吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (1): 180-187.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220232
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
相变沥青混凝土复合结构降温效果试验分析
- 1.河海大学 土木与交通学院,南京 210098
2.东南大学 能源与环境学院,南京 211189
Laboratory investigation on cooling effect of multi-layer phase change asphalt concrete
Jun CHEN1( ),Zhen-hao SUN1,Cheng ZHAO1,Xin-yi WU2,Jun-peng WANG1
),Zhen-hao SUN1,Cheng ZHAO1,Xin-yi WU2,Jun-peng WANG1
- 1.College of Civil and Transportation Engineering,Hohai University,Nanjing 210098,China
2.School of Energy and Environment,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
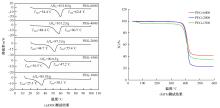
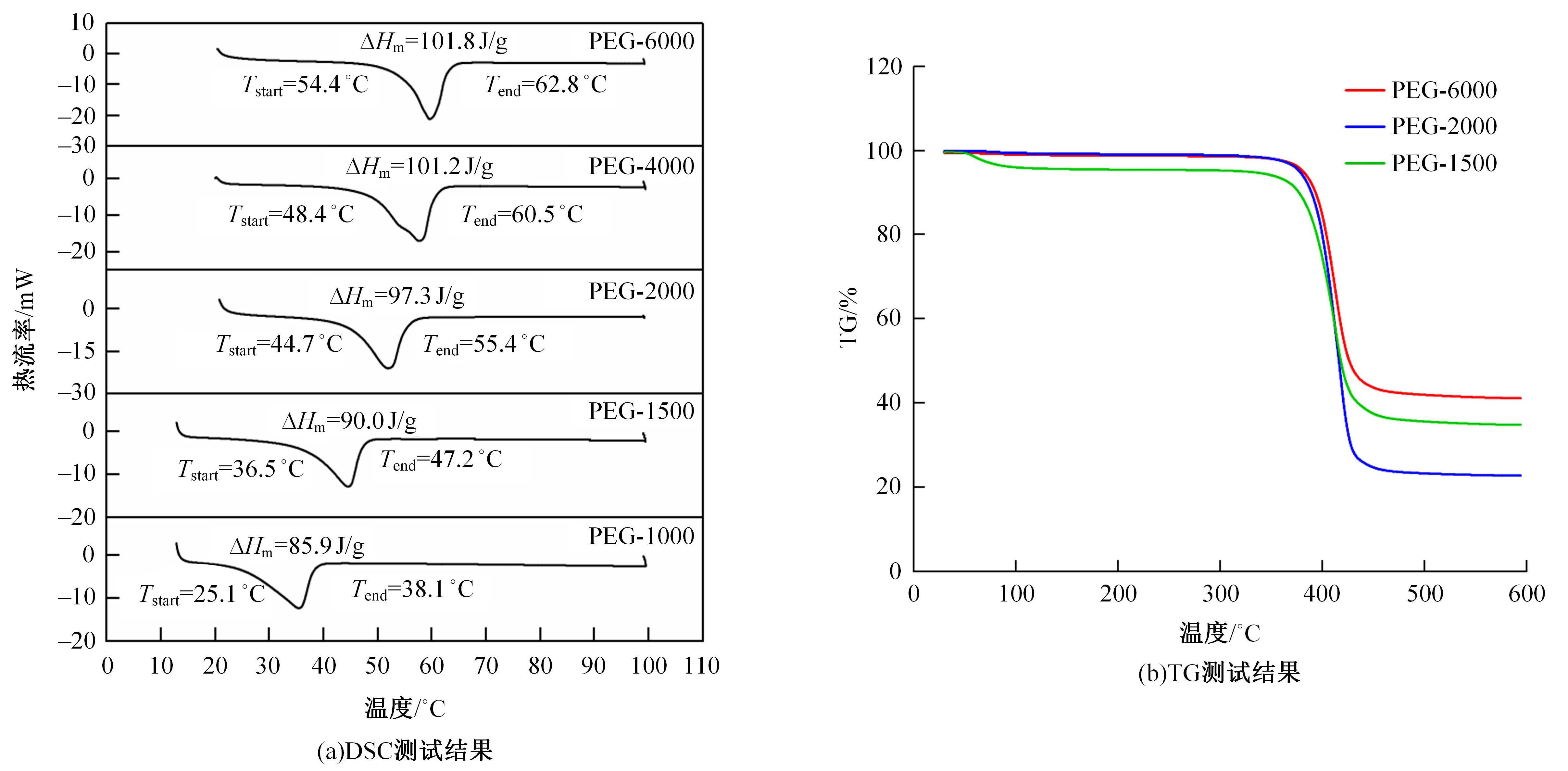
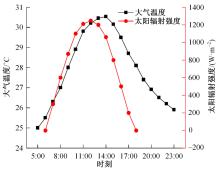
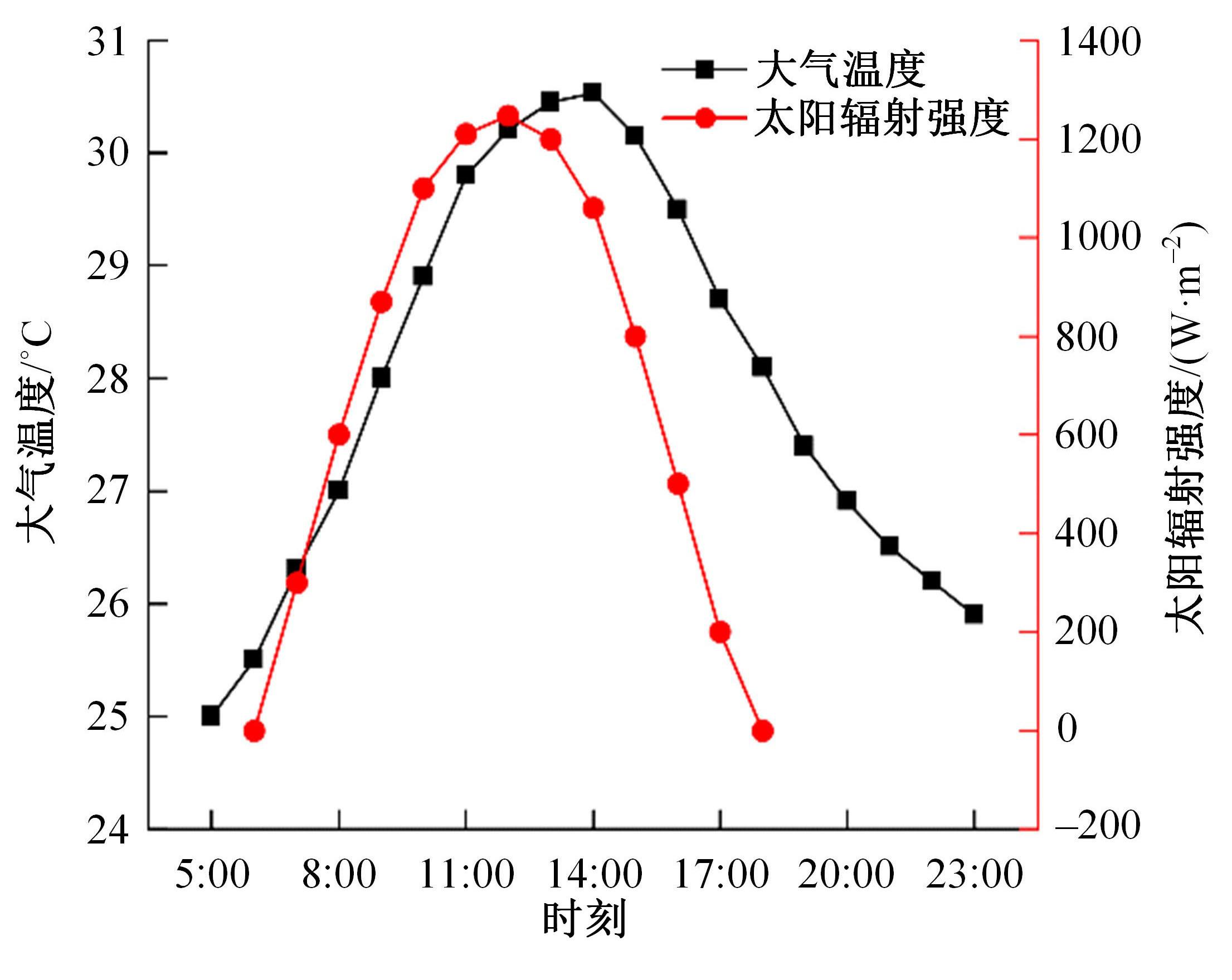
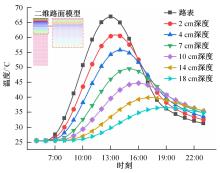
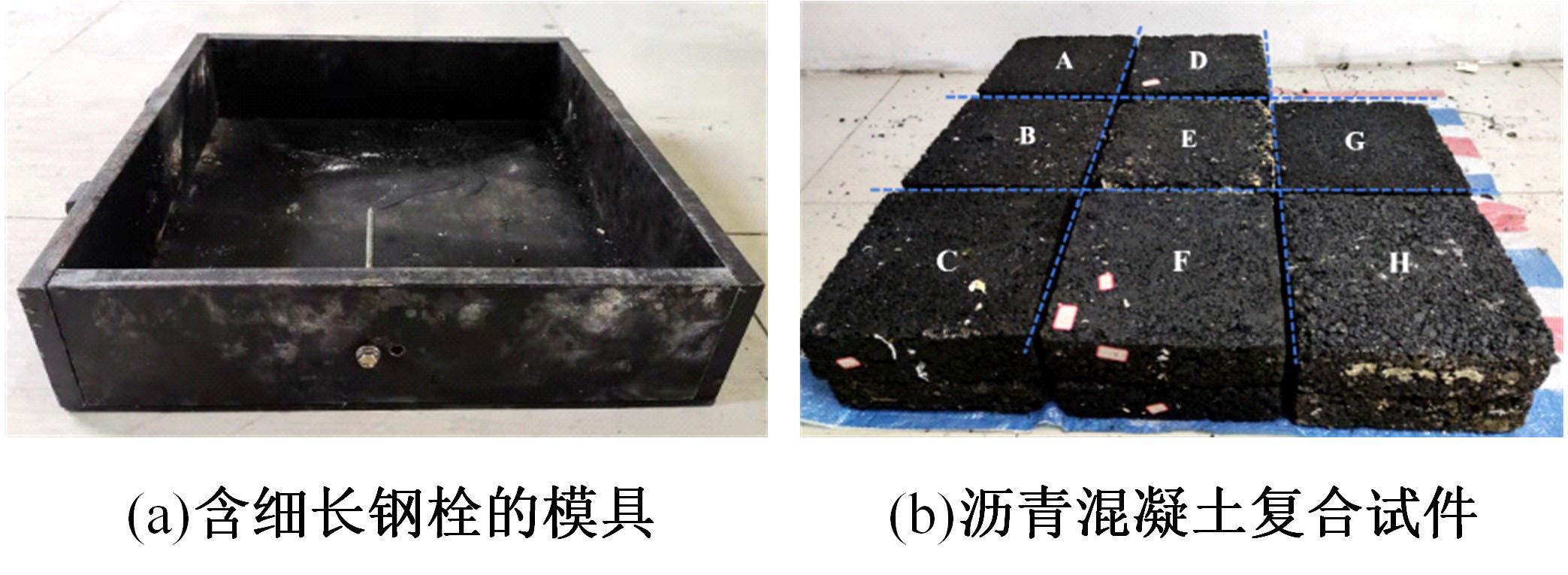
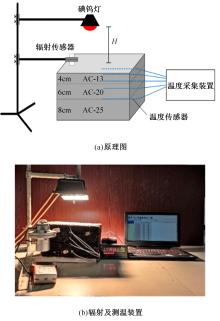
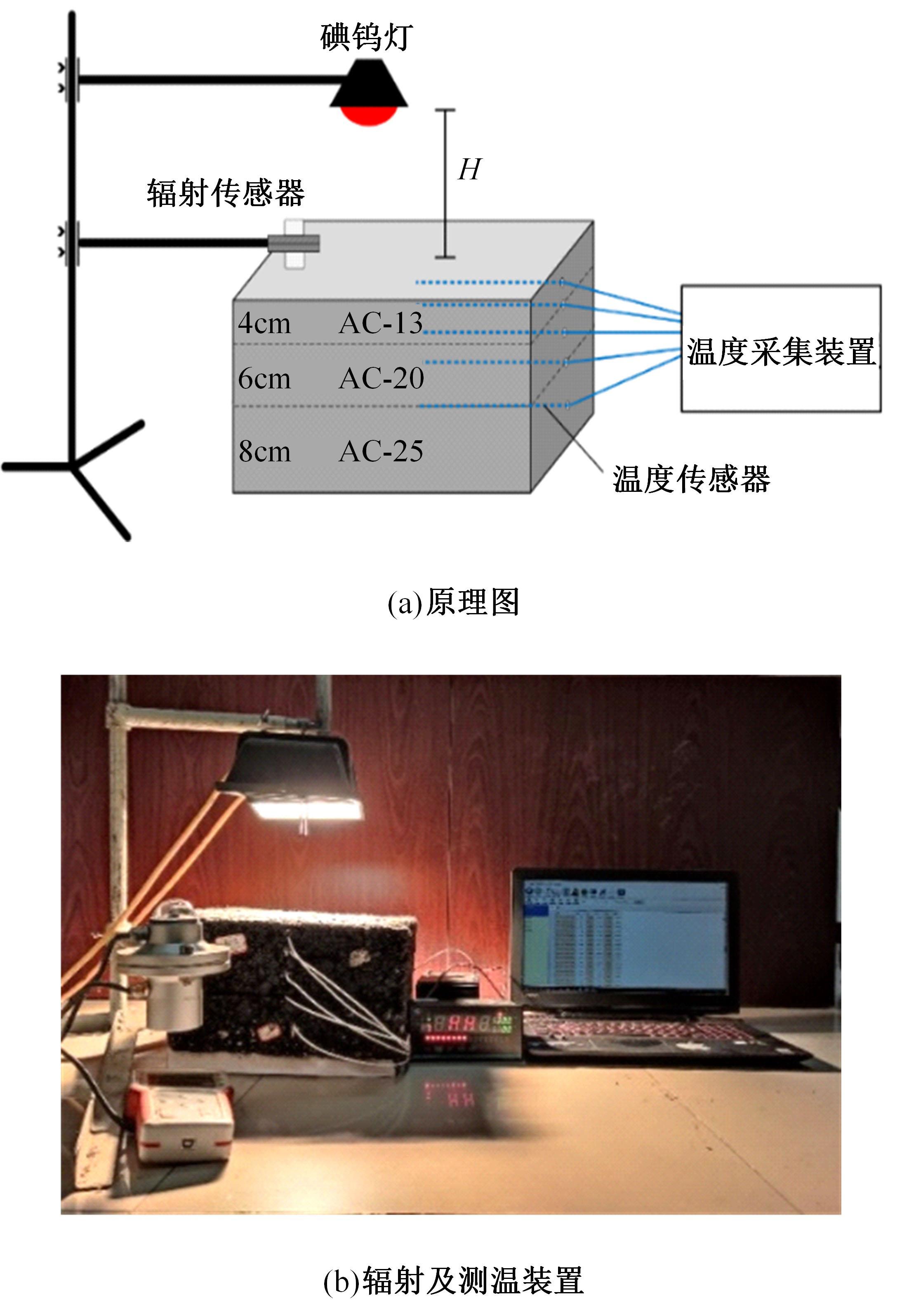
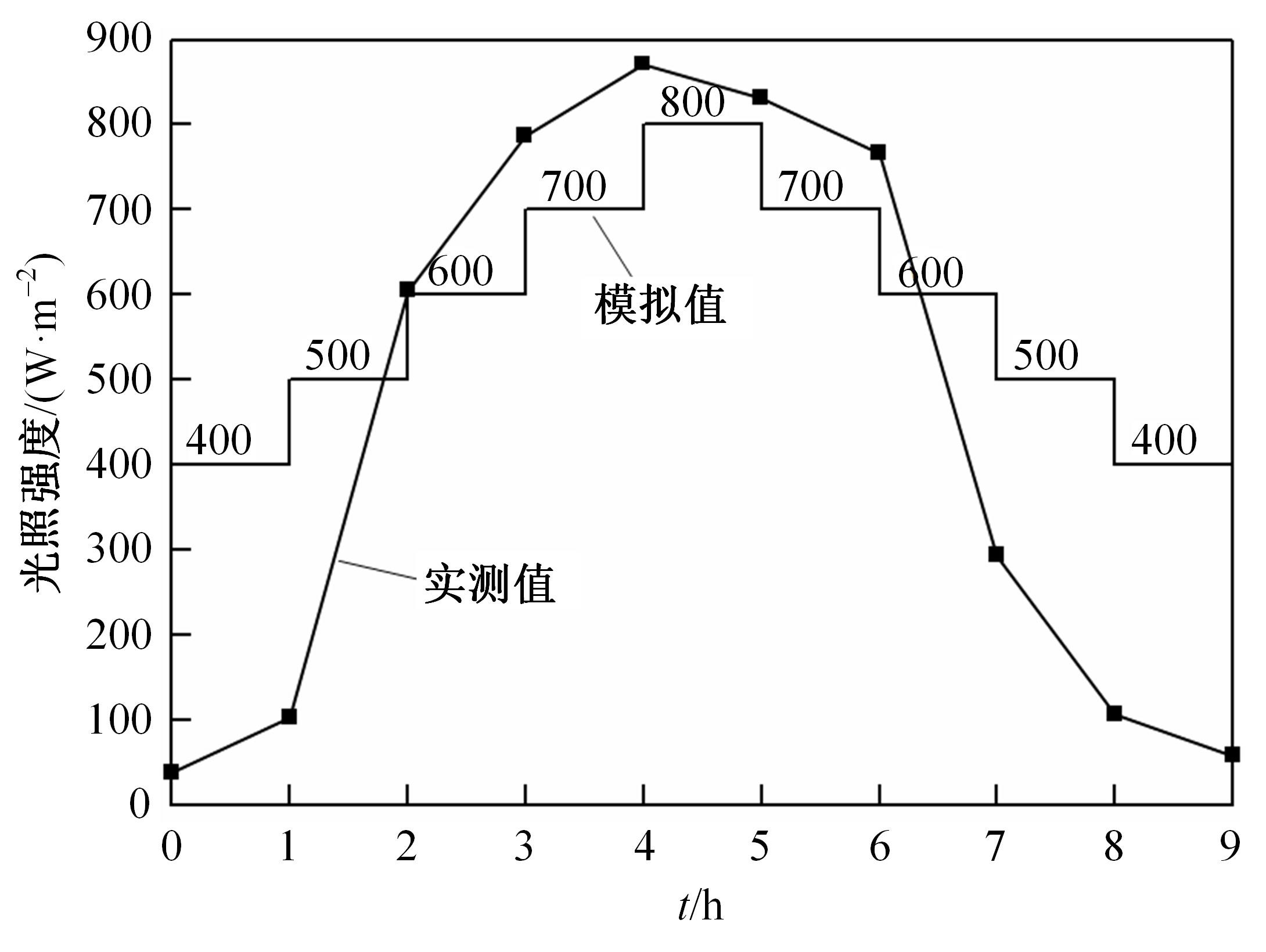
