吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2316-2324.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210236
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
冰雪天气下交叉口信号配时优化方法
- 吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Optimization methods of intersection signal timing parameters under ice and snow condition
Ci-yun LIN( ),Tian-cheng XIE,Wei QIN,Xu GUO,Zheng-hao LI,Zhen ZHENG
),Tian-cheng XIE,Wei QIN,Xu GUO,Zheng-hao LI,Zhen ZHENG
- College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
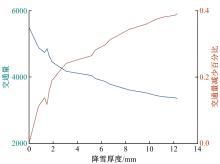
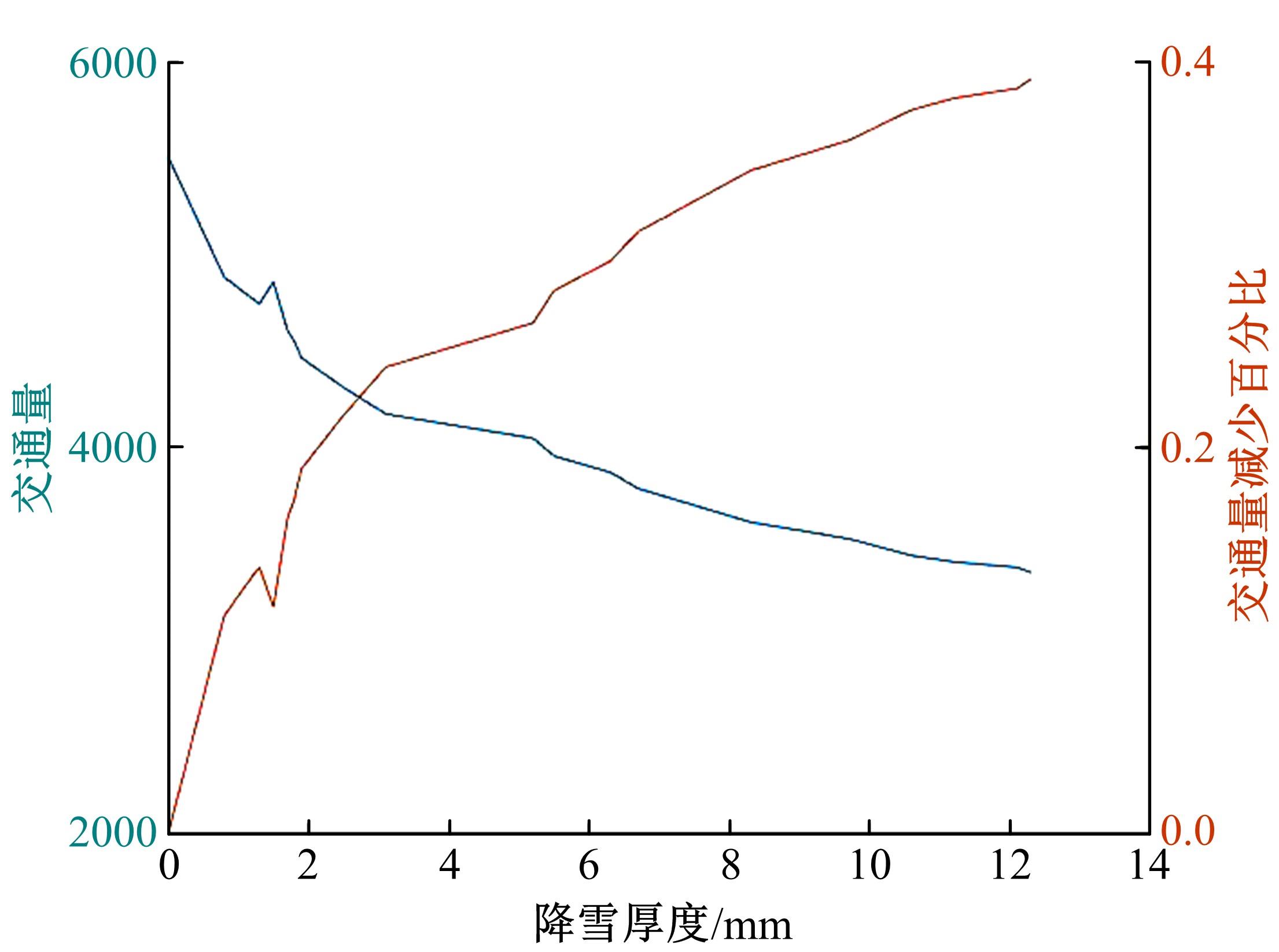
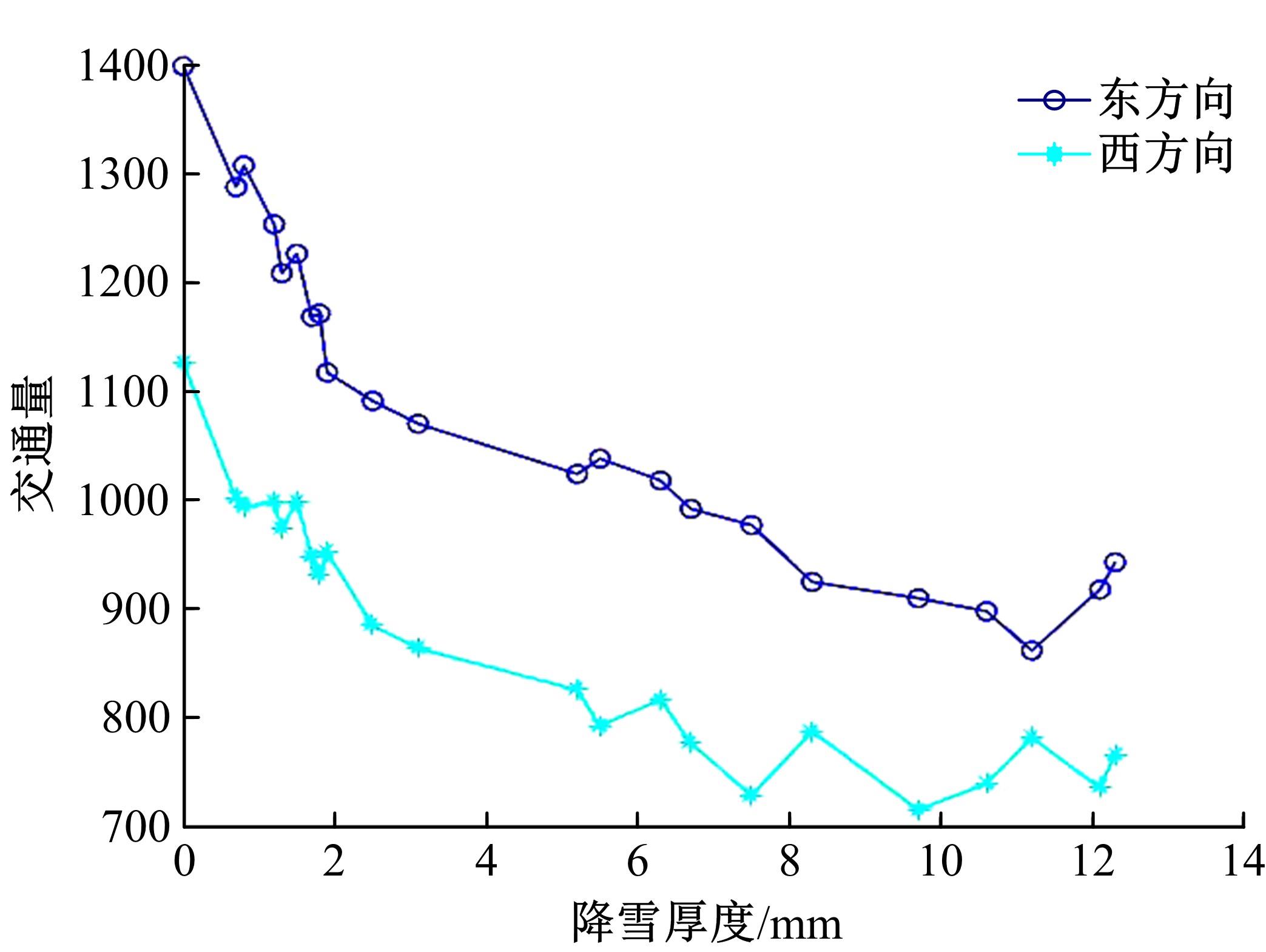
