吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (7): 2049-2056.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221141
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于循环结构的视觉Transformer
蒋磊1( ),王子其1,崔振宇2,常志勇3,4,时小虎5,6(
),王子其1,崔振宇2,常志勇3,4,时小虎5,6( )
)
- 1.莫斯科国立大学 数学力学系,莫斯科 119991
2.莫斯科国立大学 计算数学与控制理论系,莫斯科 119991
3.吉林大学 生物与农业工程学院 长春 130022
4.吉林大学 工程仿生教育部重点实验室 长春 130022
5.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
6.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
Visual Transformer based on a recurrent structure
Lei JIANG1( ),Zi-qi WANG1,Zhen-yu CUI2,Zhi-yong CHANG3,4,Xiao-hu SHI5,6(
),Zi-qi WANG1,Zhen-yu CUI2,Zhi-yong CHANG3,4,Xiao-hu SHI5,6( )
)
- 1.Faculty of Mechanics and Mathematics,Moscow State University,Moscow 119991,Russia
2.Faculty of Computational Mathematics and Cybernetics,Moscow State University,Moscow 119991,Russia
3.College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
4.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
5.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
6.Key Laboratory of Symbol Computation and Knowledge Engineering of the Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
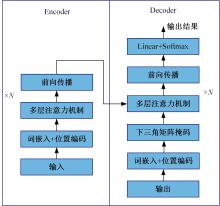
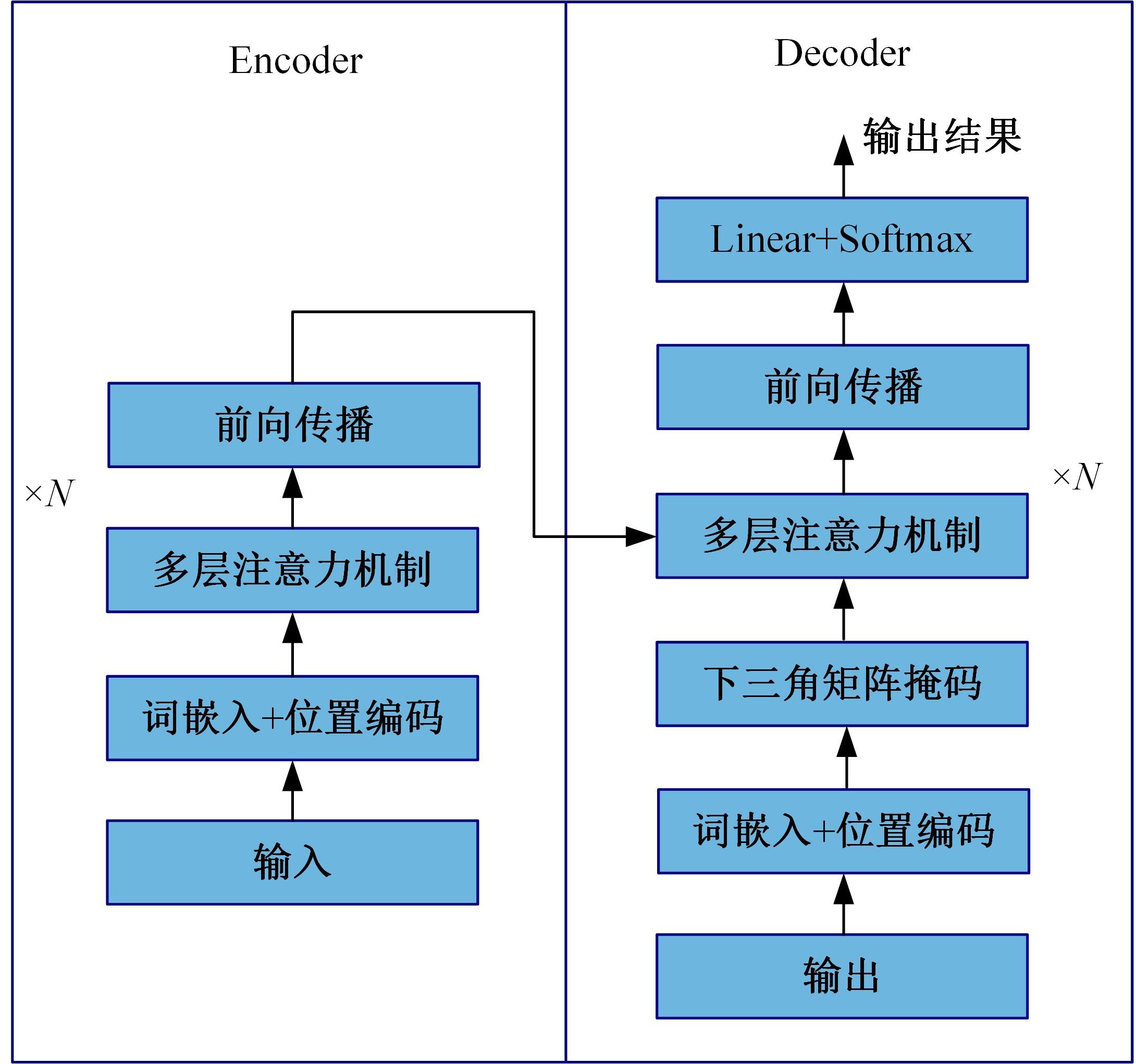
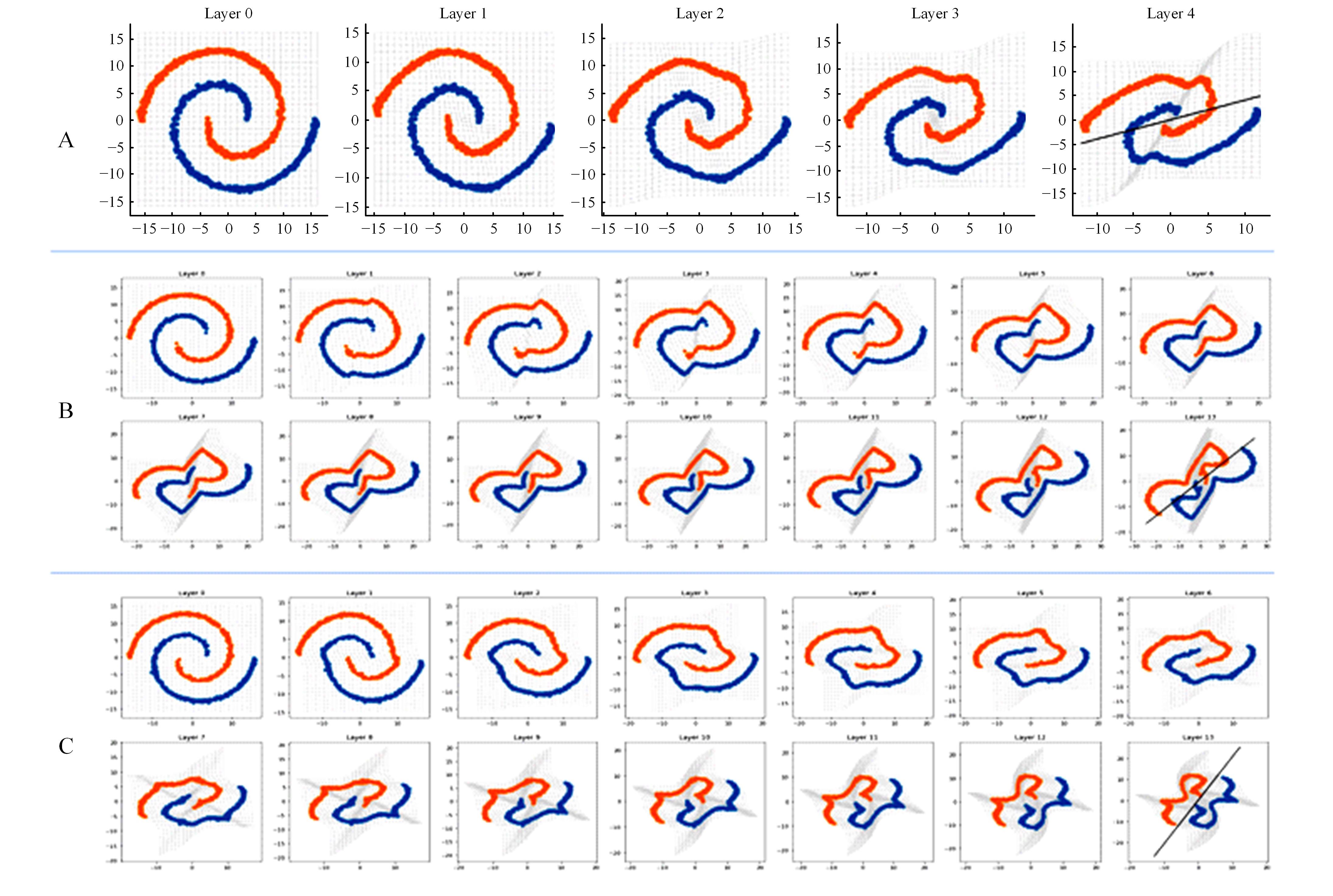
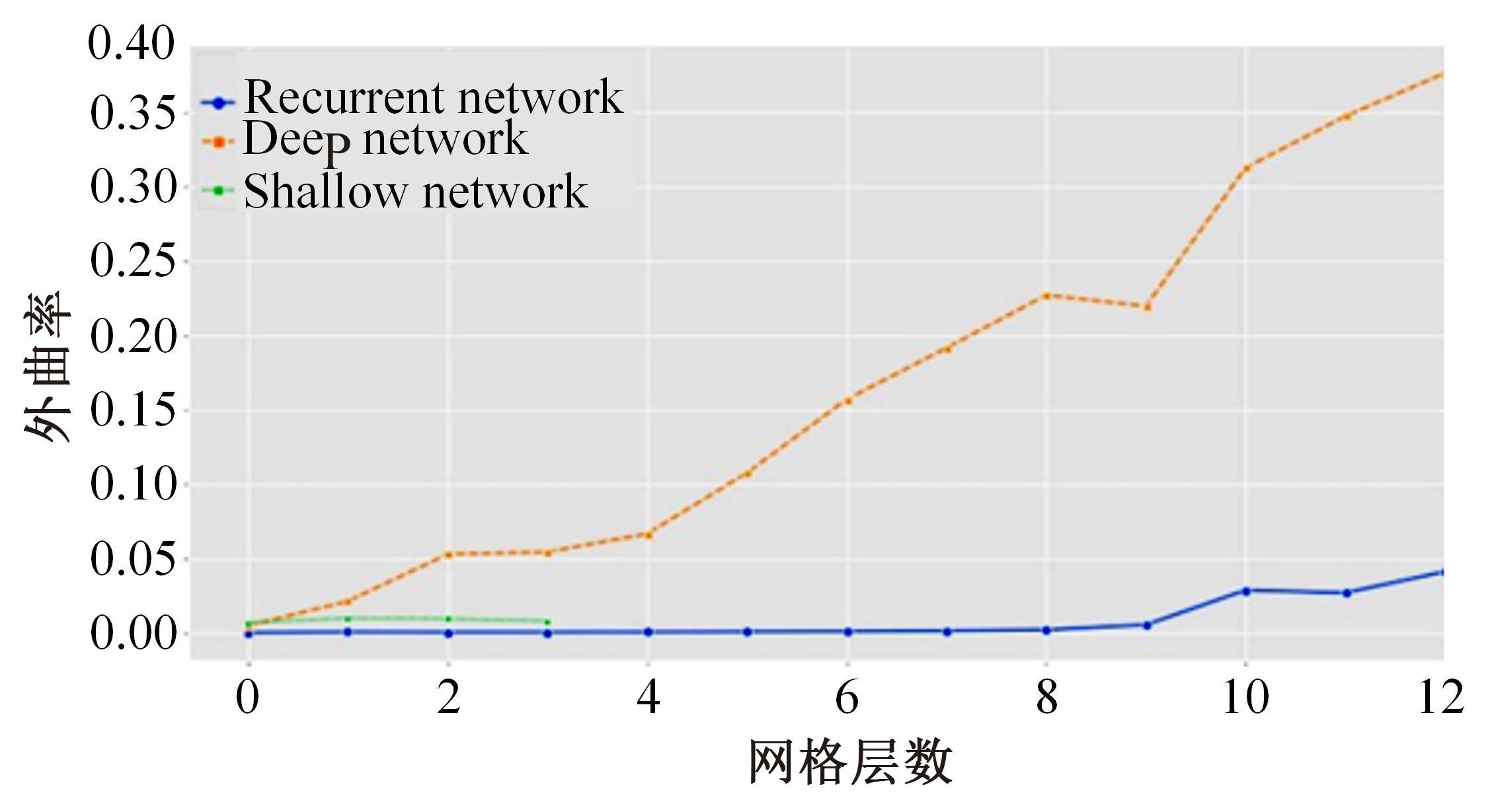
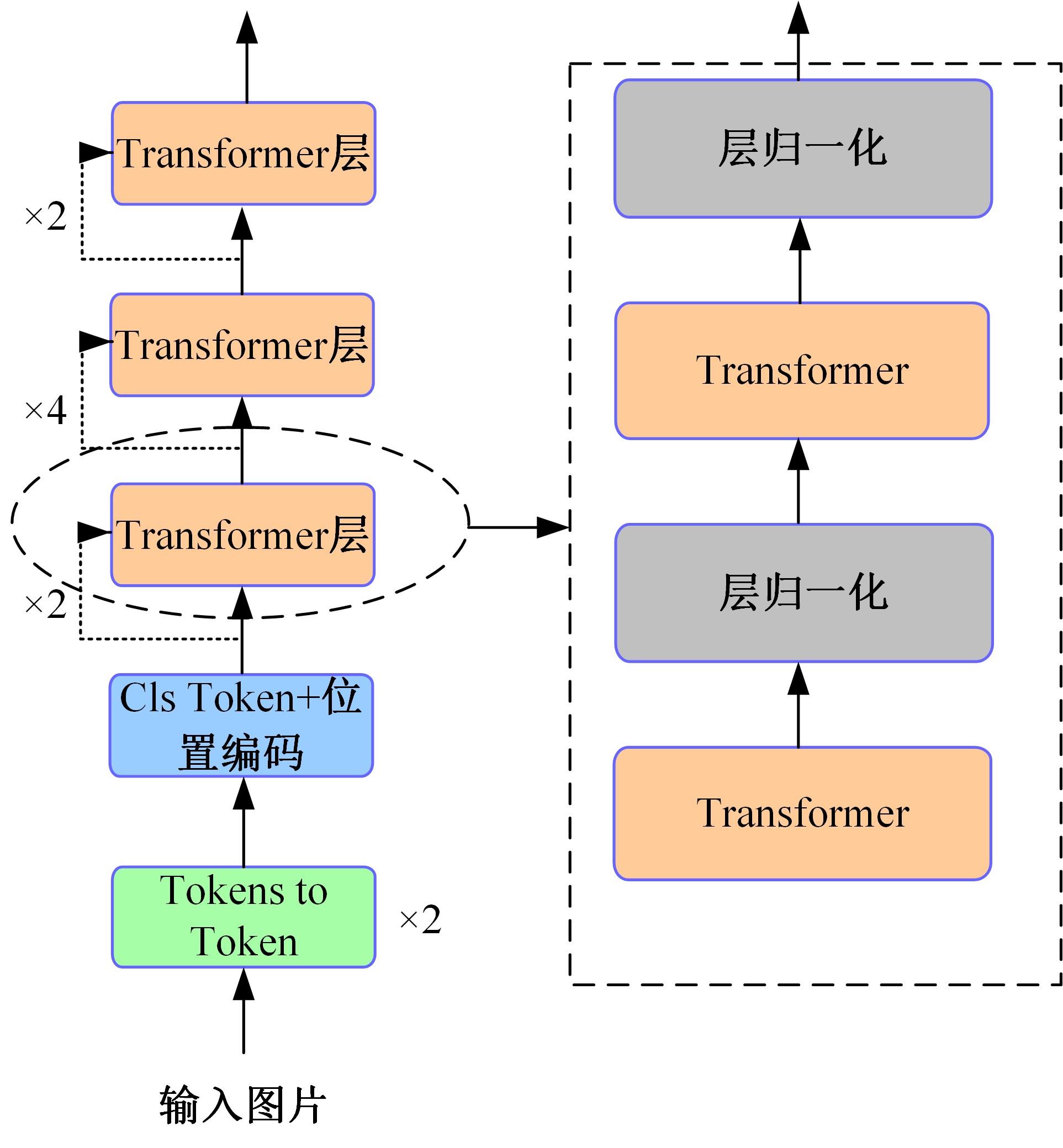
