吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (1): 49-62.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190906
柴油发动机燃烧过程数据驱动建模与滚动优化控制
胡云峰1,2( ),丁一桐2,赵志欣3,蒋冰晶2,高金武1,2(
),丁一桐2,赵志欣3,蒋冰晶2,高金武1,2( )
)
- 1.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 通信工程学院,长春 130022
3.长春师范大学 数学学院,长春 130032
Data-driven modeling and receding optimization control of diesel engine combustion process
Yun-feng HU1,2( ),Yi-tong DING2,Zhi-xin ZHAO3,Bing-jing JIANG2,Jin-wu GAO1,2(
),Yi-tong DING2,Zhi-xin ZHAO3,Bing-jing JIANG2,Jin-wu GAO1,2( )
)
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.School of Mathematics,Changchun Normal University,Changchun 130032,China
摘要:
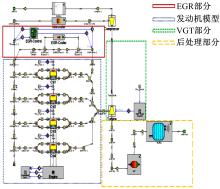
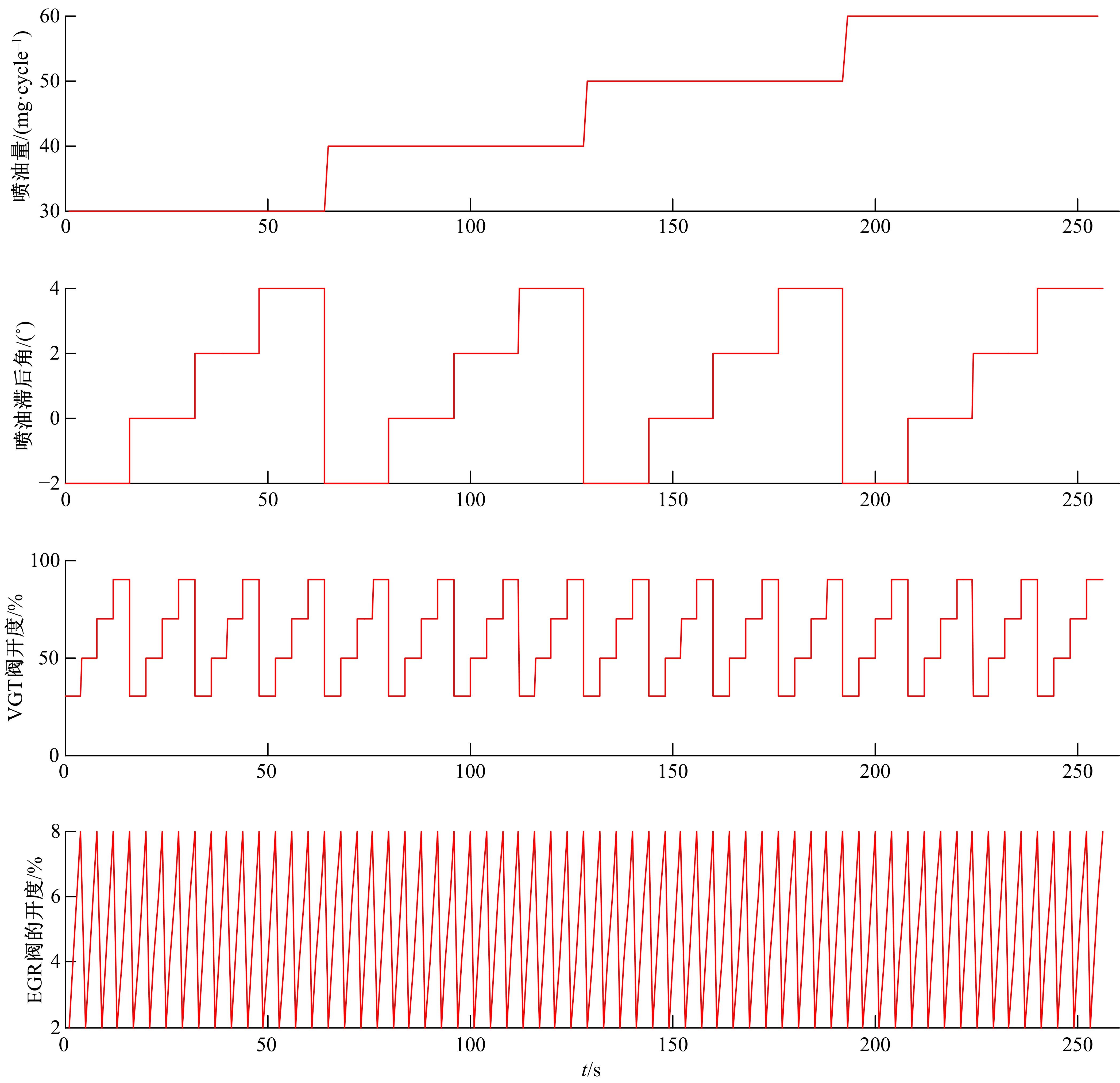
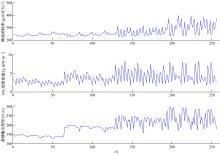
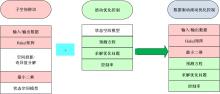
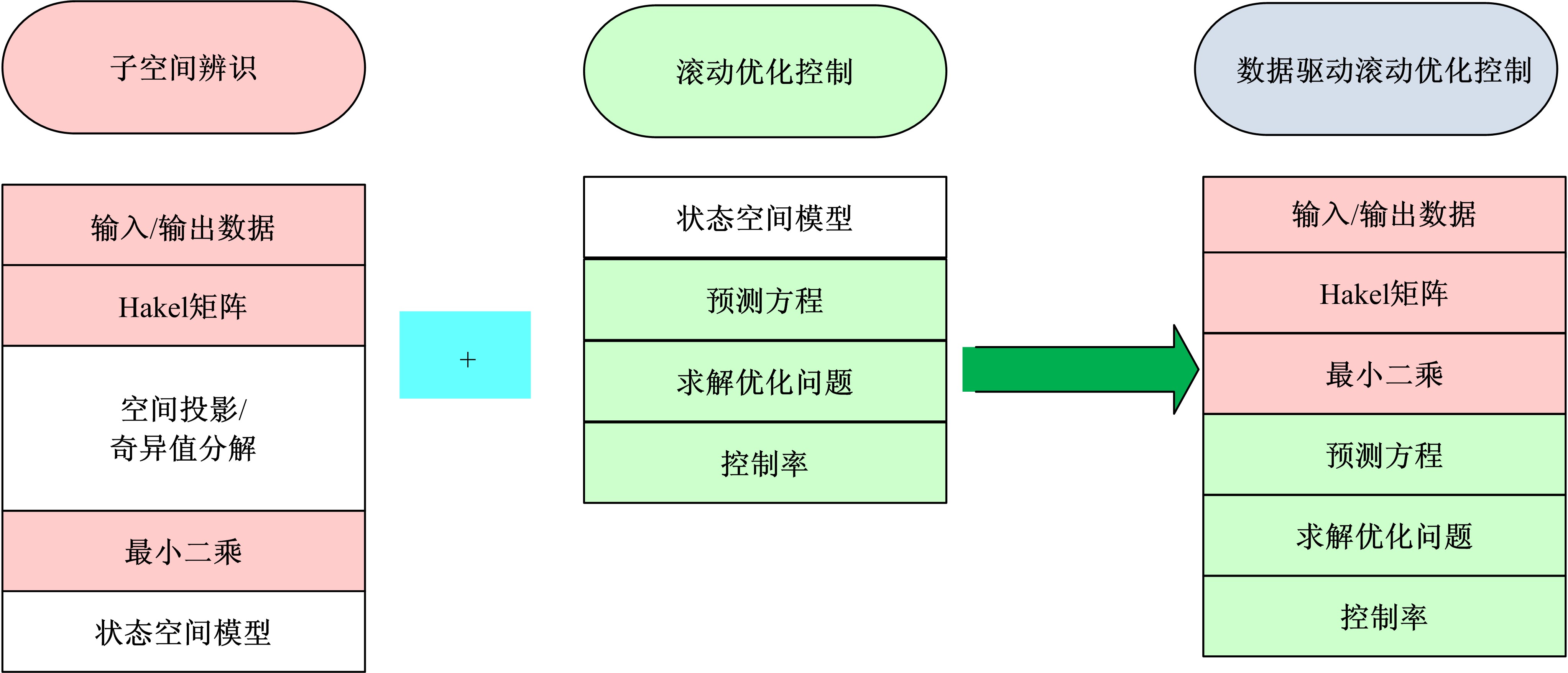
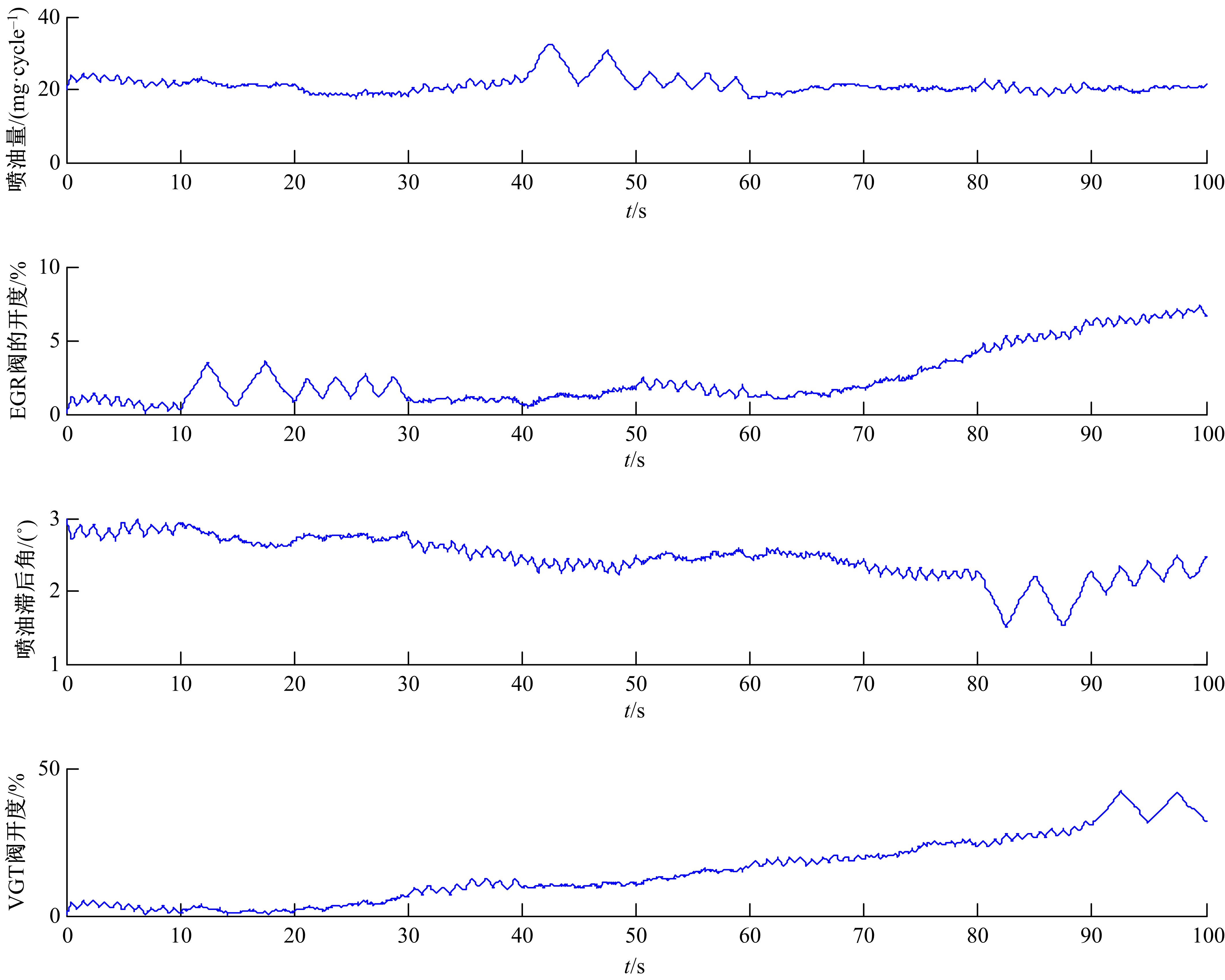
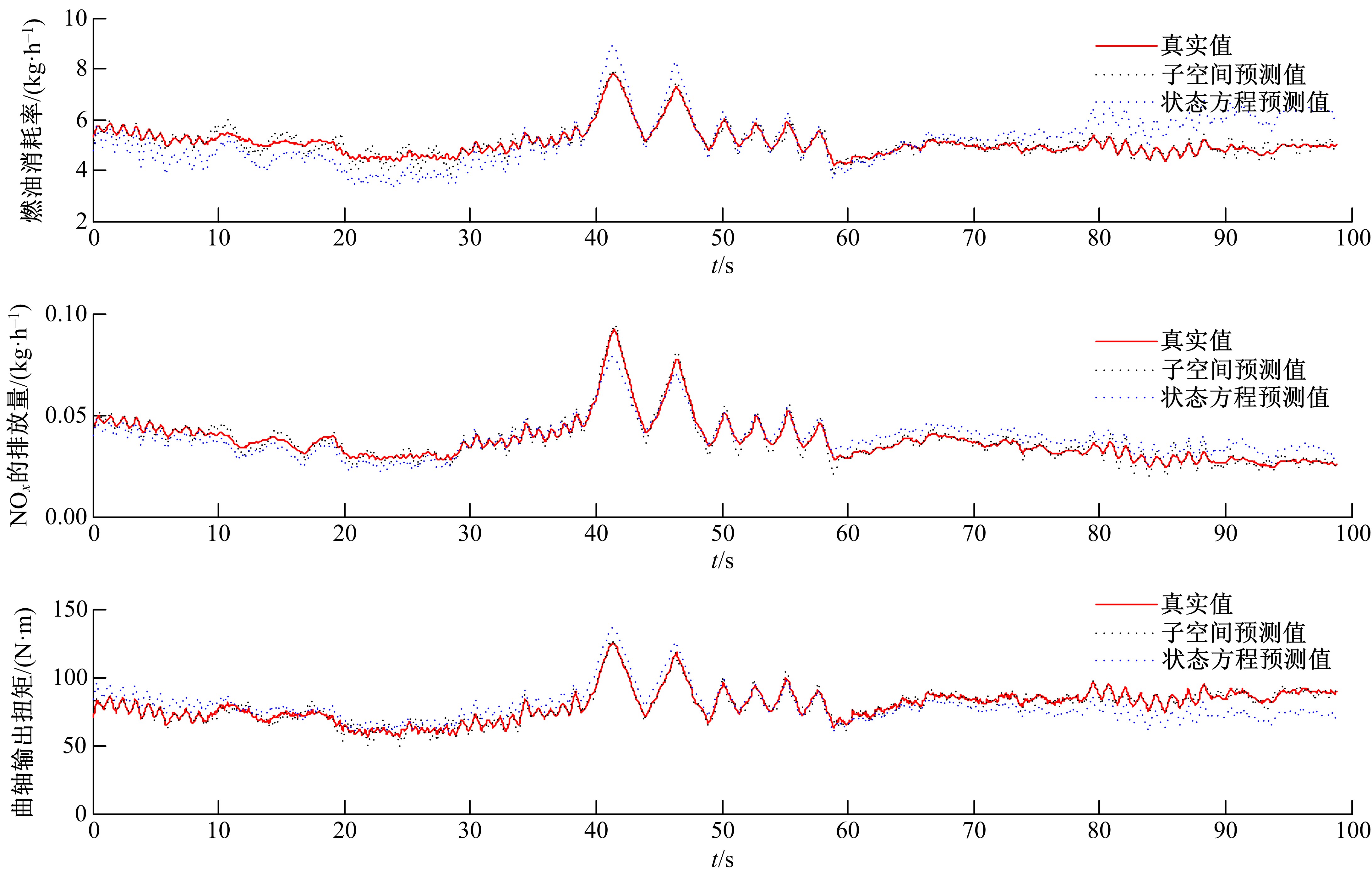
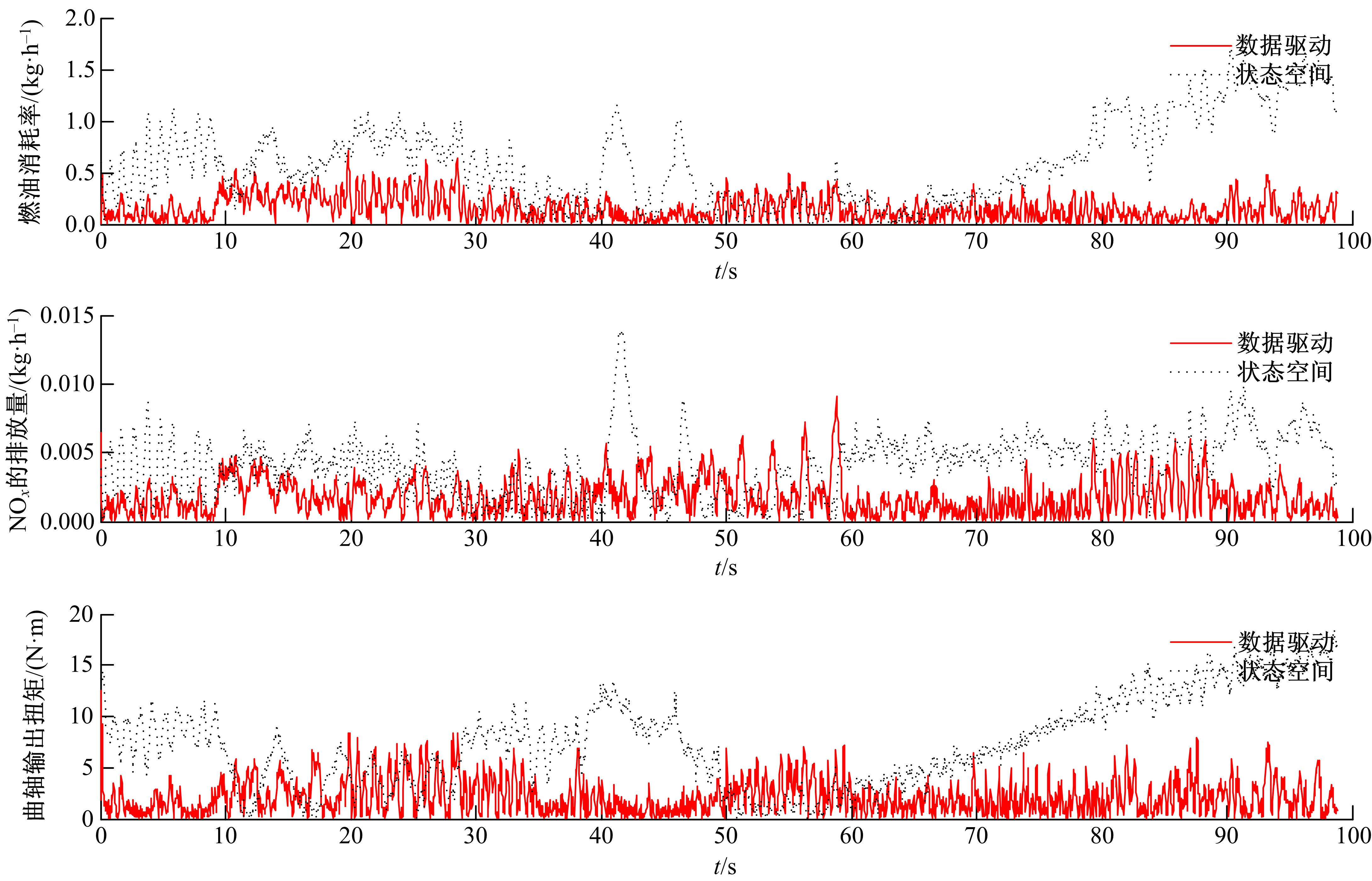
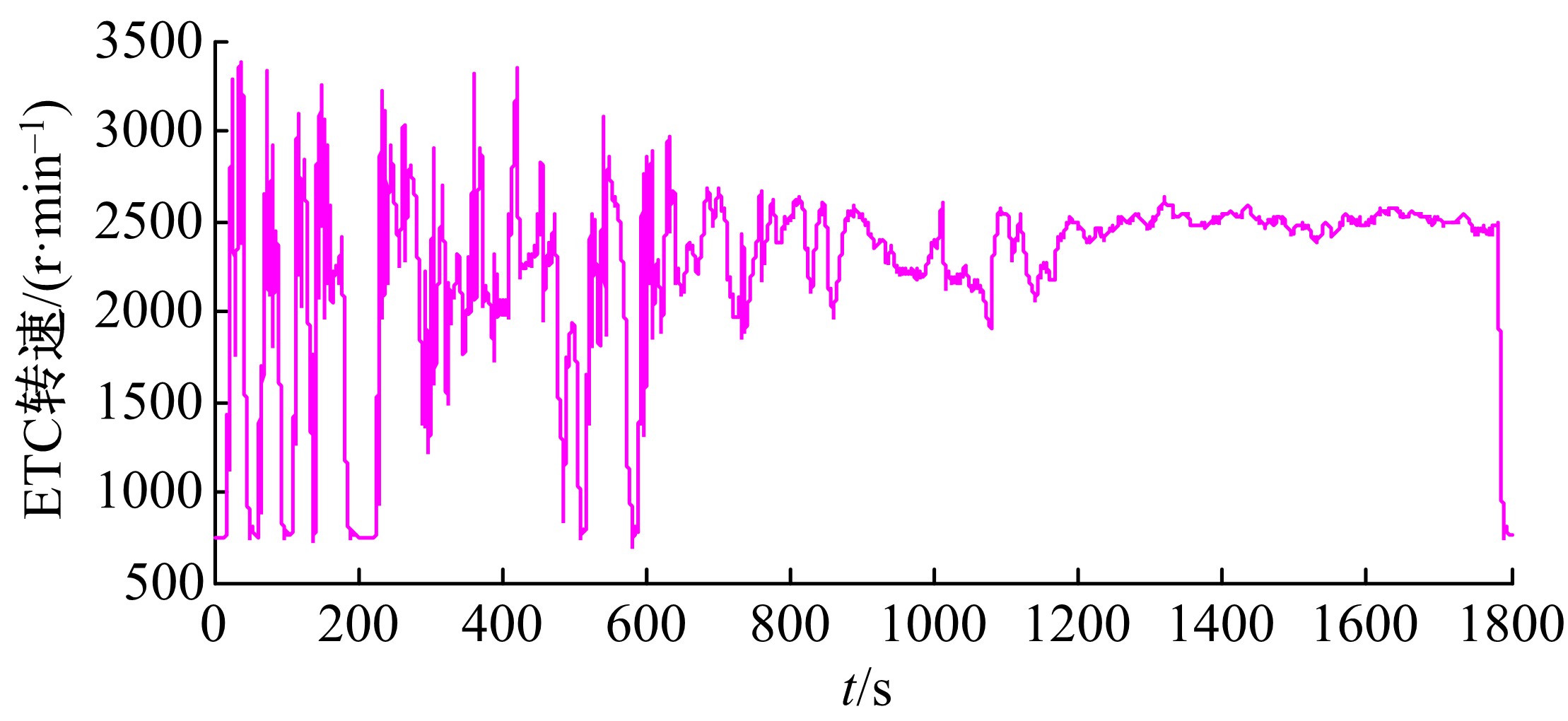
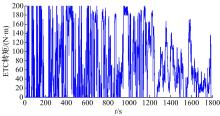
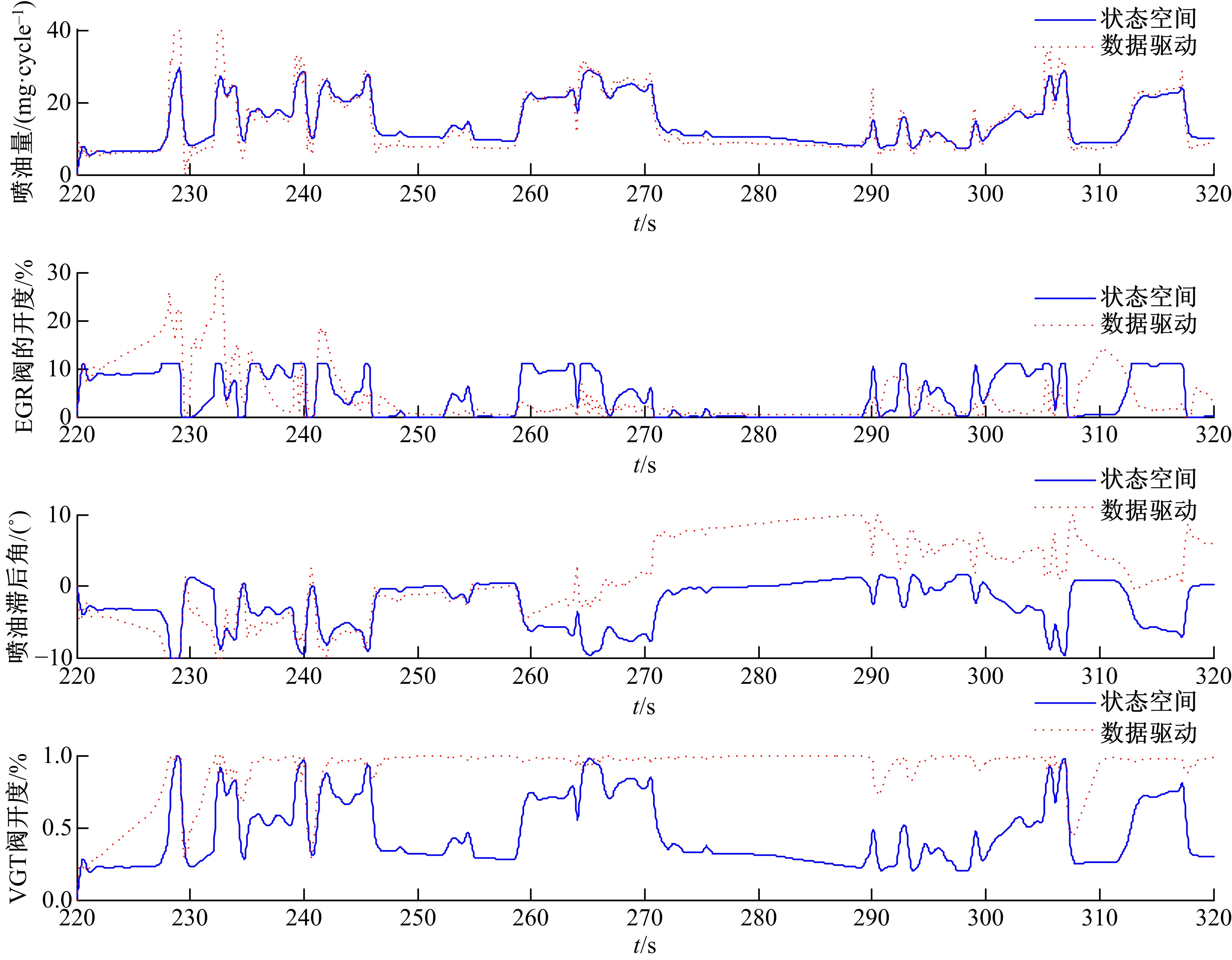
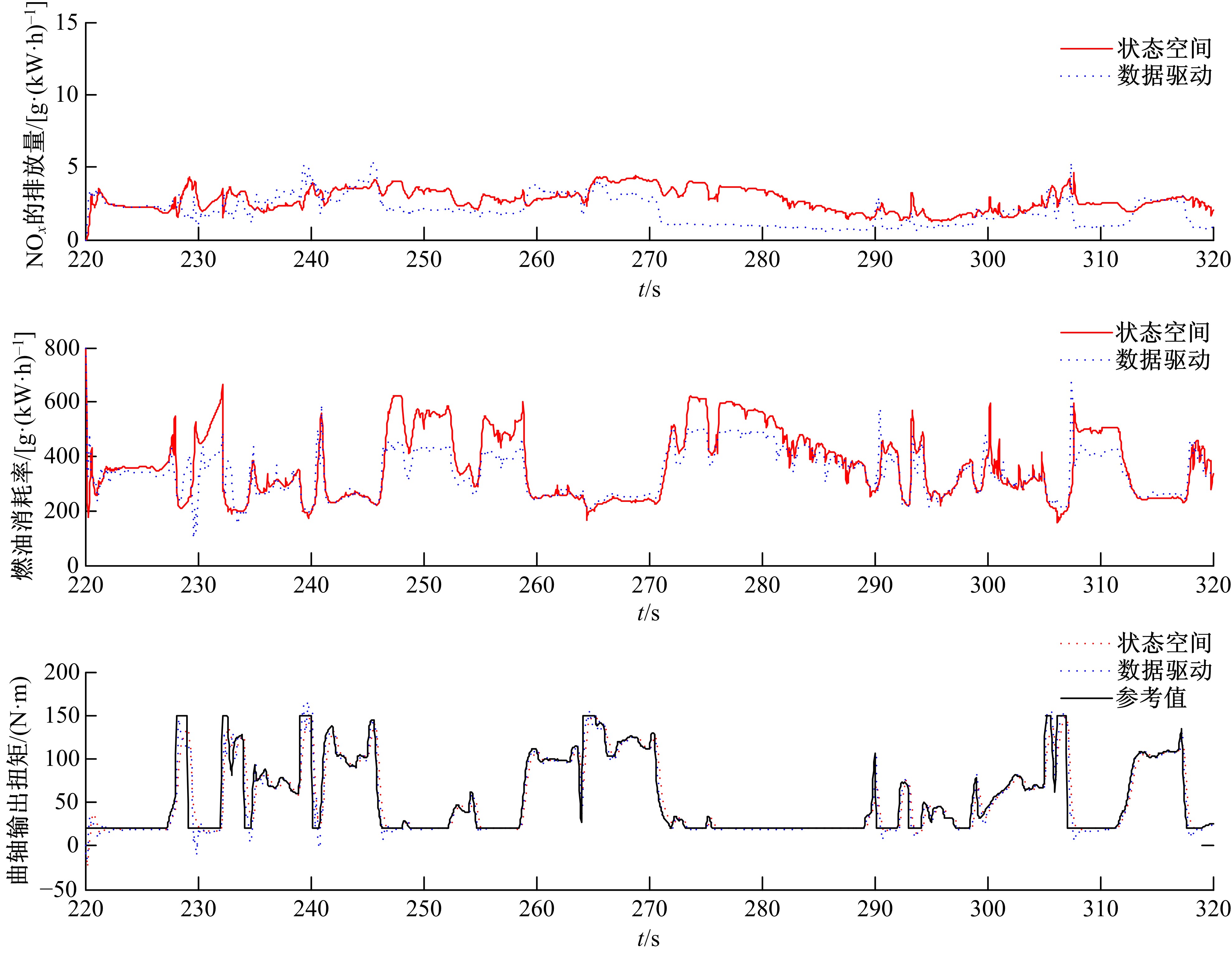