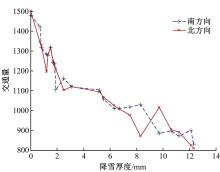
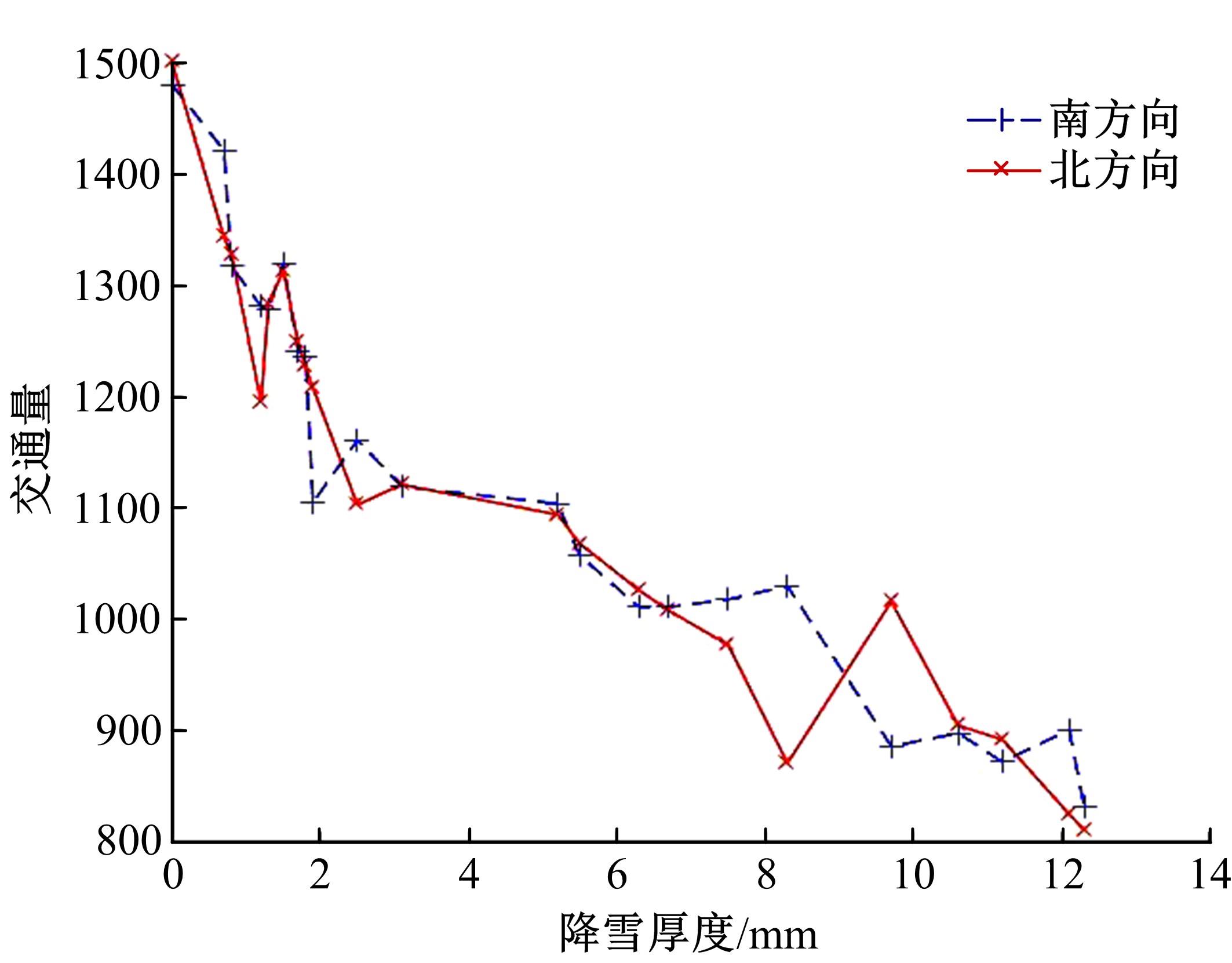
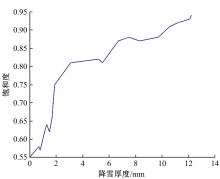
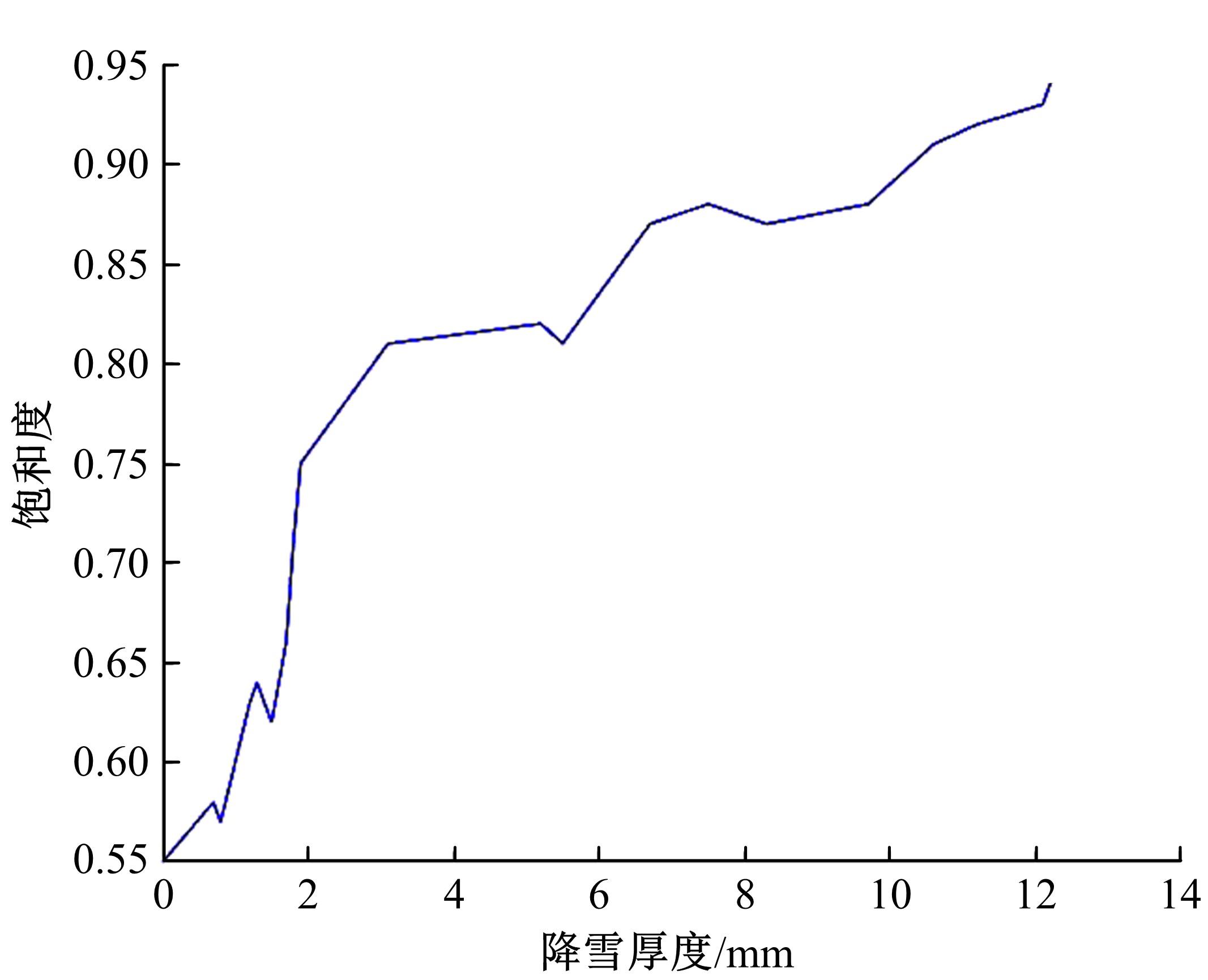
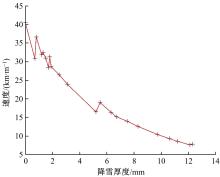
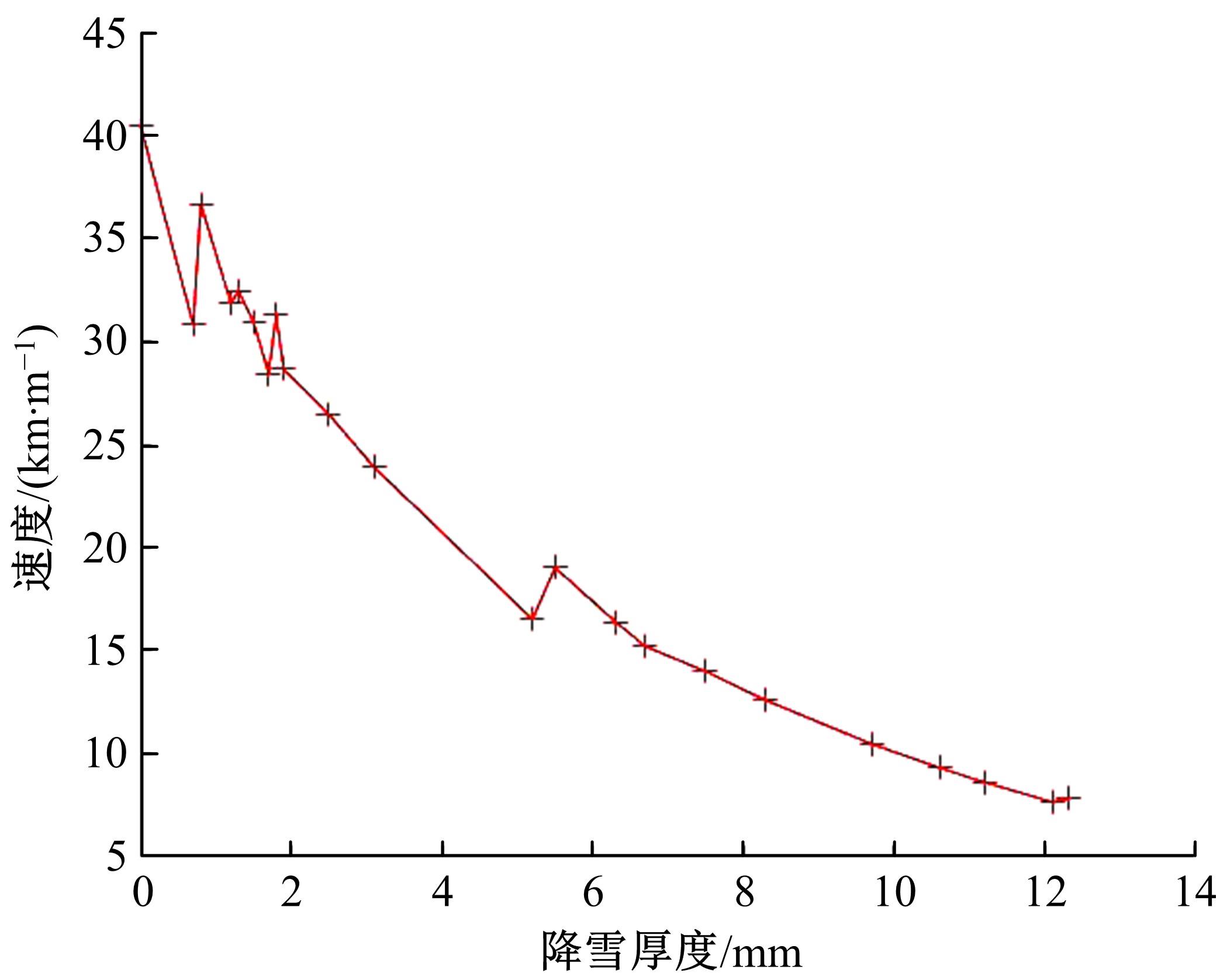
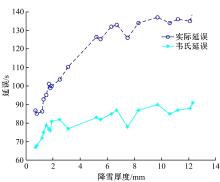
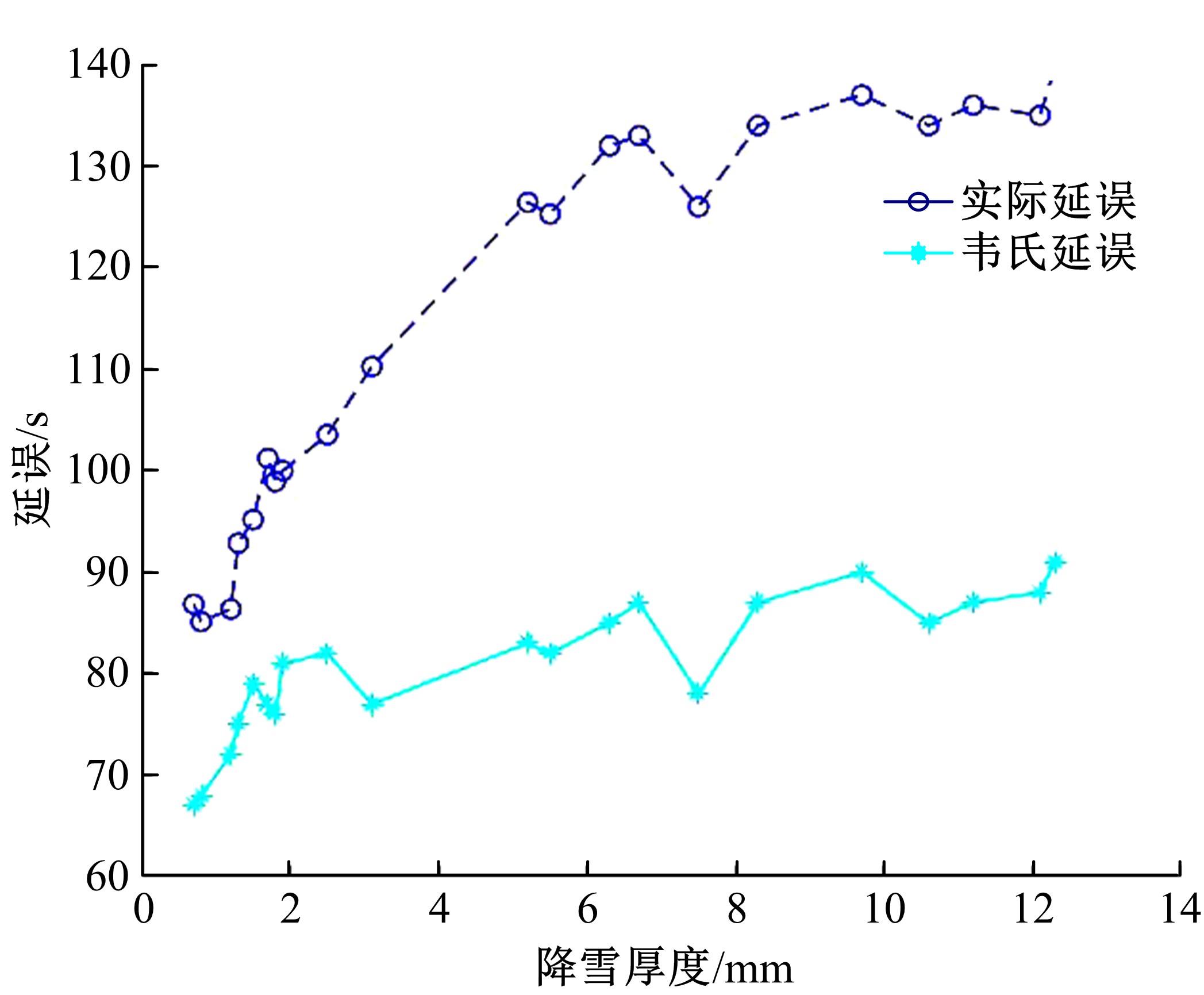
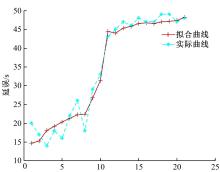
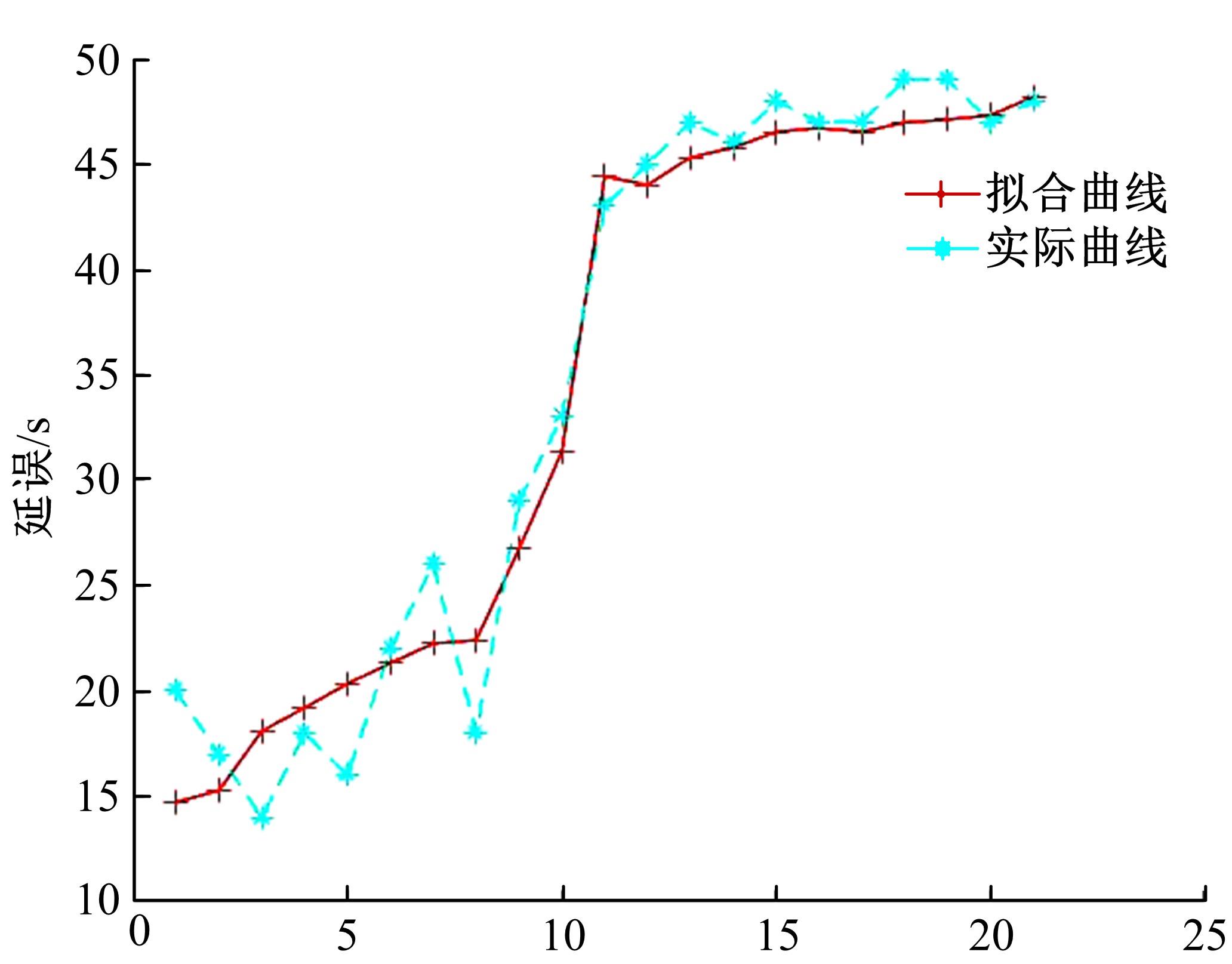
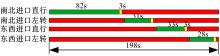
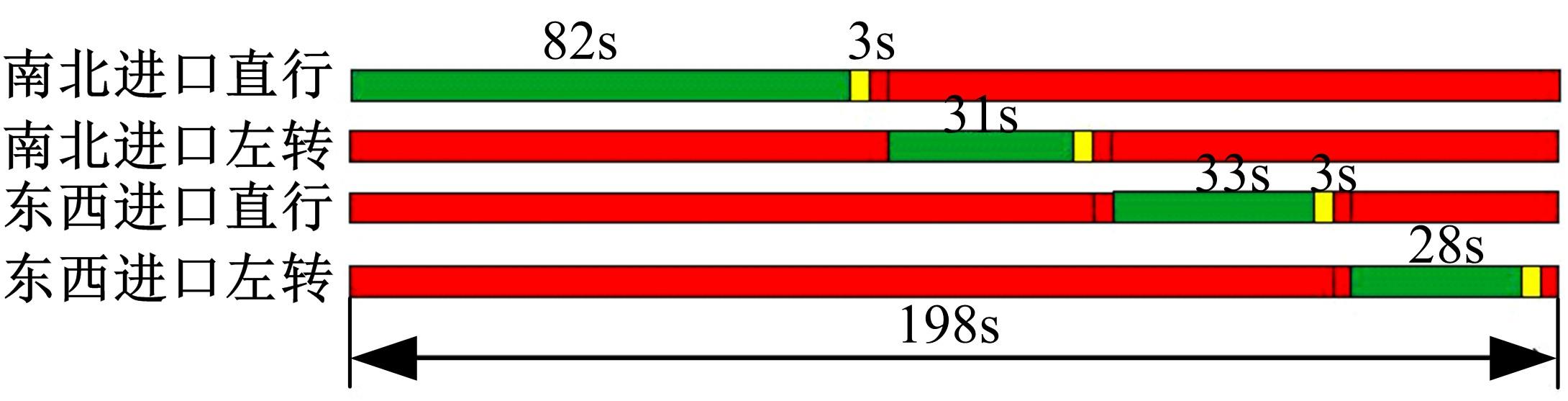
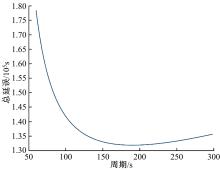
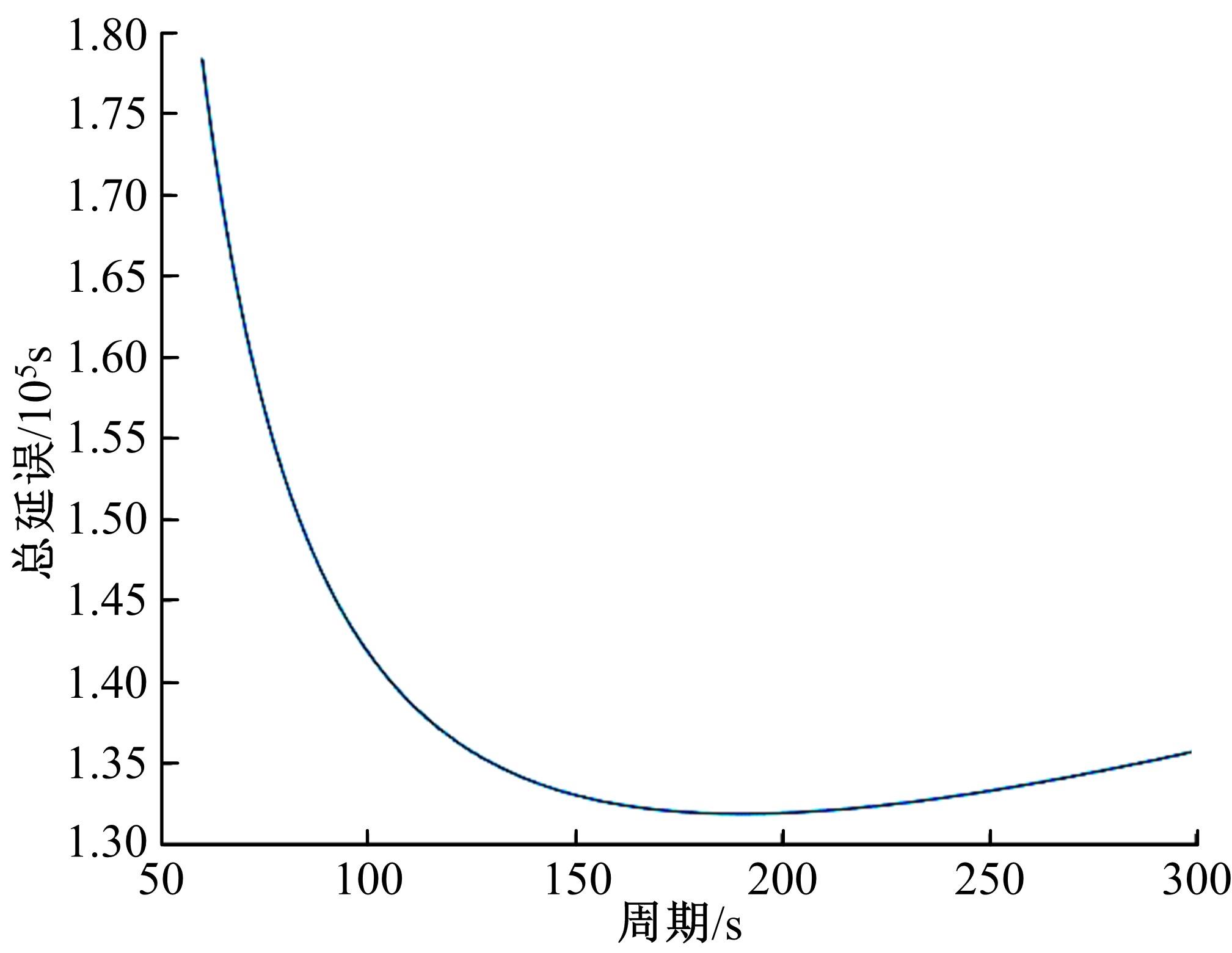
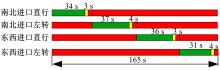
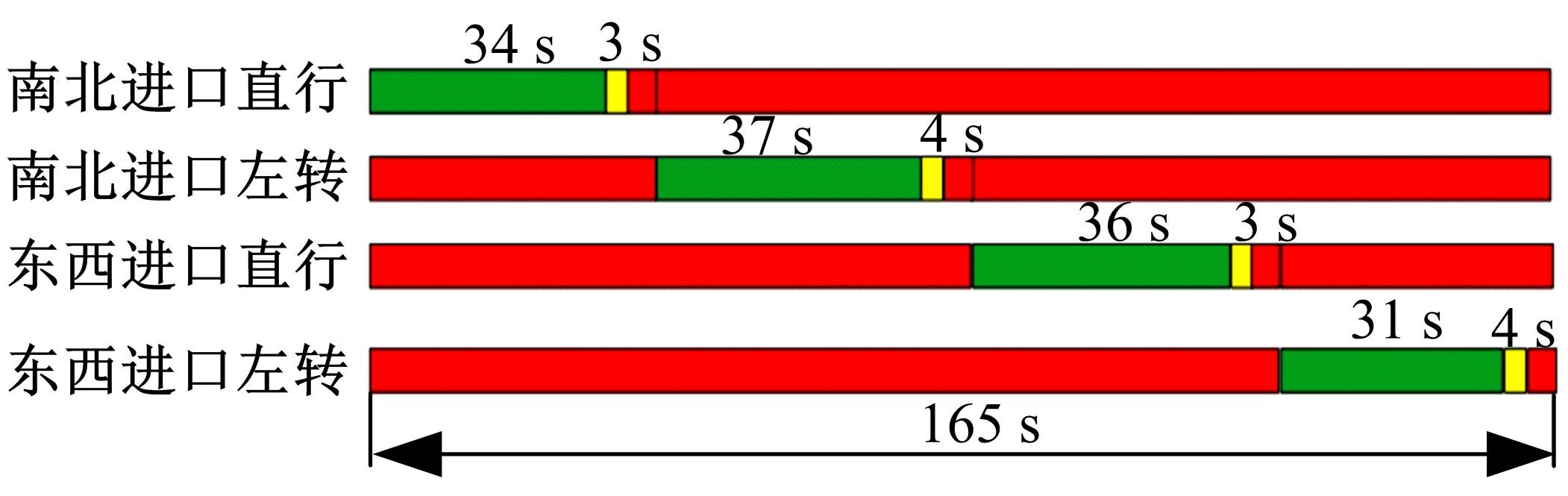
