吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2806-2815.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210479
面向刚柔耦合定位平台的模型预测控制算法
- 1.广东工业大学 省部共建精密电子制造技术与装备国家重点实验室,广州 510006
2.北京科技大学 工业过程知识自动化教育部重点实验室,北京 100083
Model predictive control algorithm for rigid⁃flexible coupling positioning stage
Zhi-jun YANG1( ),Zhong-yi GAO1,Li-jun WANG2,Guan-xin HUANG1(
),Zhong-yi GAO1,Li-jun WANG2,Guan-xin HUANG1( ),Yu-tai WEI1
),Yu-tai WEI1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Precision Electronic Manufacturing Technology and Equipment,Guangdong University of Technology,Guangzhou 510006,China
2.Key Laboratory of Industrial Process Knowledge Automation,Ministry of Education,University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083,China
摘要:
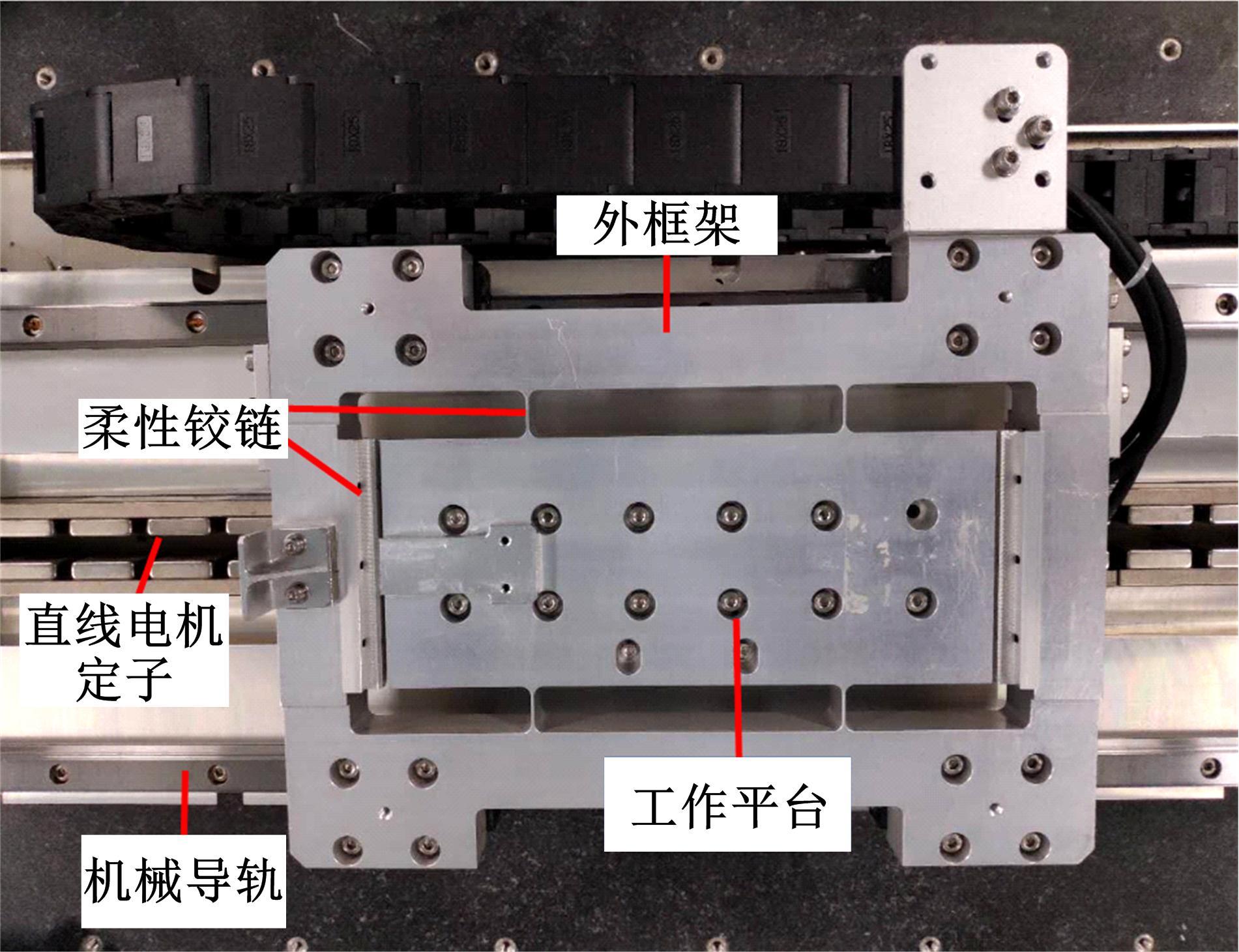
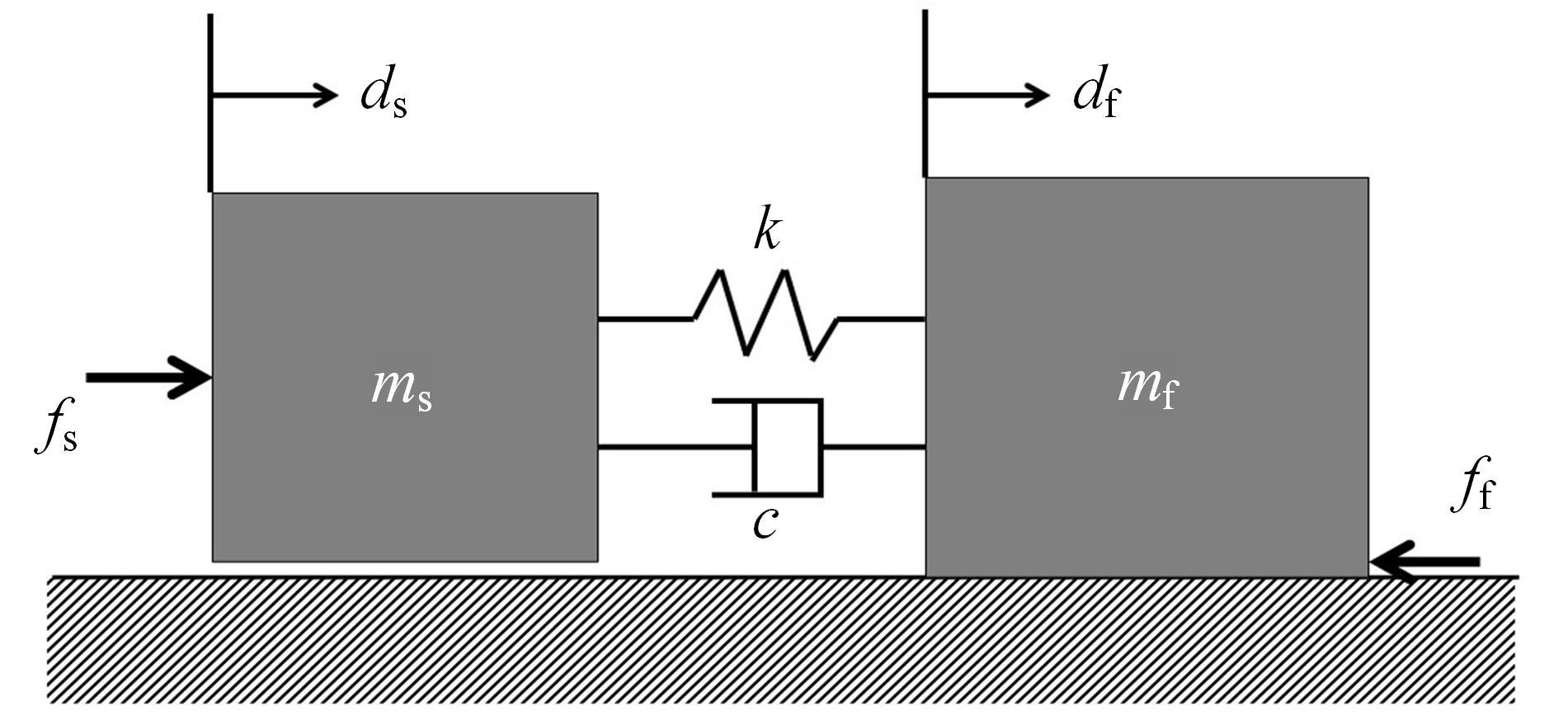
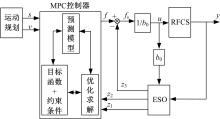
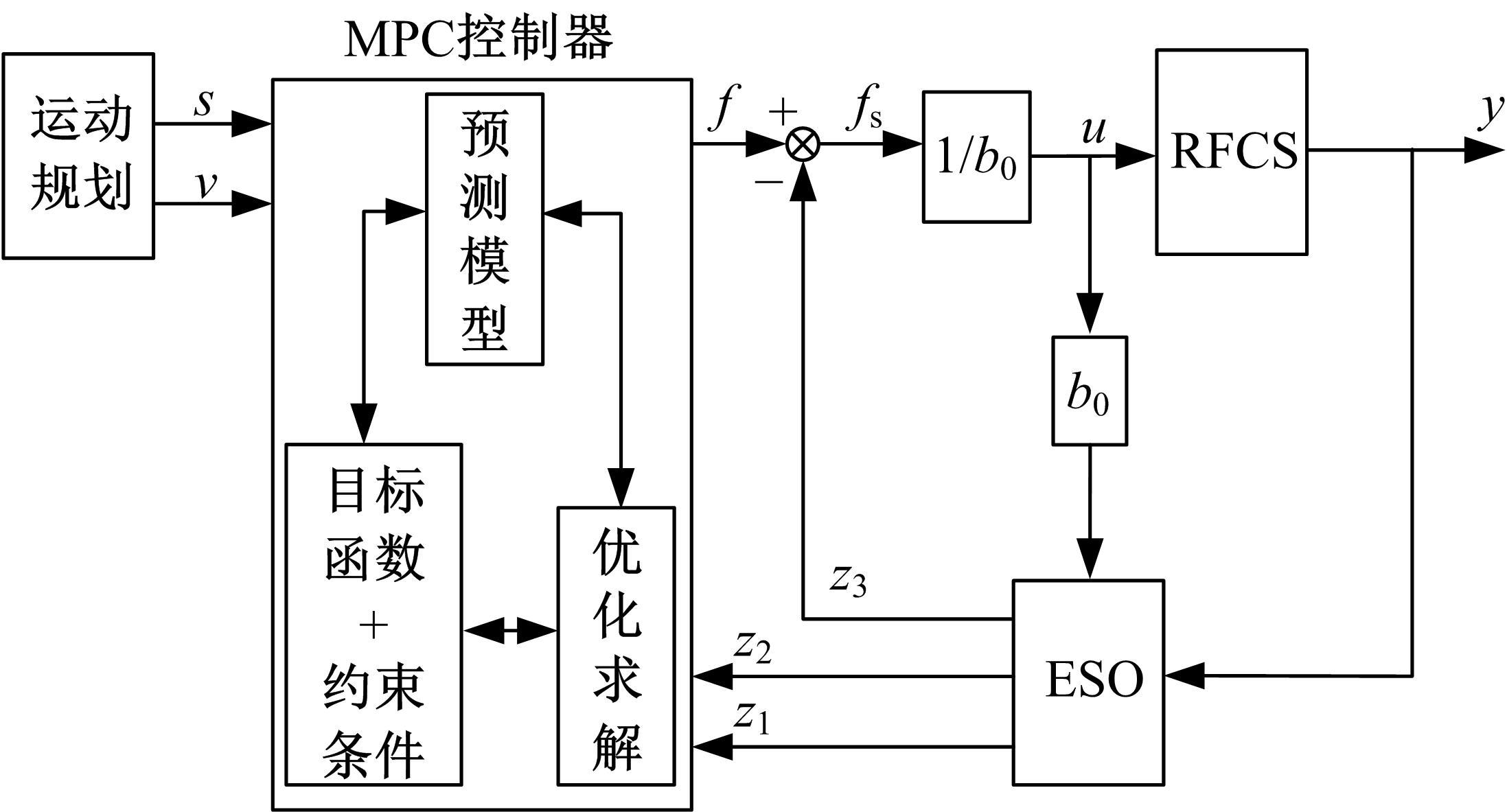
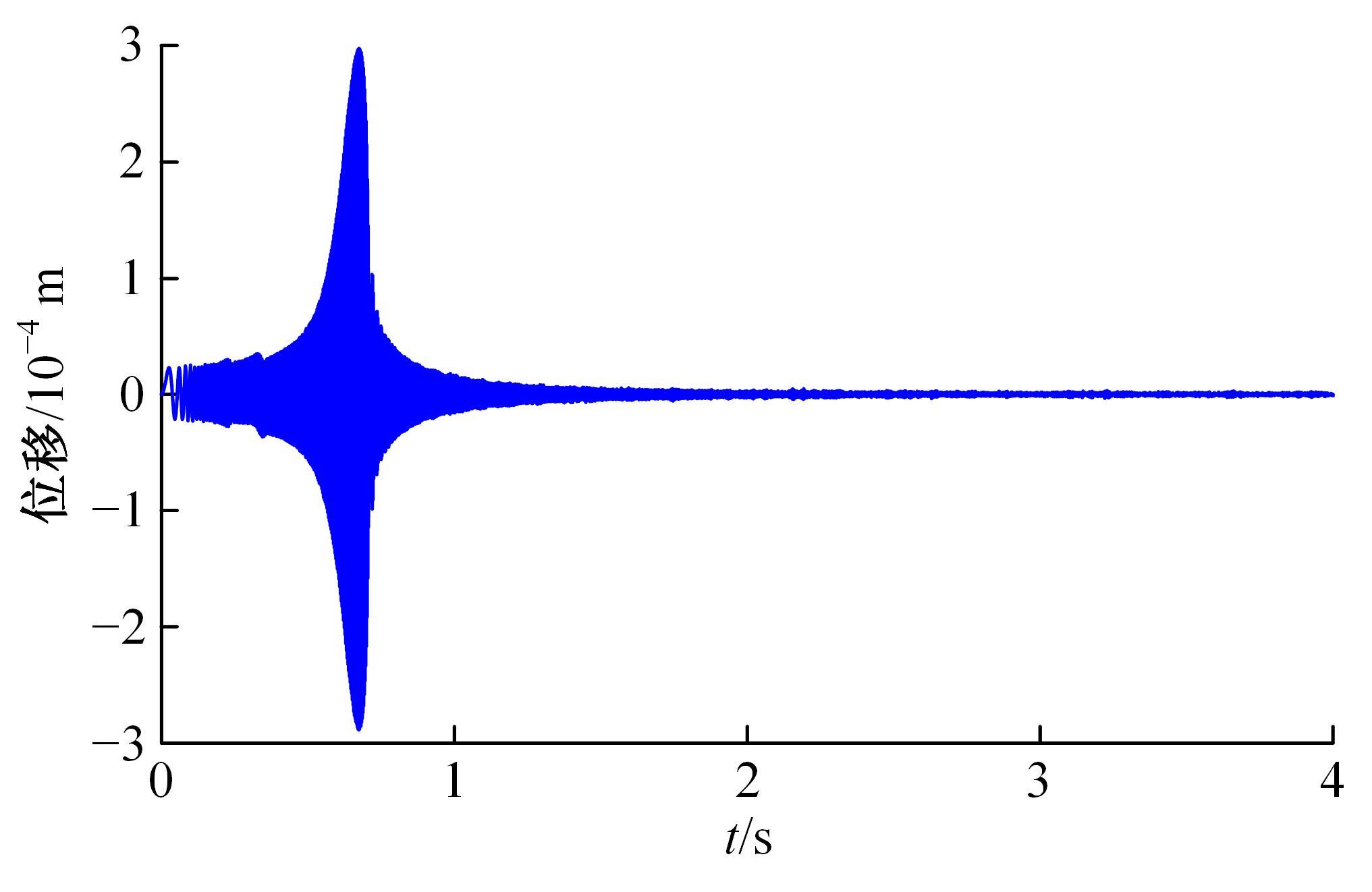
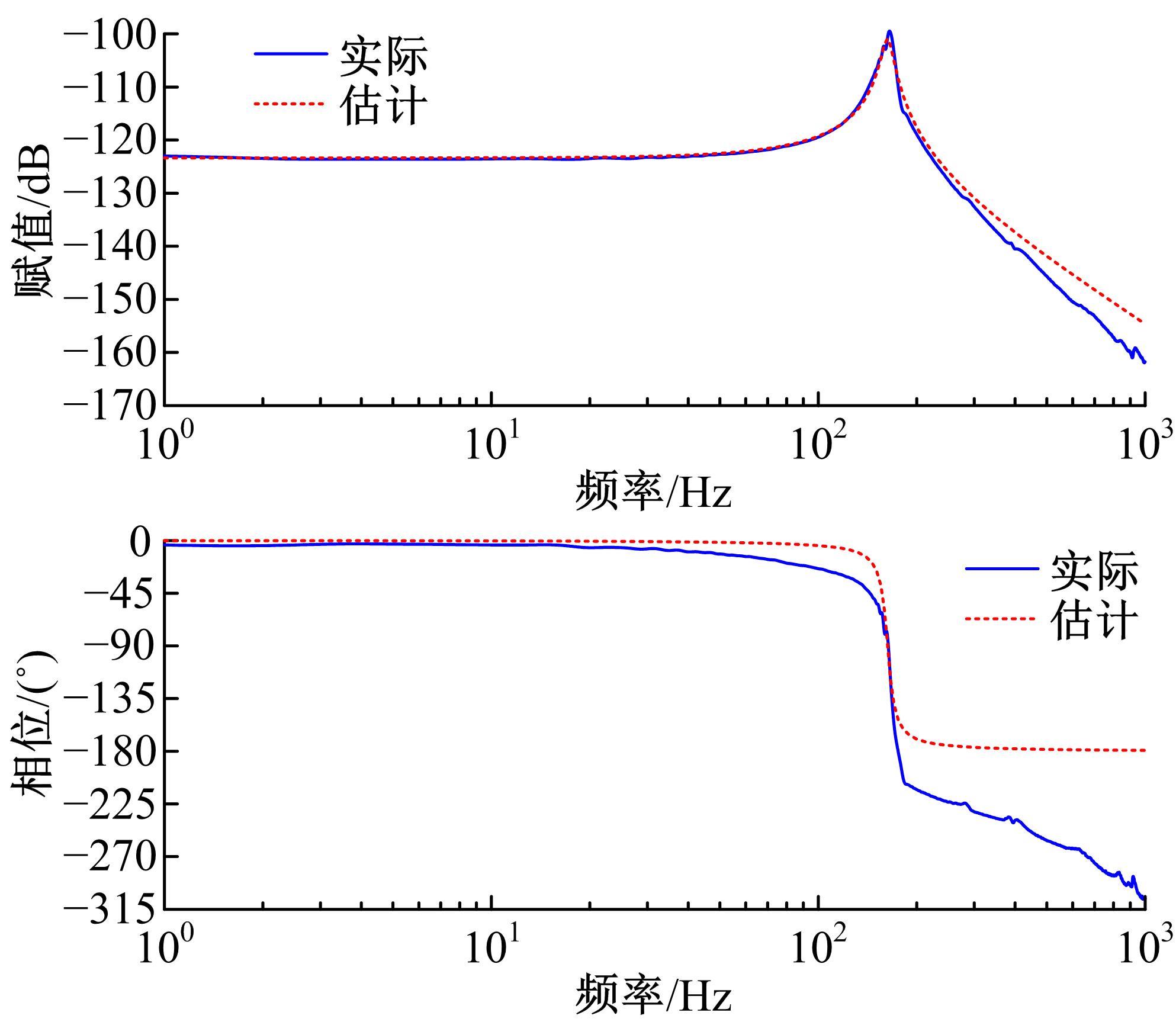
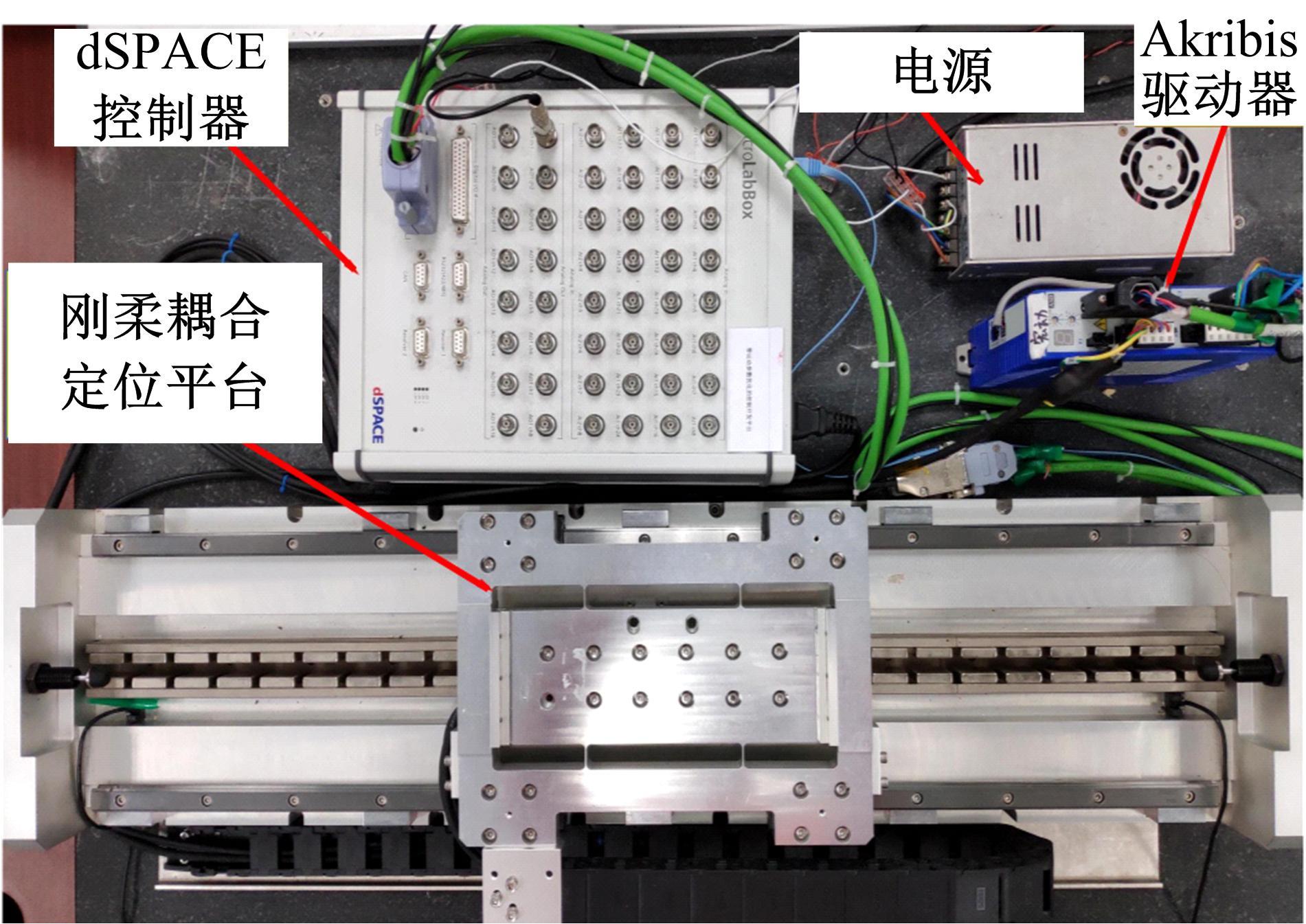
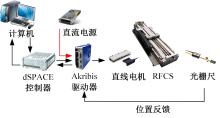
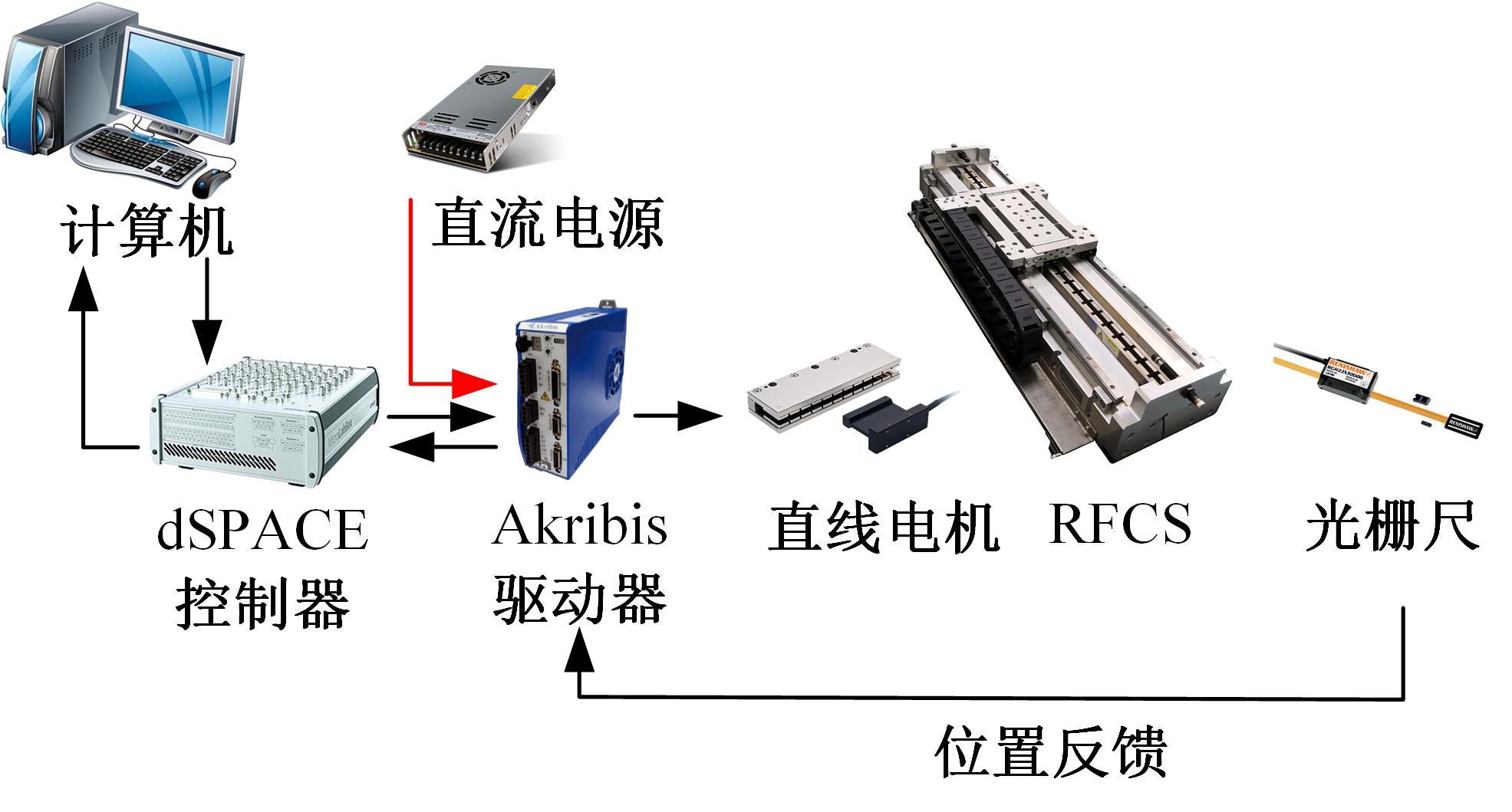
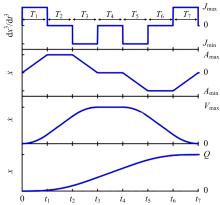
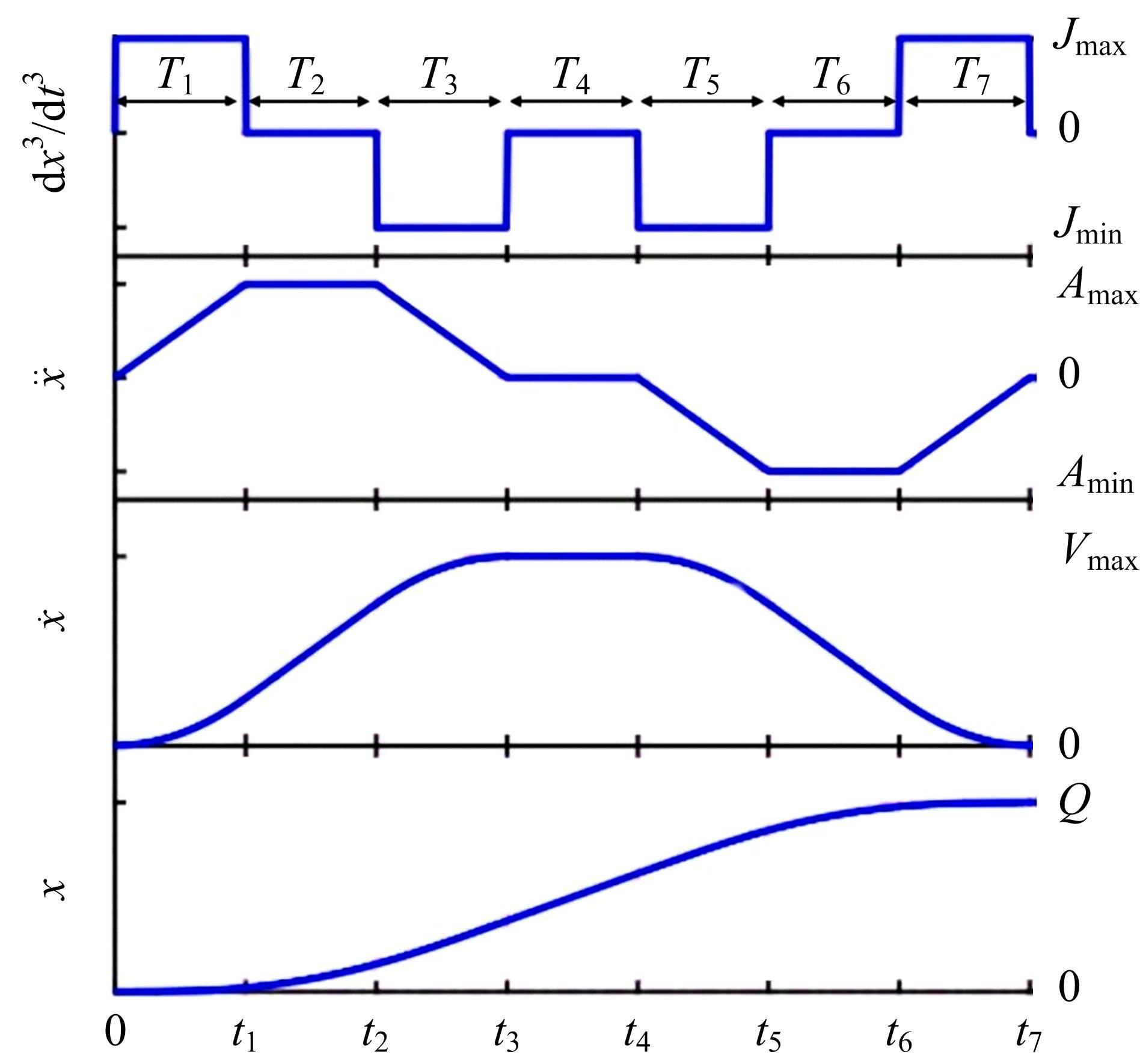
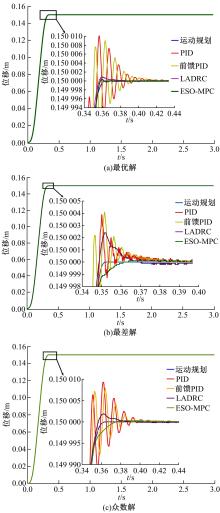
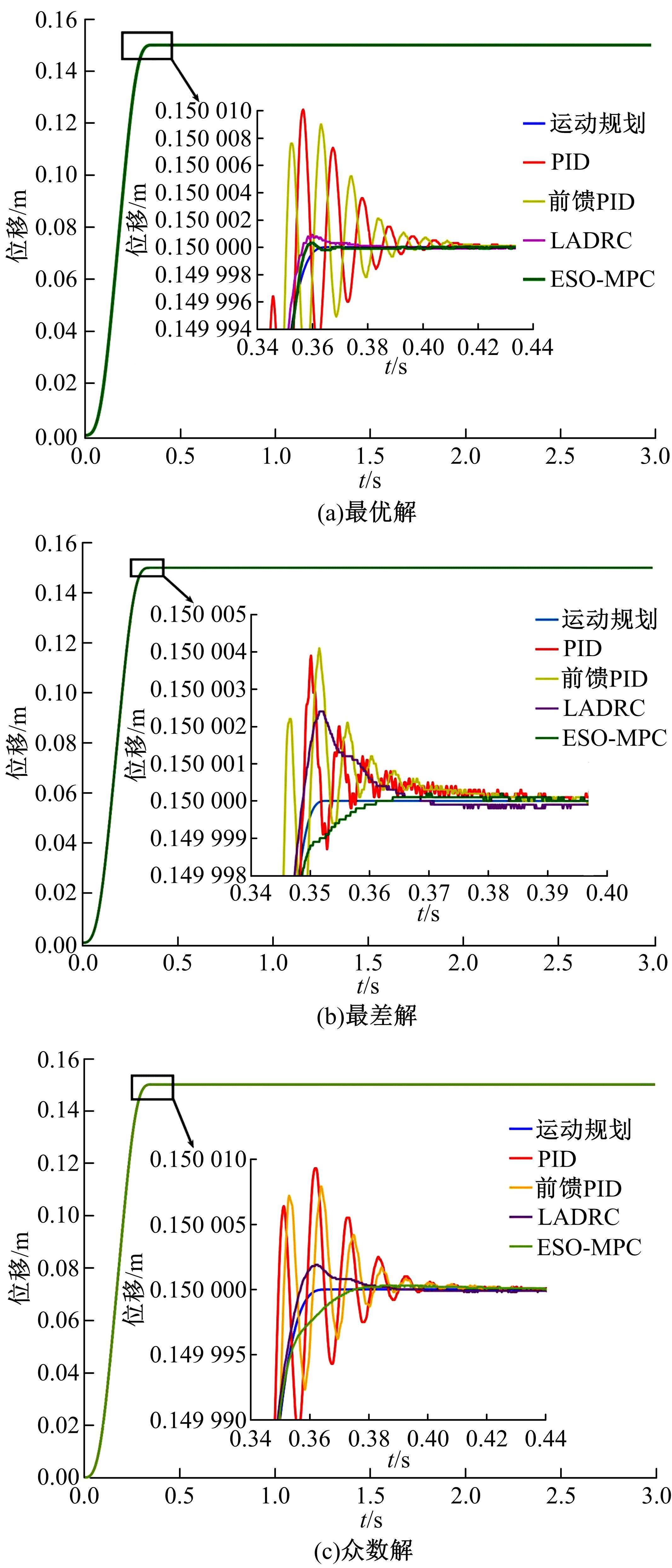
