吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1677-1685.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221343
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
尺寸和形状效应对多孔结构风阻系数的影响
王峰1( ),刘双瑞1,王佳盈1,宋佳玲2,王俊1,张久鹏1,黄晓明3
),刘双瑞1,王佳盈1,宋佳玲2,王俊1,张久鹏1,黄晓明3
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.广州大学 风工程与工程振动研究中心,广州 510006
3.东南大学 交通学院,南京 210018
Size and shape effects of wind drag coefficients for porous structures
Feng WANG1( ),Shuang-rui LIU1,Jia-ying WANG1,Jia-ling SONG2,Jun WANG1,Jiu-peng ZHANG1,Xiao-ming HUANG3
),Shuang-rui LIU1,Jia-ying WANG1,Jia-ling SONG2,Jun WANG1,Jiu-peng ZHANG1,Xiao-ming HUANG3
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.Research Center of Wind Engineering and Engineering Vibration,Guangzhou University,Guangzhou 510006,China
3.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 210018,China
摘要:
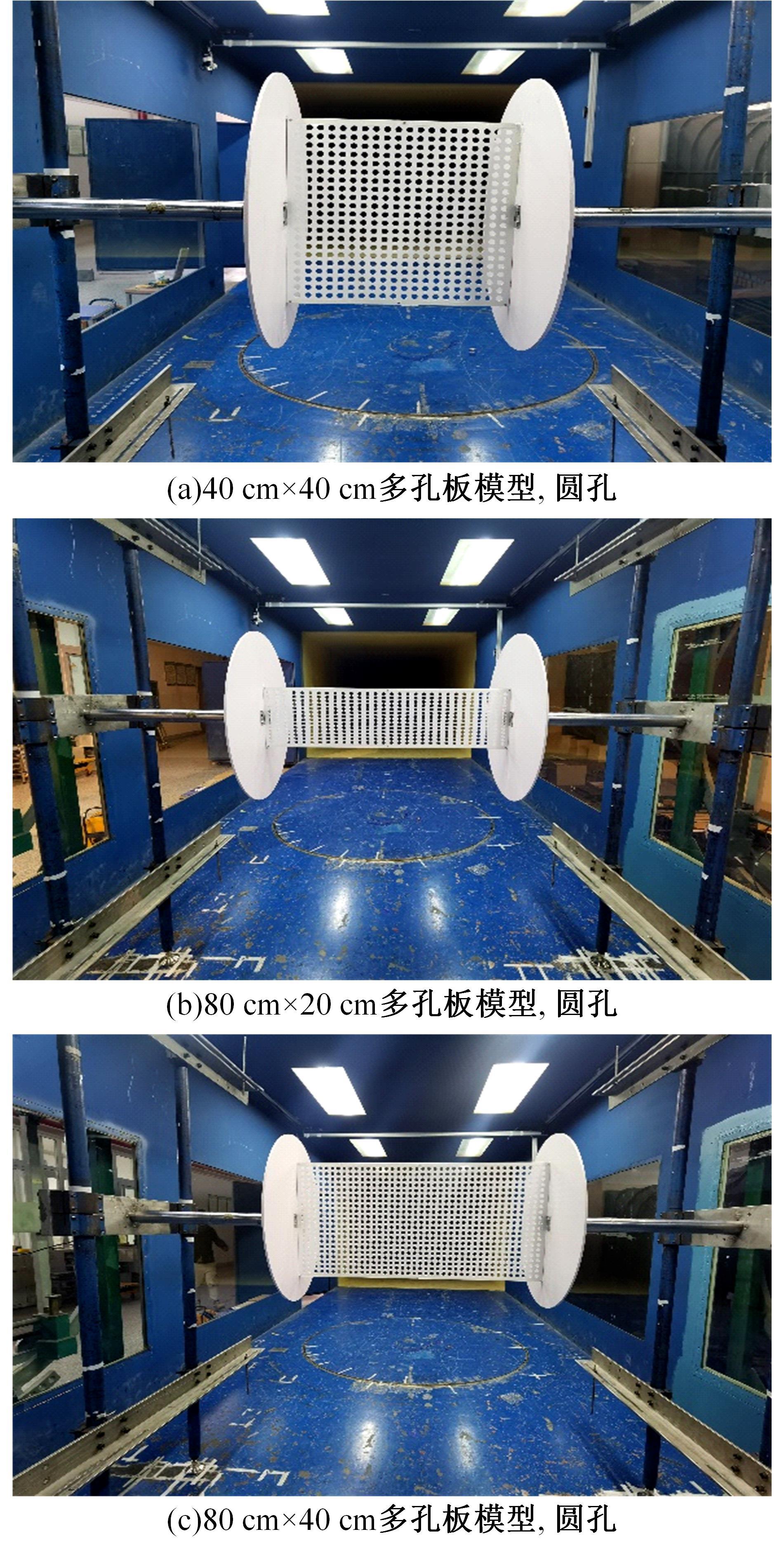
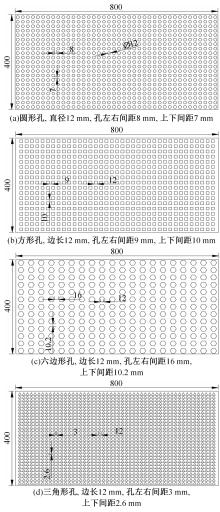
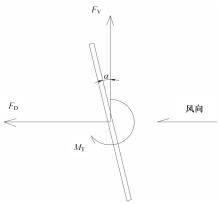
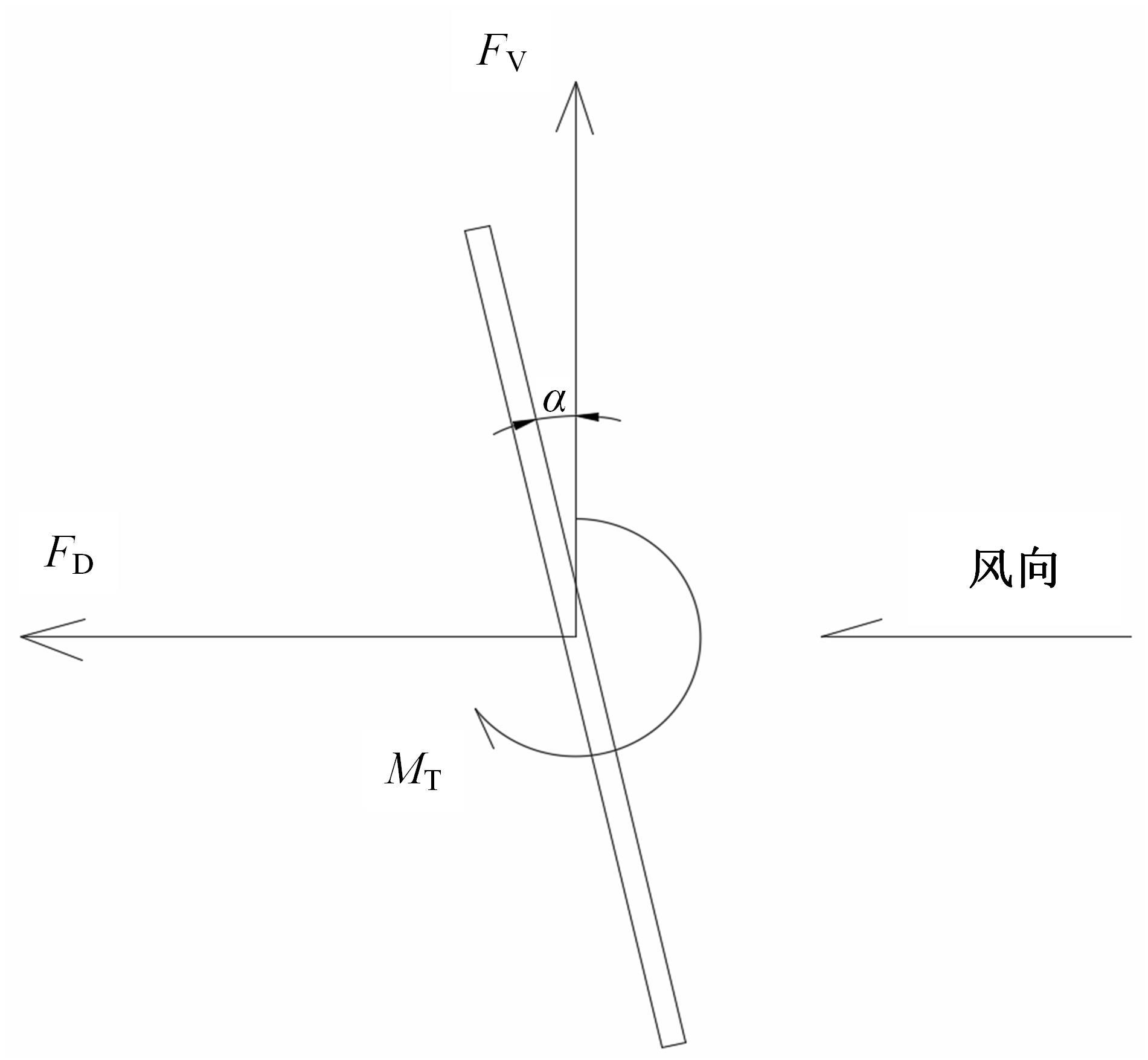
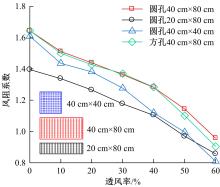
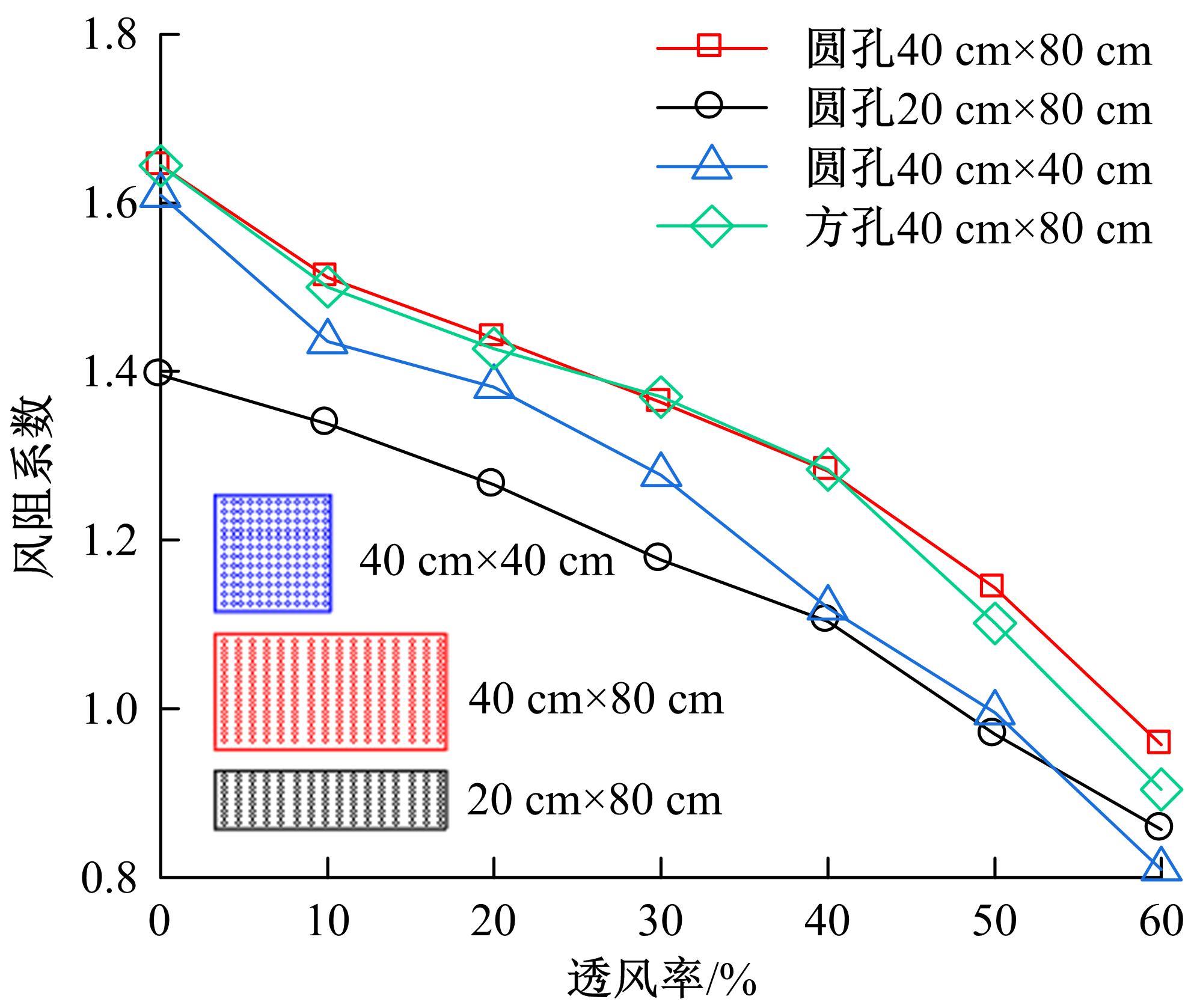
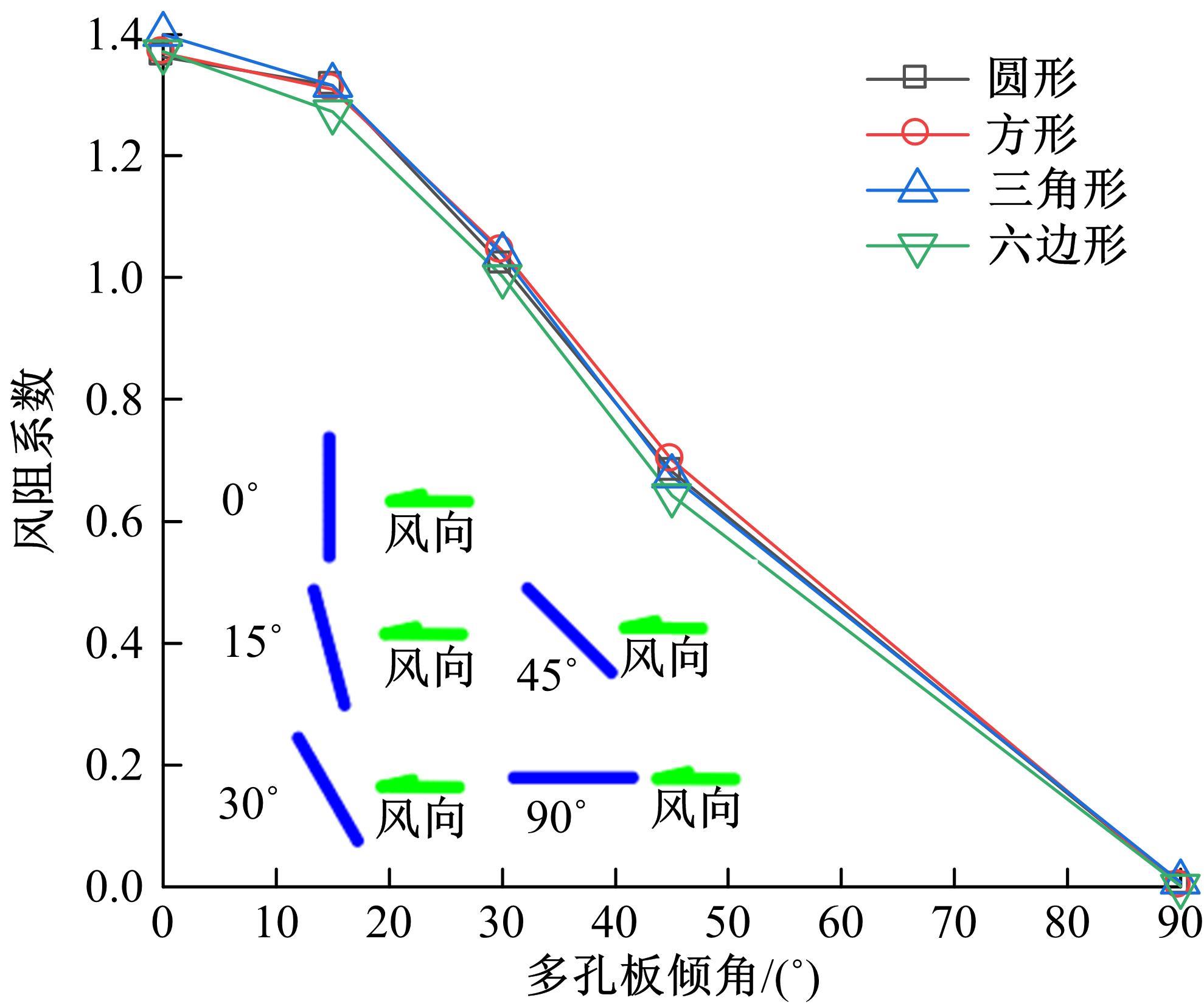
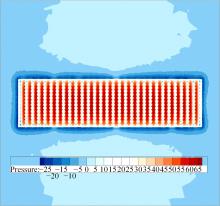
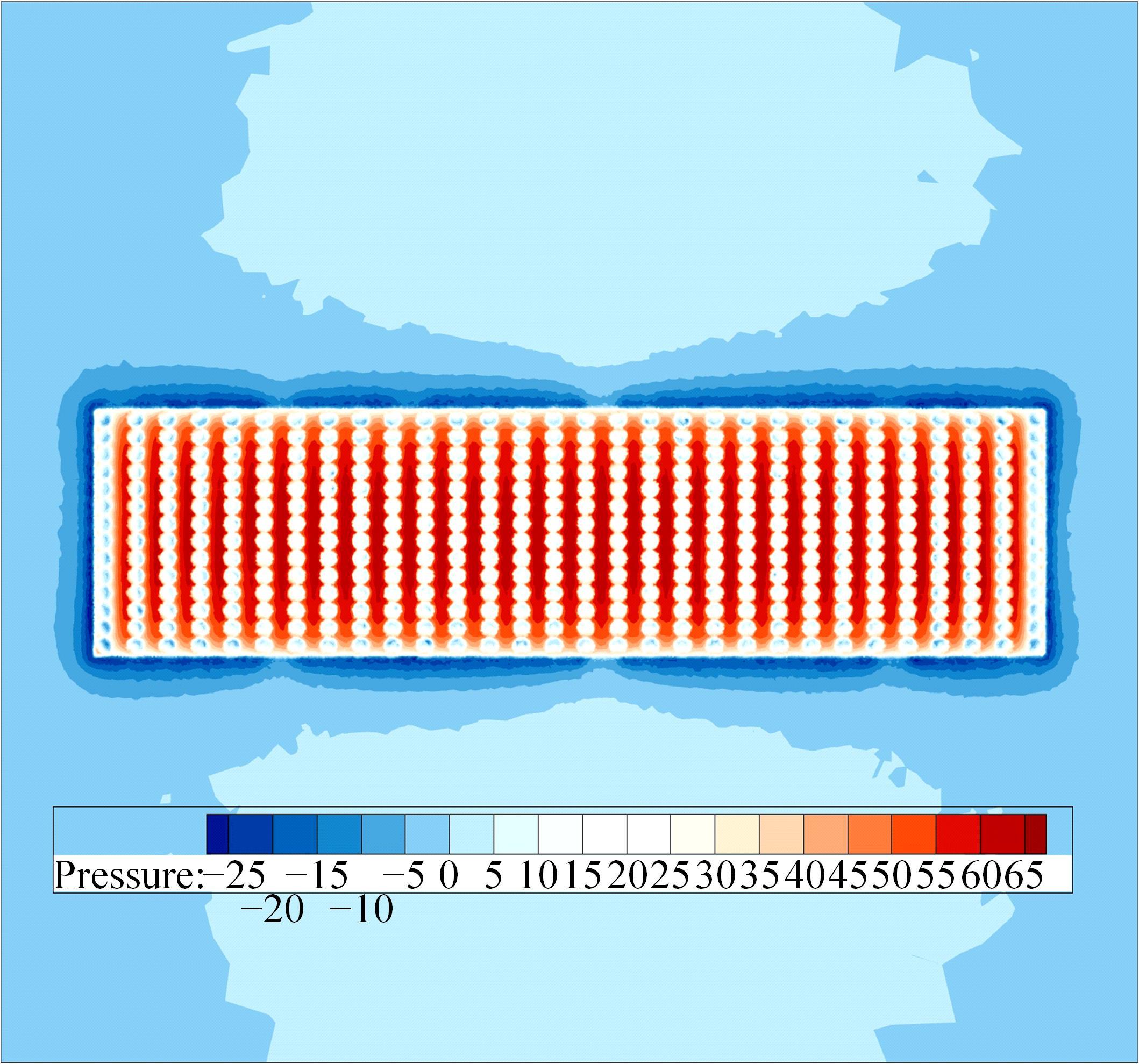
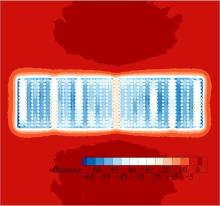
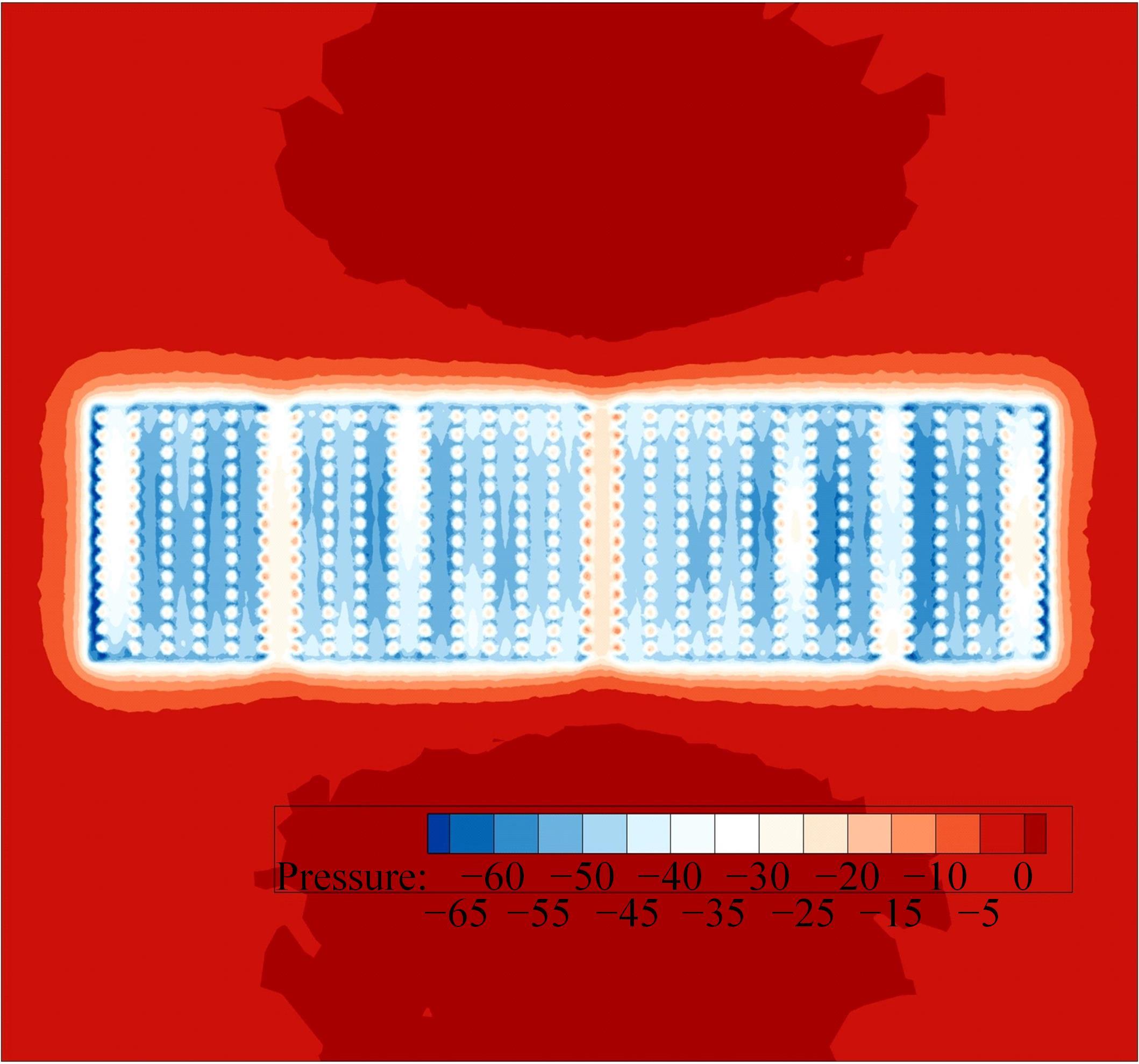
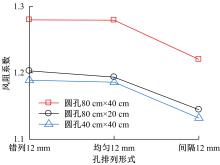
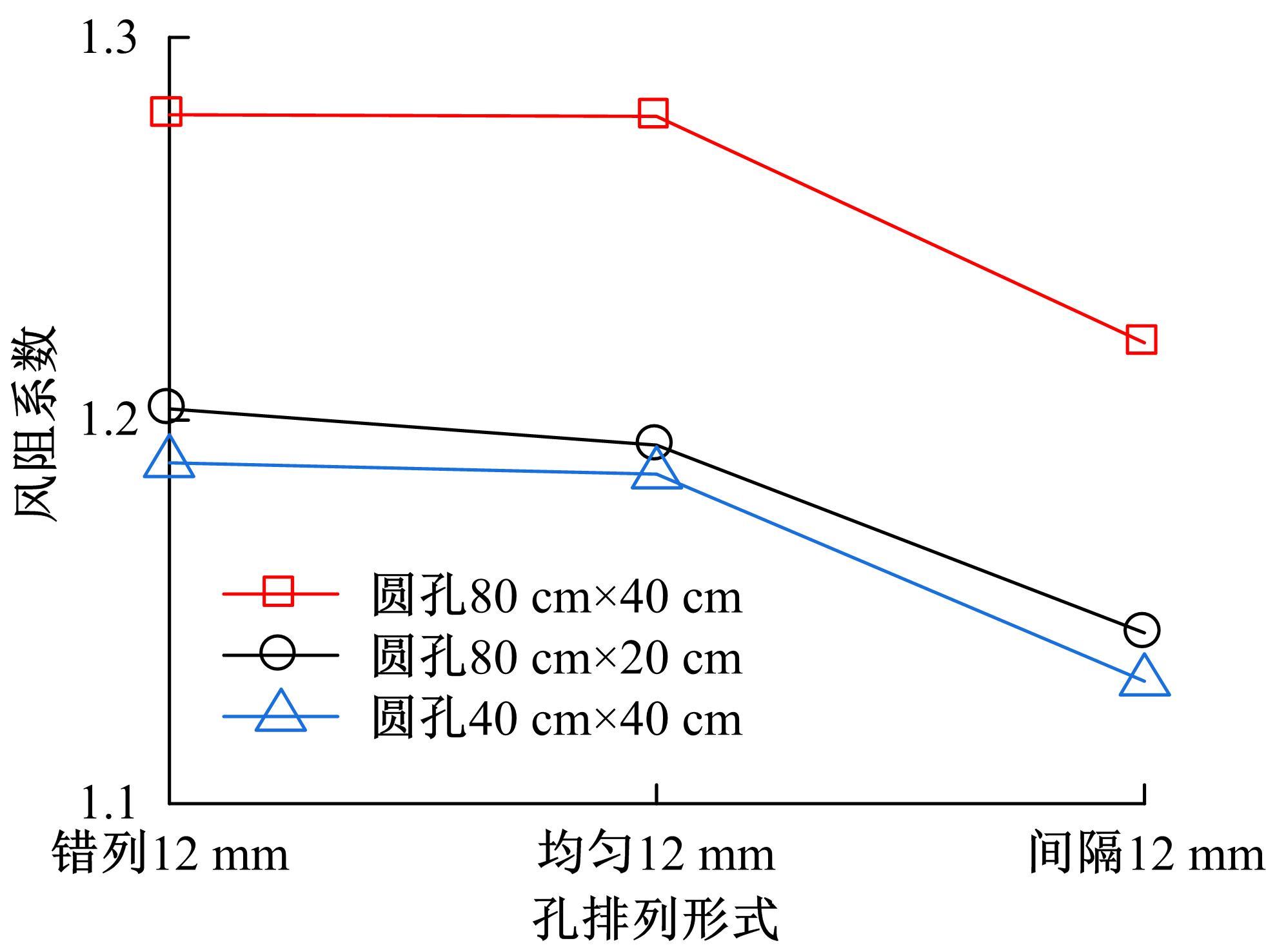
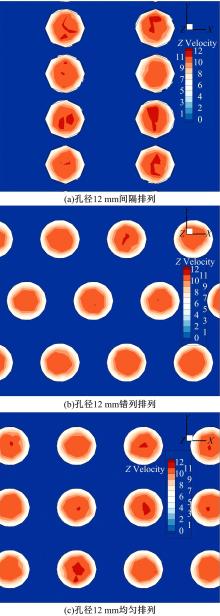
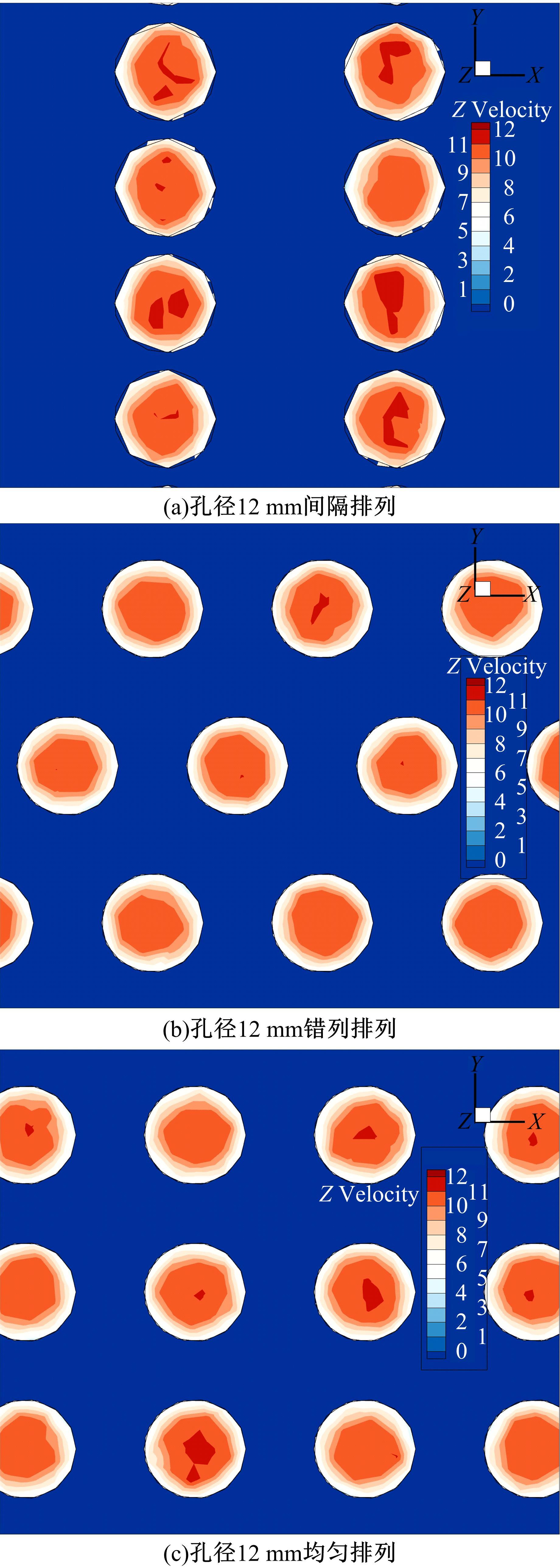
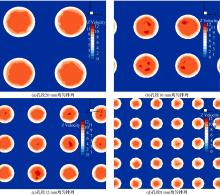
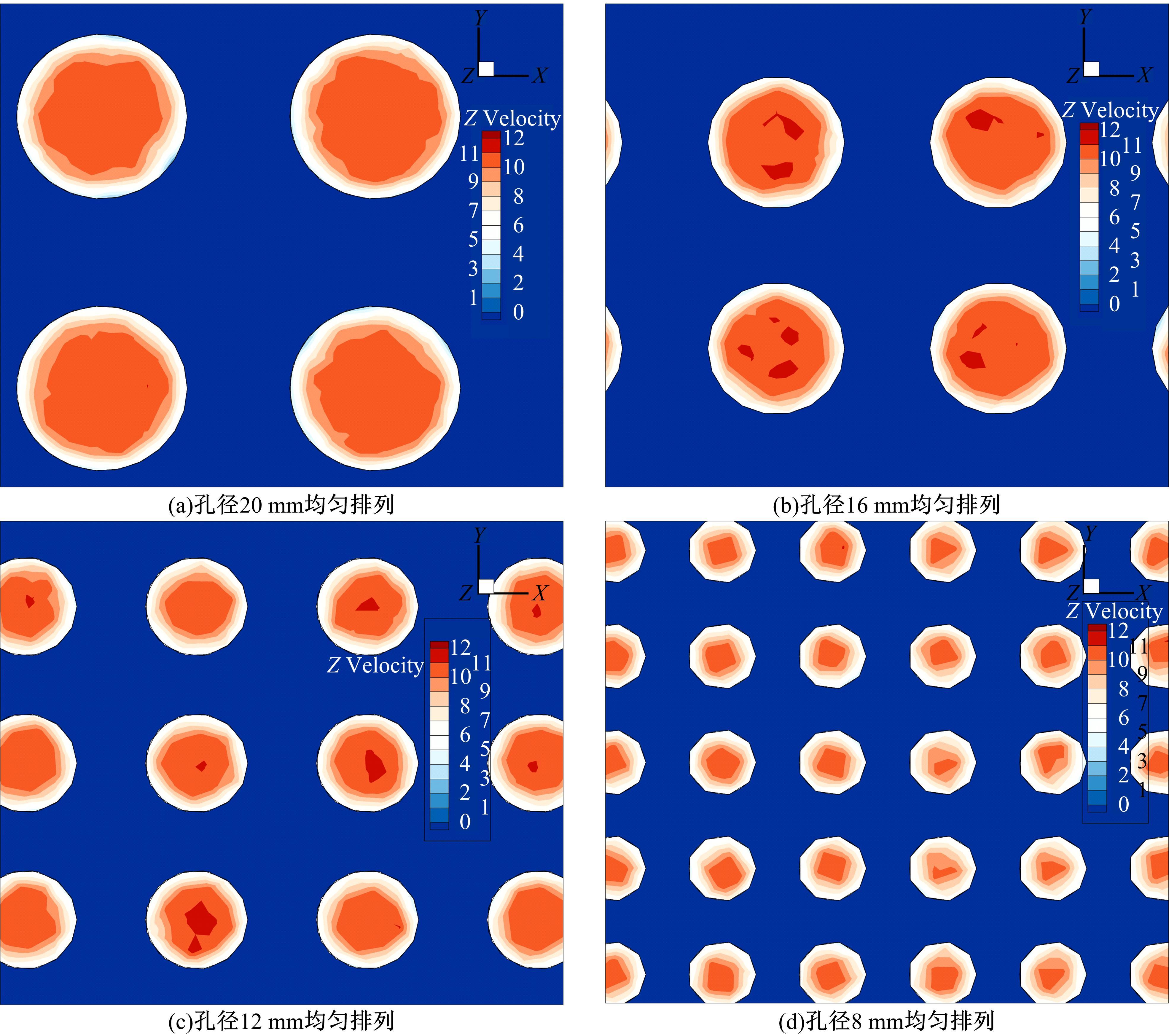
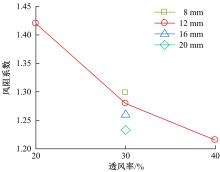
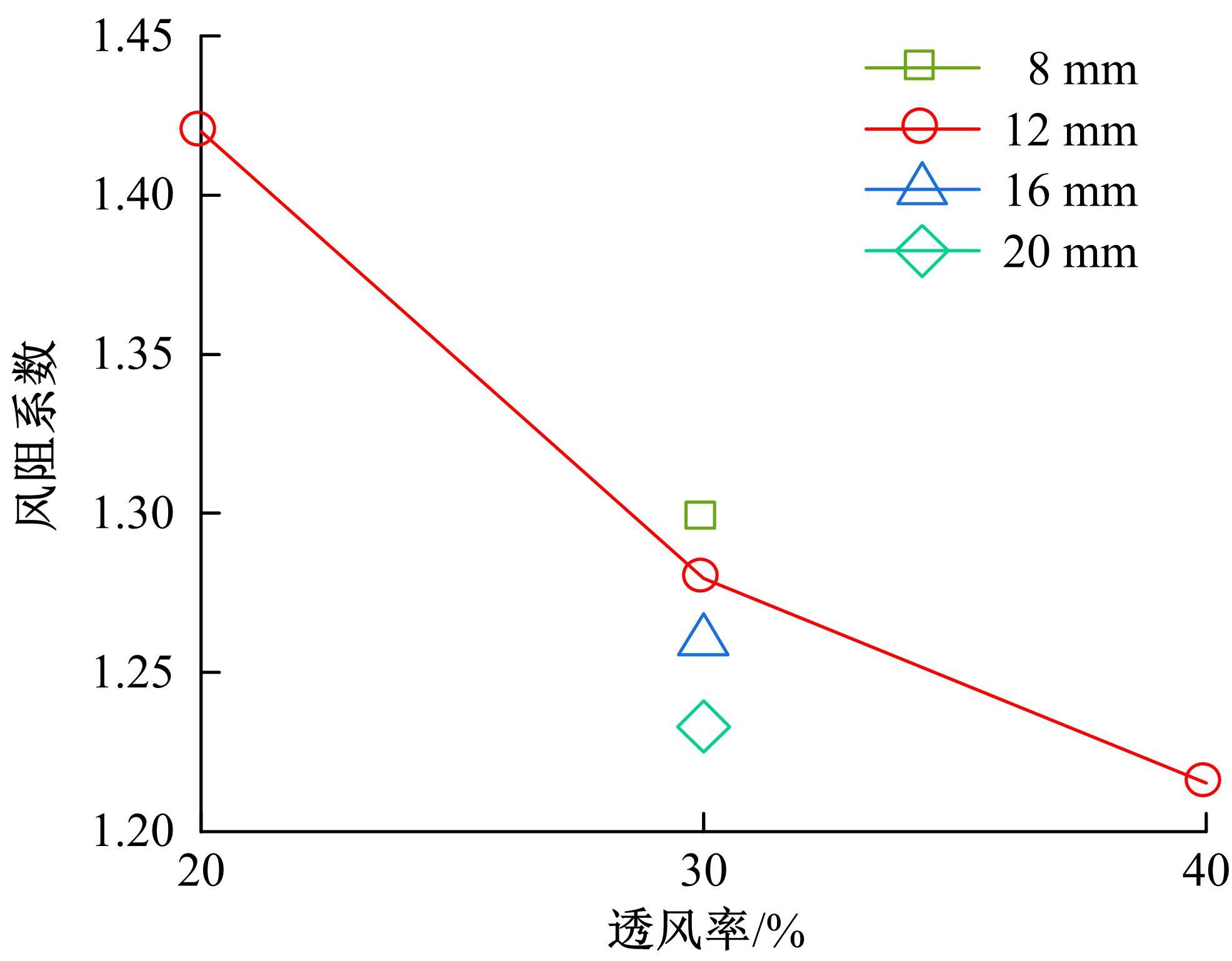
