吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 53-65.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181272
基于Hopfield神经网络的单缸插销式伸缩臂伸缩路径优化
- 吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院,长春 130022
Telescoping path optimization of a single-cylinder pin⁃type multi⁃section boom based on Hopfield neural network
- College of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
摘要:
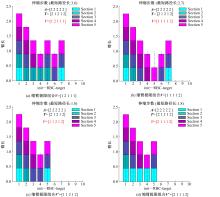
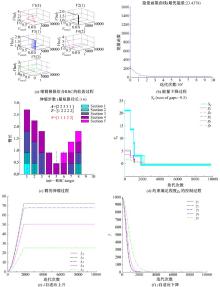
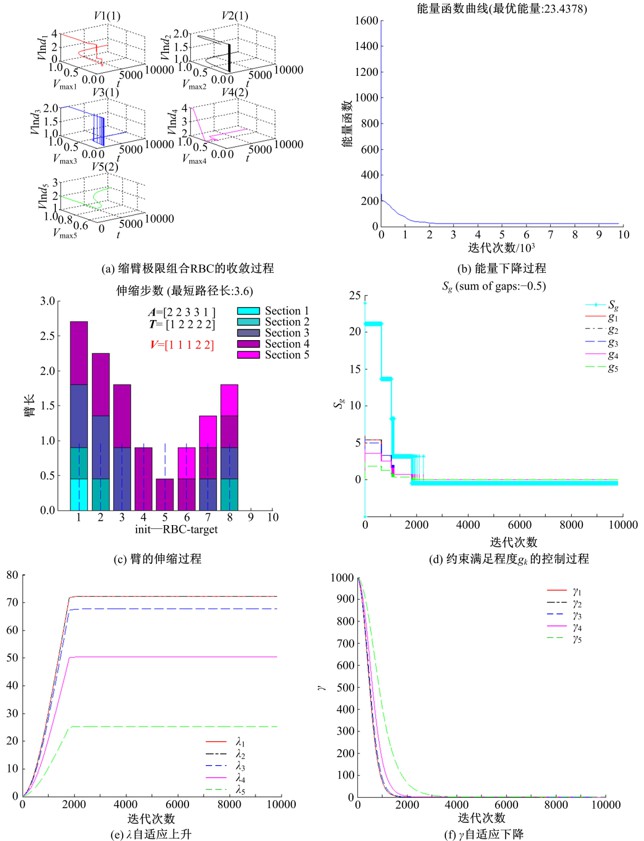
提出了单缸插销式伸缩臂伸缩路径优化问题,采用Hopfield神经网络构建了数学模型。由于能量方程中的约束项罚参数λ和目标项罚参数γ的确定往往相互矛盾:当λ占优时,能量方程更多朝向满足约束方向收敛,得到的有效解往往不是高质量解;当γ占优时,则可能收敛到无效解。为此,提出了λ为向上梯度递增、γ为向下梯度递减的曲线形式;对于λ和γ的增量确定,提出了一种基于约束边界偏差控制的PID自适应增量法,通过对约束边界偏差的PID控制使有效解的生成可控。实验结果表明:路径优化后伸缩效率能提升10%~30%。神经网络模型优化效果较好,几乎能100%收敛到有效解,同时由于PID控制使解聚集到约束边界,最优解生成率也较高,接近50%。
中图分类号:
- TH213
| 1 | Zhan Chun-xin , Liu Quan , Guo Ji-mei , et al . Single-cylinder pin-type telescopic boom track optimized control method and control system[P]. WO/ 2011/038633, 2011-07-04. |
| 2 | 毛艳, 成凯 . 一种高效的单缸插销式多级顺序伸缩路径优化方法[P]. 中国:CN 106744389B, 2018-07-17. |
| 3 | 毛艳, 成凯 . 单缸插销式多级顺序伸缩路径优化方法 [P].中国:CN 106744386B, 2018-04-10. |
| 4 | 郑飞 . 动态规划法在服装运输车辆路径优化中的应用 研究[J]. 物流科技, 2016, 39(2): 78-82. |
| Zheng Fei . Research on the application of dynamic programming method in the optimization of apparel vehicle routing[J]. Logistics Sci-Tech, 2016, 39(2): 78-82. | |
| 5 | Wen U P , Lan K M , Shih H S . A review of hopfield neural networks for solving mathematical programming problems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2009, 198(3): 675-687. |
| 6 | Hopfield J J . Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 1982, 79(8): 2554-2558. |
| 7 | Hopfield J J , Tank D W . ‘Neural’ computation of decisions in optimization problems[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1985, 52(3): 141-152. |
| 8 | Wilson G V , Pawley G S . On the stability of the travelling salesman problem algorithm of Hopfield and tank[J]. Biological Cybernetics, 1988, 58(1): 63-70. |
| 9 | Kennedy M P , Chua L O . Neural networks for nonlinear programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits & Systems, 1988, 35(5): 554-562. |
| 10 | Rodriguez-Vazquez A , Rueda A , Huertas J L , et al . Switched-capacitor neural networks for linear programming[J]. Electronics Letters, 2002, 24(8): 496-498. |
| 11 | Brandt R D , Yao W , Laub A J , et al . Alternative networks for solving the traveling salesman problem and the list-matching problem[C]∥International Conference on Neural Networks, San Diego, CA, USA, 1988: 333-340. |
| 12 | Protzel P W , Palumbo D L , Arras M K . Performance and fault-tolerance of neural networks for optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1993, 4(4): 600-614. |
| 13 | Shirazi B , Yih S . Critical analysis of applying hopfield neural net model to optimization problems[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Cambridge,MA,USA, 1989: 210-215. |
| 14 | Aiyer S V B , Niranjan M , Fallside F . A theoretical investigation into the performance of the Hopfield model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1990, 1(2): 204-215. |