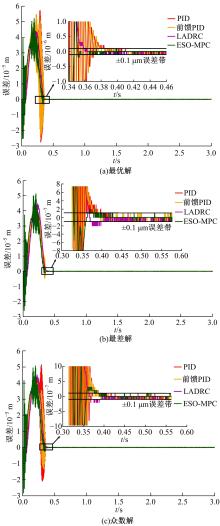
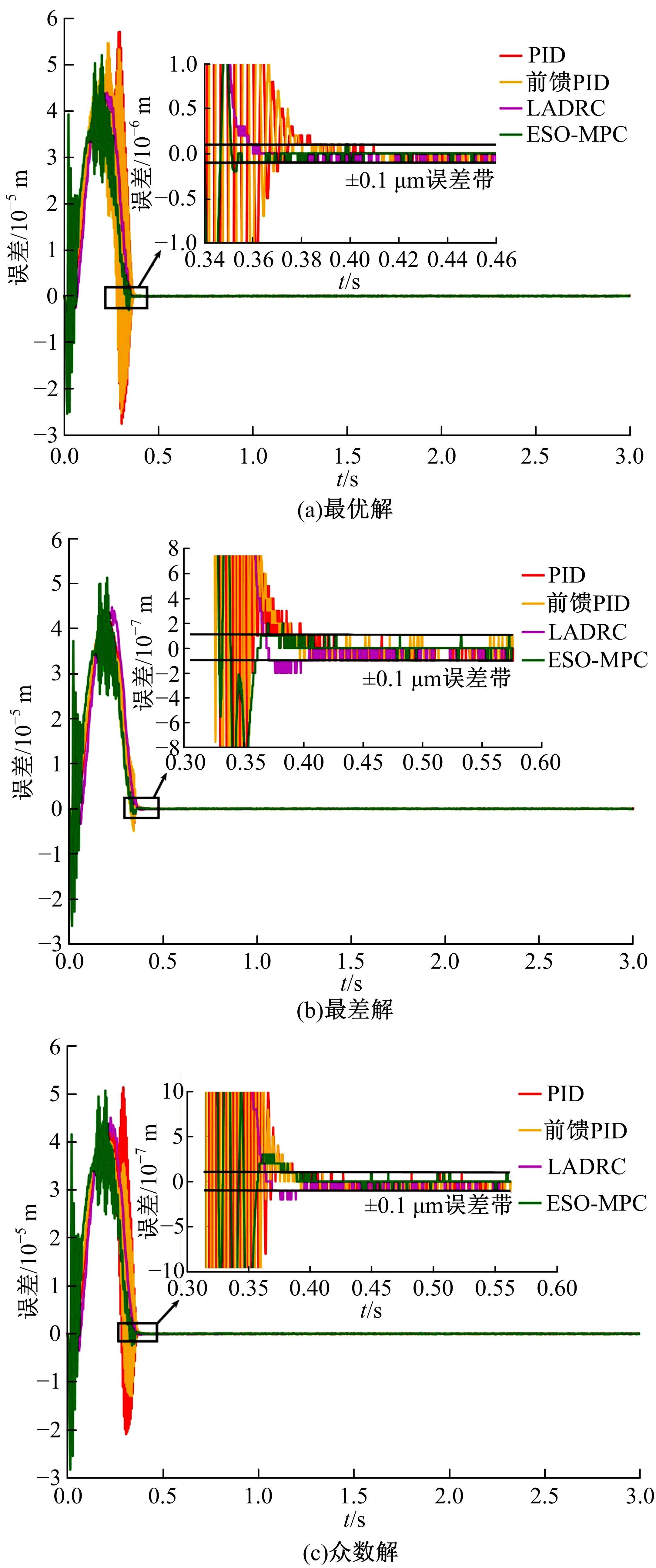
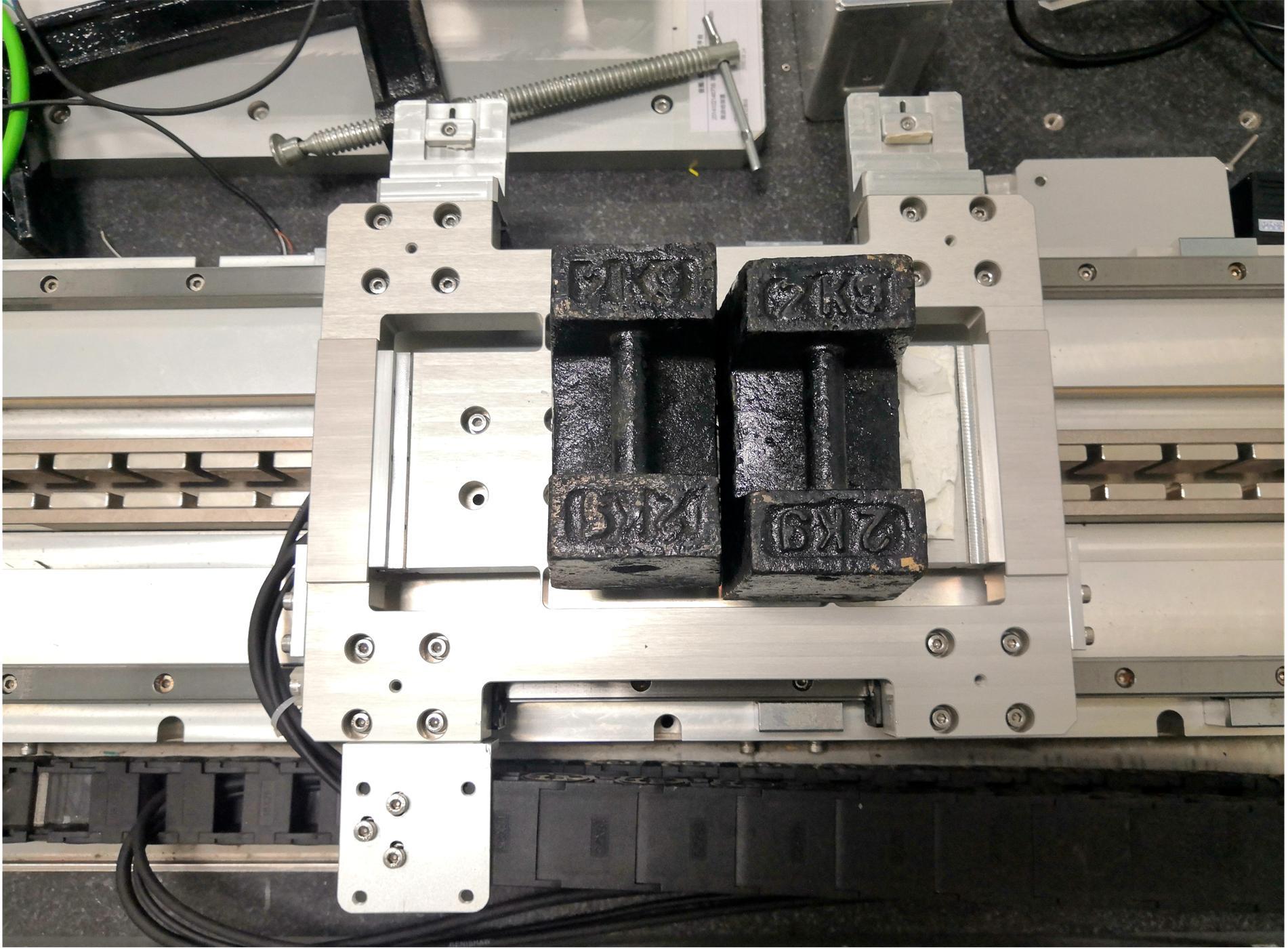
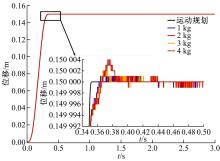
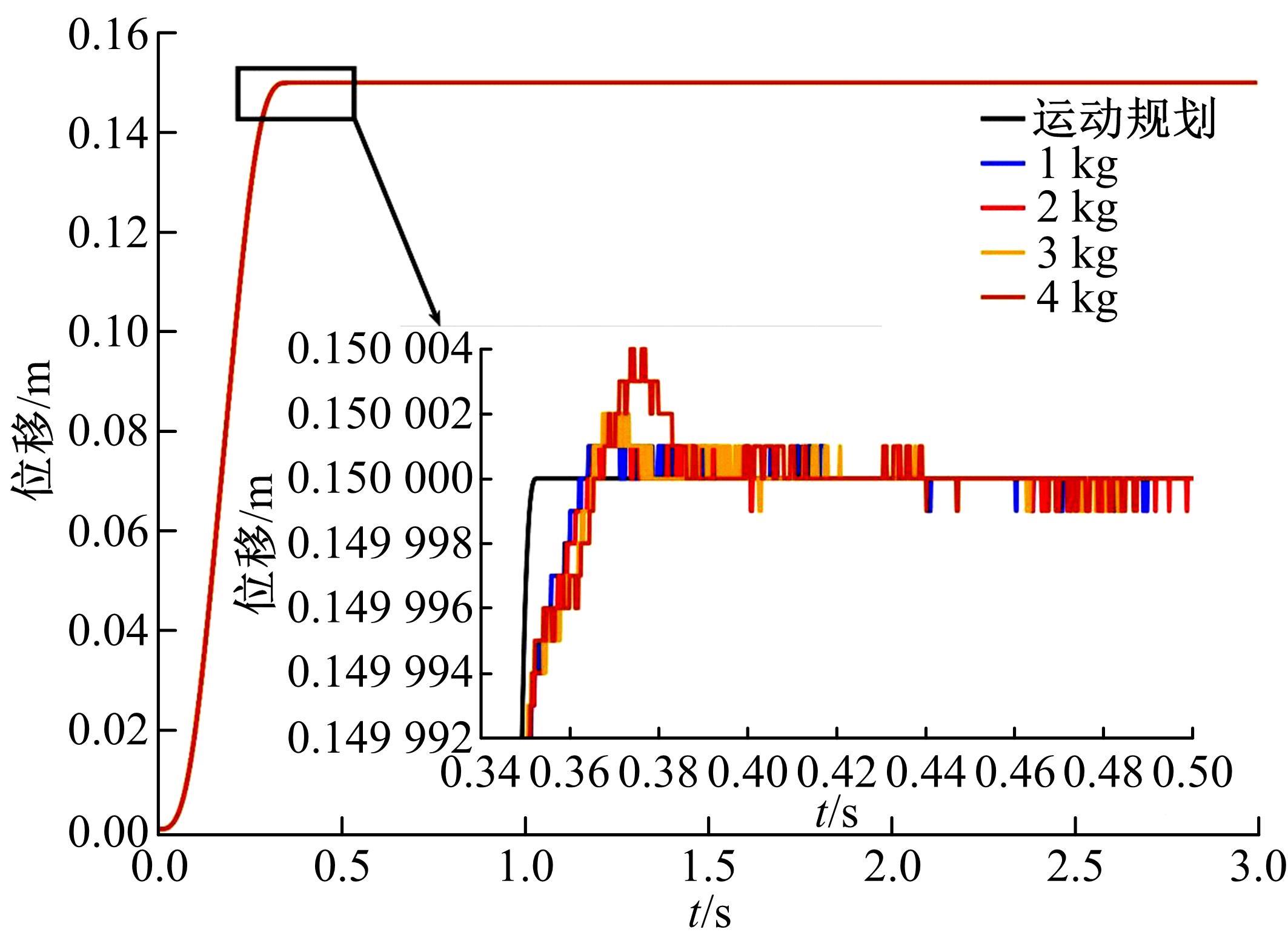
针对刚柔耦合定位平台(RFCS)在运动阶段和定位阶段模型不同的特点,提出了一种扩张状态观测器辅助的模型预测控制(ESO-MPC)算法。该算法采用时域离散的差分方程对RFCS的动力学响应进行预测,并且在时域离散时引入了可调参数应对实验模型的不确定因素。通过扩张状态观测器(ESO)获取反馈信息,对RFCS的位置、速度及柔性铰链的弹性力和阻尼力进行实时观测。通过RFCS的25组点位运动实验和负载实验,对比了传统PID、前馈PID、LADRC与ESO-MPC算法的性能。实验结果表明,4种控制方案都能达到±0.1 μm的稳态误差,而ESO-MPC算法的整定时间最短,并且通过负载实验验证了ESO-MPC算法的鲁棒性。
中图分类号:
- TP273
| 1 | 刘岗岗,王旭亮,胡锐,等. 面向多品种、小批量微电子制造过程的SPC技术应用研究[J]. 电子质量, 2020(1): 5-8. |
| Liu Gang-gang, Wang Xu-liang, Hu Rui, et al. SPC technology application research for multi-variety, small-batch microelectronics manufacturing process[J]. Electronic Quality, 2020(1): 5-8. | |
| 2 | Qin W, Li Y. Foreword: special section on "the reliability of advanced microelectronic packaging—part II: structure-property relationships"[J]. IEEE Transactions on Components, Packaging, and Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 10(10): 1587-1588. |
| 3 | 夏旭晖. 微电子封装技术的优势与应用[J]. 无线互联科技, 2021, 18(4): 102-103. |
| Xia Xu-hui. The advantages and applications of microelectronic packaging technology[J]. Wireless Internet Technology, 2021, 18(4): 102-103. | |
| 4 | 廖志伟. 微电子封装技术探讨[J]. 计算机产品与流通, 2020(2): 150. |
