吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1711-1718.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230117
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于数值仿真的简支梁桥震致残余位移分析
顾正伟1( ),张攀2,吕东冶3,吴春利1(
),张攀2,吕东冶3,吴春利1( ),杨忠4,谭国金1,黄晓明5
),杨忠4,谭国金1,黄晓明5
- 1.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
2.长春市建设工程安全监督站,长春 130033
3.吉林省交通信息通信中心,长春 130021
4.吉林省交通规划设计院,长春 130021
5.东南大学 交通学院,南京 210018
Earthquake⁃induced residual displacement analysis of simply supported beam bridge based on numerical simulation
Zheng-wei GU1( ),Pan ZHANG2,Dong-ye LYU3,Chun-li WU1(
),Pan ZHANG2,Dong-ye LYU3,Chun-li WU1( ),Zhong YANG4,Guo-jin TAN1,Xiao-ming HUANG5
),Zhong YANG4,Guo-jin TAN1,Xiao-ming HUANG5
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Changchun Construction Projects Quality Surveillance,Changchun 130033,China
3.Jilin Provincial Traffic Information and Communication Center,Changchun 130021,China
4.Jilin Traffic Planning and Design Institute,Changchun 130021,China
5.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 210018,China
摘要:
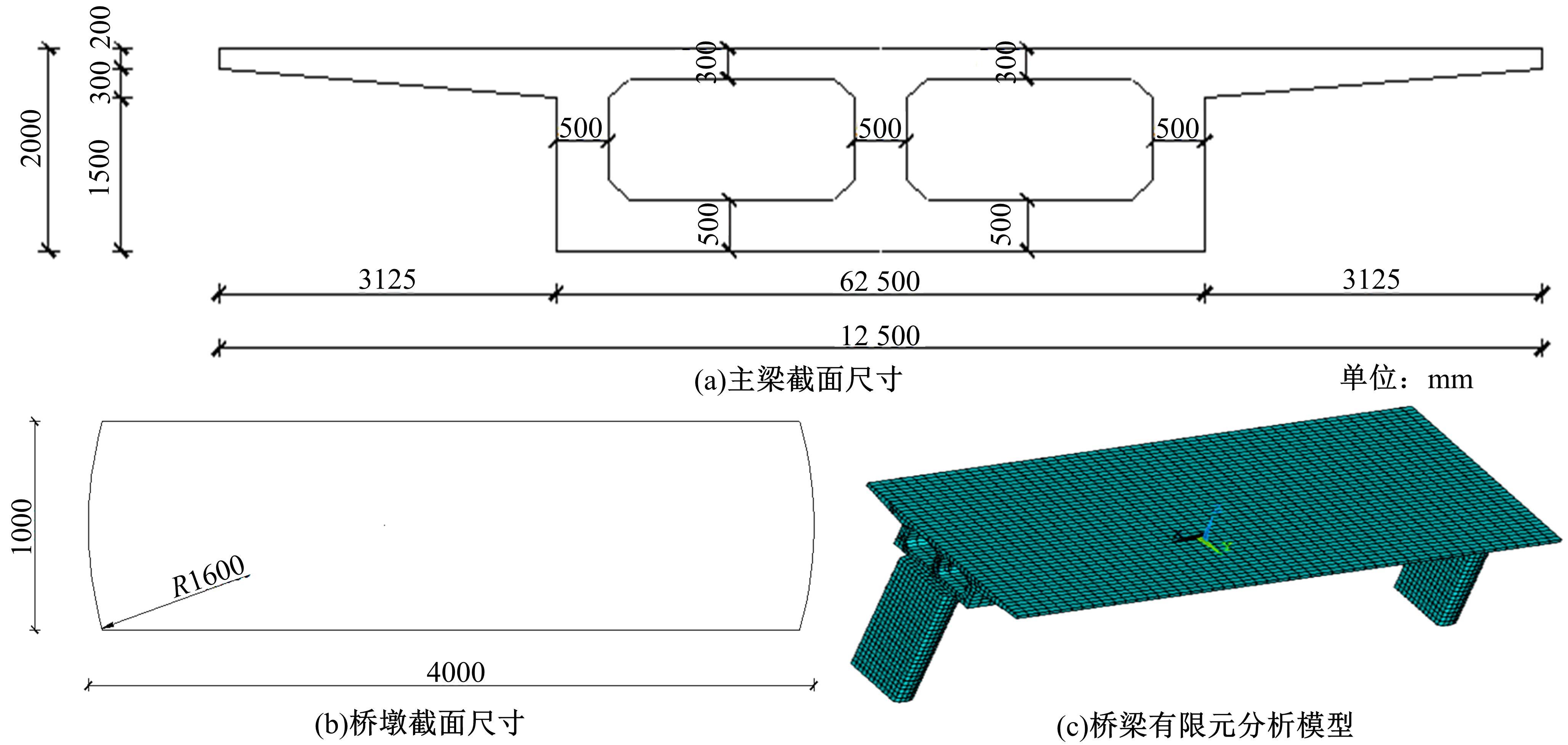
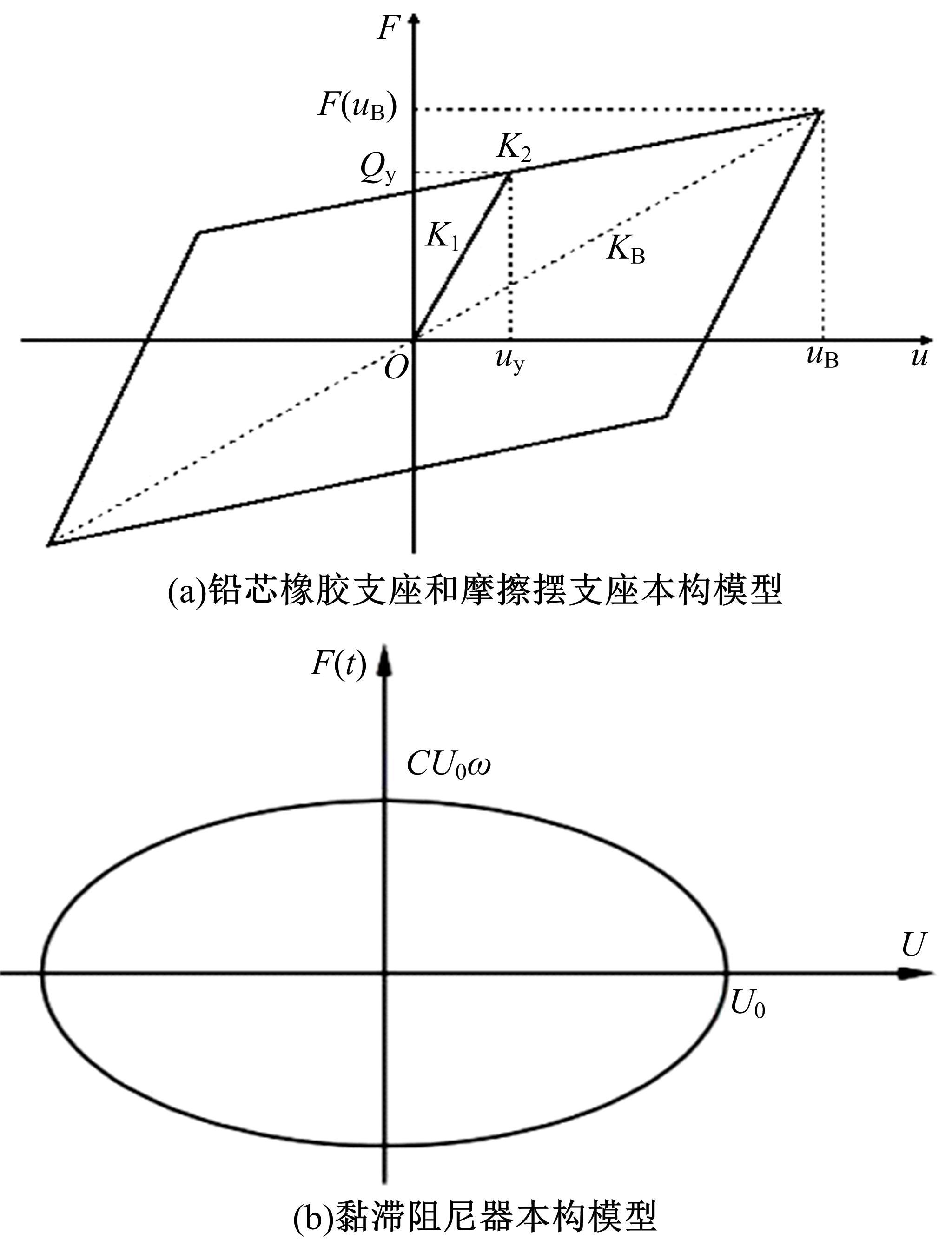
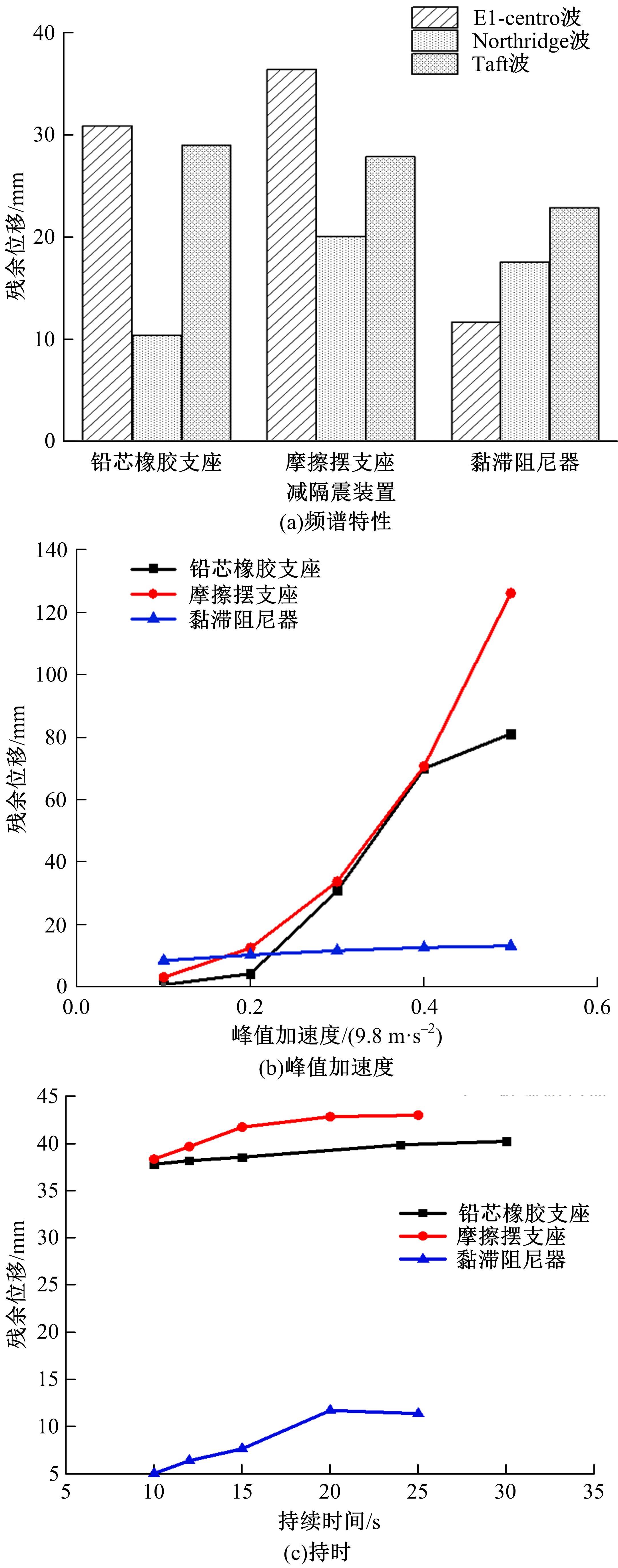
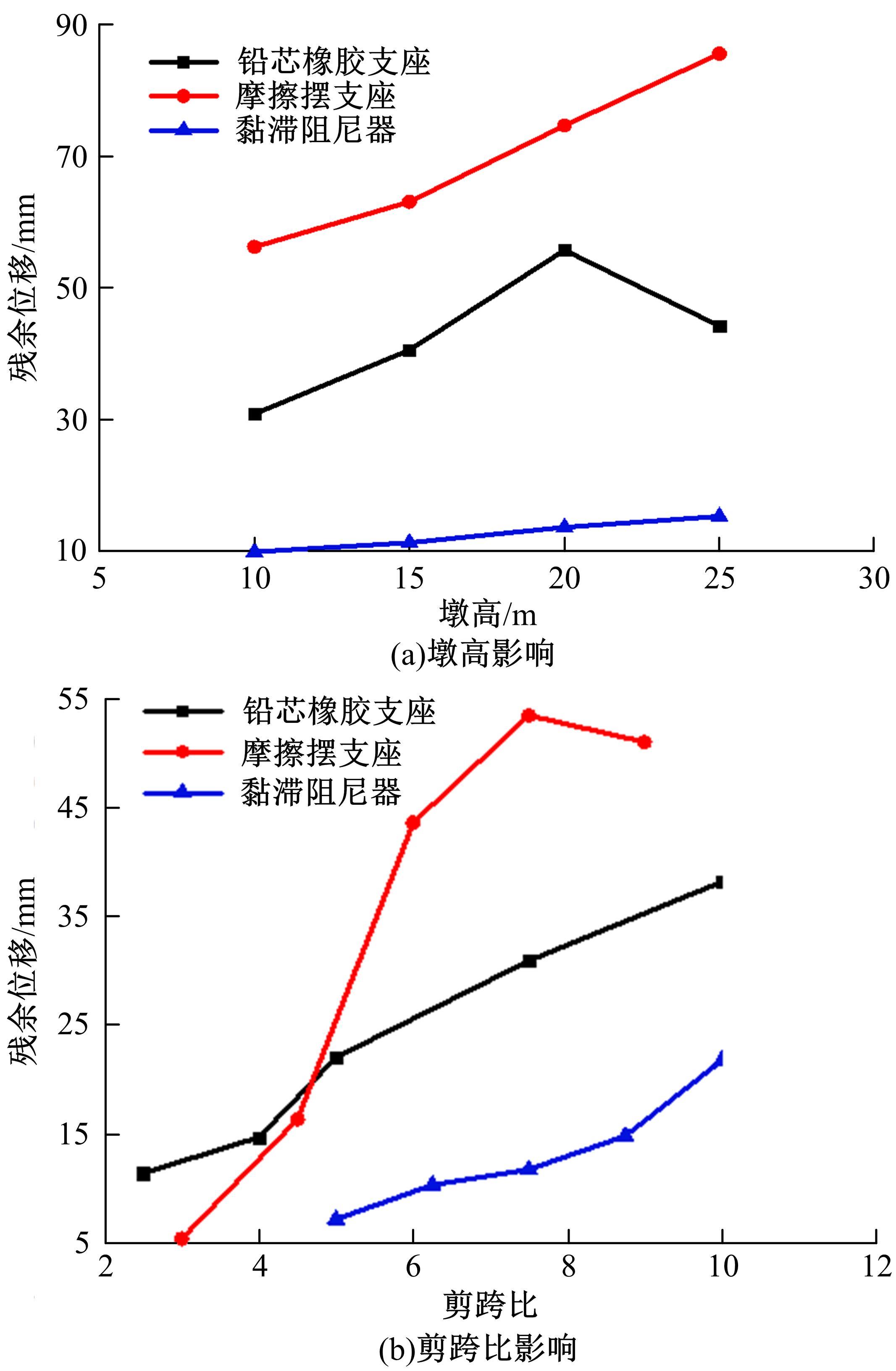
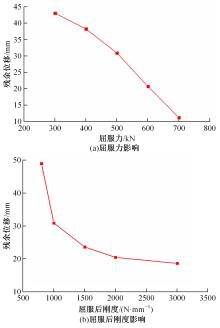
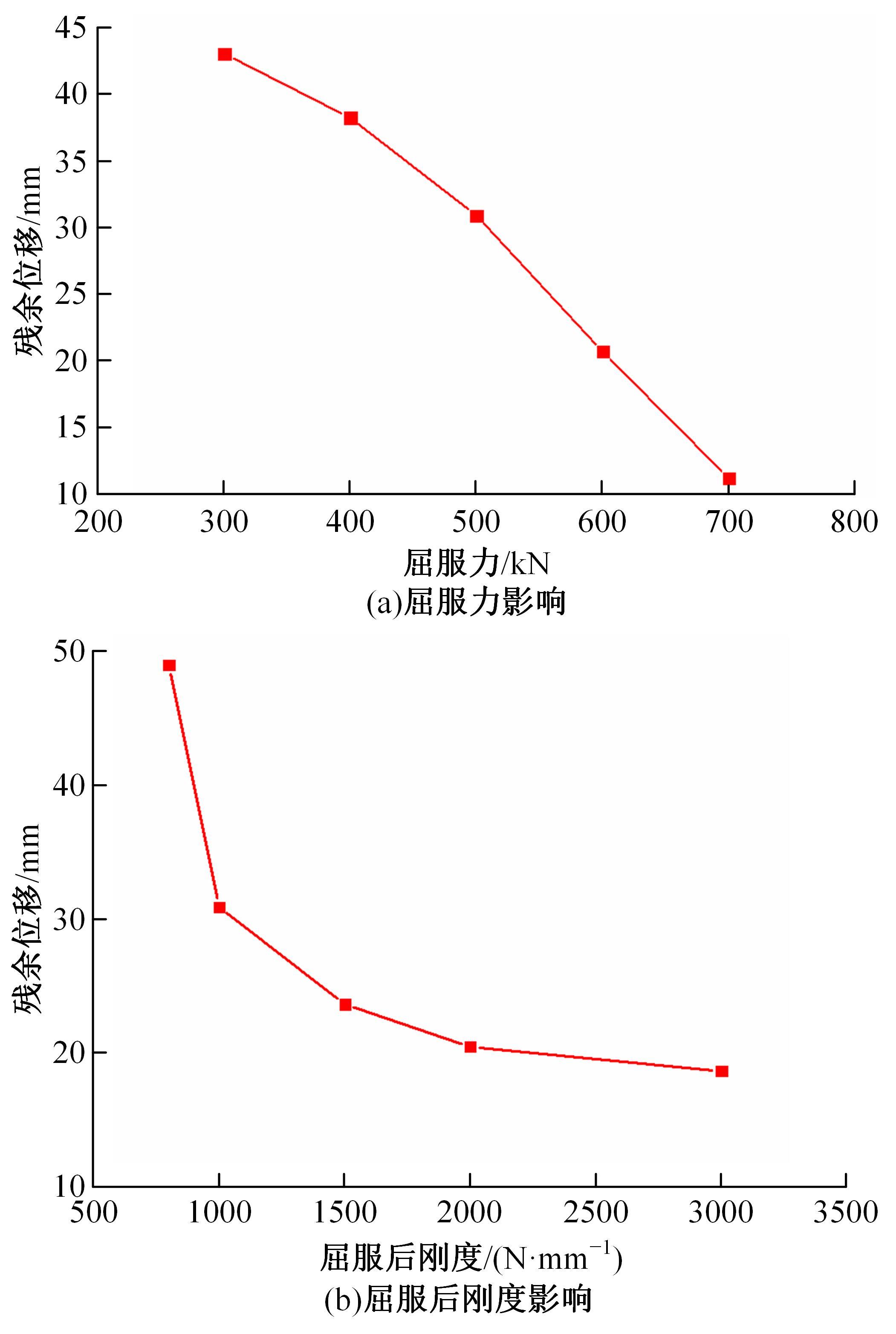
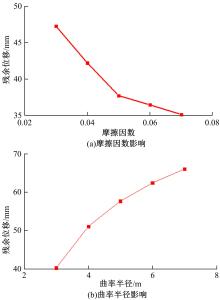
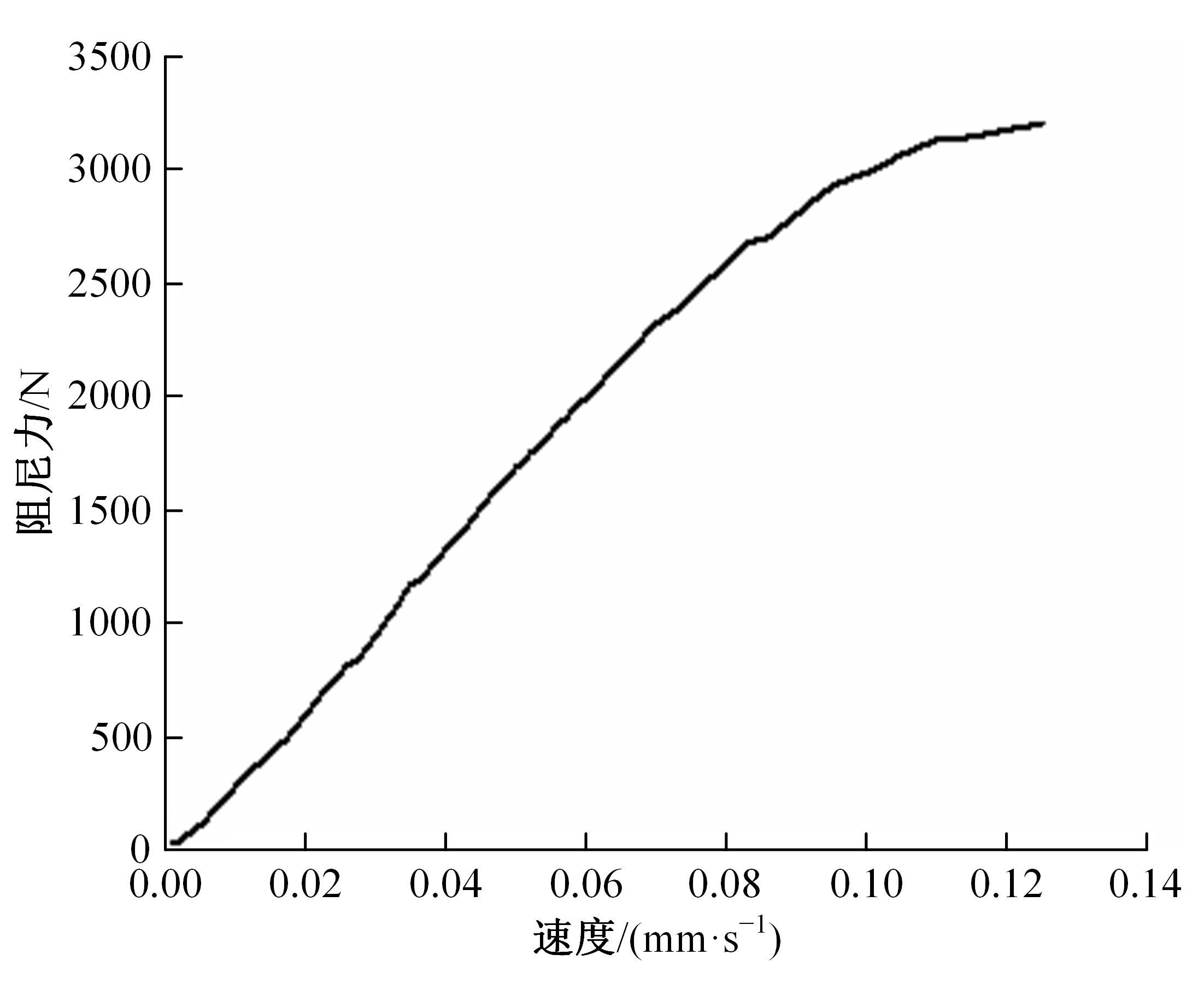
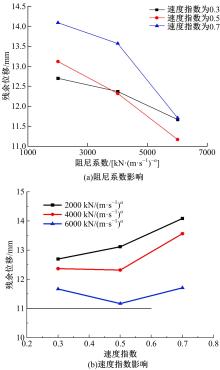
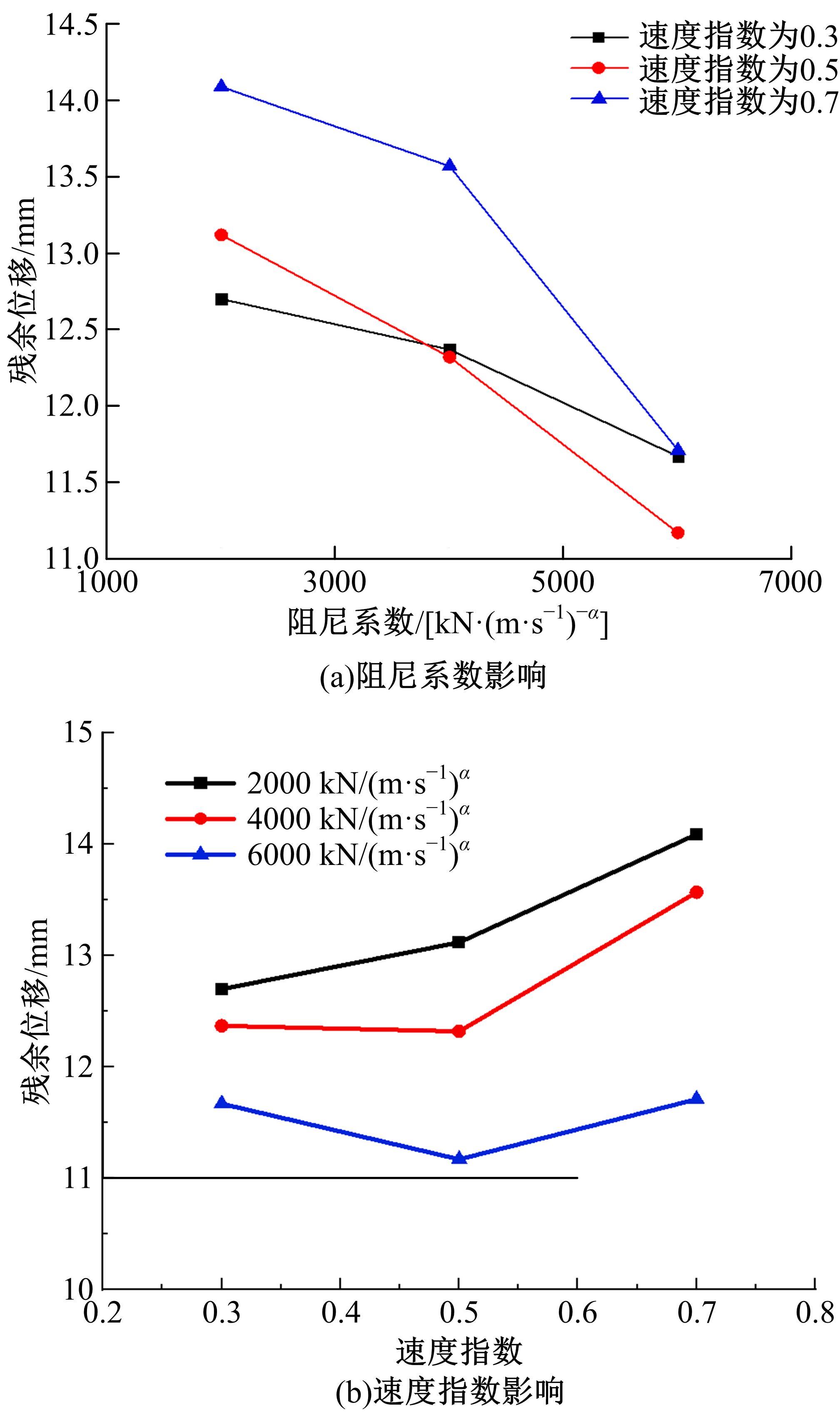
基于ANSYS建立了具有铅芯橡胶支座、摩擦摆支座和黏滞阻尼器的简支梁桥有限元模型。通过改变地震激励、结构参数和减隔震装置参数,进行了地震荷载作用下多种工况的桥梁震致残余位移分析。结果表明,残余位移对地震波频谱特性较为敏感,且随峰值加速度、剪跨比的增大显著增大,随持续时间和墩高的增加有所增大;残余位移对铅芯橡胶支座和摩擦摆支座参数变化较为敏感,黏滞阻尼器参数变化对其影响较小,可通过增大铅芯橡胶支座屈服力、屈服后刚度、摩擦摆支座摩擦因数、黏滞阻尼器阻尼孔长度、液缸外径、硅油黏度和减小摩擦摆支座曲率半径的方法降低结构震致残余位移。本文研究结果可为桥梁结构抗灾韧性提升提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