针对视觉Transformer(Vision Transformer,ViT)性能的提升依赖于网络的参数量,从而导致其应用场景受限的缺点,本文从神经学得到启发,创新性地提出将人脑神经元之间的循环结构应用在ViT上。文中首次从黎曼几何的角度解释了循环结构生效的工作原理,之后以Token-to-Token Transformer(T2T Transformer)为主干框架提出了基于循环结构的ViT。实验结果表明:循环结构的引入能在视觉Transformer参数量基本不变化的情况下大幅提高其性能,使用循环结构后,在Imagenet分类数据集下网络仅增加0.14%的参数,但带来9%的分类精度提升;在目标检测任务中,增加0.1%的参数带来10.7%的性能提升。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N,et al. Attention is all you need[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 2 | Radford A, Kim J W, Hallacy C,et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10].. |
| 3 | Ramesh A, Pavlov M, Goh G,et al. Zero-shot text-to-image generation[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 4 | Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y,et al. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 5 | Yuan L, Chen Y, Wang T,et al. Tokens-to-token vit: training vision transformers from scratch on ImageNet[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 6 | He K, Chen X, Xie S,et al. Masked autoencoders are scalable vision learners[C]∥ Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA,2022:16000-16009. |
| 7 | Lee-Thorp J, Ainslie J, Eckstein I,et al. FNet: mixing tokens with Fourier transforms[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 8 | Child R, Gray S, Radford A,et al. Generating long sequences