| 15 | 孙守宇, 郑君里 . Hopfield 网络求解 TSP的一种改进 算法和理论证明[J]. 电子学报, 1995, 23(1): 73-78. |
| Sun Shou-yu , Zheng Jun-li . A modified algorithm and theoretical analysis for hopfield network solving TSP[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 1995, 23(1): 73-78. | |
| 16 | 张军英, 许进, 保铮 . 神经网络求解TSP问题的理论分析及其改进[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 1996, (增刊1): 88-98. |
| Zhang Jun-ying , Xu Jin , Bao Zheng . Theoretical analysis and improvement of the neural network to solve the TSP problem[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1996(Sup.1): 88-98. | |
| 17 | Effati S , Jafarzadeh M . A new nonlinear neural network for solving a class of constrained parametric optimization problems[J]. Applied Mathematics & Computation, 2007, 186(1): 814-819. |
| 18 | Lemonge A C C , Barbosa H J C , Bernardino H S . Variants of an adaptive penalty scheme for steady-state genetic algorithms in engineering optimization[J]. Engineering Computations, 2015, 32(8): 2182-2215. |
| 19 | Schoenauer M , Michalewicz Z . Boundary operators for constrained optimization problems[C]∥Baeck T, ed. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Genetic Algorithms. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 1997. 322-329. |
| 20 | Wang Y , Cai Z , Guo G , et al . Multiobjective optimization and hybrid evolutionary algorithm to solve constrained optimization problems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 2007: 37(3): 560-575. |
| [1] | 贾富淳,孟宪皆,雷雨龙. 基于多目标遗传算法的二自由度动力吸振器优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1969-1976. |
| [2] | 谢志江,王昆,皮阳军,吴小勇,郭映位. 新的6⁃PSS型并联机构正向运动学求解方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1977-1985. |
| [3] | 曹恩国,刘坤,吉硕,孙震源,徐洪伟,骆星吉. 减重站起康复训练系统机械结构设计与优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1558-1566. |
| [4] | 李俊烨,刘洋,卢慧,孟文卿,杨兆军,张心明. 基于分子动力学的磨粒微切削单晶铁数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1567-1574. |
| [5] | 张艳芹,冯雅楠,孔鹏睿,于晓东,孔祥滨. 基于热油携带的静压支承油膜温度场及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1203-1211. |
| [6] | 杨成,赵永胜,刘志峰,蔡力钢. 基于多尺度理论的栓接结合部动力学建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1212-1220. |
| [7] | 王家序,倪小康,韩彦峰,向果,肖科. 轴向往复运动下微槽轴承混合润滑数值模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 888-896. |
| [8] | 王兴野,张进秋,李国强,彭志召. 惯性质量对齿轮齿条式作动器阻尼特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 881-887. |
| [9] | 刘坤,吉硕,孙震源,徐洪伟,刘勇,赵静霞. 多功能坐站辅助型如厕轮椅机械结构设计与优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 872-880. |
| [10] | 毕秋实,王国强,黄婷婷,毛瑞,鲁艳鹏. 基于DEM-FEM耦合的双齿辊破碎机辊齿强度分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1770-1776. |
| [11] | 朱伟,王传伟,顾开荣,沈惠平,许可,汪源. 一种新型张拉整体并联机构刚度及动力学分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1777-1786. |
| [12] | 刘建芳, 王记波, 刘国君, 李新波, 梁实海, 杨志刚. 基于PMMA内嵌三维流道的压电驱动微混合器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1500-1507. |
| [13] | 毛宇泽, 王黎钦. 鼠笼支撑一体化结构对薄壁球轴承承载性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1508-1514. |
| [14] | 王涛, 伞晓刚, 高世杰, 王惠先, 王晶, 倪迎雪. 光电跟踪转台垂直轴系动态特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1099-1105. |
| [15] | 谢传流, 汤方平, 孙丹丹, 张文鹏, 夏烨, 段小汇. 立式混流泵装置压力脉动的模型试验分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1114-1123. |
|
||