吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (12): 3478-3485.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230172
斜交T形焊接接头热点应力集中系数
- 1.西南交通大学 土木工程学院,成都 610031
2.中铁第一勘察设计院集团有限公司,西安 710043
Hot spot stress concentration factor for welded skewed-T joints
Xing WEI1( ),Yong-qi ZHANG2,Jun-ming ZHAO1,Hui-jun WANG1,Lin XIAO1(
),Yong-qi ZHANG2,Jun-ming ZHAO1,Hui-jun WANG1,Lin XIAO1( )
)
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610031,China
2.China Railway First Survey and Design Institute Group Ltd. ,Xi'an 710043,China
摘要:
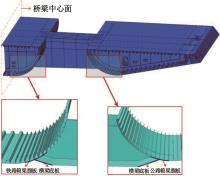
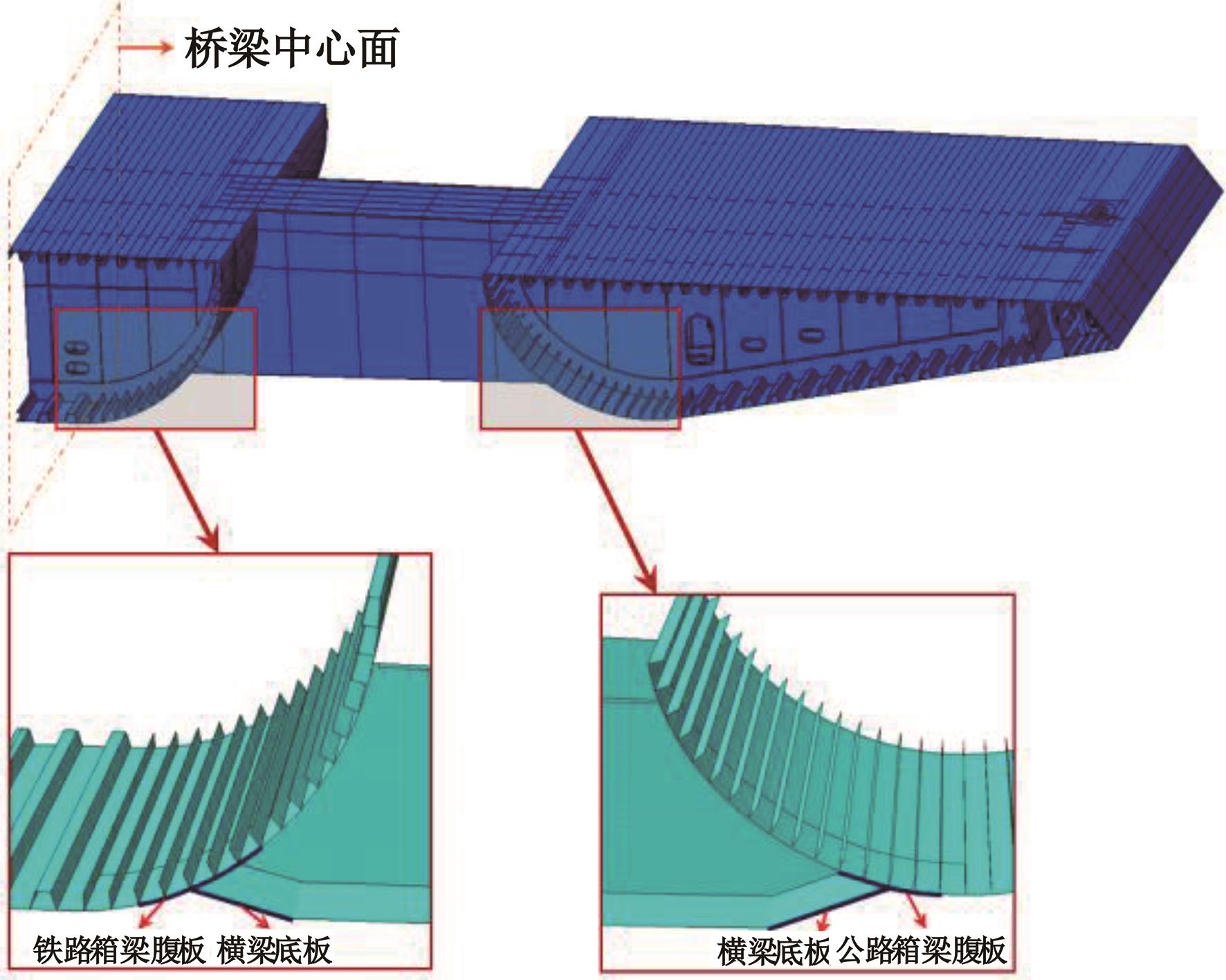
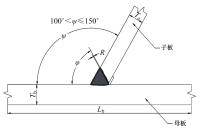
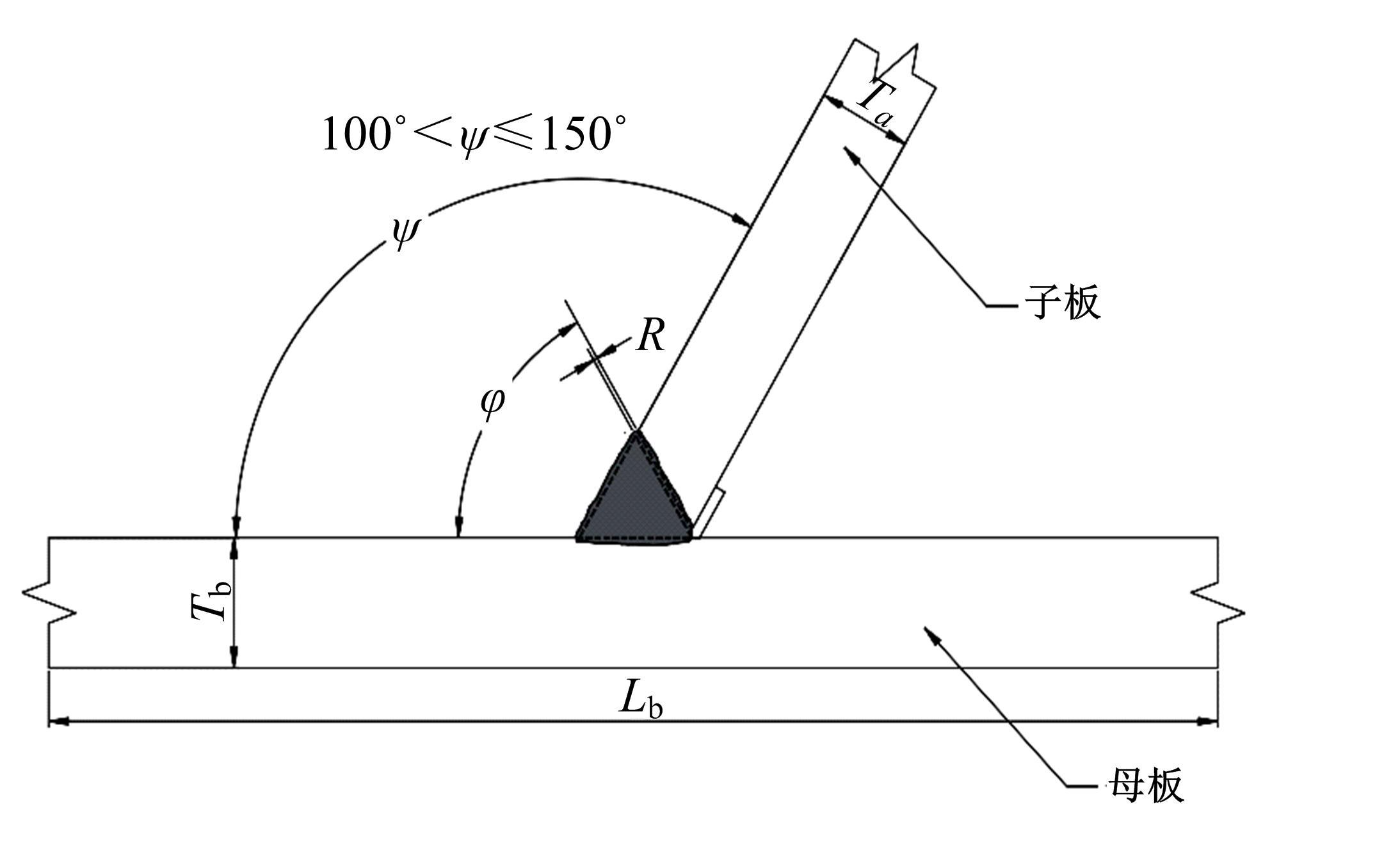
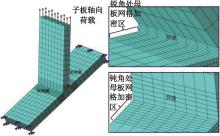
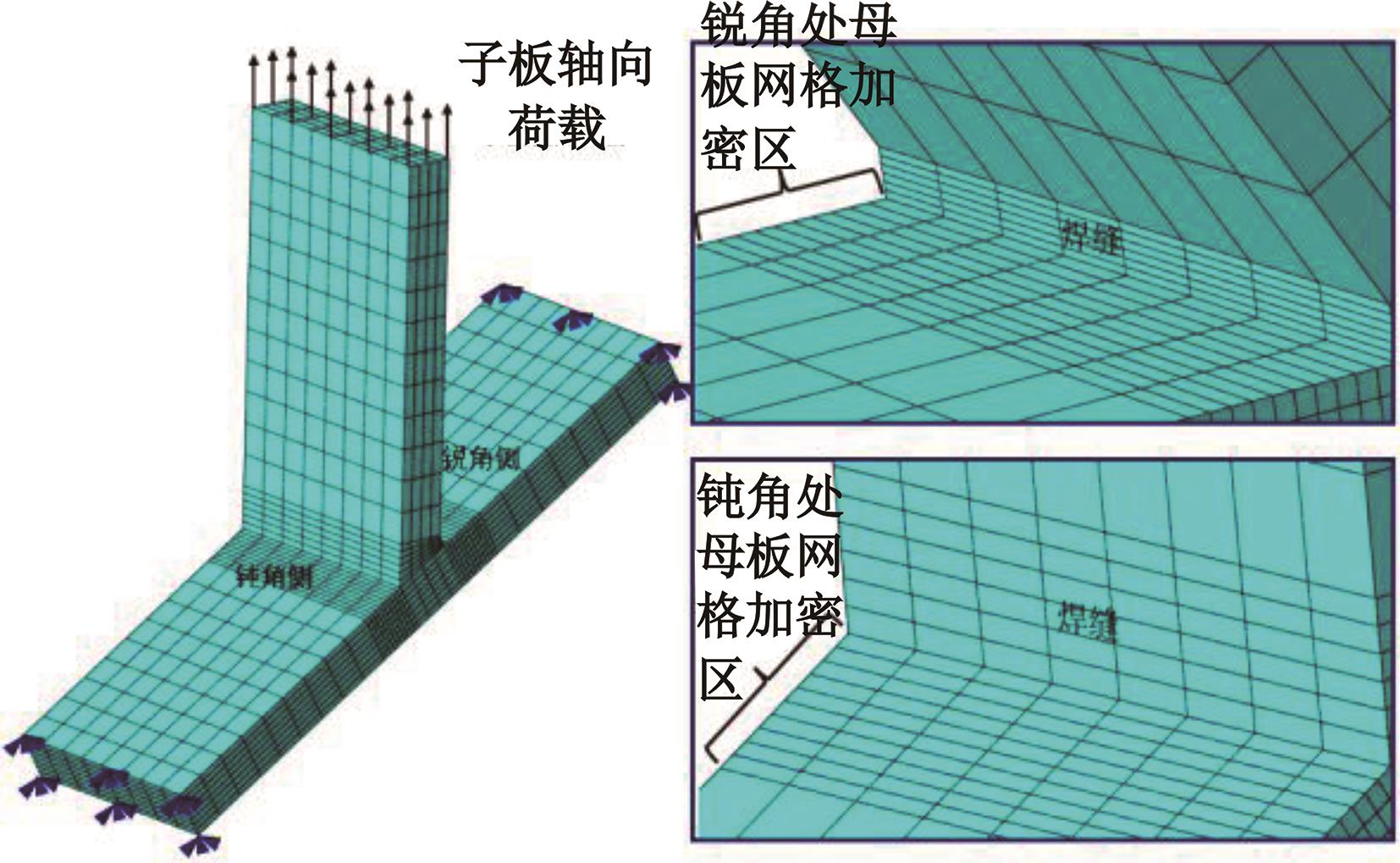
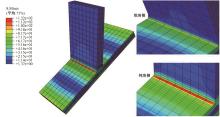
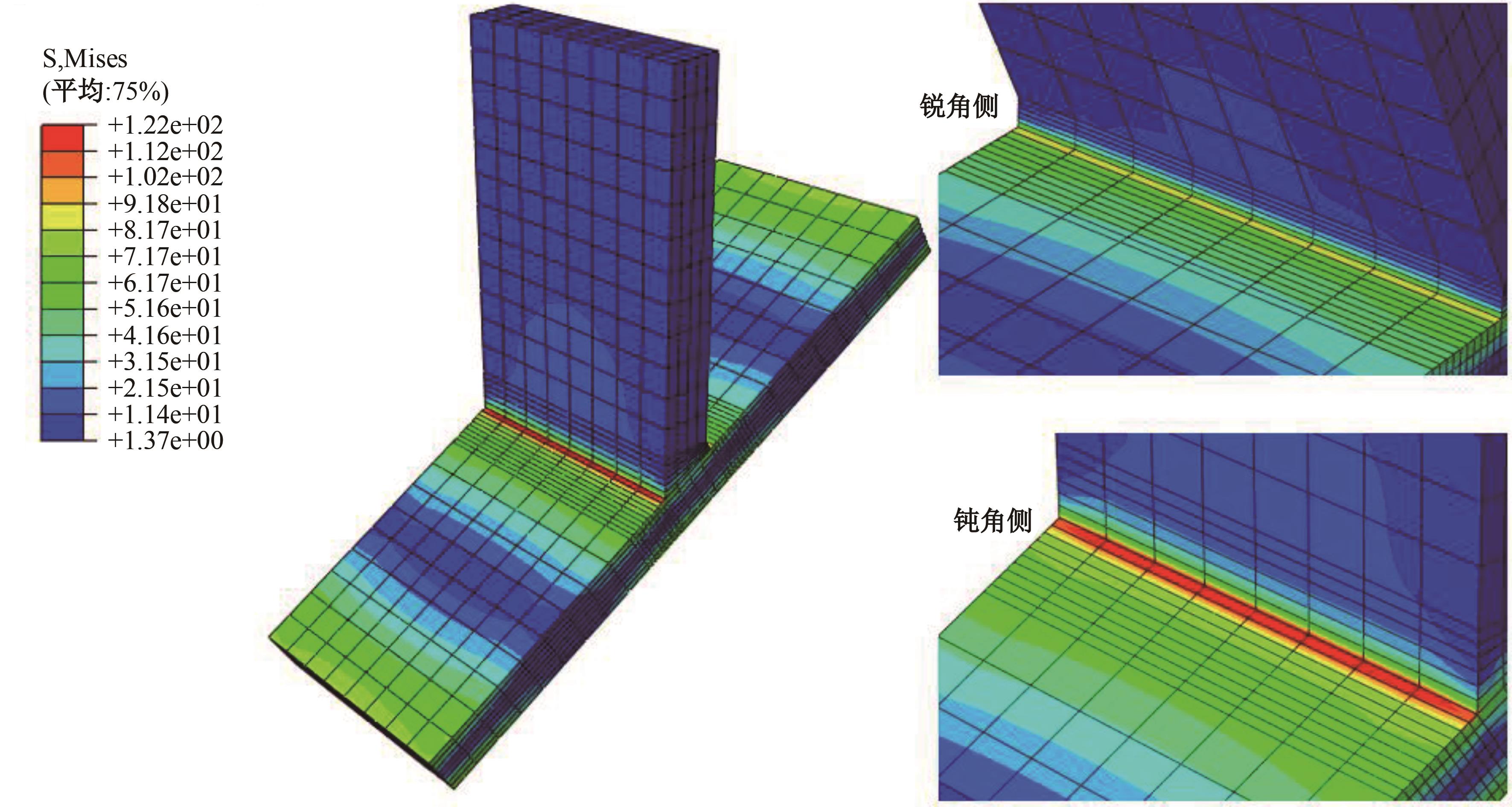
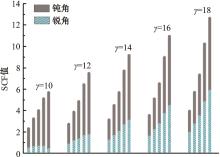
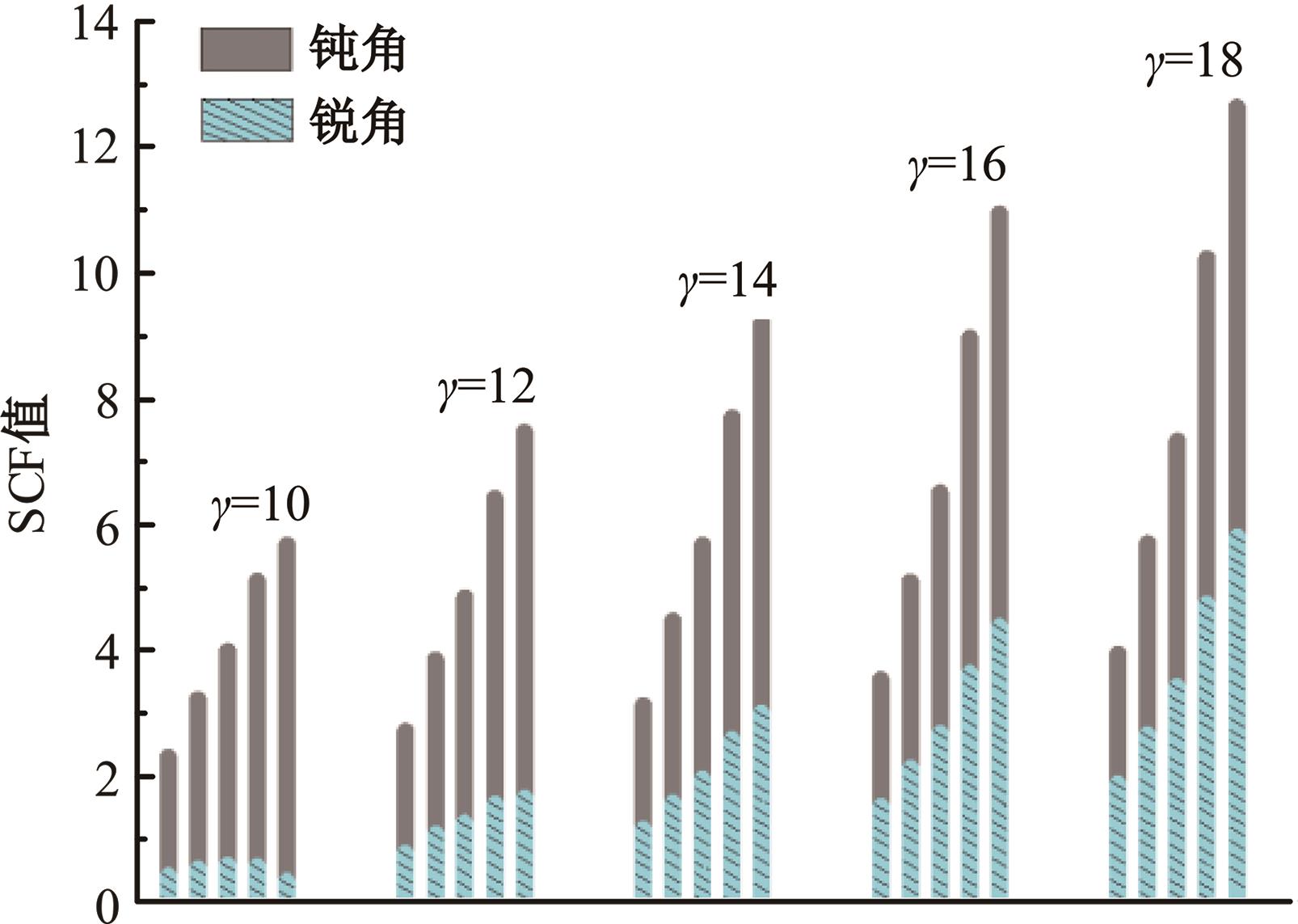
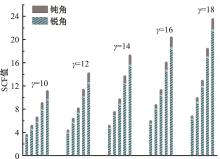