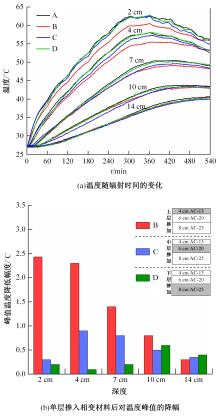
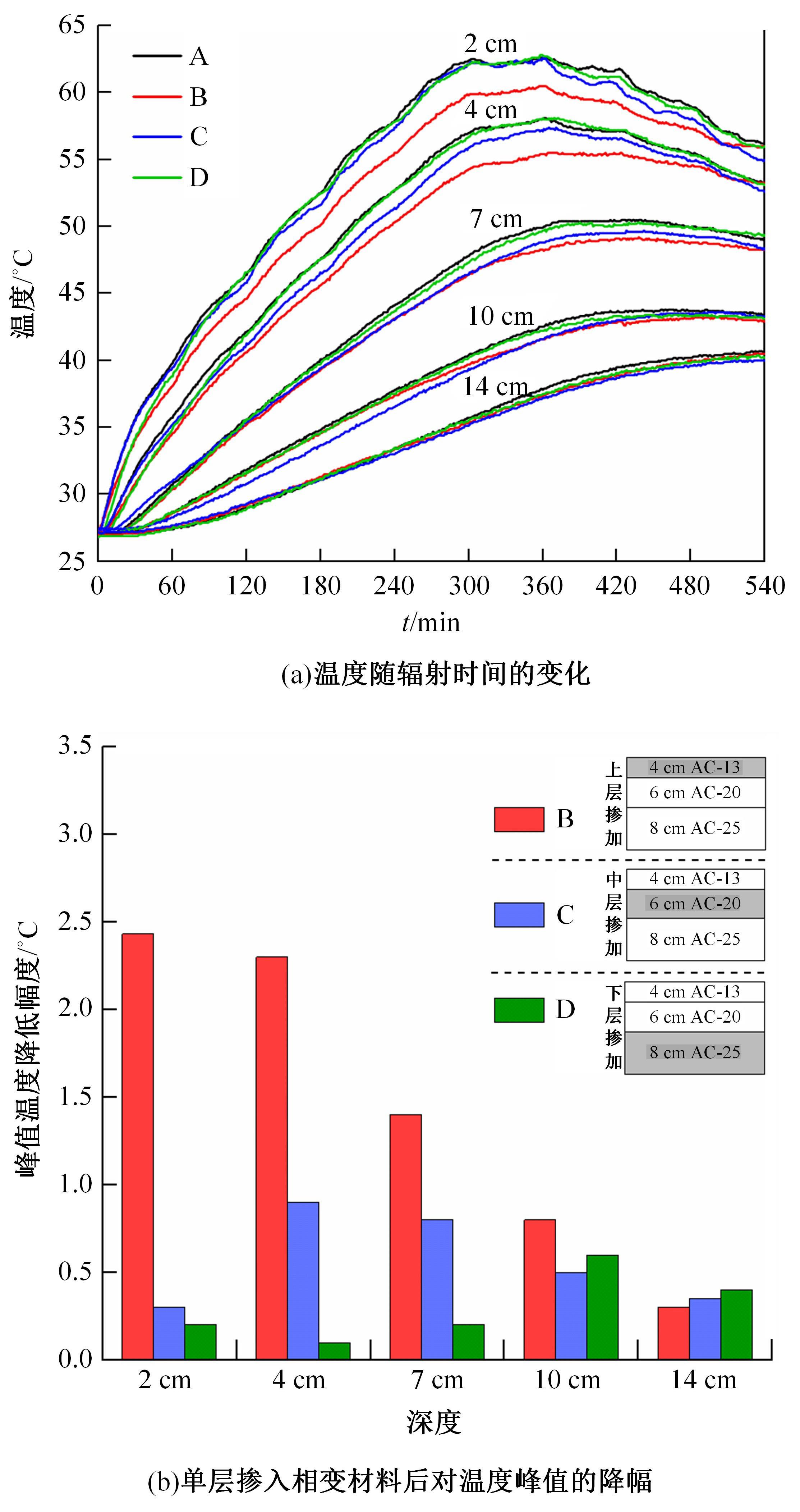
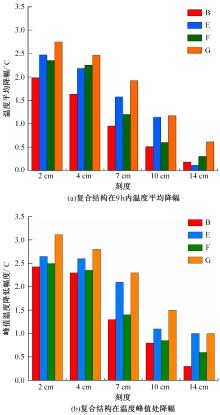
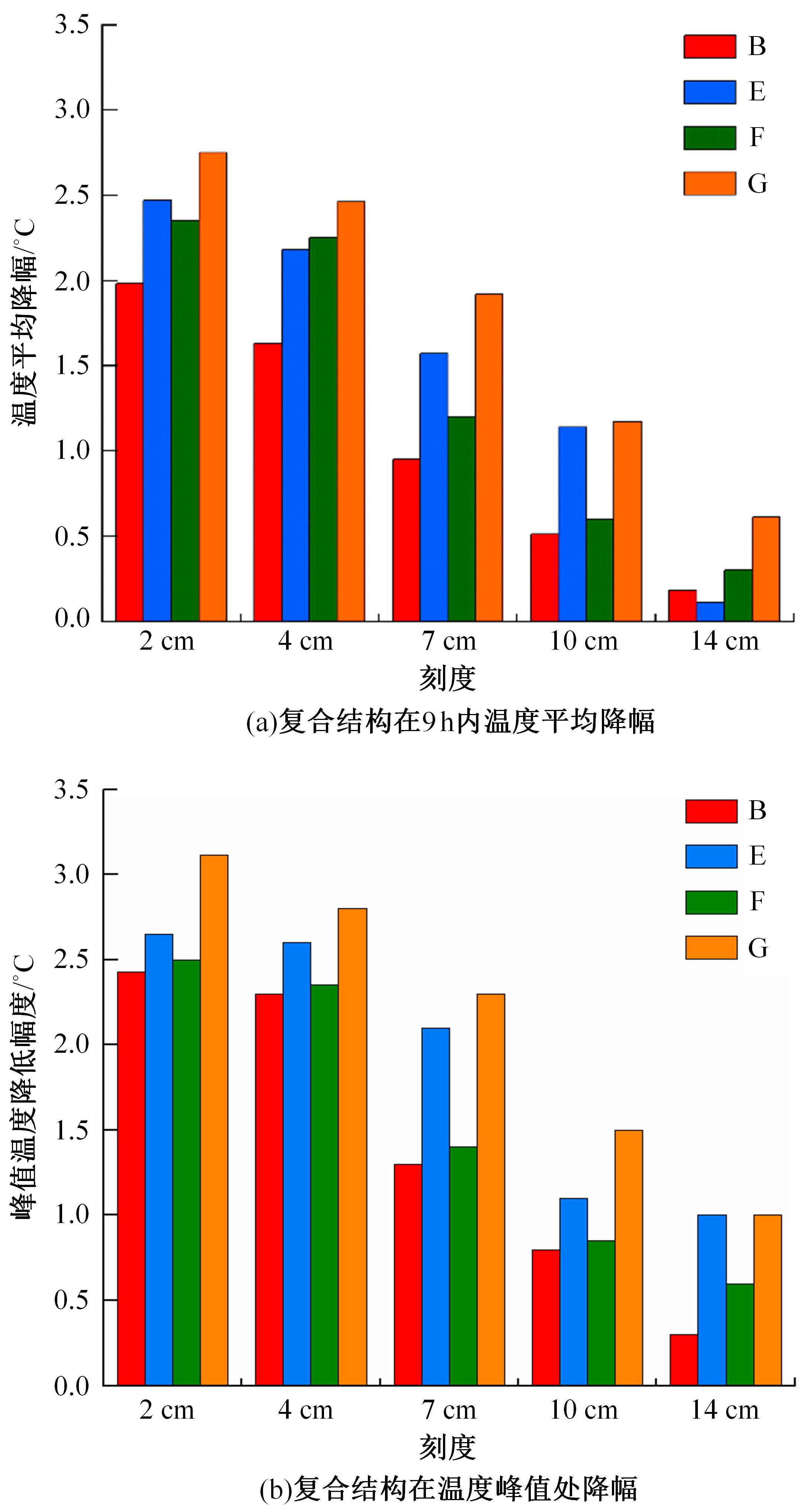
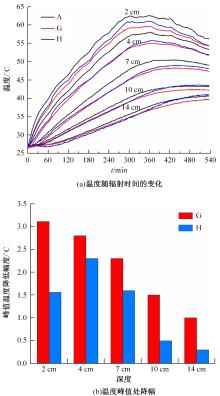
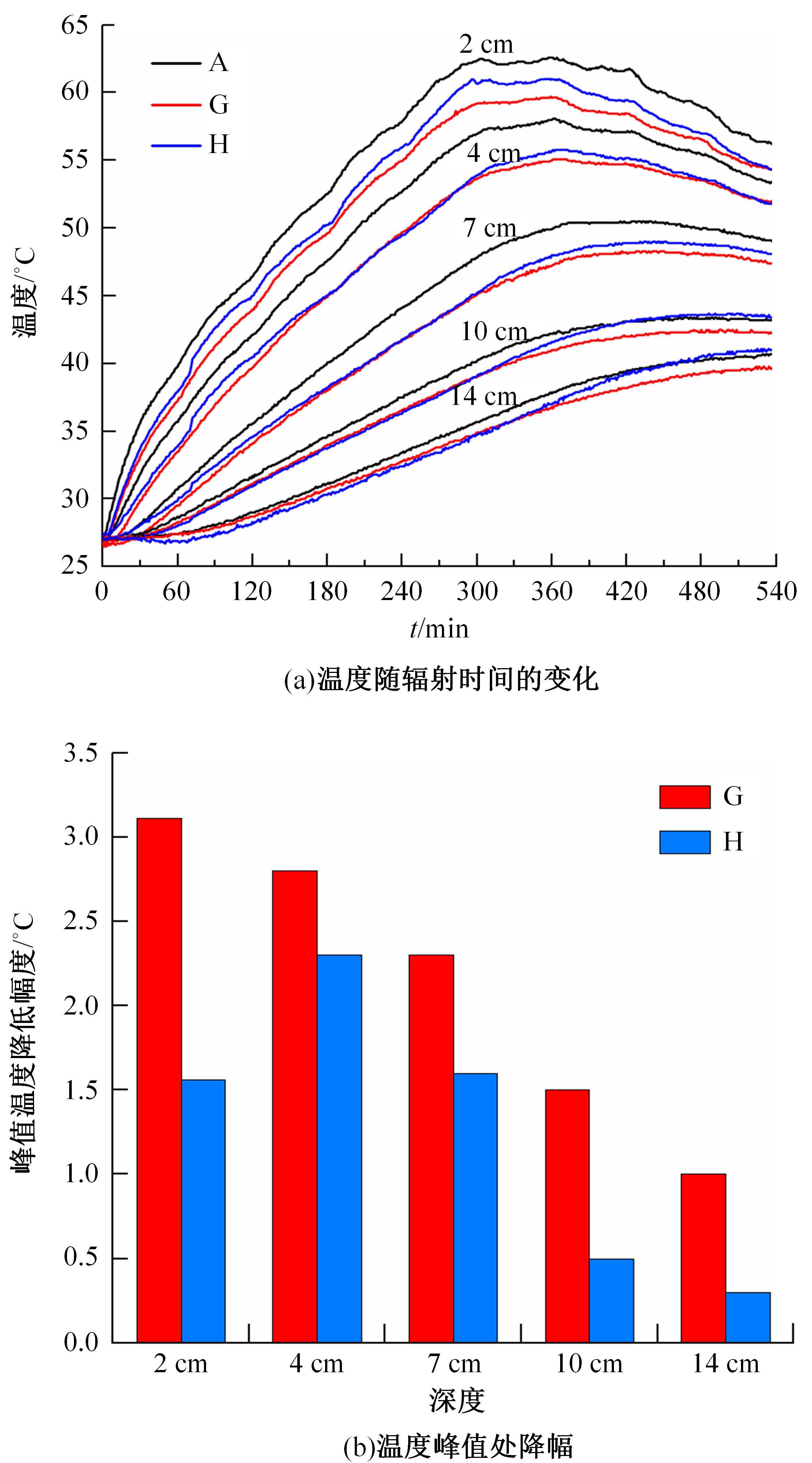
为了研究多层相变沥青混凝土复合结构的降温效果,采用差示扫描量热法测试了5组不同分子量聚乙二醇(PEG)的相变温度,结合太阳辐射下沥青路面温度场模拟结果,拟定并制备了含PEG的7组相变沥青混凝土三层复合结构,采用自行制作的热辐射及测温装置,测试了热辐射9 h内相变沥青混凝土复合结构内部温度,分析了PEG使用层位、层间组合方式、分子量对复合结构储热降温的影响。结果表明,PEG分子量从1000增大到6000时,相变起始温度从25.1 ℃增高到54.4 ℃;相变材料掺入路面结构单层后,主要对掺入层及其以下层位具有降温效果;从性价比角度看,仅上层掺入PEG的方案优于上中两层、上中下三层使用PEG的方案;在相同掺量时,分子量高的PEG对路面结构的降温效果优于分子量低的。
中图分类号:
- U414
| 1 | Badin G, Ahmad N, Ali H M. Experimental investigation into the thermal augmentation of pigmented asphalt[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2019: No.123974. |
| 2 | Babagoli R, Ziaiari H. Evaluation of rutting performance of stone matrix asphalt mixtures containing warm mix additives[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2017, 24(2):360-373. |
