吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2932-2941.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211357
基于多任务联合学习的多目标跟踪方法
- 吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
Multiple object tracking method based on multi-task joint learning
- College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
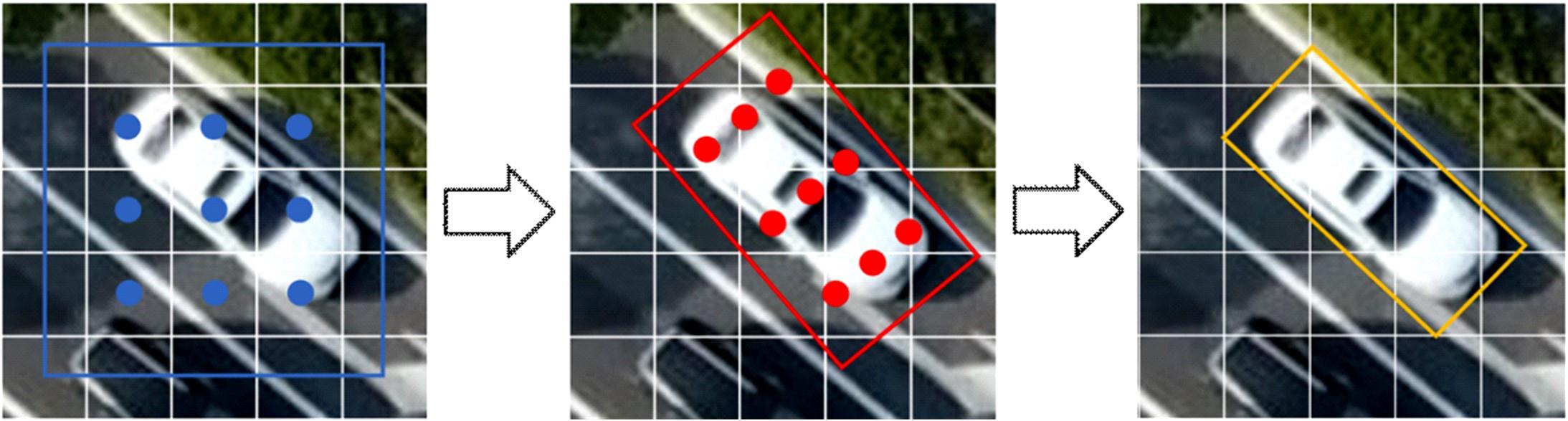
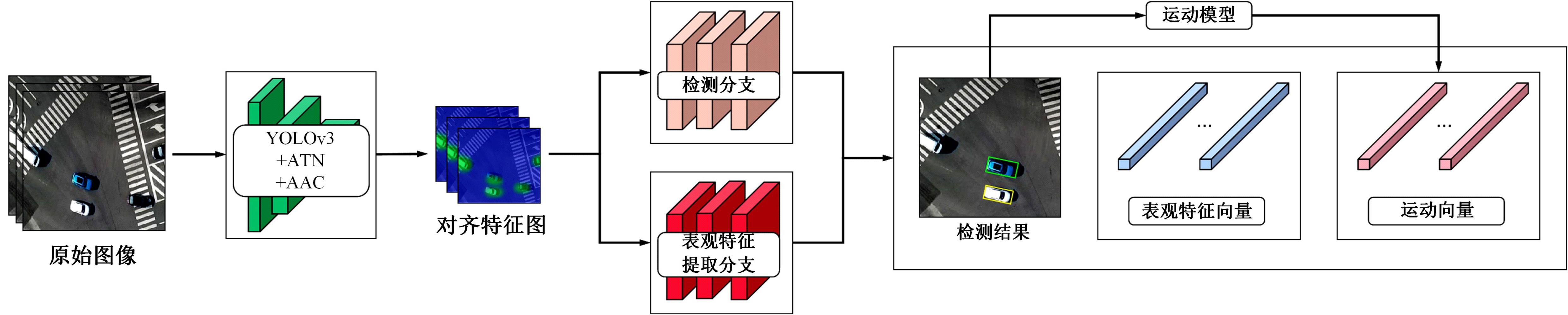
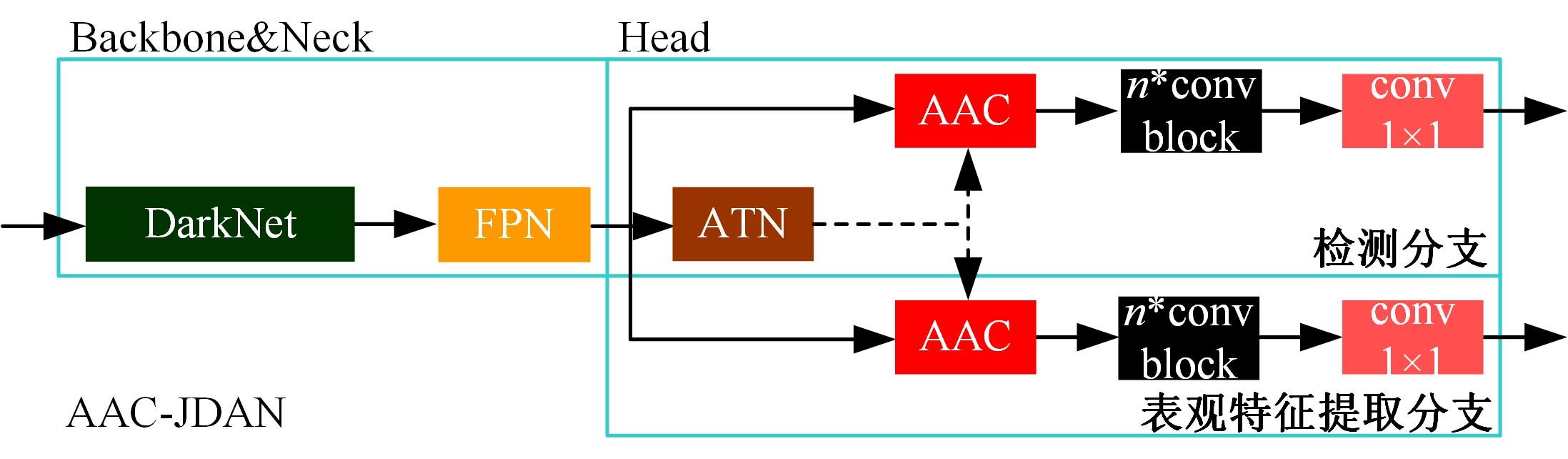
为提高多目标跟踪方法的跟踪效率,提出一种基于锚框对齐卷积特征的目标检测-表观特征提取联合网络(AAC-JDAN)。首先,在YOLOv3目标检测网络的基础上,引入锚框变换网络与锚框对齐卷积,使网络在获得旋转目标检测能力的同时,缓解现有方法中存在的检测-表观联合网络提取的表观特征与旋转目标之间关联性弱的问题;其次,通过在检测头部网络中加入目标表观特征提取分支,以多任务联合学习的方式对目标检测和目标表观特征提取两个子任务进行合并,实现对图像底层特征的共享,在检测目标的同时输出目标对应的表观特征向量,提高跟踪算法的整体效率;最后,提出一种快速的在线数据关联方法,结合AAC-JDAN获取的目标表观特征和卡尔曼滤波得到的目标运动状态预测结果,计算目标与轨迹段间的相似度矩阵并使用KM(Kuhn-Munkres)算法进行匹配,实现对视频中多个旋转目标的高效跟踪。在两个公共数据集和一个自定义数据集上进行实验,TPR指标、MOTA指标和IDF-1指标分别达到了80.4%、71.3%和69.5%,帧速率达到20 帧/s,表明本文方法在跟踪的实时性和准确性上达到了更好的平衡。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Brown M, Funke J, Erlien S, et al. Safe driving envelopes for path tracking in autonomous vehicles[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2017, 61: 307-316. |
| 2 | Tian B, Yao Q, Gu Y, et al. Video processing techniques for traffic flow monitoring: a survey[C]∥The 14th International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Washington DC,USA,2011: 1103-1108. |
| 3 | Sivanantham S, Paul N N, Iyer R S. Object tracking algorithm implementation for security applications[J]. Far East Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2016, 16(1): 1-13. |
| 4 | Onate J M B, Chipantasi D J M, Erazo Nd R V. Tracking objects using artificial neural networks and wireless connection for robotics[J]. Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering, 2017, 9(1/3): 161-164. |
| 5 | Aggarwal J K, Xia L. Human activity recognition from 3d data: a review[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2014, 48: 70-80. |
| 6 | Pfister T, Charles J, Zisserman A. Flowing ConvNets for human pose estimation in videos[C]∥IEEE International Conference of Computer Vision, Santiago,Chile, 2015: 1913-1921. |
| 7 | Choi W, Savarese S. A unified framework for multi-target tracking and collective activity recognition[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision,Florence, Italy, 2012: 215-230. |
| 8 | Hu W, Tan T, Wang L, et al. A survey on visual surveillance of object motion and behaviors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 2004, 34(3): 334-352. |
| 9 | Ciaparrone G, Sánchez F L, Tabik S, et al. Deep learning in video multi-object tracking: a survey[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 381: 61-88. |
| 10 | Yu F, Li W, Li Q, et al. POI: multiple object tracking with high performance detection and appearance feature[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 36-42. |