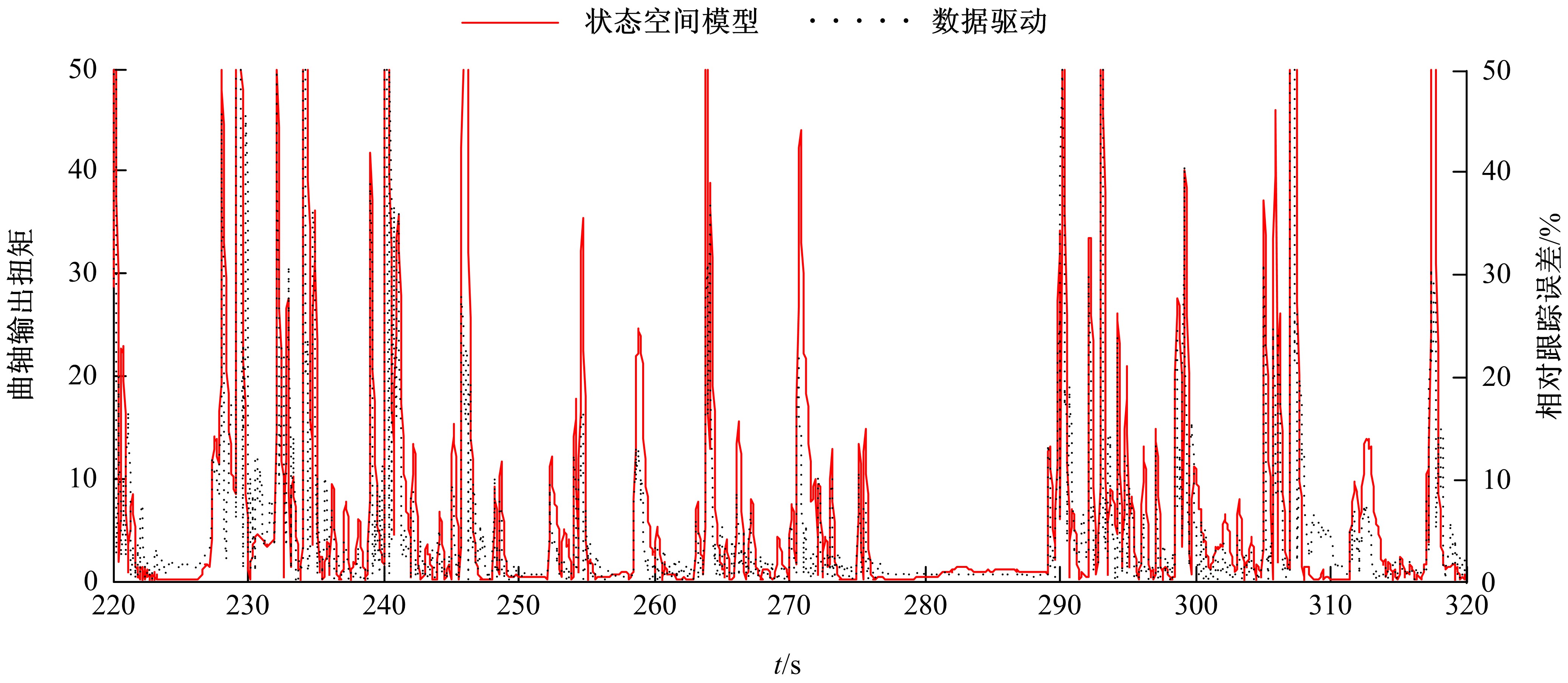
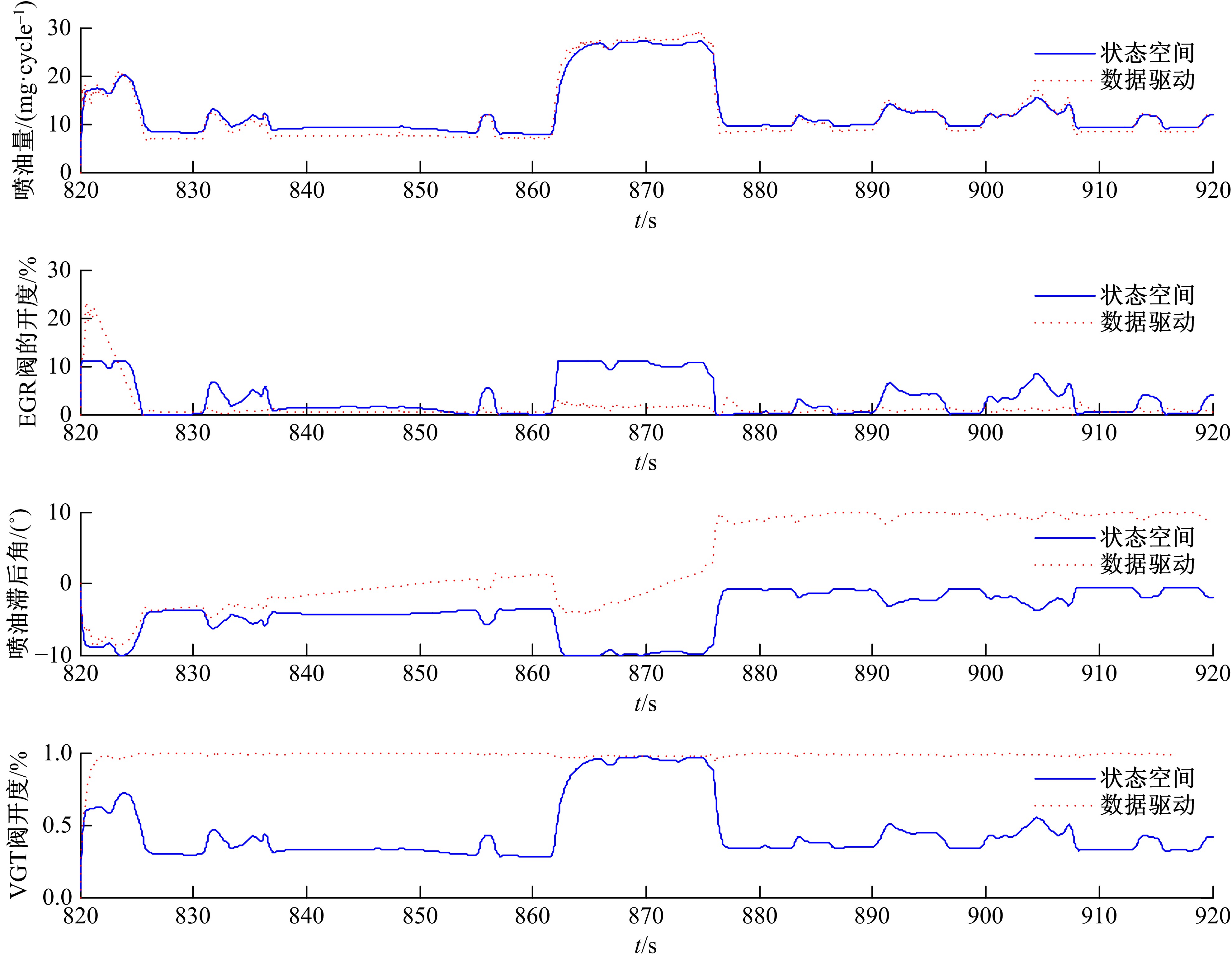
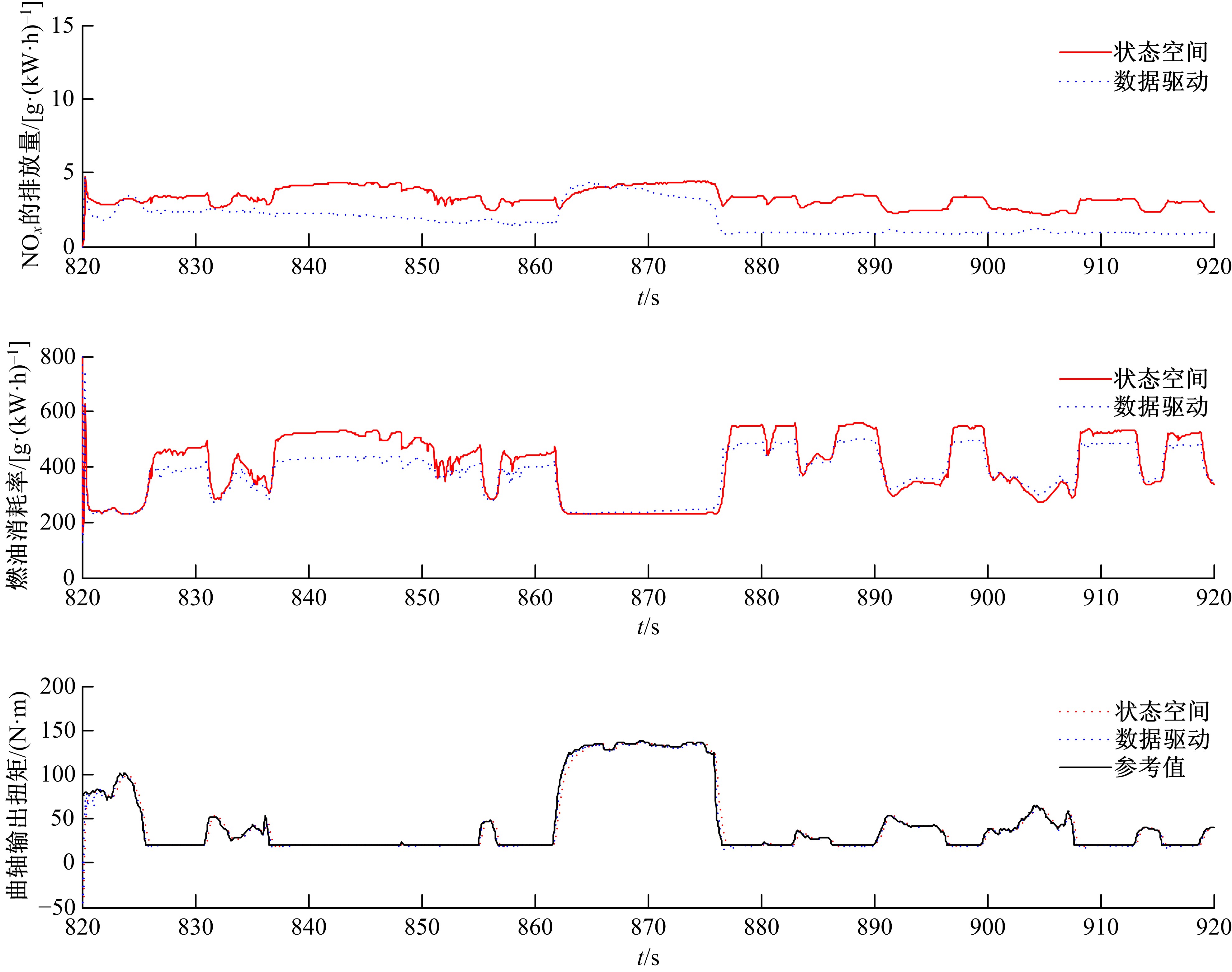
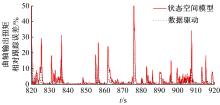
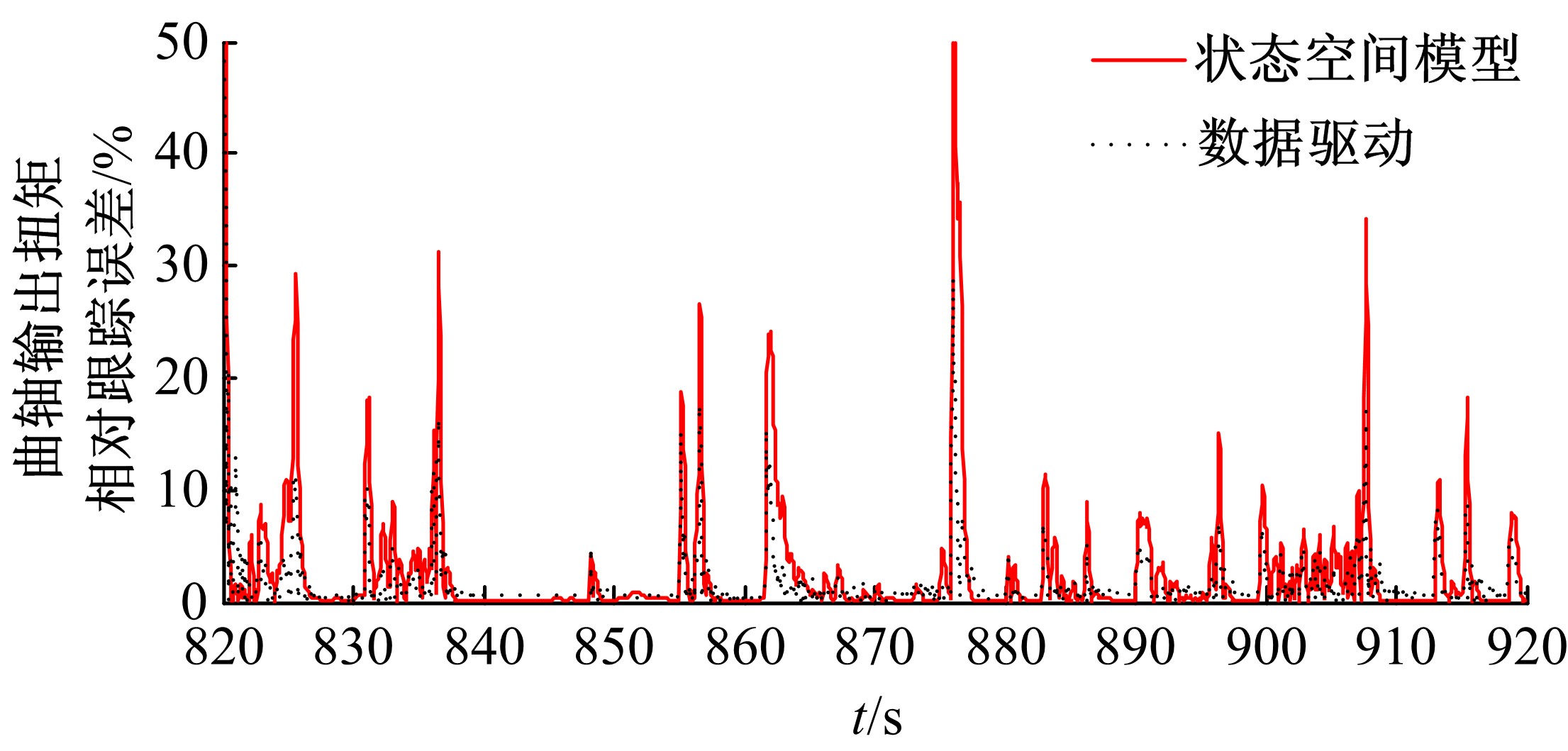
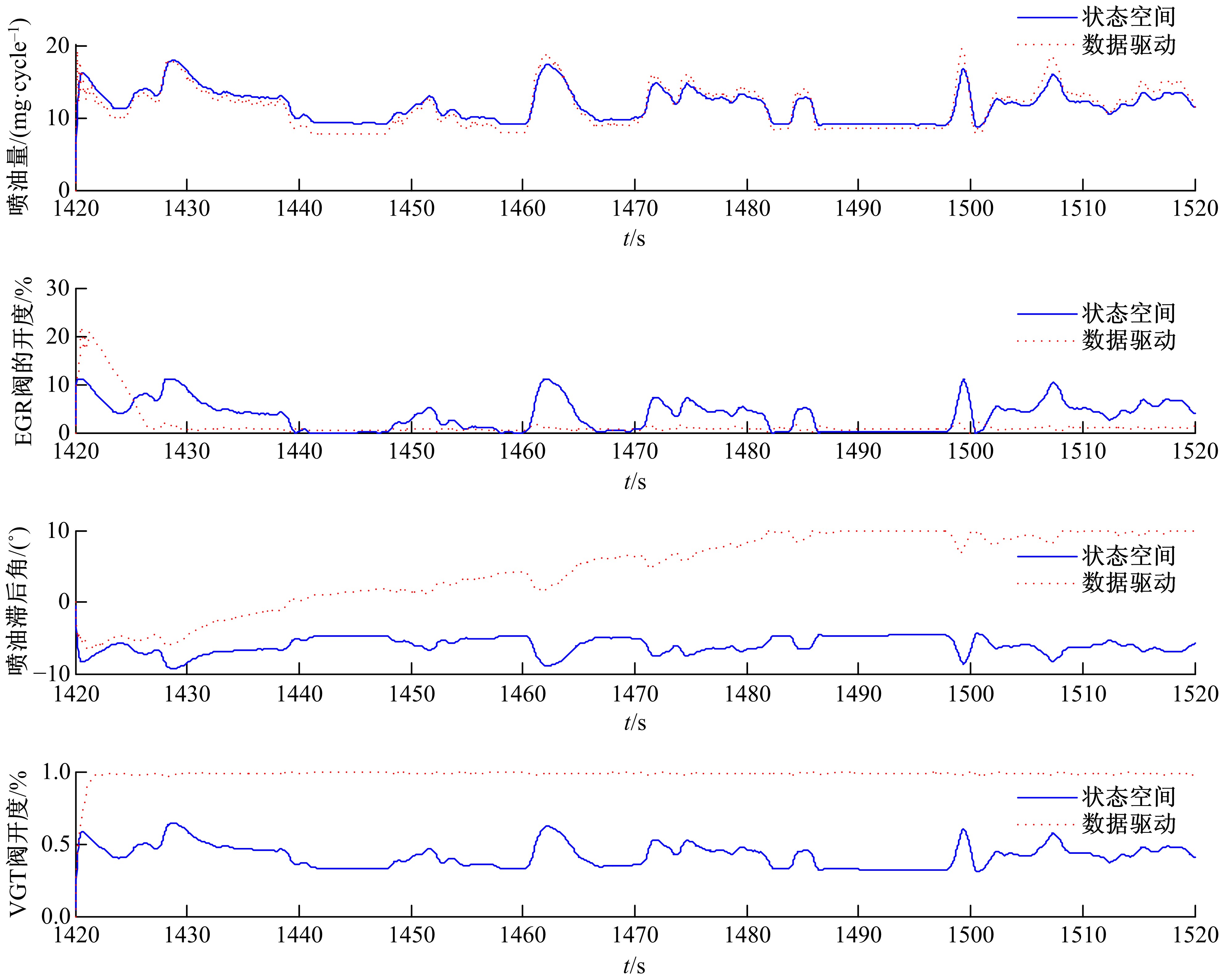
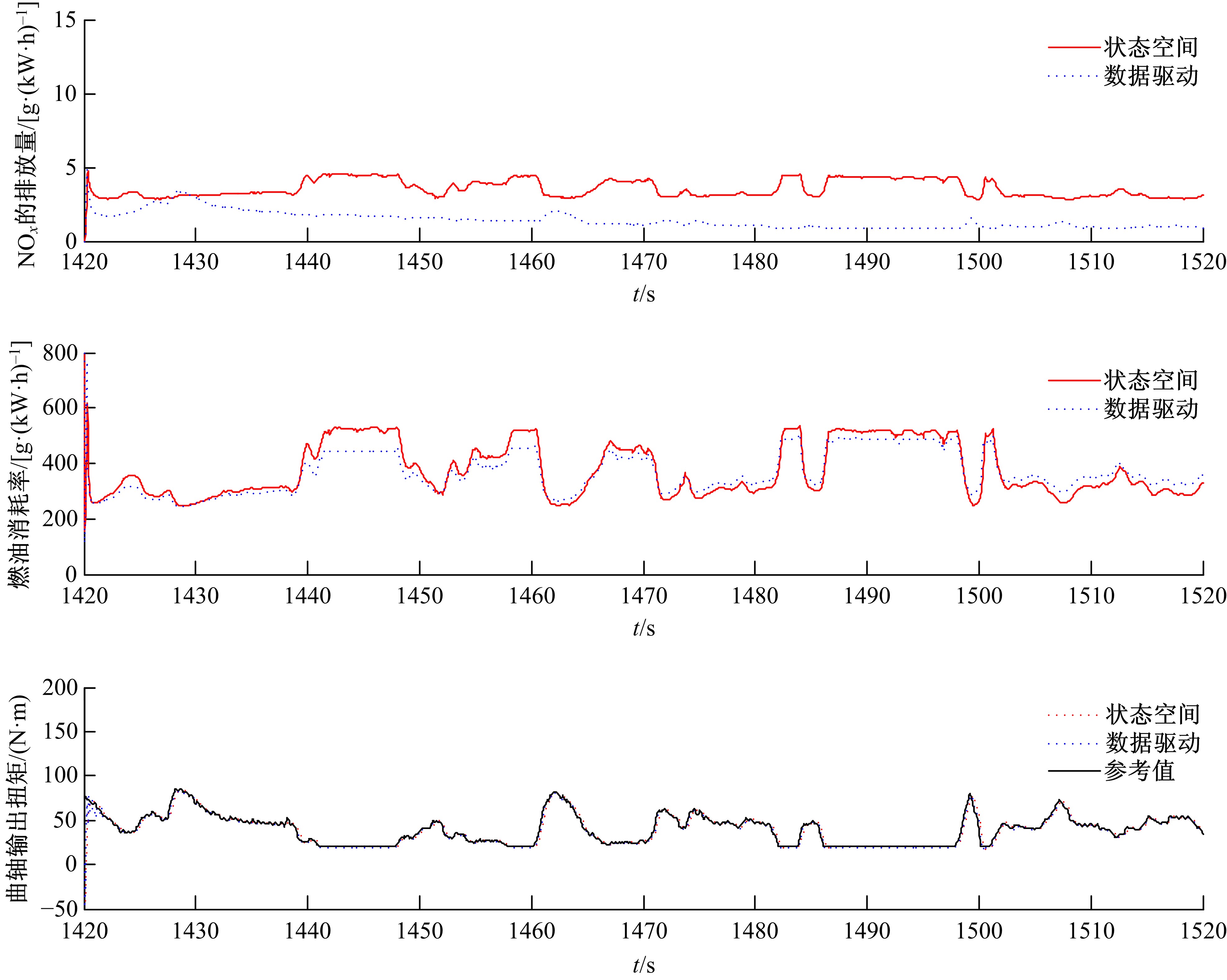
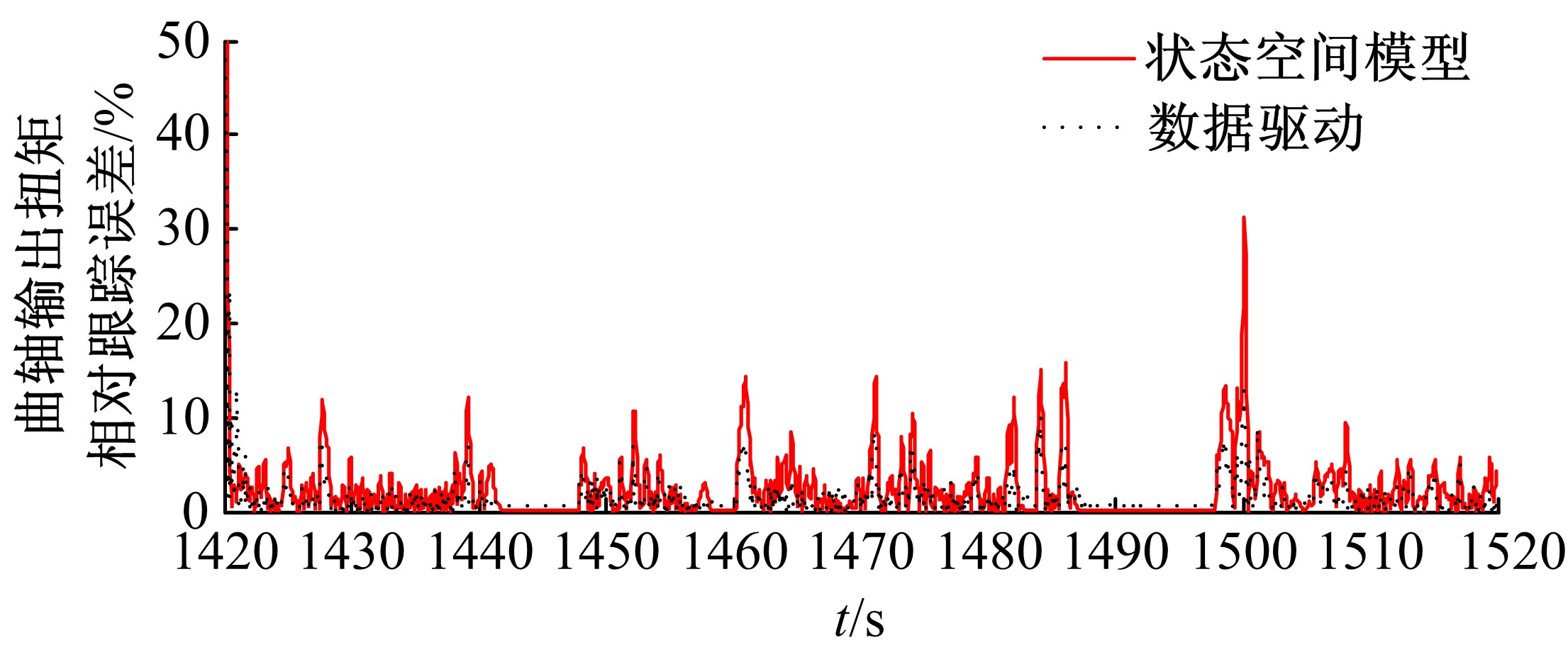
针对柴油发动机燃烧过程复杂、机理建模难、动力学耦合且存在约束等问题,以降低燃油消耗率和扭矩跟踪为目标、以氮氧化物排放及控制量限制为约束,提出了柴油发动机燃烧过程数据驱动建模与滚动优化控制方法。首先,以商用发动机模拟软件GT-suite中的一款2 L排量的柴油发动机为被控对象,分析了VGT和EGR控制阀开度、喷油角度和喷油量这4个因素对燃油消耗率、氮氧化物排放以及曲轴输出扭矩的影响;其次,利用输入和输出数据,采用子空间辨识方法得出了面向控制的预测模型;然后,以降低燃油消耗率、扭矩跟踪误差为目标,以氮氧化物排放及控制量限制为约束,通过对优化问题的在线优化求解,得到了最优的控制输入;最后,运用MATLAB与GT-suite联合仿真,验证了数据驱动滚动优化控制方法的有效性和优越性。
中图分类号:
- TK411
| 1 | 宫洵, 蒋冰晶, 胡云峰, 等. 柴油机主-从双微元Urea-SCR系统非线性状态观测器设计与分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018, 48(4): 1055-1062. |
| Gong Xun, Jiang Bing-jing, Hu Yun-feng, et al. Design and analysis of nonlinear state observer for master-slave two cell Urea-SCR system of diesel engine[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(4): 1055-1062. | |
| 2 | 唐蛟, 李国祥, 王志坚, 等. 基于欧Ⅵ柴油机EGR阀与VGT阀解耦控制策略研究[J]. 内燃机工程, 2015, 36(3): 63-67. |
