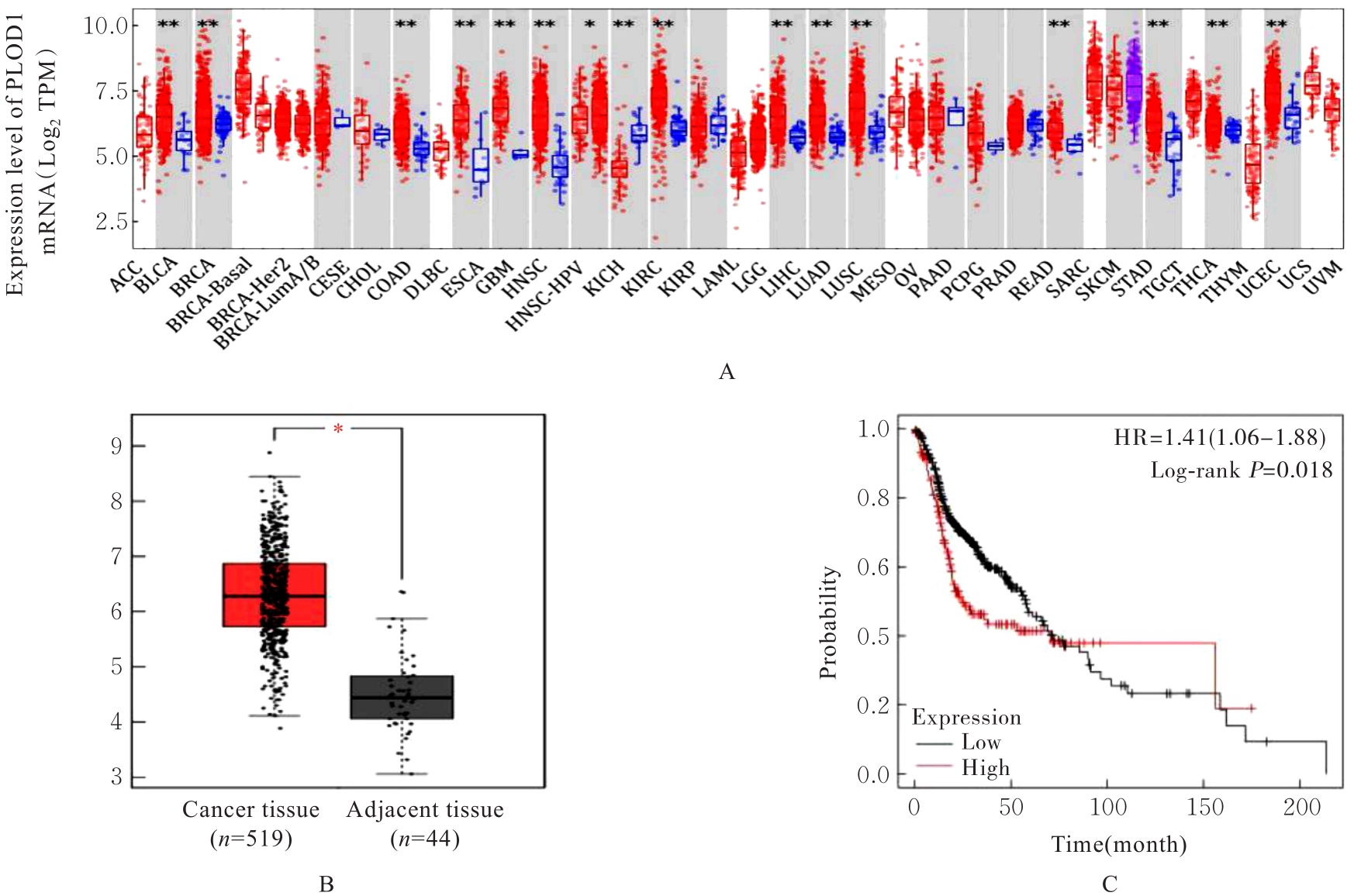
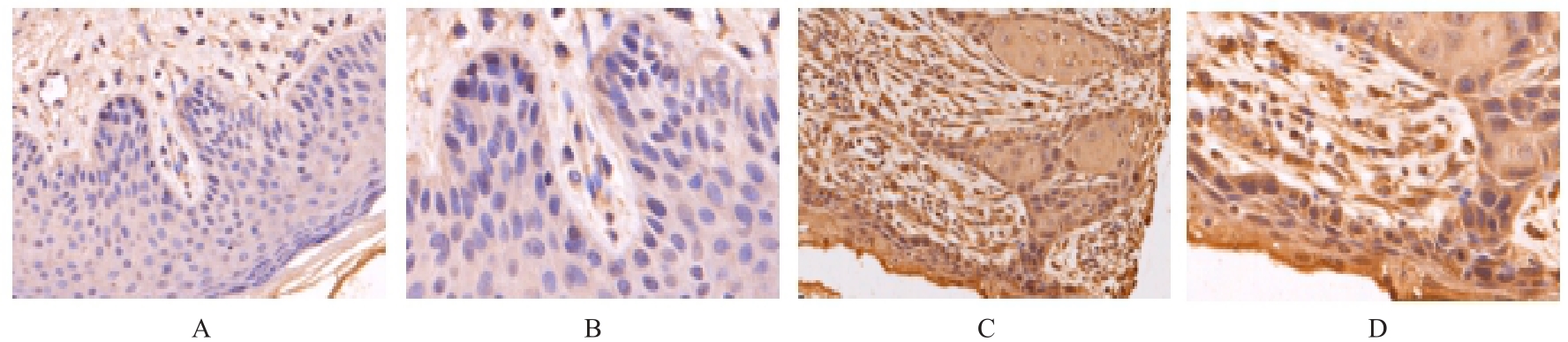
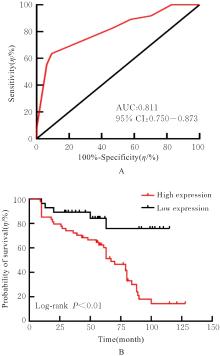
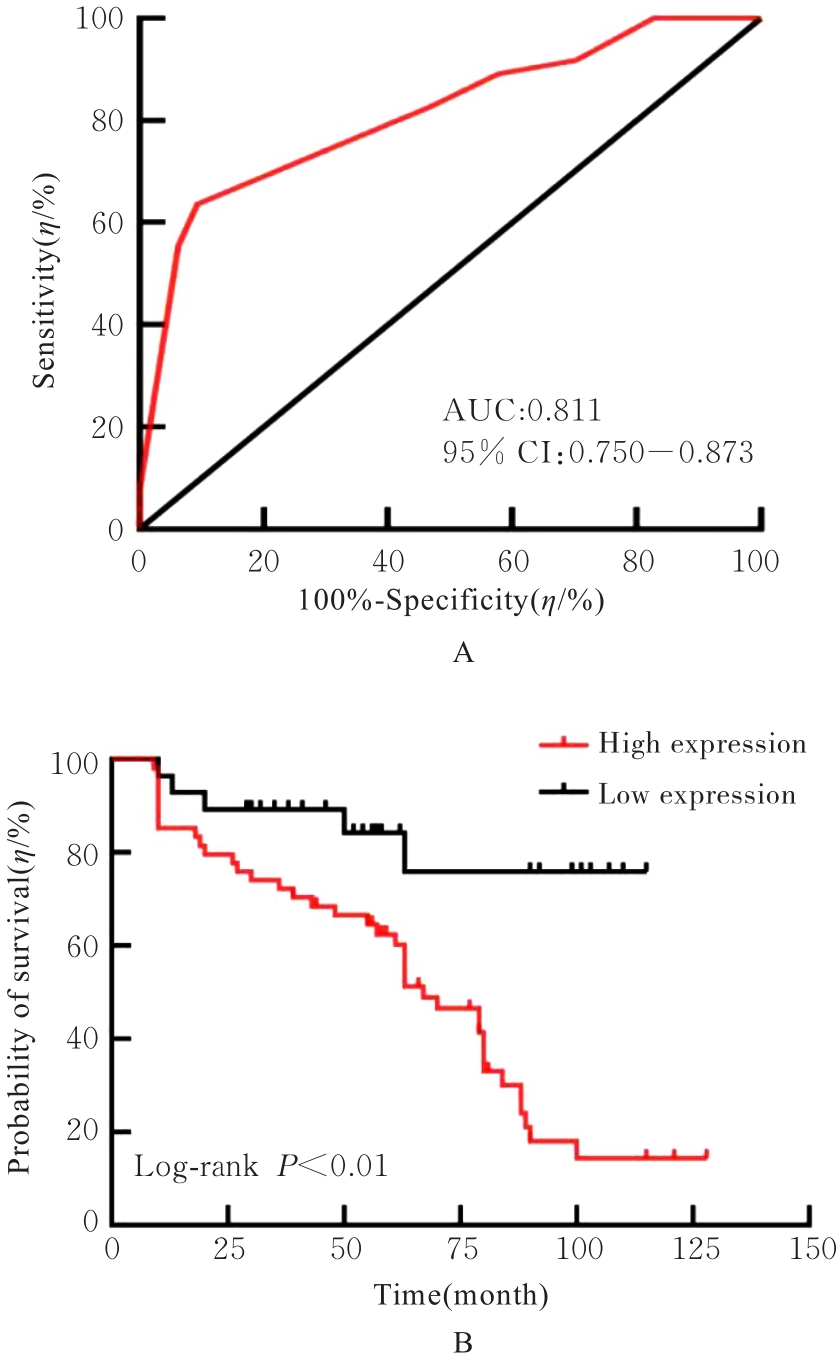
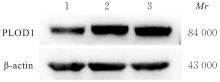
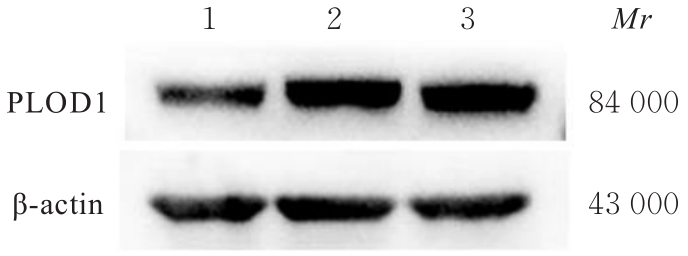
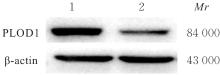
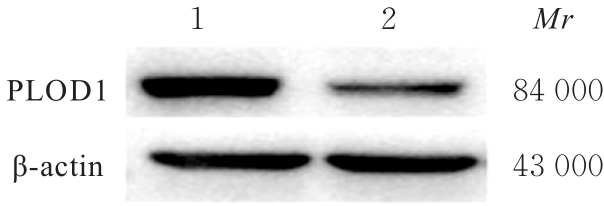
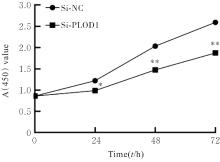
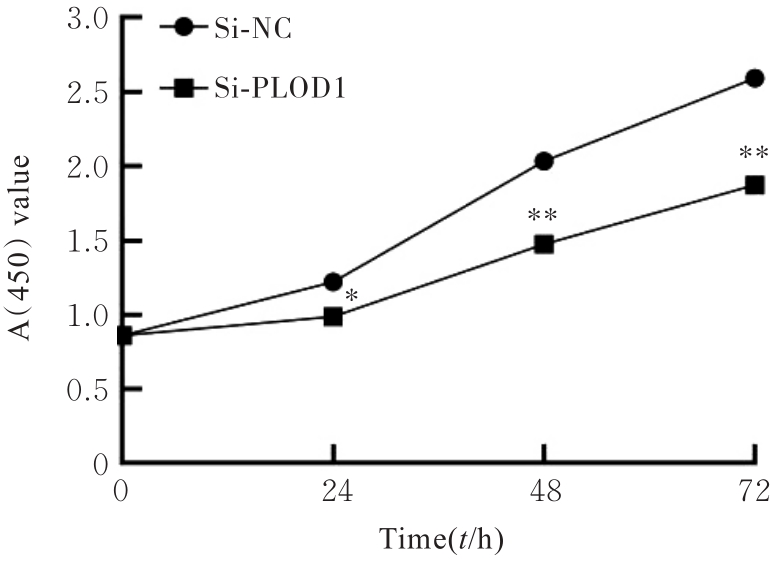
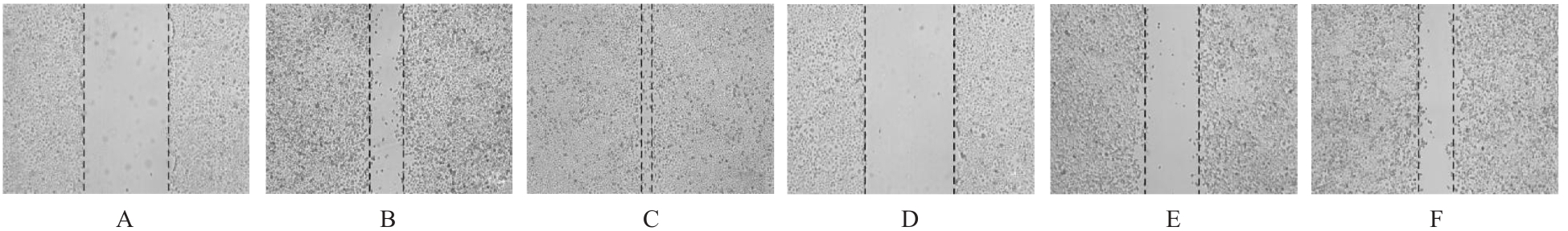