| Liao Zhi-wei. Discussion on microelectronics packaging technology[J]. Computer Products and Circulation, 2020(2): 150. | |
| 5 | 白有盾,陈新,杨志军. 刚柔分级并联驱动宏微复合运动平台设计[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2019, 49(6): 669-680. |
| Bai You-dun, Chen Xin, Yang Zhi-jun. Design of rigid-flexible hierarchical parallel drive macro-micro composite motion platform[J]. Science in China: Technical Sciences, 2019, 49(6): 669-680. | |
| 6 | Chen X, Bai Y, Yang Z, et al. A precision-positioning method for a high-acceleration low-load mechanism based on optimal spatial and temporal distribution of inertial energy[J]. Engineering, 2015, 1(3): 391-398. |
| 7 | Ruderman M, Iwasaki M. Analysis of linear feedback position control in presence of presliding friction[J]. IEEJ Journal of Industry Applications, 2016, 5(2): 61-68. |
| 8 | Sato K, Nakamoto K, Shimokohbe A. Practical control of precision positioning mechanism with friction[J]. Precision Engineering, 2004, 28(4):426-434. |
| 9 | Dong X, Okwudire C E. An experimental investigation of the effects of the compliant joint method on feedback compensation of pre-sliding/pre-rolling friction[J]. Precision Engineering, 2018, 54:81-90. |
| 10 | 韩京清. 从PID技术到“自抗扰控制”技术[J]. 控制工程, 2002(3): 13-18. |
