吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2942-2951.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220119
基于深度学习的两阶段实时显式拓扑优化方法
孙舒杨1,2( ),程玮斌1,张浩桢1,邓向萍1,齐红1,2(
),程玮斌1,张浩桢1,邓向萍1,齐红1,2( )
)
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
Deep-learning-based two-stage approach for real-time explicit topology optimization
Shu-yang SUN1,2( ),Wei-bin CHENG1,Hao-zhen ZHANG1,Xiang-ping DENG1,Hong QI1,2(
),Wei-bin CHENG1,Hao-zhen ZHANG1,Xiang-ping DENG1,Hong QI1,2( )
)
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
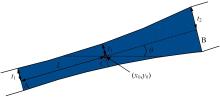
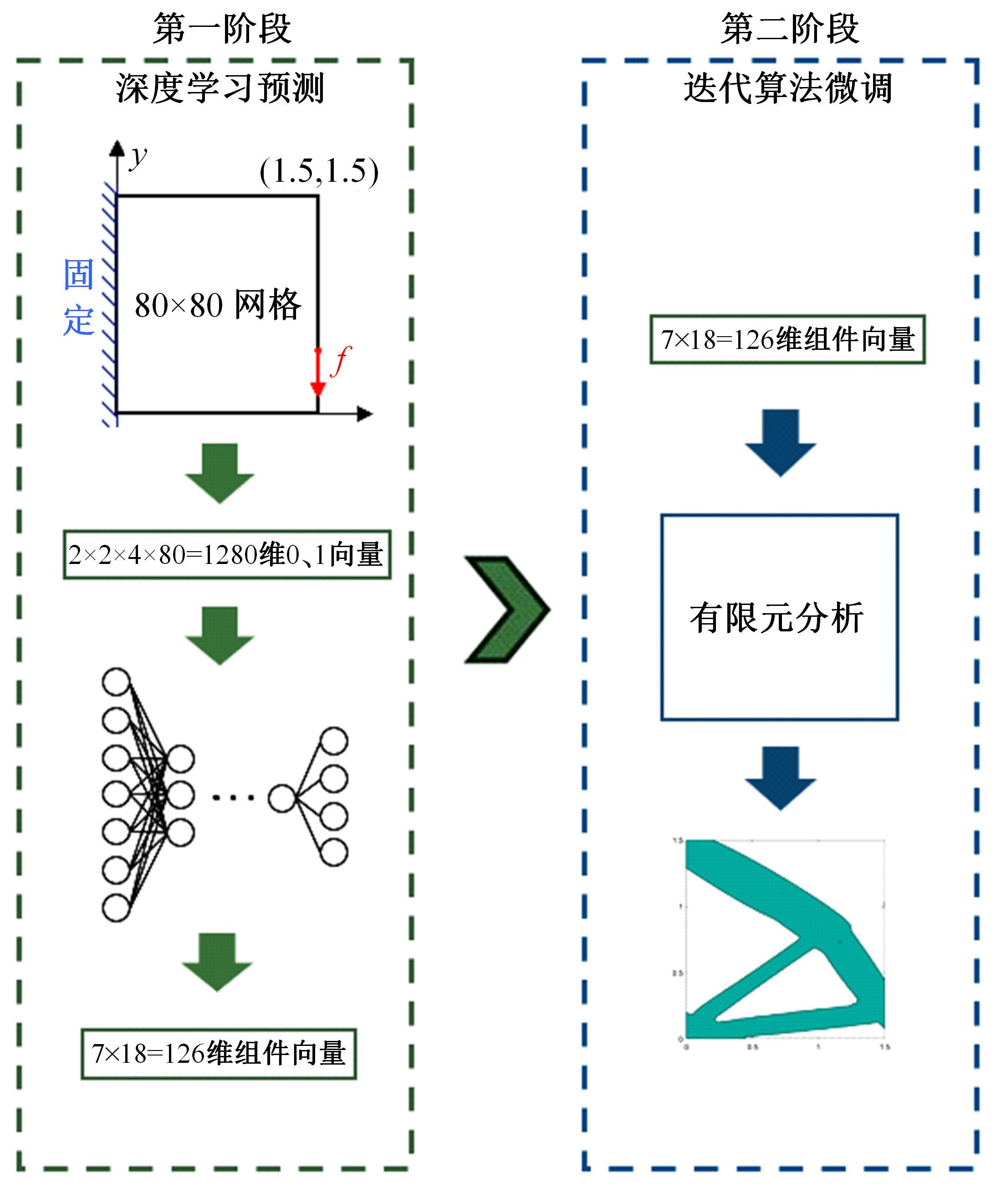
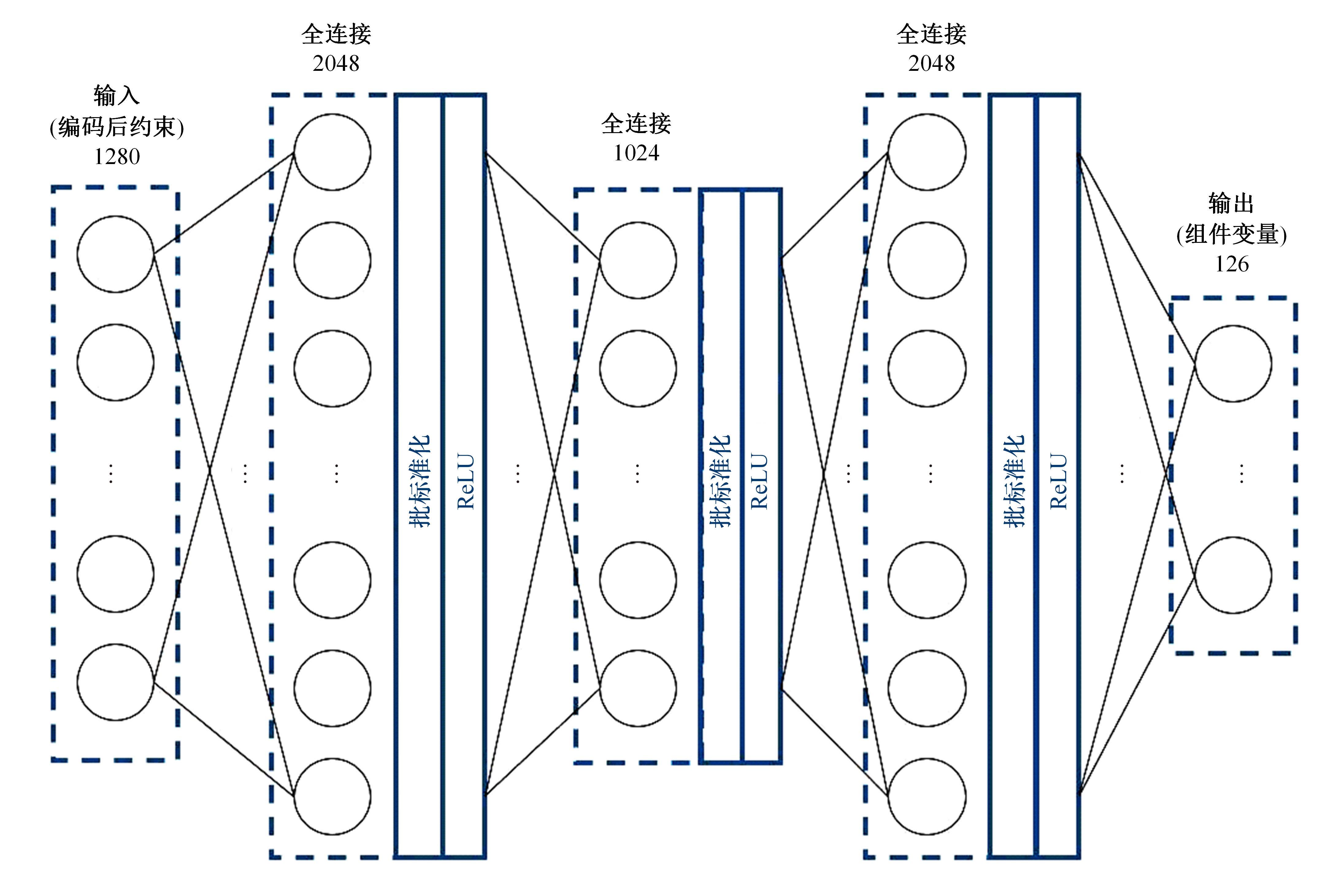
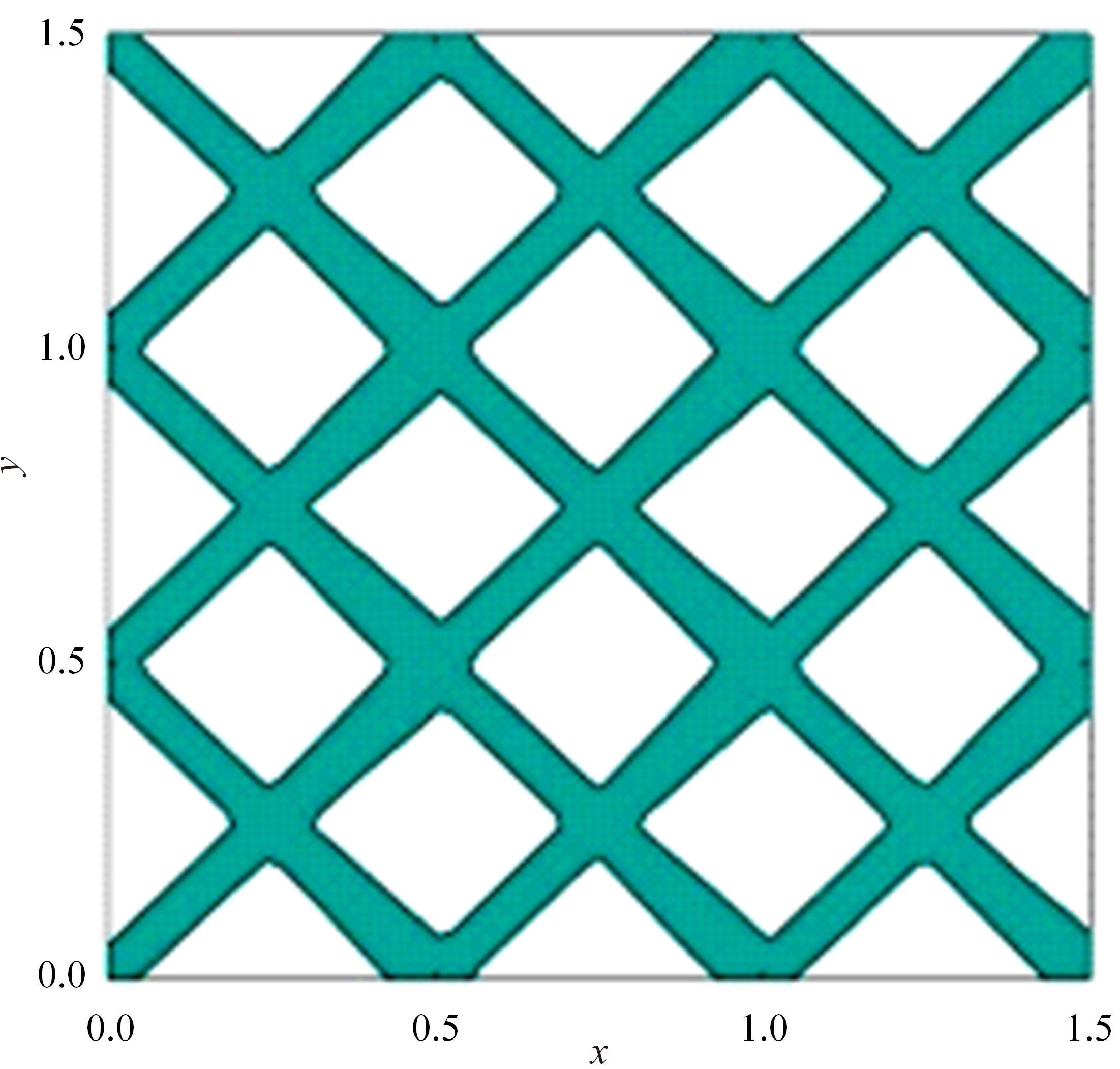
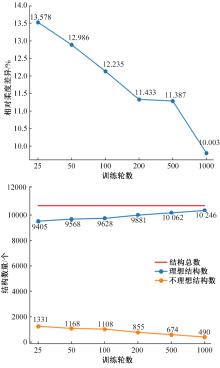
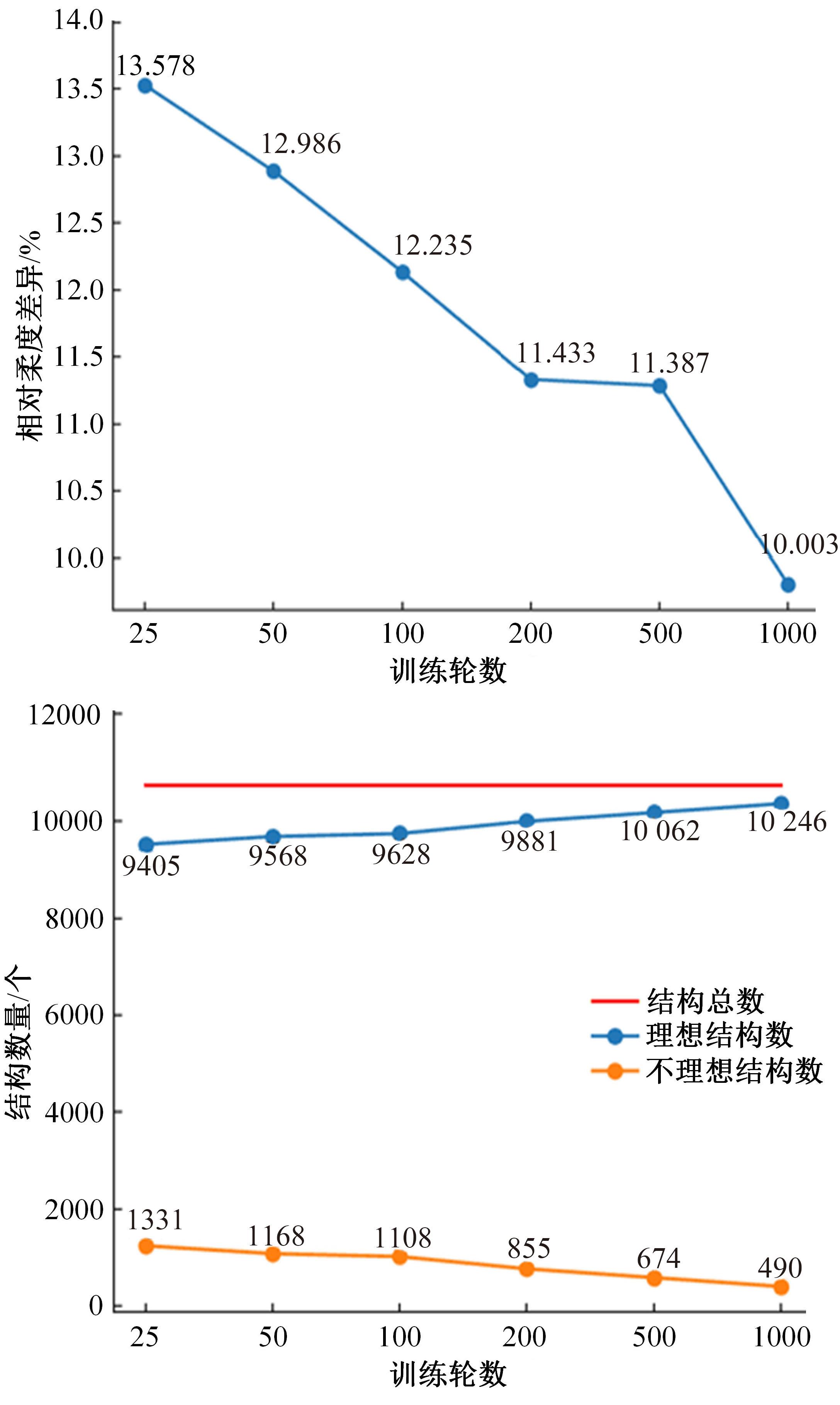
针对以固体各向同性材料法(SIMP)、水平集法(Level-set)等为代表的传统连续体拓扑优化算法存在的计算代价昂贵、生成结构几何隐式等缺陷,结合深度学习与可移动变形组件法(MMC),提出一种基于深度学习的两阶段实时显式拓扑优化方法。在第一阶段使用深度学习模型预测取代有限元分析的多数费时迭代计算,第二阶段对深度学习模型预测所得结构进行少量迭代微调,形成最终的带有显式几何特征的优化结构。在相对一般的数据集下定量与定性地验证了本文方法的可行性与有效性,并研究了第一阶段深度学习模型的训练程度与最终生成结构质量及总体耗费时间的关系。结果表明:与传统连续体拓扑优化算法相比,本文方法能在保证拓扑优化结构生成质量的同时节约90%以上的计算时间。