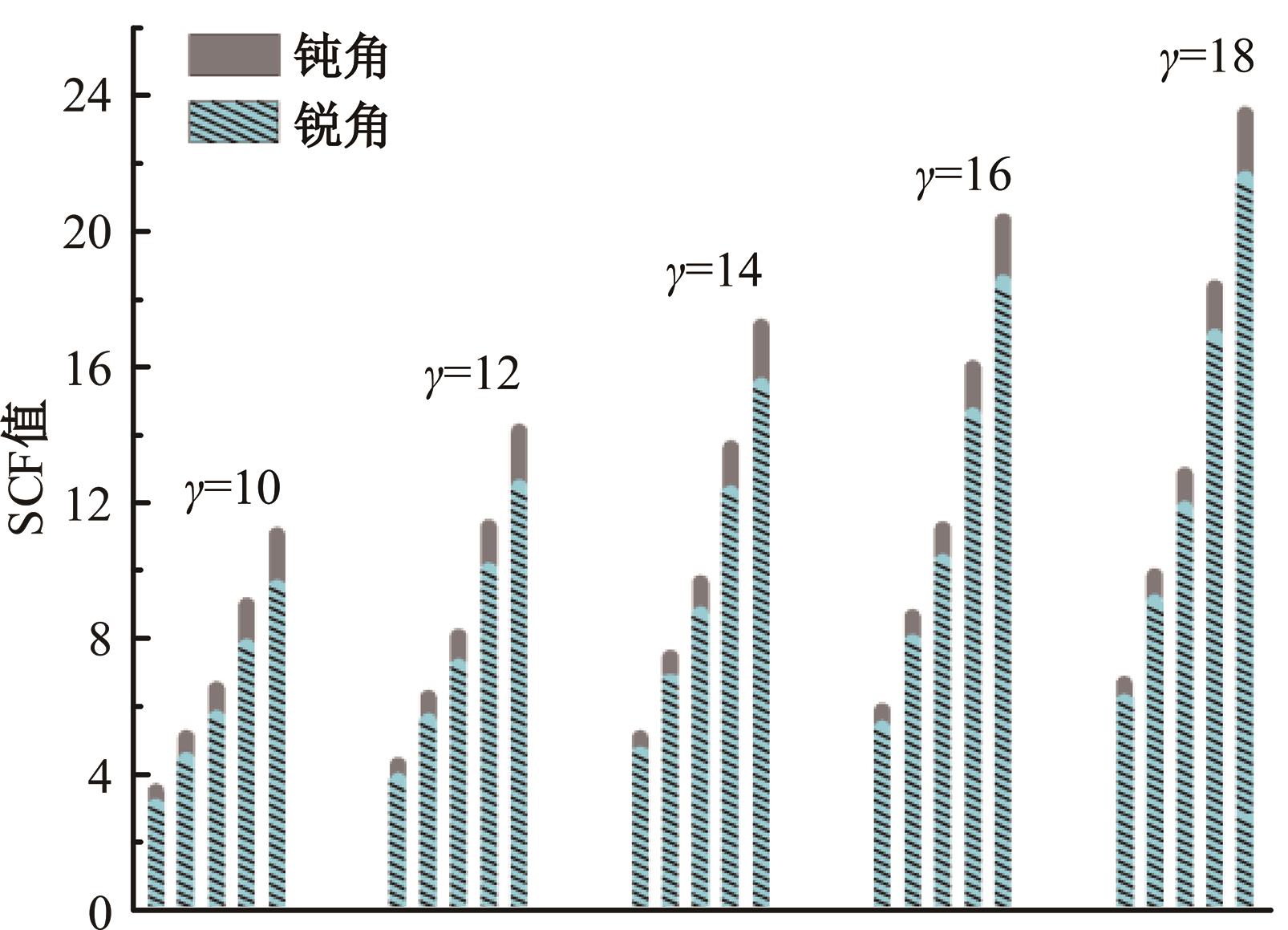
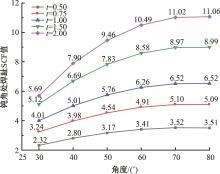
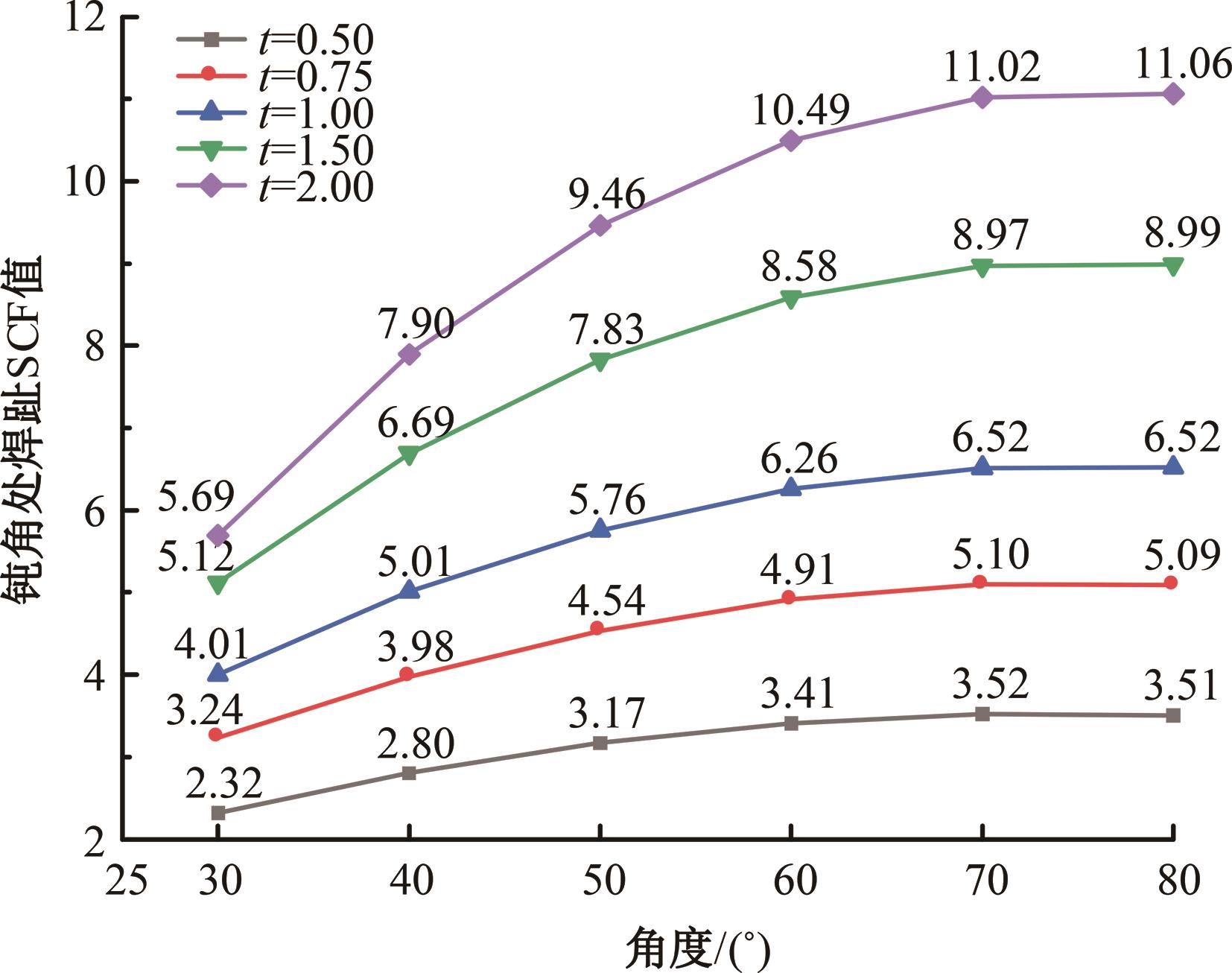
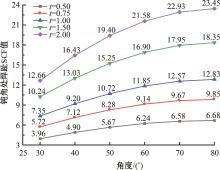
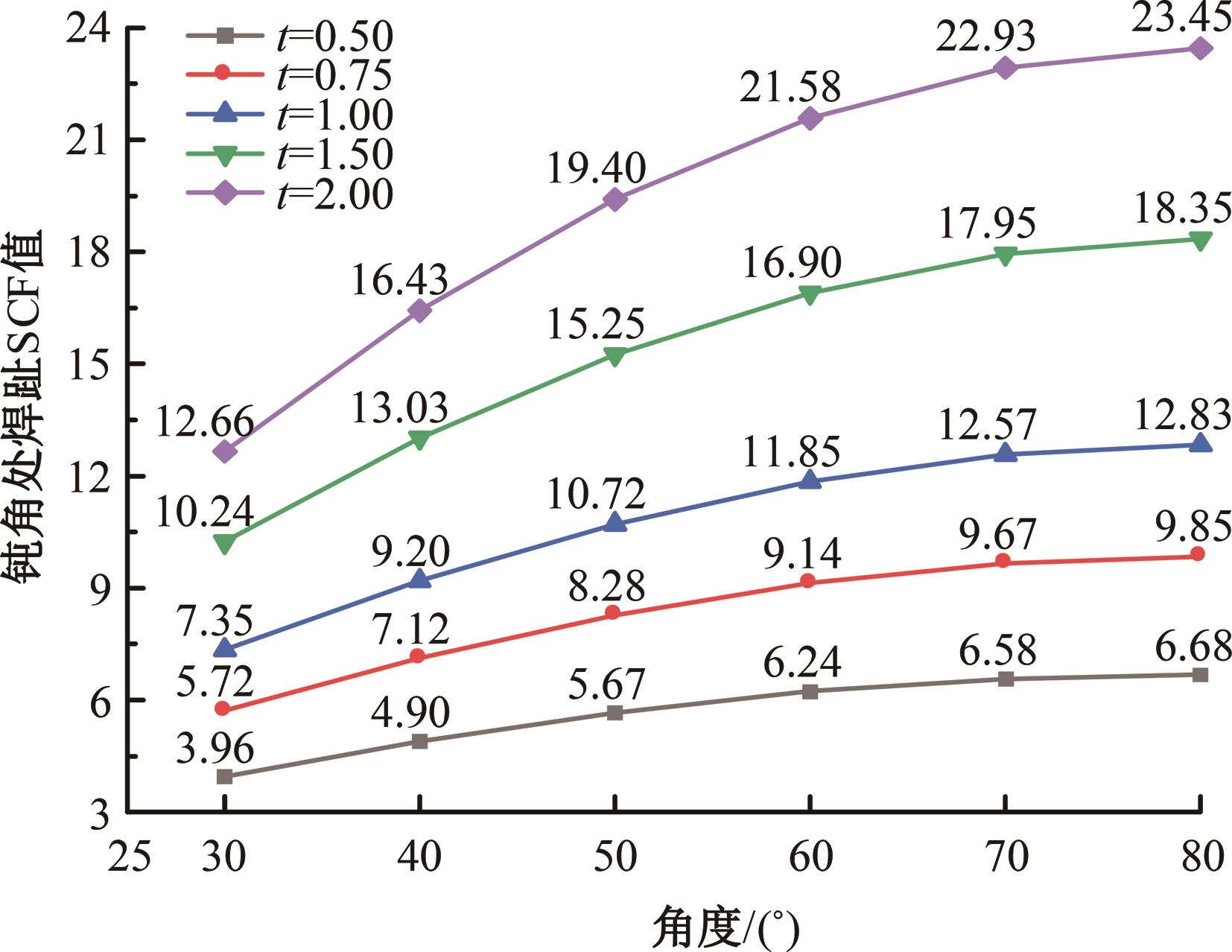
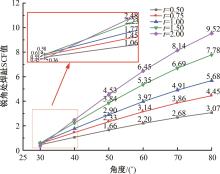
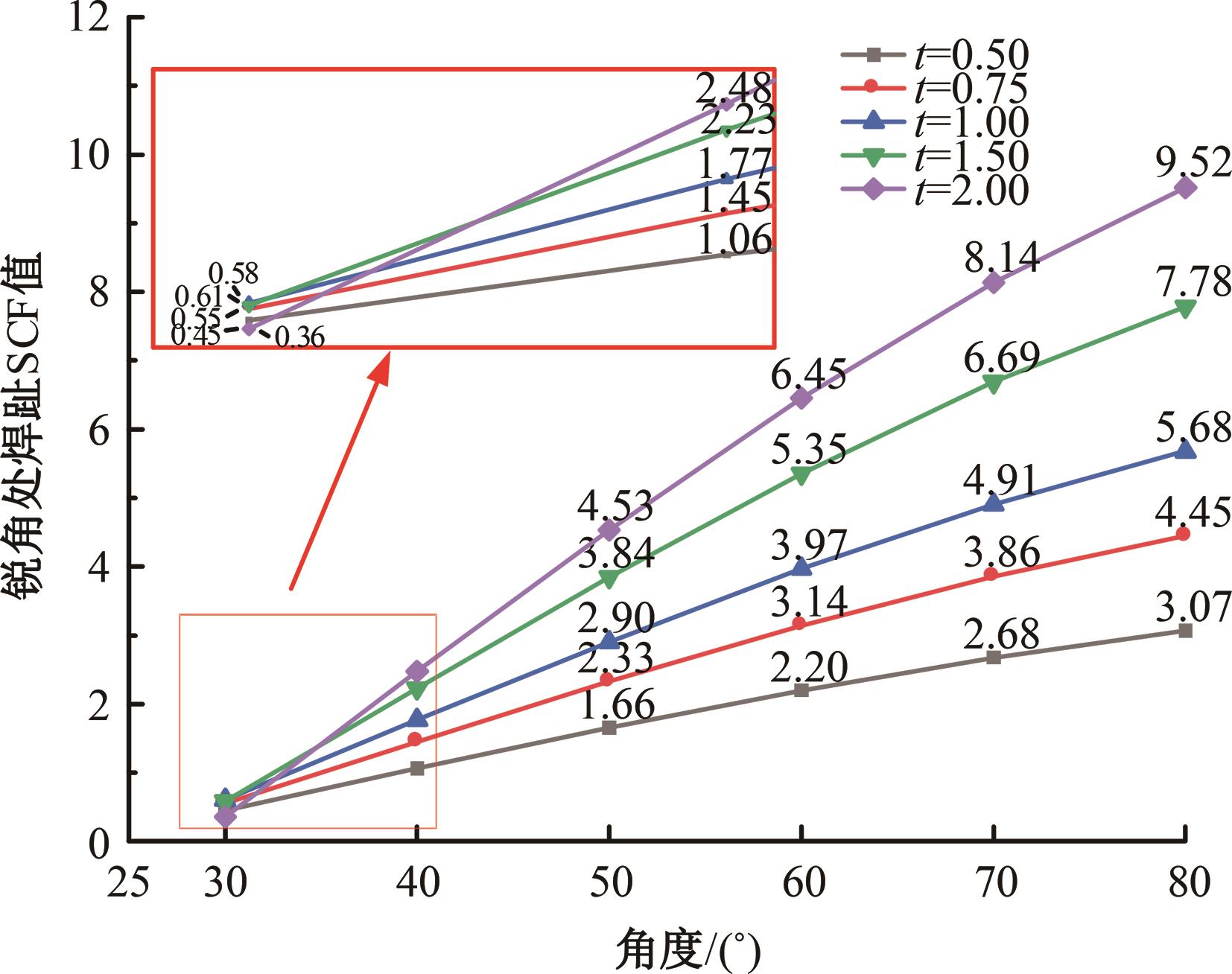
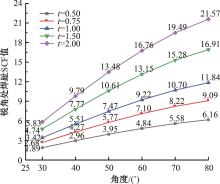
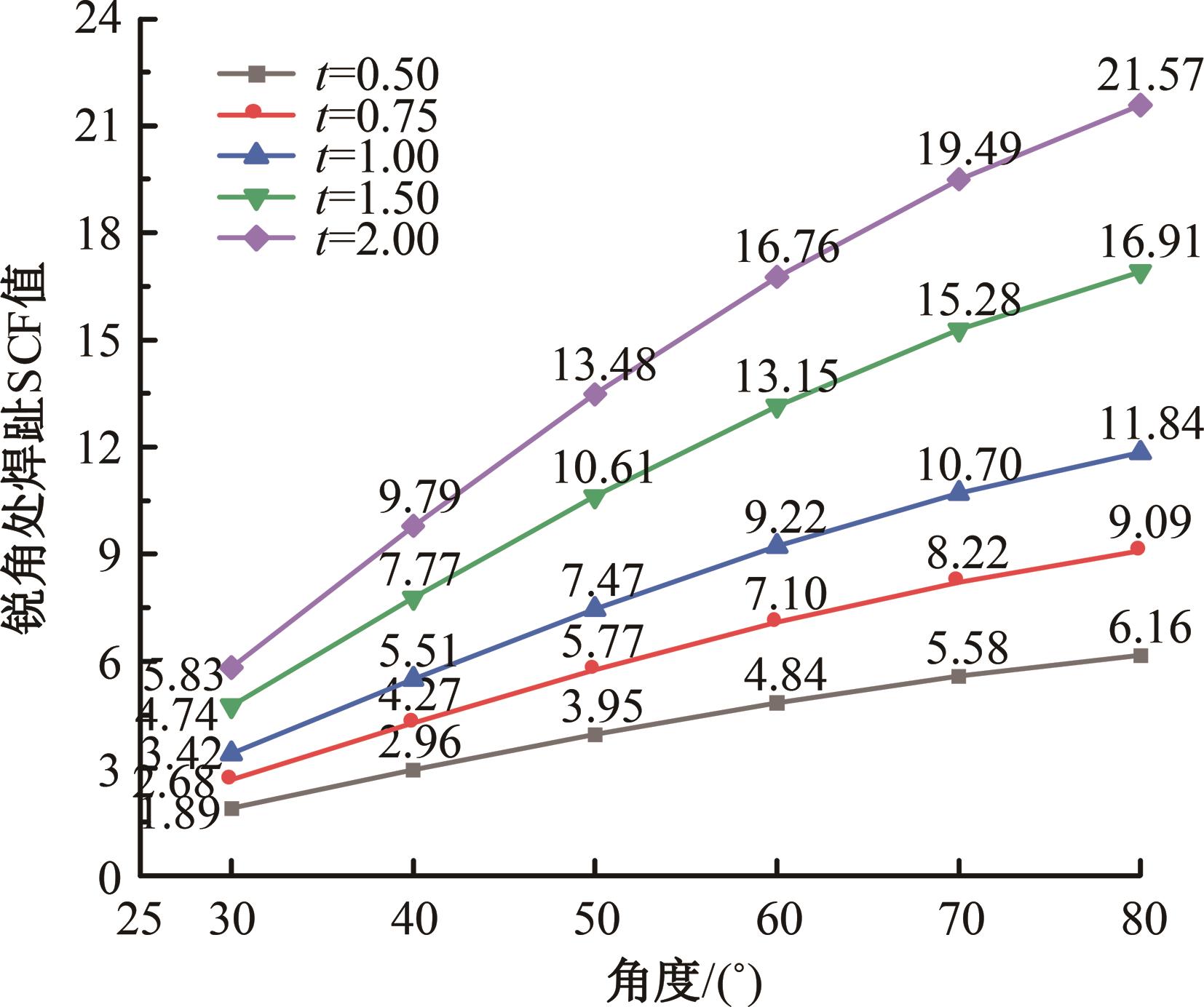
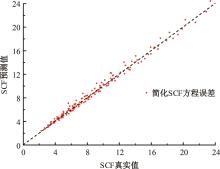
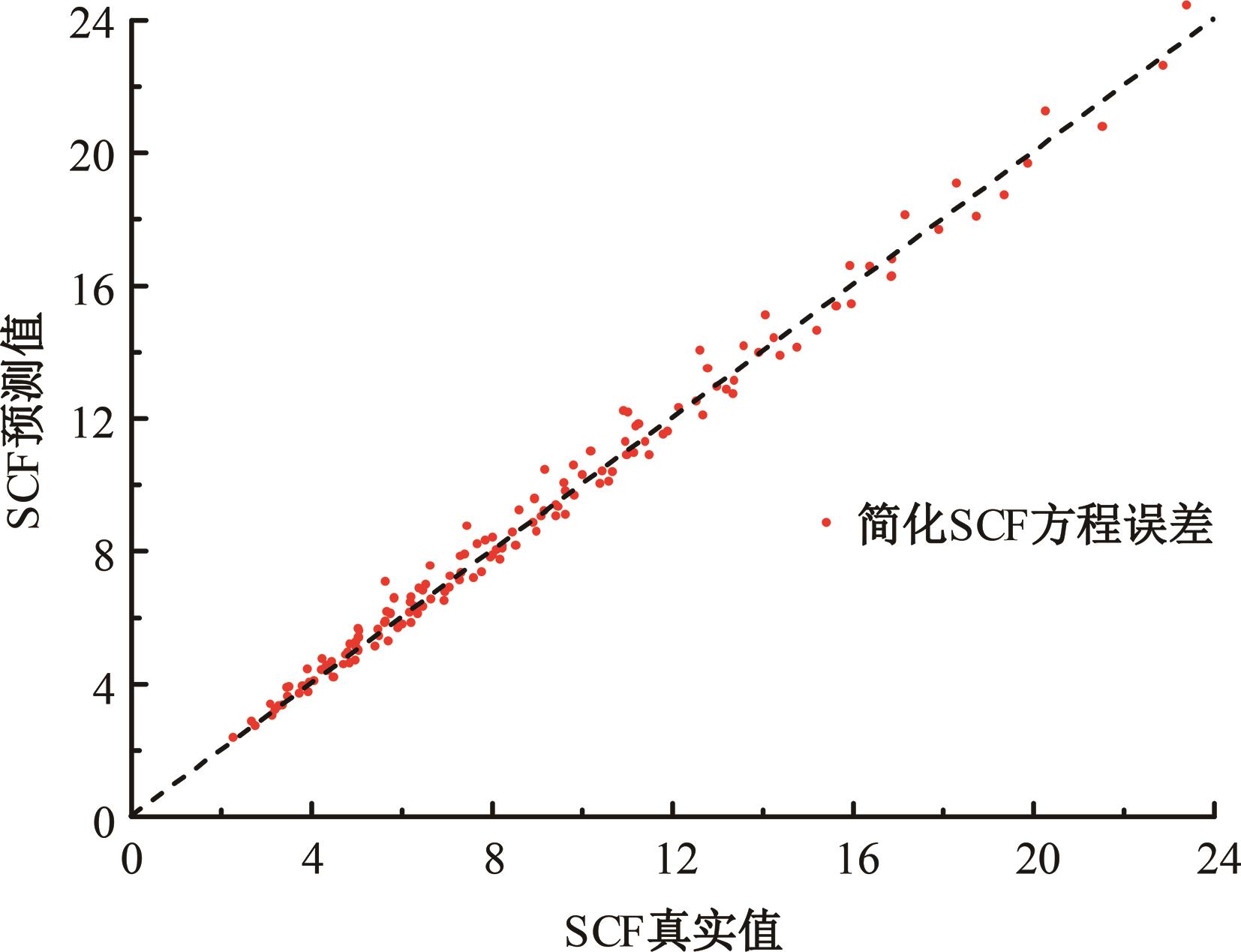
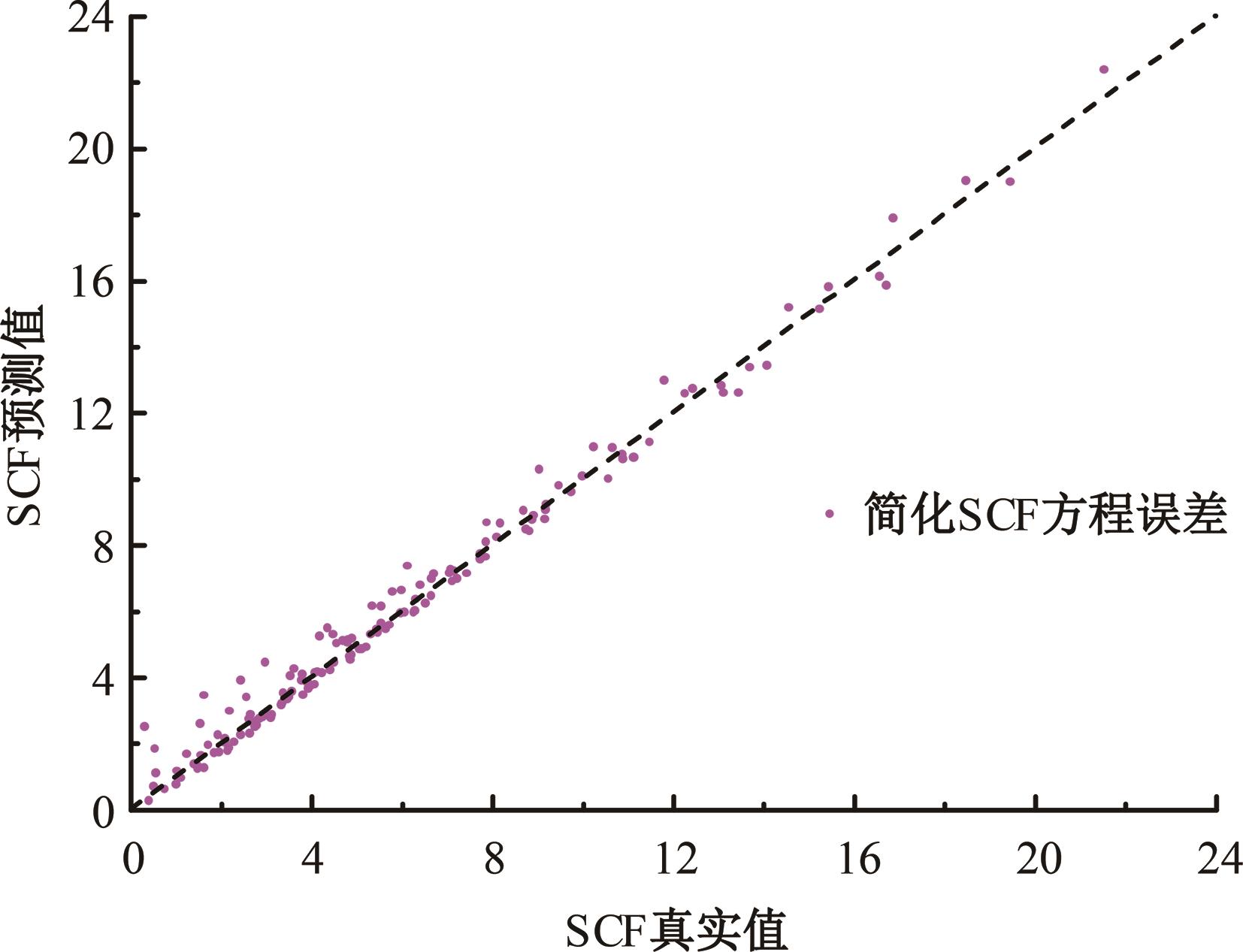
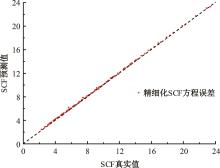
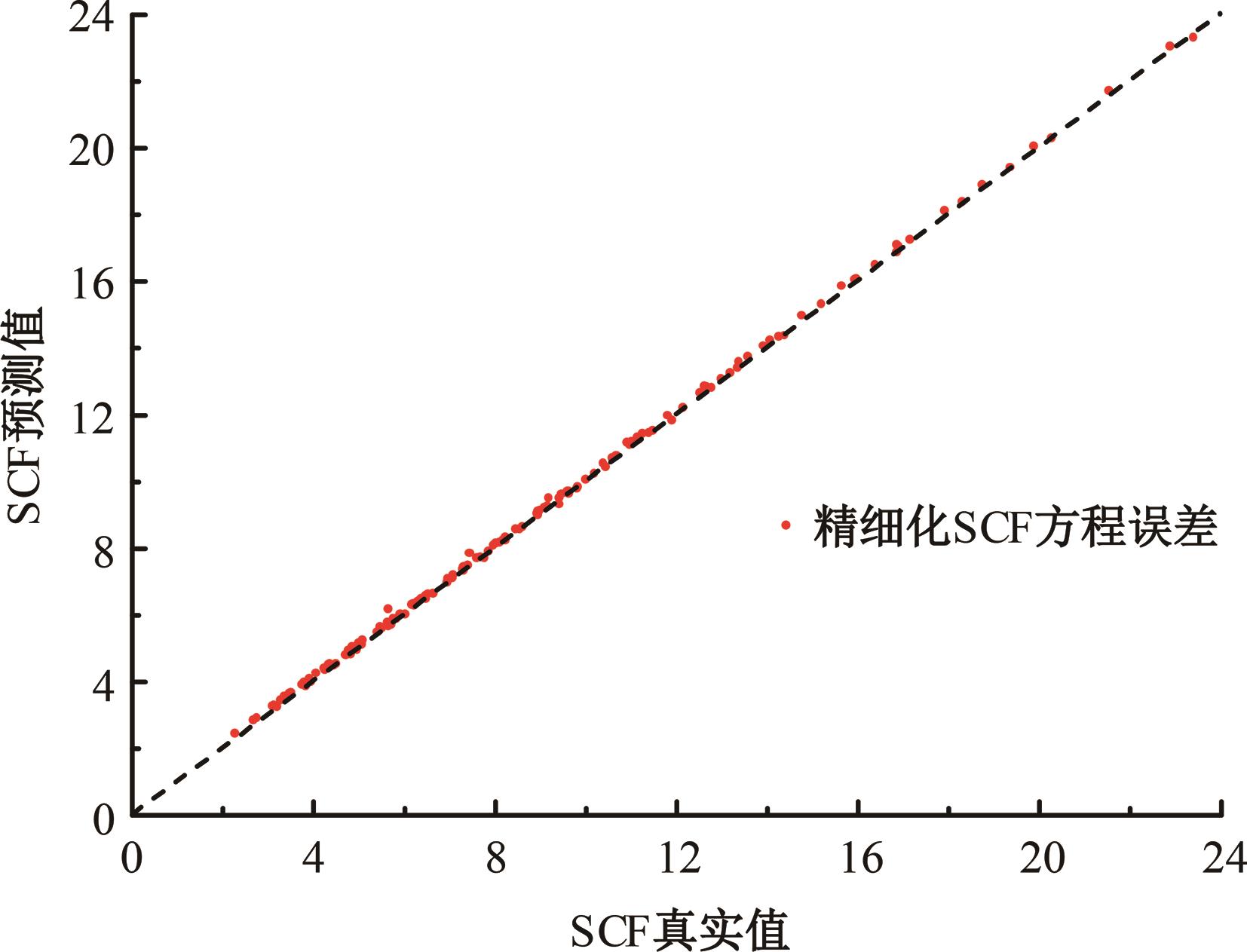
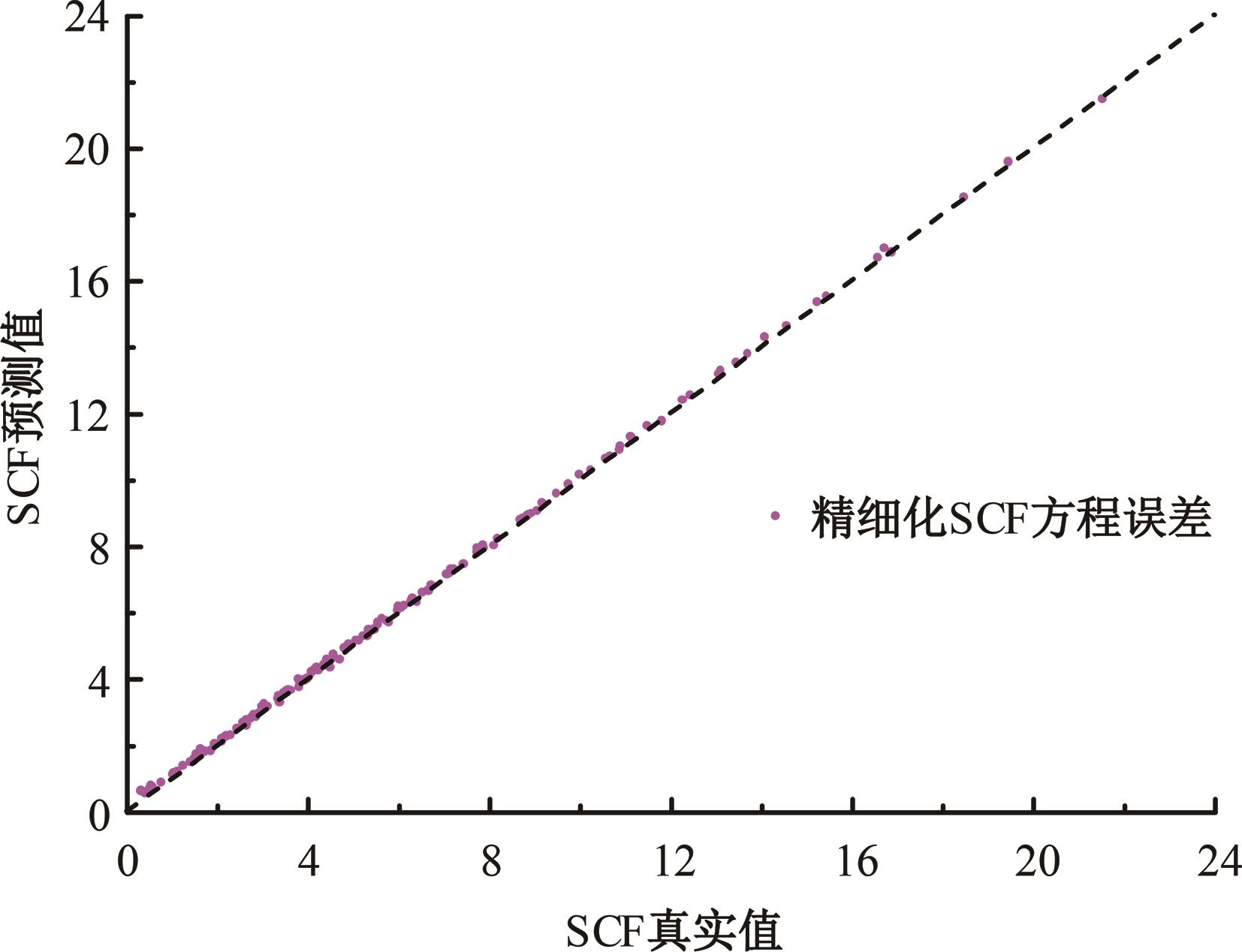
运用ABAQUS有限元软件建立150个不同角度、板厚比、长厚比的斜交T形焊接接头有限元模型,分析得到关键点最大热点应力集中系数。基于麦夸特法+通用全局优化法对数据进行拟合,给出最大热点应力集中系数简化公式和精细化公式。结果表明:钝角侧焊趾热点应力集中系数总是大于锐角侧,当角度差距减小时,两侧热点应力集中系数差值相应减小;斜交T形接头焊趾处热点应力集中系数与角度、板厚比、长厚比均呈正相关关系,角度为80°、板厚比为2、长厚比为18时达到最大值;本文所提出的最大热点应力集中系数计算公式与有限元数值结果吻合较好,精细化公式相关系数R2达到了99.97%。
中图分类号:
- U441.4
| 1 | 郑凯锋,冯霄暘,衡俊霖,等. 钢桥2020年度研究进展[J]. 土木与环境工程学报:中英文,2021,43():53-69. |