| Han Jing-qing. From PID technology to "auto-disturbance rejection control" technology[J]. Control Engineering, 2002(3): 13-18. | |
| 11 | 席裕庚,李德伟,林姝. 模型预测控制——现状与挑战[J]. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(3): 222-236. |
| Xi Yu-geng, Li De-wei, Lin Shu. Model predictive control——current situation and challenges[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(3): 222-236. | |
| 12 | Morari M, Maeder U. Nonlinear offset-free model predictive control[J]. Automatica Oxford, 2012,48(9): 2059-2067. |
| 13 | Narimani M, Wu B, Yaramasu V, et al. Finite control-set model predictive control (FCS-MPC) of nested neutral point-clamped (NNPC) converter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2015, 30(12): 7262-7269. |
| 14 | Guechi E H, Bouzoualegh S, Zennir Y, et al. MPC control and LQ optimal control of A two-link robot arm: a comparative study[J]. Machines, 2018, 6(3):No.37. |
| 15 | 杨茹楠,何晋伟,王秀瑞. 三电平双向直流变换器的模型预测电压控制研究[J]. 电源学报, 2021, 19(2): 74-80. |
| Yang Ru-nan, He Jin-wei, Wang Xiu-rui. Research on model predictive voltage control of three-level bidirectional DC converter[J]. Journal of Power Supply, 2021, 19(2): 74-80. | |
| 16 | Cursi F, Modugno V, Lanari L, et al. Bayesian neural network modeling and hierarchical MPC for a tendon-driven surgical robot with uncertainty minimization[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(2): 2642-2649. |