针对冰雪天气现有配时方案信号控制效益下降导致的交通拥堵问题,从冰雪天气的交通流运行特征入手,分析了在不同降雪量下的交通流参数变化情况。运用多元非线性回归,对现有的韦氏延误计算公式进行修正,采用Vissim软件建立了长春市解放大路与人民大街交叉口晴天与雪天的交通信号控制仿真模型,并进行了案例分析。分析表明:根据降雪量调整的信号配时方案,与仍采用正常天气情况下的信号配时方案相比,能有效降低交叉口处车辆的平均延误,提高交叉口的通行效率。本文分析结果适用于所有冰雪天气环境下的交通信号优化控制。
中图分类号:
- U491.5
| 1 | Eisenbergd D, Warner K E. Effects of snowfalls on motor vehicle collisions, injuries, and fatalities[J]. American Journal of Public Health, 2005, 95(1): 120-124. |
| 2 | Saha Shubhayu, Schramm Paul, Nolan Amanda, et al. Adverse weather conditions and fatal motor vehicle crashes in the United States, 1994-2012[J]. Environmental Health, 2016, 15(1): No.104. |
| 3 | 赵玮, 徐良杰, 冉斌, 等. 基于Adaptive Lasso及RF算法的冰雪天气交通事故分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(2): 98-103. |
| Zhao Wei, Xu Liang-jie, Ran Bin, et al. Analyzing traffic crash under iced and snow weather condition based on Adaptive Lasso and RF[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(2): 98-103. | |
| 4 | GaoW C, Li G L, Ta N. Overview of road network matching algorithms[J].Journal of Software,2018,29(2):225-250. |
| 5 | Tang Lian-sheng, Cheng Wen-ming, Zhang Ze-qiang,et al. Vehicle r outing problem with travel time reliability constrain[C]∥International Conference on Transportation Engineering, Chengdu, China, 2007:1831-1836. |