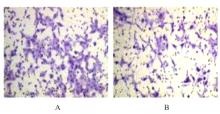
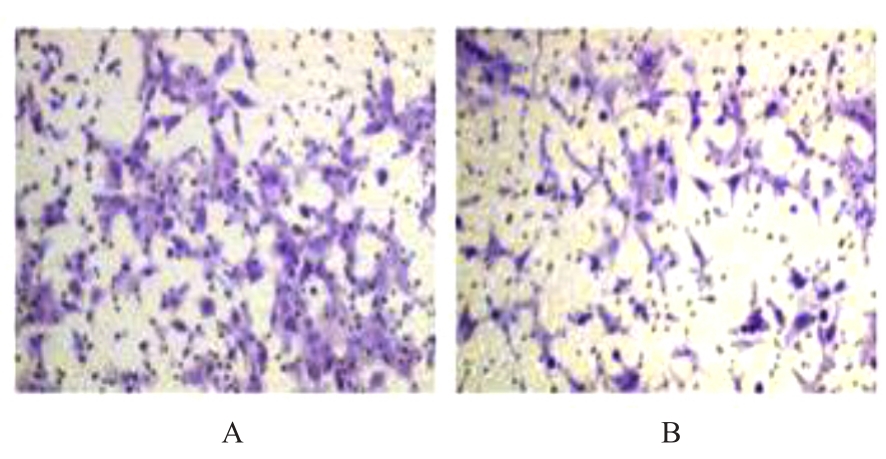
目的 探讨前胶原赖氨酸,2-酮戊二酸5-双加氧酶1(PLOD1)在口腔鳞状细胞癌(OSCC)组织和细胞中的表达及其对OSCC细胞生物学行为的影响,阐明PLOD1作为OSCC预后标志物的潜力。 方法 采用肿瘤免疫评价资源(TIMER)数据库、基因表达谱交互分析(GEPIA)数据库和Kaplan-Meier Plotter数据库分析头颈部鳞状细胞癌(HNSC)组织中PLOD1 mRMA表达水平及其与HNSC患者生存期的关联。免疫组织化学法检测110例OSCC组织和64例癌旁组织中PLOD1蛋白表达情况,分析其与OSCC患者临床病理特征和预后的关系。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线下面积(AUC)评估PLOD1在OSCC诊断中的价值。