- U442.55
| 1 | Bojorquez E, Ruiz G J. Residual drift demands in moment-resisting steel frames subjected to narrow-band earthquake ground motions[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 2013, 42(11): 1583-1598. |
| 2 | 王军文, 李海洋, 闫聚考, 等. 地震作用下钢筋混凝土桥墩残余位移研究[J]. 振动与冲击,2018, 37(13): 130-134. |
| Wang Jun-wen, Li Hai-yang, Yan Ju-kao, et al. Residual displacements of RC piers under action of earthquake[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(13): 130-134. | |
| 3 | 曾武华, 卓卫东, 王东升. RC桥墩残余位移指标影响因素分析及贝叶斯估计[J]. 振动与冲击,2021, 40(19): 145-150. |
| Zeng Wu-hua, Zhuo Wei-dong, Wang Dong-sheng. Influence factors analysis and bayesian estimation for residual displacement index of RC pie[J]. Journal of Vibration and shock, 2021, 40(19): 145-150. | |
| 4 | 余波, 刘迪, 杨绿峰. 考虑P-Δ效应的桥梁结构震后概率残余位移分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(1): 154-161. |
| Yu Bo, Liu Di, Yang Lv-feng. Probabilistic residual displacement analysis of bridge structures considering P-Δ effect[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(1): 154-161. | |
| 5 | 孙治国, 张振涛, 伍隋文, 等. 考虑PSSI的桩柱式桥墩震后残余位移分析[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2022, 30(3): 684-694. |
| Sun Zhi-guo, Zhang Zhen-tao, Wu Sui-wen, et al. Analysis on the residual displacement of extended pile-shafts considering pile-soil-structure interaction (PSSI) after earthquakes[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2022,30(3): 684-694. | |
| 6 | 申纪创. 中小跨径梁式桥地震残余位移分析与控制方法研究[D]. 重庆:重庆交通大学土木工程学院 2016. |
| Shen Ji-chuang. Analysis and control method of seismic residual displacement of small and medium-span beam bridge[D]. Chongqing: School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 