为研究孔径、孔间距、孔隙形状和透风率等因素对风障这类多孔结构应用性能的影响,进行了多个参数的多孔板测力风洞试验,对比了各个参数对多孔板风阻系数的影响效应,通过数值模拟对不同参数下多孔板的流场特性及压力降变化规律进行分析,讨论了相同透风率下,孔径大小和孔间距对边界层厚度、有效透风率的影响,并与风洞试验结果进行对比。结果表明:孔隙形状对多孔板风阻系数影响较小,而长宽比、孔径和孔间距对多孔板风阻系数影响较大,可作为影响多孔结构风阻系数的关键性参数。
中图分类号:
- TU312
| 1 | Allori D, Bartoli G, Mannini C. Wind tunnel tests on macro-porous structural elements: a scaling procedure[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2013, 123: 291-299. |
| 2 | 李春光, 王龙, 韩艳, 等. 风屏障对流线型箱梁涡振性能影响机理试验研究[J]. 湖南大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 48(11): 12-21. |
| Li Chun-guang, Wang Long, Han Yan, et al. Experimental study on influence of wind barrier permeability on characteristics of main girder vortex-induced vibration[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2021, 48(11): 12-21. | |
| 3 | Buljac A, Kozmar H, Pospíšil S, et al. Flutter and galloping of cable-supported bridges with porous wind barriers[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2017, 171: 304-318. |
| 4 | Dong Z, Luo W, Qian G, et al. A wind tunnel simulation of the mean velocity fields behind upright porous fences[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2007, 146(1/2): 82-93. |
| 5 | Jr P A K, van Winkle M. Discharge coefficients through perforated plates[J]. AIChE Journal, 1957, 3(3): 305-312. |
| 6 | Jr P L S, van Winkle M. Discharge coefficients through perforated plates at Reynolds numbers of 400 to 3,000[J]. AIChE Journal, 1958, 4(3): 266-268. |
| 7 | Huang S, Ma T, Wang D, et al. Study on discharge coefficient of perforated orifices as a new kind of flowmeter[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2013, 46: 74-83. |
| 8 | 田红, 高旭, 汤珂, 等. 结构参数对多孔板低温流量计性能影响分析[J]. 低温工程, 2015(6): 43-48. |