| Zheng Kai-feng, Feng Xiao-yang, Heng Jun-lin, et al. State-of-the-art review of steel bridges in 2020[J]. Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2021, 43(Sup.1): 53-69. | |
| 2 | A. Structural welding codesheet steel [S]. |
| 3 | 吴琛泰. 钢管混凝土桁架焊接节点热点应力集中系数研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学土木工程学院,2019. |
| Wu Chen-tai. Study on hot spot stress concentration factor of welded concrete-filled stell tubular truss joints[D].Chengdu: School of Civil Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 4 | Brennan F P, Peleties P, Hellier A K. Predicting weld toe stress concentration factors for T and skewed T-joint plate connections[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2000, 22(7): 573-584. |
| 5 | Dabiri M, Ghafouri M, Raftar H R R, et al. Neural network-based assessment of the stress concentration factor in a T-welded joint[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2017, 128: 567-578. |
| 6 | Terán G, Albiter A, Cuamatzi-Meléndez R. Parametric evaluation of the stress concentration factors in T-butt welded connections[J]. Engineering Structures, 2013, 56: 1484-1495. |
| 7 | Molski K L, Tarasiuk P. Stress concentration factors for welded plate T-Joints subjected to tensile, bending and shearing loads[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(3): 1-22. |
| 8 | 陈团海,陈国明.T型焊接管节点应力集中系数数值分析[J].焊接学报,2010,31(11):45-48, 115. |
| Chen Tuan-hai, Chen Guo-ming. Numerical analysis on stress concentration factors of joints in welded T-tube[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(11): 45-48, 115. | |
| 9 | 陈娟,聂建国,周成野. 钢管混凝土T形相贯节点应力集中系数研究[J].建筑结构学报,2018,39(3): 149-157. |
| Chen Juan, Nie Jian-guo, Zhou Cheng-ye. Study on stress concentration factor of concrete-filled steel tubular T-joints[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2018, 39(3): 149-157. | |
| 10 | 杨德磊,童乐为. 支管受轴向受拉工况下CHS-CFSHS T型节点应力集中系数计算公式[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版,2019,49(6): 1891-1899. |