| 6 | Asakura Yasuo. Evaluation of network reliability using stochastic user equilibrium[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 1999, 33(2): 147-158. |
| 7 | Perrin H J, Hansen M A, Peter J, et al. Modifying signal timing during inclement weather[J]. Transportation Research Record Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2001, 1748(1): 66-71. |
| 8 | Botha J L, Kruse T R. Flow rates at signalized intersections under cold winter conditions[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 1992, 118(3): 439-450. |
| 9 | 刘力力. 不良天气条件下城市交叉口交通流特征参数研究[D]. 北京:北京工业大学交通工程北京市重点实验室,2013. |
| Liu Li-li.Research on traffic flow characteristic parameters of city intersection in adverse weather conditions[D].Beijing:Beijing Key Laboratory of Traffic Engineering,Beijing University of Technology,2013. | |
| 10 | Ibrahim A T, Hall FL. Effect of adverse weather conditions on speed-flow-occupancy relationships[C]//Transportation Research Record,1994,1457:184-191. |
| 11 | Liang W L, Kyte M, Kitchener F, et al. Effect of environmental factors on driver speed: a case study[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1998, 1635(1): 155-161. |
| 12 | 冷军强, 张亚平, 韩丽飞, 等. 冰雪条件下城市路网容量可靠性[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2010, 42(4): 592-596. |