| Tian Hong, Gao Xu, Tang Ke, et al. Influence of geometric parameters on performance of a cryogenic fluid flowmeter with perforated plate[J]. Cryogenics, 2015(6): 43-48. | |
| 9 | 王慧锋, 凌长玺. 几何特征对多孔板特性的影响[J]. 华东理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 41(5): 677-685. |
| Wang Hui-feng, Ling Chang-xi. Effect of general geometric characteristics for multi-hole orifices'features[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2015, 41(5): 677-685. | |
| 10 | 赵天怡, 张吉礼. 多孔孔板节流特性主效应因素试验[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2007, 39(12): 1878-1881. |
| Zhao Tian-yi, Zhang Ji-li. Experimental study on main factor affecting throttling characteristic for multi-hole orifice[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007, 39(12): 1878-1881. | |
| 11 | 韩伟, 董志勇, 邴斌, 等. 多孔板压力特性的试验研究[J].水力发电学报, 2014, 33(6): 126-131. |
| Han Wei, Dong Zhi-yong, Bing Bin, et al. Experimental study of pressure characteristics behind multi-orifice plates[J]. Journal of Hydroelectric Engineering, 2014, 33(6): 126-131. | |
| 12 | 马有福, 王凡, 吕俊复. 孔数与孔厚对多孔板压损系数的影响机理[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(2): 446-452. |
| Ma You-fu, Wang Fan, Jun-fu Lü. Influencing mechanism of orifice number and thickness on pressure loss coefficient of multi-orifice plates[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(2): 446-452. | |
| 13 | 李艺, 苏悦琦. 基于不同孔径范围的碳化作用下纤维混凝土的气体渗透性能和细观结构[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1287-1295. |
| Li Yi, Su Yue-qi. Gas permeability and meso-structure of fiber reinforced concrete under carbonation based on different pore sizes[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1287-1295. |