7 | Liossatou E, Fardis MN. Residual displacements of RC structures as SDOF systems[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 2015, 44(5): 713-734. |
| 8 | 张艳霞, 黄威振, 刘安然, 等. 自复位免修复摩擦耗能支撑性能研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(4): 136-146. |
| Zhang Yan-xia, Huang Wei-zhen, Liu An-ran, et al. A study on the behavior of self-centering and free-repair braces with friction dampers[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2018, 37(4): 136-146. | |
| 9 | 李刚, 王甲飞, 胡雪飞. 自复位变摩擦阻尼器有限元分析[J]. 结构工程师, 2020, 36(5): 66-73. |
| Li Gang, Wang Jia-fei, Hu Xue-fei. Finite element analysis of self-resetting variable friction damper[J]. Structural Engineer, 2020, 36(5): 66-73. | |
| 10 | 刘云帅, 韩建平. 自复位单向摩擦阻尼器梁桥数值模拟及混合试验[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020(): 294-300. |
| Liu Yun-shuai, Han Jian-ping. Numerical simulation and hybrid test of the girder bridge with self-centering unidirectional friction damper[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020(Sup.2): 294-300. | |
| 11 | 马永涛, 龙晓鸿, 陈兴望, 等. SMA-LRB复合型支座隔震连续梁桥地震易损性分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 2022, 42(3): 95-103. |
| Ma Yong-tao, Long Xiao-ou, Chen Xing-wang, et al. Seismic fragility analysis of continuous girder bridges with SMA-LRB [J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 2022, 42(3): 95-103. | |
| 12 | 杨毅. SMA-FPS复合支座及其在连续梁桥中的隔震研究[D]. 南京:东南大学土木工程学院, 2017. |
| Yang Yi. Research on SMA-FPS composite bearing and seismic isolation to continuous bridge under earthquakes[D] Nanjing: School of Civil Engineering, Southeast University, 2017. | |
| 13 | Taylor D P, Metzger J C. Structural control using functionally upgraded spring-damper isolator having integral gapping elements[C]∥Structures Congress, Texas, USA, 2009: 850-859. |