中图分类号:
- TP399
| 1 | Bendsøe M P. Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem[J]. Structural Optimization, 1989, 1(4): 193-202. |
| 2 | Wang M Y, Wang X, Guo D. A level set method for structural topology optimization[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 192(1/2):227-246. |
| 3 | Guo X, Zhang W, Zhong W. Doing topology optimization explicitly and geometrically—a new moving morphable components based framework[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2014, 81(8): No.081009. |
| 4 | Sosnovik I, Oseledets I. Neural networks for topology optimization[J]. Russian Journal of Numerical Analysis and Mathematical Modelling, 2019, 34(4): 215-223. |
| 5 | Yu Y, Hur T, Jung J, et al. Deep learning for determining a near-optimal topological design without any iteration[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2019, 59(3): 787-799. |
| 6 | Liu K, Tovar A, Nutwell E, et al. Towards nonlinear multimaterial topology optimization using unsupervised machine learning and metamodel-based optimization[C]∥International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Boston, USA, 2015. |
| 7 | Banga S, Gehani H, Bhilare S, et al. 3D topology optimization using convolutional neural networks[DB/OL].[2018-02-11]. . |
| 8 | Rawat S, Shen M H. A novel topology optimization approach using conditional deep learning[DB/OL]. [2019-03-14]. . |
| 9 | Lei X, Liu C, Du Z, et al. Machine learning-driven real-time topology optimization under moving morphable component-based framework[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2019, 86(1): No.011004. |
| 10 | Zhang W, Yuan J, Zhang J, et al. A new topology optimization approach based on moving morphable components (MMC) and the ERSATZ material model[J]. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization, 2016, 53(6): 1243-1260. |