| 17 | 李寿涛,王蕊,徐靖淳,等. 一种基于模型预测复合控制的车辆避碰控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(2): 738-746. |
| Li Shou-tao, Wang Rui, Xu Jing-chun, et al. A vehicle collision avoidance control method based on model predictive compound control[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 738-746. | |
| 18 | 黄一,韩京清. 非线性连续二阶扩张状态观测器的分析与设计[J]. 科学通报, 2000(13): 1373-1379. |
| Huang Yi, Han Jing-qing. Analysis and design of nonlinear continuous extended second order state observer[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000(13): 1373-1379. | |
| 19 | Han Jing-qing. From PID to active disturbance rejection control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(3): 900-906. |
| 20 | 李静,韩佐悦,杨威,等. 基于非线性模型的磁流变半主动悬架驱动系统[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018, 48(3): 645-651. |
| Li Jing, Han Zuo-yue, Yang Wei, et al. Magnetorheological semi-active suspension drive system based on nonlinear model[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(3): 645-651. | |
| 21 | 王春阳,辛瑞昊,史红伟. 针对大滞后系统的滞后时间削弱自抗扰控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(4): 1231-1237. |
| Wang Chun-yang, Xin Rui-hao, Shi Hong-wei. The lag time weakened auto disturbance rejection control method for the large lag system[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(4): 1231-1237. | |