| 11 | Fang K, Xiang Y, Li X, et al. Recurrent autoregressive networks for online multi-object tracking[C]∥IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision,Santa Rosa, USA, 2017: 466-475. |
| 12 | Zhou Z, Xing J, Zhang M, et al. Online Multi-target tracking with tensor-based high-order graph matching[C]∥The 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Beijing, China, 2018: 1809-1814. |
| 13 | Mahmoudi N, Ahadi S M, Rahmati M. Multi-target tracking using CNN-based features: CNNMTT[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78(6): 7077-7096. |
| 14 | Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. |
| 15 | Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision,Amsterdam, Netherlands,2016: 21-37. |
| 16 | Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: an incremental improvement[J/OL].[2018-04-21]. arXiv preprint arXiv:. |
| 17 | Voigtlaender P, Krause M, Osep A, et al. MOTS: multi-object tracking and segmentation[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Angeles, USA, 2019: 7934-7943. |
| 18 | Wang Z, Zheng L, Liu Y, et al. Towards real-time multi-object tracking[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Online, 2020: 107-122. |
| 19 | Zhang Y, Wang C, Wang X, et al. FairMOT: on the fairness of detection and re-identification in multiple object tracking[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 129: 3069-3087. |
| 20 | Arulampalam M S, Maskell S, Gordon N, et al. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2002, 50(2): 174-188. |
| 21 | Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P. Kernel-based object tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(5): 564-577. |
| 22 | Magee D R. Tracking multiple vehicles using foreground, background and motion models[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2004, 22(2): 143-155. |
| 23 | Indu S, Gupta M, Bhattacharyya A. Vehicle tracking and speed estimation using optical flow method[J]. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2011, 3(1): 429-434. |
| 24 | Niknejad H T, Takeuchi A, Mita S, et al. On-road multivehicle tracking using deformable object model and particle filter with improved likelihood estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(2): 748-758. |
| 25 | 王林, 胥中南.改进的KCF算法在车辆跟踪中的应用[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2019, 27(7): 195-199. |
| Wang Lin, Xu Zhong-nan. Application of improved KCF algorithm in vehicle tracking[J]. Computer Measurement and Control, 2019, 27(7): 195-199. | |
| 26 | Yang X, Yang J, Yan J, et al. SCRDet: Towards More Robust Detection for Small, Cluttered and Rotated Objects[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 8231-8240. |
| 27 | Yang X, Sun H, Fu K, et al. Automatic ship detection of remote sensing images from google earth in complex scenes based on multi-scale rotation dense feature pyramid networks[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(1): 132. |