with sparse transformers[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 9 | Han S, Pool J, Tran J,et al. Learning both weights and connections for efficient neural networks[C]∥ Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015:1135-1143. |
| 10 | Yang H, Yin H, Molchanov P,et al. NViT: vision transformer compression and parameter redistribution[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 11 | Nagel M, Fournarakis M, Amjad R A,et al. A white paper on neural network quantization[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 12 | Mehta S, Rastegari M. MobileViT: light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 13 | Callaway, Edward M. Feedforward, feedback and inhibitory connections in primate visual cortex[J]. Neural Networks, 2004, 17(5,6): 625-632. |
| 14 | Briggs F. Role of feedback connections in central visual processing[J]. Annual Review of Vision Science, 2020, 6(1): 313-334. |
| 15 | Kubilius J, Schrimpf M, Nayebi A, et al. Cornet: modeling the neural mechanisms of core object recognition[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 16 | Messina N, Amato G, Carrara F,et al. Recurrent vision transformer for solving visual reasoning problems[DB/OL]. [2022-01-10]. . |
| 17 | Hauser, Michael, Asok R. Principles of riemannian geometry in neural networks[C]∥ Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017:30. |
| 18 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K,et al. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding [DB/OL]. [2022-01-12]. . |
| 19 | Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale[DB/OL]. [2022-01-12]. . |
| 20 | He K M, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| 21 | Balduzzi D, et al. The shattered gradients problem: if resnets are the answer, then what is the question? [C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 342-350. |
| 22 | Tarnowski W, Warcho P, Jastrzbski S,et al. Dynamical isometry is achieved in residual networks in a universal way for any activation function[DB/OL]. [2022-01-12]. . |
| 23 | Zaeemzadeh A, Rahnavard N, Shah M. Norm-preservation: why residual networks can become extremely deep?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 43(11): 3980-3990. |
| 24 | Deng J, Wei D, Richard S,et al. Imagenet: a large-scale hierarchical image database[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248-255. |
| 25 | Loshchilov I, Hutter F. Decoupled weight decay regularization[DB/OL]. [2022-01-12]. . |
| 26 | Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. |
| [1] | 张云佐,郑宇鑫,武存宇,张天. 基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902. |