| 22 | Yang Jun, Li Shi-hua, Yu Xing-huo. Sliding-mode control for systems with mismatched uncertainties via a disturbance observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2013, 60(1): 160-169. |
| 23 | Dinh T N, Park J, Park K S. Design and evaluation of disturbance observer algorithm for cable-driven parallel robots[J]. Microsystem Technologies, 2020, 26(1): 3377-3387. |
| 24 | Kim K S, Rew K H. Reduced order disturbance observer for discrete-time linear systems[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(4): 968-975. |
| 25 | Tran T P, Yokokura Y, Ohishi K, et al. FPGA-based high performance bilateral control of different master-slave mechanism using highorder disturbance observer[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics, Vicenza, Italy, 2013: No.13518547. |
| 26 | Ri S, Huang J, Tao C J, et al. A high-order disturbance observer based sliding mode velocity control of mobile wheeled inverted pendulum systems[C]∥2016 12th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA), Guilin, China, 2016: No. 16341068. |
| 27 | 韩京清. 自抗扰控制器及其应用[J]. 控制与决策, 1998(1): 19-23. |
| Han Jing-qing. Auto disturbance rejection controller and its application[J]. Control and Decision, 1998(1): 19-23. | |
| 28 | 黄一,薛文超,赵春哲. 自抗扰控制纵横谈[J]. 系统科学与数学, 2011, 31(9): 1111-1129. |
| Huang Yi, Xue Wen-chao, Zhao Chun-zhe. Discussion on active disturbance rejection control[J]. System Science and Mathematics, 2011, 31(9): 1111-1129. | |
| 29 | Gao Zhi-qiang. Scaling and bandwidth-parameterization based controller tuning[J]. Proceedings of the 2003 American Control Conference: IEEE, 2003: 4989-4996. |
| 30 | Daafouz J, Riedinger P, Iung C. Stability analysis and control synthesis for switched systems: a switched Lyapunov function approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2002, 47(11): 1883-1887. |
| 31 | Grimm G, Messina M J, Tuna S E, et al. Model predictive control: for want of a local control Lyapunov function, all is not lost[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(5): 546-558. |
| 32 | Singhose W, Eloundou R, Lawrence J. Command generation for flexible systems by input shaping and command smoothing[J]. Journal of Guidance Control & Dynamics, 2012, 33(6): 1697-1707. |
| [1] | 胡云峰,于彤,杨惠策,孙耀. 低温环境下燃料电池启动优化控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2034-2043. |
| [2] | 蒋林,周玲,赵慧. 液压伺服柔驱机构设计及其刚度连续可调分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1499-1508. |