| 3 | Kaphle R. Improving the thermal properties of asphalt concrete to reduce urban heat island effects[D]. San Antonio: The University of Texas,2018. |
| 4 | Sen S, Roesler J. Thermal and optical characterization of asphalt field cores for microscale urban heat island analysis[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 217(30):600-611. |
| 5 | Shi X, Rew Y, Ibers E, et al. Effects of thermally modified asphalt concrete on pavement temperature, International Journal of Pavement Engineering, 2019, 20(6): 669-681. |
| 6 | Hai V V, Park D W, Seo W J, et al. Evaluation of asphalt mixture modified with graphite and carbon fibers for winter adaptation: thermal conductivity improvement[J]. Journal of materials in civil engineering, 2017, 29(1):No.04016176. |
| 7 | Chen J, Zhou Z, Wu J, et al. Field and laboratory measurement of albedo and heat transfer for pavement materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 202:46-57. |
| 8 | 姬彪.沥青路面热反射涂层的研究与发展[J].科技创新与应用,2017(16):229. |
| Ji Biao. Research and development of thermal reflective coating for asphalt pavement[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2017(16): 229. | |
| 9 | 孙斌祥,黄尹泰,沈航,等.沥青路面热反射涂层的降温性能研究综述[J].科学技术与工程,2021,21(9):3446-3456. |
| Sun Bin-xiang, Huang Yin-tai, Shen Hang, et al. Overview of studies on cooling performance of thermal reflection coating on asphalt pavement[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(9): 3446-3456. | |
| 10 | 沙爱民,蒋玮.环保型多孔路面材料设计理念与架构[J].中国公路学报,2018,31(9):1-6. |
| Sha Ai-min, Jiang Wei. Design philosophy and architecture of eco-friendly porous pavement materials[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2018,31(9): 1-6. | |
| 11 | 张睿.保水路面蒸发降温模型与实验研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学,2019. |
| Zhang Rui. Modeling and experimental studies on the evaporative cooling of water-retaining pavements[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2019. | |
| 12 | 于华洋,马涛,王大为,等.中国路面工程学术研究综述·2020[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(10):1-66. |