| Yang De-lei, Tong Le-wei. Calculation formula of SCF for CHS-CFSHS welded T-joints with brace under axial tension[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1891-1899. | |
| 11 | 卫星,赵骏铭,肖林,等. 钢管混凝土桁架焊接型管节点热点应力集中系数研究[J].中国铁道科学,2022,43(2): 1-9. |
| Wei Xing, Zhao Jun-ming, Xiao Lin, et al. Hot spot stress concentration factor of welded tubular T-ointsin concrete-filled steel tube truss[J]. China Railway Science, 2022, 43(2): 1-9. | |
| 12 | 揭志羽,李亚东,卫星,等. 复杂应力场下焊接接头疲劳寿命评估的热点应力法[J].中国公路学报,2017,30(5): 97-103. |
| Zhi-yu Jie, Li Ya-dong, Wei Xing, et al. Hot spot stress method for fatigue life assessment of welded joints under complex stress fields[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(5): 97-103. | |
| 13 | IIW Document IIW-1823-07 ex XIII-2151r4-07/ XV-1254r4-07 recommended fatigue design procedure for welded hollow section joints [S]. |
| 14 | Marquardt D W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters[J]. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1963, 11(2): 431-441. |
| 15 | 李松柏, Stefan Kirchberg,谢磊,等. PP+FeSi复合材料流变性能测试及数值模拟[J].高分子材料科学与工程,2010,26(3): 164-167, 171. |
| Li Song-bai, Stefan Kirchberg, Xie Lei, et al. Rheological Experiment and numerical simulation of PP+FeSi composite materials[J]. Polymeric Materials Science and Engineering, 2010, 26(3): 164-167, 171. | |
| 16 | 范金龙,宋国良,宋维健,等. 内嵌逆流柱型风帽阻力特性冷态试验研究[J].动力工程学报,2015,35(7): 531-536. |
| Fan Jin-long, Song Guo-liang, Song Wei-jian, et al.Experimental study on resistance characteristics ofInternal counterflow wind caps with inner tubes[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2015, 35(7): 531-536. | |
| 17 | 舒志乐,刘保县,黄山,等. 软岩非线性黏弹塑性蠕变模型及参数识别[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2017,34(4): 803-809. |
| Shu Zhi-le, Liu Bao-xian, Huang Shan, et al. Nonlinear viscoelasto-plastic creep model of soft rock and its parameters identification[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2017, 34(4): 803-809. | |