| Tang Jiao, Li Guo-xiang, Wang Zhi-jian, et al. Study of EGR/VGT decoupling control strategy based on euroⅥ diesel engines[J]. Chinese Internal Combustion Engine Engineering, 2015, 36(3): 63-67. | |
| 3 | Hong S, Park I, Chung J, et al. Gain scheduled controller of EGR and VGT systems with a model-based gain scheduling strategy for diesel engines[J]. IFAC- Papers On Line, 2015, 48(15): 109-116. |
| 4 | 祖象欢, 杨传雷, 王贺春, 等. 船用柴油机EGR性能评估及应用研究[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2019, 49(3): 805-815. |
| Zu Xiang-huan, Yang Chuan-lei, Wang He-chun, et al. Research on EGR performance evaluation of marine diesel engine and its application[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 805-815. | |
| 5 | Najafi B, Akbarian E, Lashkarpour S M, et al. Modeling of a dual fueled diesel engine operated by a novel fuel containing glycerol triacetate additive and biodiesel using artificial neural network tuned by genetic algorithm to reduce engine emissions[J]. Energy, 2019, 168: 1128-1137. |
| 6 | Gogoi T K, Baruah D C. A cycle simulation model for predicting the performance of a diesel engine fuelled by diesel and biodiesel blends[J]. Energy, 2010, 35(3): 1317-1323. |