| Yu Hua-yang, Ma Tao, Wang Da-wei, et al. Review on China’s pavement engineering research·2020[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020,33(10): 1-66. | |
| 13 | 刘涛,郭乃胜,谭忆秋,等. 路用相变材料研究现状和发展趋势[J].材料导报,2020,34(23):23179-23189. |
| Liu Tao, Guo Nai-sheng, Tan Yi-qiu, et al. Research and development trend of road usage phase change materials[J]. Materials Reports, 2020,34(23): 23179-23189. | |
| 14 | 李文虎,何丽红,朱洪洲,等.PEG/SiO2相变颗粒对沥青混合料储热及高温性能的影响[J]. 公路交通科技,2015,32(4):16-20. |
| Li Wen-hu, He Li-hong, Zhu Hong-zhou, et al. Effect of PEG/SiO2 phase change particles on heat storage and high temperature performance of asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2015,32(4): 16-20. | |
| 15 | 雷宝财,范贤鹏,郑木莲. PEG/SiO2型控温相变沥青混合料的性能[J].筑路机械与施工机械化,2020,37():6-9. |
| Lei Bao-cai, Fan Xian-peng, Zheng Mu-lian. Performance of asphalt mixture with temperature-controlling phase change material of PEG/SiO2 [J]. Road Machinery and Construction Mechanization, 2020,37(Sup.1): 6-9. | |
