吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 716-724.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200838
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
基于虾螯的仿生多胞薄壁管耐撞性分析及优化
黄晗1( ),闫庆昊1,向枳昕1,杨鑫涛1,陈金宝1,许述财2(
),闫庆昊1,向枳昕1,杨鑫涛1,陈金宝1,许述财2( )
)
- 1.南京航空航天大学 航天学院,南京 211106
2.清华大学 汽车安全与节能国家重点实验室,北京 100084
Crashworthiness investigation and optimization of bionic multi⁃cell tube based on shrimp chela
Han HUANG1( ),Qing-hao YAN1,Zhi-xin XIANG1,Xin-tao YANG1,Jin-bao CHEN1,Shu-cai XU2(
),Qing-hao YAN1,Zhi-xin XIANG1,Xin-tao YANG1,Jin-bao CHEN1,Shu-cai XU2( )
)
- 1.Academy of Astronautics,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Nanjing 211106,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Safety and Energy,Tsinghua University,Beijing 100084,China
摘要:
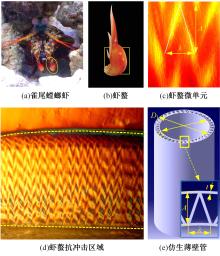
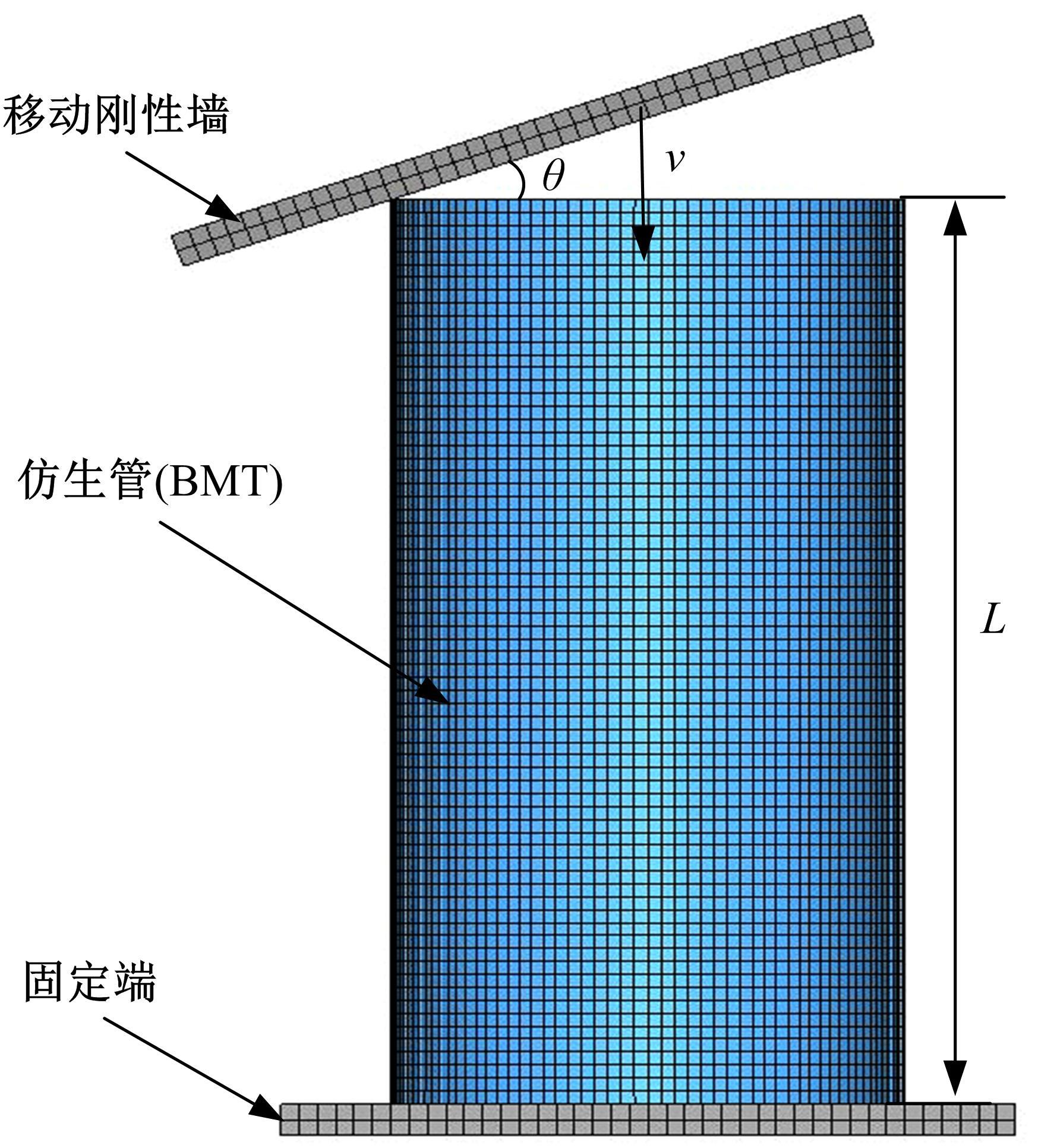
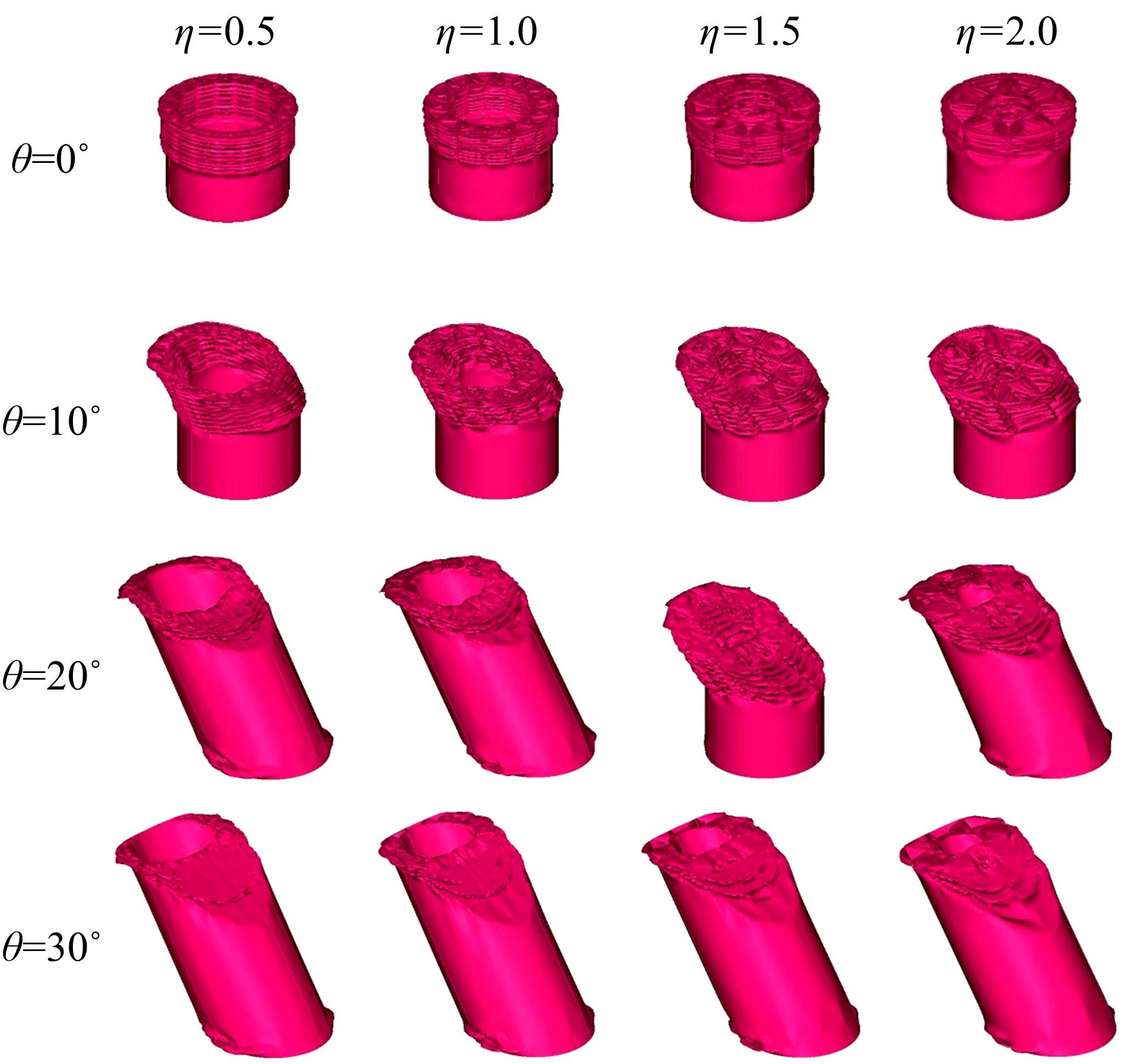
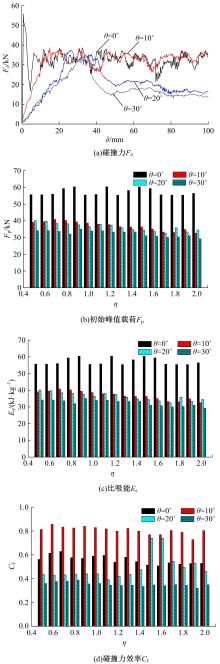
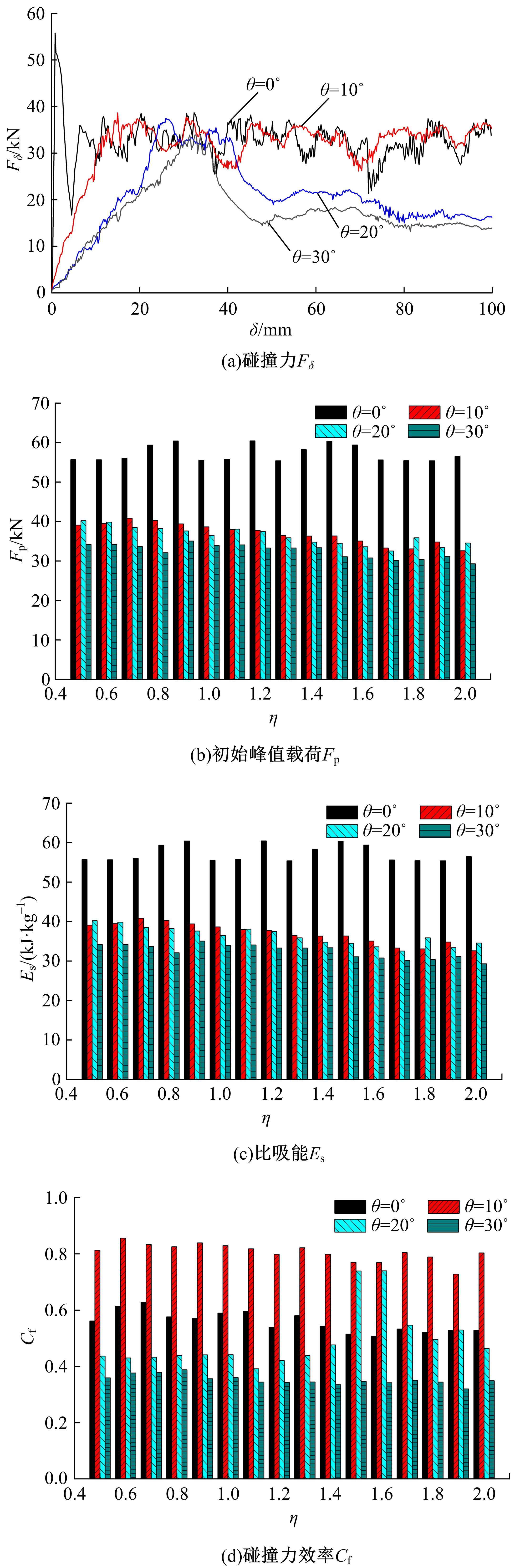
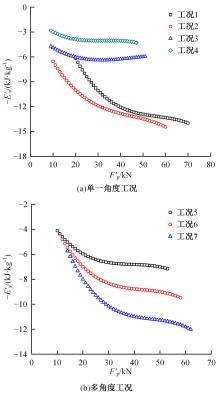
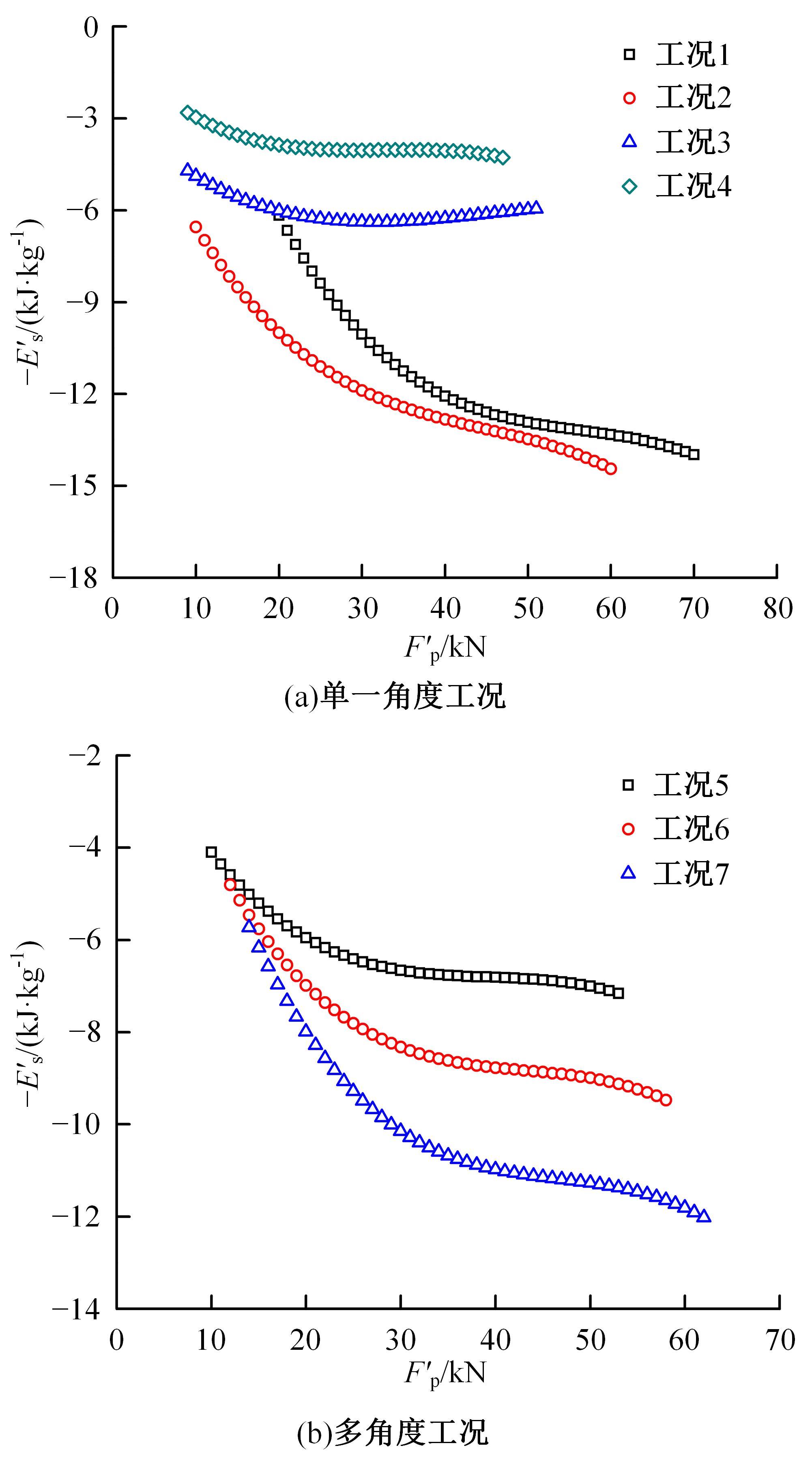