| [3] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [4] | 李文航,倪涛,赵丁选,张泮虹,师小波. 基于集合卡尔曼滤波的高机动救援车辆主动悬挂控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2816-2826. |
| [5] | 彭浩楠,唐明环,查奇文,王伟忠,王伟达,项昌乐,刘玉龙. 自动驾驶汽车双车道换道最优轨迹规划方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2852-2863. |
| [6] | 胡鹏,朱建新,刘昌盛,张大庆. 液压挖掘机动臂势能交互回收利用系统特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2256-2264. |
| [7] | 李学勇,赵仲秋,张春松,路长厚. 基于有限元的人体⁃机械手交互力计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1612-1619. |
| [8] | 施昕昕,黄家才,高芳征. 基于分数阶BICO滤波器的运动控制测量噪声抑制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1873-1878. |
| [9] | 于萍,穆特,朱黎辉,周子业,宋杰. 钻具输送装置非线性动力学分析及稳定性控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 820-830. |
| [10] | 姜继海,赵存然,张冠隆,车明阳. 航空煤油柱塞泵摩擦副涂层材料摩擦性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 147-153. |
| [11] | 胡明伟,王洪光,潘新安. 基于正交设计的协作机器人全域结构优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 370-378. |
| [12] | 贾超,徐洪泽,王龙生. 基于多质点模型的列车自动驾驶非线性模型预测控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1913-1922. |
| [13] | 马苗苗,潘军军,刘向杰. 含电动汽车的微电网模型预测负荷频率控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1644-1652. |
| [14] | 顾万里, 张森, 胡云峰, 陈虹. 有刷直流电机非线性控制系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 900-907. |
| [15] | 唐晓峰, 高峰, 徐国艳, 丁能根, 蔡尧, 刘建行. 基于智能空间-车框架理论的车辆行驶运动学状态的预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1395-1401. |
|