| 16 | Kuai C, Chen J, Shi X, et al. Regulating porous asphalt concrete temperature using PEG/SiO2 phase change composite: experiment and simulation[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 273(3):No.122043. |
| 17 | Chen J, Li J, Wang H, et al. Preparation and effectiveness of composite phase change material for performance improvement of open graded friction course[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 214: 259-269. |
| 18 | Chen J, Zhang W, Shi X, et al. Use of PEG/SiO2 phase change composite to control porous asphalt concrete temperature[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 245:No.111845. |
| 19 | 李伊,刘黎萍,孙立军.全厚式沥青路面温度场预估模型[J].同济大学学报:自然科学版,2020,48(3):377-382. |
| Li Yi, Liu Li-ping, Sun Li-jun. Temperature field prediction model for thick asphalt layer[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2020,48(3): 377-382. | |
| 20 | 张东.沥青路面控温用定形相变材料的制备与性能研究[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学材料科学与工程学院,2019. |
| Zhang Dong. Research on preparation and performance of shape-formed phase change materials for asphalt pavement temperature-control[D]. Wuhan: School of Materials Science and Engineering,Wuhan University of Technology, 2019. | |
| 21 | 刘大龙,马岚,赵辉辉.城市复杂辐射场形成机理[J].太阳能学报,2021,42(10):458-463. |
| Liu Da-long, Ma Lan, Zhao Hui-hui. Formation mechanism of urban complex radiation field[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021,42(10): 458-463. |
| [1] | 王壮,冯振刚,姚冬冬,崔奇,沈若廷,李新军. 导电沥青混凝土研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 1-21. |
| [2] | 赵胜前,丛卓红,游庆龙,李源. 沥青-集料黏附和剥落研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2437-2464. |
| [3] | 马涛,马源,黄晓明. 基于多元非线性回归的智能压实关键参数最优解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [4] | 杨柳,王创业,王梦言,程阳. 设置自动驾驶小客车专用车道的六车道高速公路交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [5] | 周正峰,于晓涛,陶雅乐,郑茂,颜川奇. 基于灰色关联分析的树脂与弹性体高黏沥青高温性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2078-2088. |
| [6] | 张青霞,侯吉林,安新好,胡晓阳,段忠东. 基于车辆脉冲响应的路面不平度识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1765-1772. |