| 7 | Bougrine S, Richard S, Michel J B, et al. Simulation of CO and NO emissions in a SI engine using a 0D coherent flame model coupled with a tabulated chemistry approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 113: 1199-1215. |
| 8 | Maroteaux F, Saad C. Diesel engine combustion modeling for hardware in the loop applications: Effects of ignition delay time model[J]. Energy, 2013, 57: 641-652. |
| 9 | 龚英利. 基于EGR和低温燃烧概念的柴油机燃烧过程研究[D]. 天津:天津大学机械工程学院, 2009. |
| Gong Ying-li. The investigation on combustion process of diesel engine based on the concept on EGR and LTC[D]. Tianjin: School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, 2009. | |
| 10 | 张全长. 柴油机低温燃烧基础理论和燃烧控制策略的试验研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学机械工程学院, 2010. |
| Zhang Quan-chang. Experimental study on combustion fundamental theory and control strategy of diesel Low-Temperature Combustion[D]. Tianjin: School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University, 2010. | |
| 11 | Hong S, Park I, Chung J, et al. Gain scheduled controller of EGR and VGT systems with a model-based gain scheduling strategy for diesel engines[J]. IFAC-Papers OnLine, 2015, 48(15): 109-116. |
| 12 | Bridjesh P, Periyasamy P, Mallikarjuna M V. Selecting optimal combination of operating parameters of diesel engine using analytic hierarchy process[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2017, 4(8): 7457-7466. |
| 13 | Nishio Y, Murata Y, Yamaya Y, et al. Optimal calibration scheme for map-based control of diesel engines[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61(7): 68-81. |
| 14 | Costa M, Bianchi G M, Forte C, et al. A numerical methodology for the multi-objective optimization of the DI diesel engine combustion[J]. Energy Procedia, 2014, 45: 711-720. |
| 15 | Deb M, Banerjee R, Majumder A, et al. Multi objective optimization of performance parameters of a single cylinder diesel engine with hydrogen as a dual fuel using pareto-based genetic algorithm[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(15): 8063-8077. |
| 16 | Tanner F X, Srinivasan S. CFD-based optimization of fuel injection strategies in a diesel engine using an adaptive gradient method[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2009, 33(3): 1366-1385. |