| [2] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [3] | 李延风,刘名扬,胡嘉明,孙华栋,孟婕妤,王奥颖,张涵玥,杨华民,韩开旭. 基于梯度转移和自编码器的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1777-1787. |
| [4] | 张自超,陈建. 基于双目仿鹰眼视觉与超分辨的果园三维点云重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1469-1481. |
| [5] | 王海涛,刘慧卓,张学永,韦健,郭校源,肖俊哲. 基于单目视觉的车辆屏显式封闭驾驶舱前视视野重现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1435-1442. |
| [6] | 王殿伟,张池,房杰,许志杰. 基于高分辨率孪生网络的无人机目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1426-1434. |
| [7] | 高云龙,任明,吴川,高文. 基于注意力机制改进的无锚框舰船检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [8] | 张西广,张龙飞,马钰锡,樊银亭. 基于密度峰值的海量云数据模糊聚类算法设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1401-1406. |
| [9] | 曲福恒,潘曰涛,杨勇,胡雅婷,宋剑飞,魏成宇. 基于加权空间划分的高效全局K-means聚类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1393-1400. |
| [10] | 王宇,赵凯. 基于亚像素定位的人体姿态热图后处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1385-1392. |
| [11] | 陈涛,周志刚,雷楠南. 粒子群算法下汽车机械式自动变速系统参数多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1214-1220. |
| [12] | 韩绍程,张鹏,刘欢,王博. 基于Tucker分解和双置乱加密的立体图像零水印算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1065-1077. |
| [13] | 李晓旭,安文娟,武继杰,李真,张珂,马占宇. 通道注意力双线性度量网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 524-532. |
| [14] | 李雄飞,宋紫萱,朱芮,张小利. 基于多尺度融合的遥感图像变化检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [15] | 刘浏,丁鲲,刘姗姗,刘茗. 基于机器阅读理解的事件检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 533-539. |
|
||