为提高薄壁吸能结构的耐撞性,基于雀尾螳螂虾螯的微观结构,提出了一种新型含“人”字形仿生单元的多胞薄壁管结构。通过有限元模型仿真分析了不同碰撞角度θ(0°、10°、20°和30°)条件下,仿生单元高宽比η(单元高度A与宽度λ的比值)对薄壁管耐撞性的影响。结果表明:轴向(θ=0°)和小角度斜向(θ=10°)载荷碰撞条件下,仿生薄壁管均呈现渐进折叠变形,且θ=10°的薄壁管具有较大的比吸能Es和碰撞力效率Cf,以及较小的初始峰值载荷Fp。通过复杂比例法评价了薄壁管的耐撞性,η值分别为0.6~1.0和1.5~1.7时的薄壁管具有较好的耐撞性,仿生单元高宽比η最优值为1.5。采用多目标优化方法和多目标粒子群优化算法对不同碰撞角度工况的薄壁管结构参数进行了优化,最优结果是壁厚t为0.75~1.2 mm、单元宽度λ为5.5~9.5 mm、初始峰值载荷为59.8 kN、比吸能最大值为13.28 kJ/kg,该薄壁管仿生设计方法和优化方法为吸能元件的轻量化设计提供了新思路。
中图分类号:
- TB17
| 1 | Baroutaji A, Sajjia M, Olabi A G. On the crashworthiness performance of thin-walled energy absorbers: recent advances and future developments[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2017, 118: 137-163. |
| 2 | 周俊先, 秦睿贤, 陈秉智. 双面梯度多角薄壁结构的吸能特性[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(5):1584-1592. |
| Zhou Jun-xian, Qin Rui-xian, Chen Bing-zhi. Energy absorption properties of multi-corner thin-walled columns with double surface gradients[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5):1584-1592. | |
| 3 | Tran T N. Crushing analysis under multiple impact loading cases for multi-cell triangular tubes[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2017, 113:262-272. |