实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法和Western blotting法检测人正常口腔上皮HOK细胞和OSCC SCC15和CAL27细胞中PLOD1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平。利用脂质体法将小干扰RNA(siRNA)片段转染至SCC15细胞,分为si-NC组(转染阴性对照si-NC)和si-PLOD1组(转染si-PLOD1),采用CCK-8法、细胞划痕愈合实验和Transwell小室实验分别检测2组细胞增殖活性、划痕愈合率和侵袭细胞数。 结果 公共数据库分析,HNSC组织中PLOD1 mRNA 表达水平高于癌旁组织(P<0.05); 与 PLOD1 低表达组比较, PLOD1 高表达组HNSC患者生存期较短(HR=1.41, P=0.018)。PLOD1蛋白主要表达于 OSCC 细胞的细胞质中,OSCC组织中PLOD1 表达强度高于癌旁组织(P<0.01),并与 OSCC 患者 T 分期和 TNM 分期有关(P=0.021,P=0.004)。PLOD1 诊断 OSCC 的 AUC 为 0.811,特异度和灵敏度分别 63.64% 和90.63%。Kaplan-Meier生存分析,与PLOD1低表达组比较,PLOD1高表达组OSCC患者生存率降低(P<0.01);COX回归分析,PLOD1高表达是影响OSCC预后的独立危险因素(P=0.012)。OSCC细胞中PLOD1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平高于HOK细胞(P<0.05)。与si-NC组比较,si-PLOD1组细胞增殖活性和划痕愈合率降低(P<0.05),侵袭细胞数减少(P<0.01)。 结论 PLOD1在OSCC组织和细胞中高表达,沉默PLOD1表达可抑制OSCC细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭。PLOD1可能是OSCC新的治疗靶点和预后标志物。
中图分类号:
- R739.8