| [7] | 姜屏,陈业文,陈先华,张伟清,李娜,王伟. 改性石灰土在干湿和冻融循环下的无侧限抗压性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1809-1818. |
| [8] | 司春棣,崔亚宁,许忠印,凡涛涛. 层间粘结失效后桥面沥青铺装层细观力学行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1719-1728. |
| [9] | 李岩,张久鹏,陈子璇,黄果敬,王培. 基于PCA-PSO-SVM的沥青路面使用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1729-1735. |
| [10] | 刘状壮,郑文清,郑健,李轶峥,季鹏宇,沙爱民. 基于网格化的路表温度感知技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1746-1755. |
| [11] | 赵晓康,胡哲,张久鹏,裴建中,石宁. 基于光纤传感技术的路面结冰智能监测研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1566-1579. |
| [12] | 惠冰,杨心怡,张乐扬,李扬. 检测车轨迹偏移对沥青路面磨耗计算误差的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1756-1764. |
| [13] | 李崛,张安顺,张军辉,钱俊峰. 级配碎石基层结构动力响应模型测试及数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1782-1789. |
| [14] | 李博,李欣,芮红,梁媛. 基于变分模态分解和灰狼优化极限学习机的隧道口边坡位移预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1853-1860. |
| [15] | 王宁,马涛,陈丰,付永强. 影响智能骨料感知的关键因素及数据分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1799-1808. |
|
||