| 18 | 李萍,念腾飞,魏定邦,等. FTIR定量分析方法与老化沥青流变参数新探[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 46(2): 34-39. |
| Li Ping, Teng-fei Nian, Wei Ding-bang, et al. Quantitative analysis method for FTIR and exploration on rheological parameters of aging asphalt binders[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(2): 34-39. |
| [1] | 孙永新,蔺鹏臻,杨子江,冀伟. 考虑黏结-滑移效应的UHPC梁裂缝宽度计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2600-2608. |
| [2] | 薛宇欣,周勇军,王业路,范凯翔,赵煜. 基于悬锤系统的简支梁桥冲击系数测试方法适用性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2557-2567. |
| [3] | 郭雪莲,韩万水,王涛,周恺,张修石,张书颖. 大件车通行弯桥抗倾覆稳定安全系数评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2229-2237. |
| [4] | 肖林,魏欢博,卫星,康志锐. 钢混组合梁栓钉锈胀下混凝土板开裂行为数值分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1958-1965. |
| [5] | 张春雷,邵长宇,苏庆田,戴昌源. 球扁钢肋钢纤维混凝土组合桥面板正弯矩受力性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1634-1642. |
| [6] | 张彦玲,贾云飞,贾晓远,郑旺,李运生. 装配式小箱梁桥内力横向分布系数建议公式[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1688-1700. |