| [1] | 陈贵升,罗国焱,李靓雪,黄震,李一. 柴油机颗粒捕集器孔道流场及其高原环境下噪声特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1892-1901. |
| [2] | 刘子玉,陈士通,支墨墨,黄晓明,陈哲心. 可“临-永”转换抢修钢墩应急使用极限承载力[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1601-1611. |
| [3] | 冯宇,郝键铭,王峰,张久鹏,黄晓明. 非平稳极端风作用下大跨桥梁瞬态风致效应分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1638-1649. |
| [4] | 王华,王龙林,张子墨,何昕. 基于裂缝宽度变化的连续刚构桥安全性预警技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1650-1657. |
| [5] | 王俊,李加武,王峰,张久鹏,黄晓明. 简化U形峡谷风速分布及其对悬索桥抖振响应的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1658-1668. |
| [6] | 吴春利,黄诗茗,李魁,顾正伟,黄晓明,张炳涛,杨润超. 基于数值仿真和统计分析的洪水作用下桥墩作用效应分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1612-1620. |
| [7] | 江辉,李新,白晓宇. 桥梁抗震结构体系发展述评:从延性到韧性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1550-1565. |
| [8] | 谭国金,孔庆雯,何昕,张攀,杨润超,朝阳军,杨忠. 基于动力特性和改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷深度识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1592-1600. |
| [9] | 张玥,刘传森,宋飞. 桥台背墙对连续梁桥地震易损性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1372-1380. |
| [10] | 魏海斌,韩栓业,毕海鹏,刘琼辉,马子鹏. 智能感知道路主动除冰雪系统及实验技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1411-1417. |
| [11] | 兰树伟,周东华,陈旭,莫南明. 双柱式高墩桥梁整体稳定性的实用算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1105-1111. |
| [12] | 金敬福,董新桔,贾志成,王康,贺连彬,邹猛,齐迎春. 板簧式弹性金属车轮胎面弹片结构优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 964-972. |
| [13] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [14] | 孙琪凯,张楠,刘潇,周子骥. 基于Timoshenko梁理论的钢-混组合梁动力折减系数[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 488-495. |
| [15] | 卢晓红,乔金辉,周宇,马冲,隋国川,孙卓. 搅拌摩擦焊温度场研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 1-17. |
|
||