| [1] | 冯宇,郝键铭,王峰,张久鹏,黄晓明. 非平稳极端风作用下大跨桥梁瞬态风致效应分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1638-1649. |
| [2] | 王华,王龙林,张子墨,何昕. 基于裂缝宽度变化的连续刚构桥安全性预警技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1650-1657. |
| [3] | 王俊,李加武,王峰,张久鹏,黄晓明. 简化U形峡谷风速分布及其对悬索桥抖振响应的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1658-1668. |
| [4] | 王峰,刘双瑞,王佳盈,宋佳玲,王俊,张久鹏,黄晓明. 尺寸和形状效应对多孔结构风阻系数的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1677-1685. |
| [5] | 吴春利,黄诗茗,李魁,顾正伟,黄晓明,张炳涛,杨润超. 基于数值仿真和统计分析的洪水作用下桥墩作用效应分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1612-1620. |
| [6] | 江辉,李新,白晓宇. 桥梁抗震结构体系发展述评:从延性到韧性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1550-1565. |
| [7] | 谭国金,孔庆雯,何昕,张攀,杨润超,朝阳军,杨忠. 基于动力特性和改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷深度识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1592-1600. |
| [8] | 刘子玉,陈士通,支墨墨,黄晓明,陈哲心. 可“临-永”转换抢修钢墩应急使用极限承载力[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1601-1611. |
| [9] | 袁野. 温度和车辆作用下梁式桥梁结构固有频率分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1702-1710. |
| [10] | 魏海斌,韩栓业,毕海鹏,刘琼辉,马子鹏. 智能感知道路主动除冰雪系统及实验技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1411-1417. |
| [11] | 张玥,刘传森,宋飞. 桥台背墙对连续梁桥地震易损性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1372-1380. |
| [12] | 兰树伟,周东华,陈旭,莫南明. 双柱式高墩桥梁整体稳定性的实用算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1105-1111. |
| [13] | 金敬福,董新桔,贾志成,王康,贺连彬,邹猛,齐迎春. 板簧式弹性金属车轮胎面弹片结构优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 964-972. |
| [14] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [15] | 孙琪凯,张楠,刘潇,周子骥. 基于Timoshenko梁理论的钢-混组合梁动力折减系数[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 488-495. |
|
||