| 17 | Lino P, Maione B, Rizzo A. Nonlinear modelling and control of a common rail injection system for diesel engines[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2007, 31(9): 1770-1784. |
| 18 | 马朝臣, 郭林福, 施新, 等. VGT对柴油机排放性能影响的试验研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2004, 24(10): 849-853. |
| Ma Chao-chen, Guo Lin-fu, Shi Xin, et al. Influence of variable geometry turbocharging to the emission of diesel engine[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2004, 24(10): 849-853. | |
| 19 | 李幼凤, 苏宏业, 褚健. 子空间模型辨识方法综述[J]. 化工学报, 2006, 57(3): 473-479. |
| Li You-feng, Su Hong-ye, Chu Jian. Overview on subspace model identification methods[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering(China), 2006, 57(3): 473-479. | |
| 20 | 侯忠生, 许建新. 数据驱动控制理论及方法的回顾和展望[J]. 自动化学报, 2009, 35(6): 650-667. |
| Hou Zhong-sheng, Xu Jian-xin. On data-driven control theory: the state of the art and persprctive[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2009, 35(6): 650-667. | |
| 21 | 蒋冰晶. 基于数据驱动的柴油机燃烧过程建模及控制[D]. 长春:吉林大学通信工程学院, 2018. |
| Jiang Bing-jing. Data-driven based diesel engine combustion procress modeling and control[D]. Changchun: College of Communication Engineering, Jilin University, 2018. | |