| [7] | 黄汉辉,陈康明,吴庆雄. 钢管混凝土桁式弦杆组合连续梁抗弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1665-1676. |
| [8] | 邵长江,崔皓蒙,漆启明,庄卫林. 近断层大跨RC轻柔拱桥纵向阻尼器减震研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1355-1367. |
| [9] | 赵秋,陈鹏,赵煜炜,余澳. 台后设置拱形结构的无缝桥梁整体受力性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(4): 1016-1027. |
| [10] | 张洪,朱志伟,胡天宇,龚燕峰,周建庭. 基于改进YOLOv5s的桥梁螺栓缺陷识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 749-760. |
| [11] | 许良,肖景厚,宋万万,周松. 碳纤维复合材料层合板三点弯曲疲劳性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 400-409. |
| [12] | 韩智强,谢刚,卓亚娟,骆佐龙,李华腾. 基于车轮-桥面相干激励的大跨连续梁桥振动响应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 436-444. |
| [13] | 杨国俊,齐亚辉,石秀名. 基于数字图像技术的桥梁裂缝检测综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
| [14] | 张协力,吴冲,苏庆田. 压型钢板-混凝土组合桥面板极限承载力试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2870-2883. |
| [15] | 黄卿维,吴庆雄,陈宝春,陈康明,叶智威. 单圆管CFST拱桥面外弹性分支屈曲临界荷载计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2930-2940. |
|