| 11 | Hou W, Gai Y, Zhu X, et al. Explicit isogeometric topology optimization using moving morphable components[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 326: 694-712. |
| 12 | Guo X, Zhao K, Wang M Y. A new approach for simultaneous shape and topology optimization based on dynamic implicit surface function[J]. Control Cybern, 2005, 34(1): 255-282. |
| 13 | Svanberg K. The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1987, 24(2): 359-373. |
| [1] | 霍光,林大为,刘元宁,朱晓冬,袁梦,盖迪. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的轻量级虹膜分割模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [2] | 何颖,王卓然,周旭,刘衍珩. 融合社交地理信息加权矩阵分解的兴趣点推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2632-2639. |
| [3] | 张云佐,董旭,蔡昭权. 拟合下肢几何特征的多视角步态周期检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2611-2619. |
| [4] | 肖明尧,李雄飞,朱芮. 基于NSST域像素相关分析的医学图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2640-2648. |
| [5] | 赵亚慧,李飞雨,崔荣一,金国哲,张振国,李德,金小峰. 基于跨语言预训练模型的朝汉翻译质量评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [6] | 金小俊,孙艳霞,于佳琳,陈勇. 基于深度学习与图像处理的蔬菜苗期杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2421-2429. |
| [7] | 车翔玖,徐欢,潘明阳,刘全乐. 生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [8] | 耿庆田,刘植,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [9] | 王连明,吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [10] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [11] | 刘培勇,董洁,谢罗峰,朱杨洋,殷国富. 基于多支路卷积神经网络的磁瓦表面缺陷检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1449-1457. |
| [12] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [13] | 张则强,梁巍,谢梦柯,郑红斌. 混流双边拆卸线平衡问题的精英差分进化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1297-1304. |
| [14] | 于鹏,朴燕. 基于多尺度特征的行人重识别属性提取新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1155-1162. |
| [15] | 吴飞,农皓业,马晨浩. 基于粒子群优化算法⁃长短时记忆模型的刀具磨损预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 989-997. |
|
||