| 22 | 范亚南. 基于数据驱动的发动机空燃比预测控制[D]. 长春:吉林大学通信工程学院, 2014. |
| Fan Ya-nan. Data-driven based engine air-fuel ratio predictive control[D]. Changchun: College of Communication Engineering, Jilin University, 2014. | |
| 23 | 陈虹. 模型预测控制[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2013. |
| 24 | 车胜新. 解析重型汽车、发动机污染物排放限值及测量方法(中国Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅴ阶段)标准[J]. 机械工业标准化与质量, 2005(12): 30-31. |
| Che Sheng-xin. Analyse to the discharge of pollutants from heavy-duty vehicles and engine(China Ⅲ phase, Ⅳ, Ⅴ)[J]. Mechanical Industry Standardization and Quality, 2005(12): 30-31. |
| [1] | 王忠,李游,张美娟,刘帅,李瑞娜,赵怀北. 柴油机排气阶段颗粒碰撞过程动力学特征分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 39-48. |
| [2] | 王建,许鑫,顾晗,张多军,刘胜吉. 基于排气热管理的柴油机氧化催化器升温特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 408-416. |
| [3] | 宋昌庆,陈文淼,李君,曲大为,崔昊. 不同当量比下单双点火对天然气燃烧特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1929-1935. |
| [4] | 朱一骁,何小民,金义. 联焰板宽度对单凹腔驻涡燃烧室流线形态的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1936-1944. |
| [5] | 刘长铖,刘忠长,田径,许允,杨泽宇. 重型增压柴油机燃烧过程中的缸内㶲损失[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1911-1919. |