| 28 | Sohn K. Improved deep metric learning with multi-class N-pair loss objective[C]∥Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems,Honolulu, USA, 2016: 1857-1865. |
| 29 | Kumbasar T. Revisiting KM algorithms: a linear programming approach[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems,Zhangjiajie, China,2015:1-6. |
| 30 | Fan H, Du D, Wen L, et al. VisDrone-MOT2020: the vision meets drone multiple object tracking challenge results[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Online, 2020: 713-727. |
| 31 | Yu H, Li G, Zhang W, et al. The unmanned aerial vehicle benchmark: object detection, tracking and baseline[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(5): 1141-1159. |
| 32 | Bernardin K, Stiefelhagen R. Evaluating multiple object tracking performance: the CLEAR MOT metrics[J]. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing, 2008: No.246309. |
| 33 | Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, et al. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 17-35. |
| 34 | Wojke N, Bewley A, Paulus D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Image Processing,Beijing, China, 2017: 3645-3649. |
| 35 | Yu F, Li W, Li Q, et al. POI: multiple object tracking with high performance detection and appearance feature[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 36-42. |
| [1] | 霍光,林大为,刘元宁,朱晓冬,袁梦,盖迪. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的轻量级虹膜分割模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [2] | 何颖,王卓然,周旭,刘衍珩. 融合社交地理信息加权矩阵分解的兴趣点推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2632-2639. |
| [3] | 张云佐,董旭,蔡昭权. 拟合下肢几何特征的多视角步态周期检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2611-2619. |
| [4] | 肖明尧,李雄飞,朱芮. 基于NSST域像素相关分析的医学图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2640-2648. |
| [5] | 赵亚慧,李飞雨,崔荣一,金国哲,张振国,李德,金小峰. 基于跨语言预训练模型的朝汉翻译质量评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [6] | 金小俊,孙艳霞,于佳琳,陈勇. 基于深度学习与图像处理的蔬菜苗期杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2421-2429. |
| [7] | 车翔玖,徐欢,潘明阳,刘全乐. 生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [8] | 耿庆田,刘植,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [9] | 王连明,吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [10] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [11] | 刘培勇,董洁,谢罗峰,朱杨洋,殷国富. 基于多支路卷积神经网络的磁瓦表面缺陷检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1449-1457. |
| [12] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [13] | 张则强,梁巍,谢梦柯,郑红斌. 混流双边拆卸线平衡问题的精英差分进化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1297-1304. |
| [14] | 于鹏,朴燕. 基于多尺度特征的行人重识别属性提取新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1155-1162. |
| [15] | 吴飞,农皓业,马晨浩. 基于粒子群优化算法⁃长短时记忆模型的刀具磨损预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 989-997. |
|
||