| 4 | Chen T T, Zhang Y, Lin J M, et al. Theoretical analysis and crashworthiness optimization of hybrid multi-cell structures[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2019, 142:116-131. |
| 5 | Li Z X, Ma W, Xu P, et al. Crashworthiness of multi-cell circumferentially corrugated square tubes with cosine and triangular configurations[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2020, 165: No.105205. |
| 6 | Song J F, Xu S C, Wang H X, et al. Bionic design and multi-objective optimization for variable wall thickness tube inspired bamboo structures[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 125: 76-88. |
| 7 | 白芳华, 张林伟, 白中浩, 等. 基于甲虫鞘翅的客车八边形仿生多胞薄壁管耐撞性研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(21):24-30. |
| Bai Fang-hua, Zhang Lin-wei, Bai Zhong-hao, et al. Crashworthiness of coach's octagonal bionic multi-cell thin-walled tubes based on beetle elytra[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(21):24-30. | |
| 8 | Zhang L W, Bai Z H, Bai F H. Crashworthiness design for bio-inspired multi-cell tubes with quadrilateral, hexagonal and octagonal sections[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 122:42-51. |
| 9 | 邹猛, 于用军, 张荣荣, 等. 仿牛角结构薄壁管吸能特性仿真分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2015,45(6):1863-1868. |
| Zou Meng, Yu Yong-jun, Zhang Rong-rong, et al. Simulation analysis of energy-absorption properties of thin-walled tube based on horn structure[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(6): 1863-1868. | |
| 10 | Xu Tao, Liu Nian, Yu Zheng-lei, et al. Crashworthiness design for bionic bumper structures inspired by cattail and bamboo[J/OL]. [2020-10-25]. |
| 11 | Liu S T, Tong Z Q, Tang Z L, et al. Bionic design modification of non-convex multi-corner thin-walled columns for improving energy absorption through adding bulkheads[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2015, 88: 70-81. |
| 12 | Weaver J C, Milliron G W, Miserez A, et al. The stomatopod dactyl club: a formidable damage-tolerant biological hammer[J]. Science, 2012, 336(6086): 1275-1280. |
| 13 | Yaraghi N A, Guarín‐Zapata N, Grunenfelder L K, et al. A sinusoidally architected helicoidal biocomposite[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(32): 6835-6844. |