| [6] | 胡潇宇,李国祥,白书战,孙柯,李思远. 考虑加热面粗糙度和材料的沸腾换热修正模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1945-1950. |
| [7] | 王德军,吕志超,王启明,张建瑞,丁建楠. 基于EKF及调制傅式级数的缸压辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1174-1185. |
| [8] | 臧鹏飞,王哲,高洋,孙晨乐. 直线电机/发动机系统稳态运行综合控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 798-804. |
| [9] | 董伟,宋佰达,邱立涛,孙昊天,孙平,蒲超杰. 直喷汽油机暖机过程中两次喷射比例对燃烧和排放的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1755-1761. |
| [10] | 李志军, 汪昊, 何丽, 曹丽娟, 张玉池, 赵新顺. 催化型微粒捕集器碳烟分布及其影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1466-1474. |
| [11] | 林学东, 江涛, 许涛, 李德刚, 郭亮. 高压共轨柴油机起动工况高压泵控制策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1436-1443. |
| [12] | 秦静, 徐鹤, 裴毅强, 左子农, 卢莉莉. 初始温度和初始压力对甲烷-甲醇裂解气预混层流燃烧特性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1475-1482. |
| [13] | 宫洵, 蒋冰晶, 胡云峰, 曲婷, 陈虹. 柴油机主-从双微元Urea-SCR系统非线性状态观测器设计与分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1055-1062. |
| [14] | 席雷, 徐亮, 高建民, 赵振, 王明森. 厚壁矩形带肋通道内蒸汽流动及传热特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 752-759. |
| [15] | 钟兵, 洪伟, 金兆辉, 苏岩, 解方喜, 张富伟. 进气门早关液压可变气门机构运动特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 727-734. |
|
||