| 14 | Patek S N, Korff W L, Caldwell R L. Biomechanics: deadly strike mechanism of a mantis shrimp[J]. Nature, 2004, 428(6985):819-820. |
| 15 | Huang H, Xu S C. Crashworthiness analysis and bionic design of multi-cell tubes under axial and oblique impact loads[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2019, 144(C): No.106333. |
| 16 | Yin H F, Xiao Y Y, Wen G L, et al. Multiobjective optimization for foam-filled multi-cell thin-walled structures under lateral impact[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2015, 94:1-12. |
| 17 | Barakat S, Bani-Hani K, Taha M Q. Multi-objective reliability-based optimization of prestressed concrete beams[J]. Structural Safety, 2004, 26(3): 311-342. |
| [1] | 姜斌祥,姜彤彤,王永雷. 基于文化遗传算法的毒品检验区块链共识算法优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 684-692. |
| [2] | 张立杰,阿喜塔,田笑,李稳. 基于Gamma过程的加速退化试验多目标优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 361-367. |
| [3] | 陈奕颖,金敬福,丛茜,陈廷坤,任露泉. 不同冰点介质对冰黏附强度的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1926-1932. |
| [4] | 于征磊,陈立新,徐泽洲,信仁龙,马龙,金敬福,张志辉,江山. 基于增材制造的仿生防护结构力学及回复特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1540-1547. |
| [5] | 于征磊,信仁龙,陈立新,朱奕凝,张志辉,曹青,金敬福,赵杰亮. 仿蜂窝防护结构的承载特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1140-1145. |
| [6] | 周炳海,何朝旭. 基于静态半成套策略的多目标准时化物料配送调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 910-916. |
| [7] | 孙宝凤,任欣欣,郑再思,李国一. 考虑工人负荷的多目标流水车间优化调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 900-909. |
| [8] | 黄继承,沈成,纪爱敏,李显旺,张彬,田昆鹏,刘浩鲁. 工业大麻收割机切割⁃输送关键部件作业参数优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 772-780. |
| [9] | 周炳海,吴琼. 基于多目标的机器人装配线平衡算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [10] | 马芳武,韩丽,吴量,李金杭,杨龙帆. 基于遗传与粒子群算法的隔振平台减振性能优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1608-1616. |
| [11] | 陈学深,陈涛,武涛,马旭,曾令超,陈林涛. 覆草冬种马铃薯收获机稻草分离机构设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 749-757. |
| [12] | 李银平,靳添絮,刘立. 纯电动铲运机弓网续能系统设计与动态特性仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 454-463. |
| [13] | 马芳武,梁鸿宇,赵颖,杨猛,蒲永锋. 内凹三角形负泊松比结构耐撞性多目标优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 29-35. |
| [14] | 蔡中义,孟凡响,陈庆敏,赵轩. 复杂钩舌锻件近净成形的预锻形状优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 84-90. |
| [15] | 刘春宝,陈山石,盛闯,钱志辉,任露泉,任雷. 蜘蛛生物液压驱动原理及其功能仿生探索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 375-381. |
|
||