| Leng Jun-qiang, Zhang Ya-ping, Han Li-fei, et al. Reliability of urban road network capacity under snow and ice conditions[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2010, 42(4): 592-596. | |
| 13 | Ries G L. Impact of weather on freeway capacity[R]. Minneapolis, MN: Minnesota Department of Transportation. Office of Traffic Enginneering,1981:178-183. |
| 14 | Maki P J. Adverse weather traffic signal timing[C]∥The 69th Annual Meeting of the Institute of Transportation Engineers, Lasvegas, Nevada, 1999:1-5. |
| 15 | 刘力力, 翁剑成, 荣建. 降雪条件下城市快速路交通流特性研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2012, 30(1): 10-14. |
| Liu Li-li, Weng Jian-cheng, Rong Jian. Research on traffic flow characteristics of urban expressway under snowfall condition[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2012, 30(1): 10-14. | |
| 16 | 杨中良, 林瑜, 高霄. 恶劣天气条件下城市快速路通行能力研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2010, 28(1): 75-78. |
| Yang Zhong-liang, Lin Yu, Gao Xiao. Study on urban expressway capacity under severe weather conditions[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2010, 28(1): 75-78. | |
| 17 | 蒋贤才, 汪贝, 曾永松. 不良天气和路面环境对交通信号配时方案的影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2014, 31(7): 135-142, 158. |
| Jiang Xian-cai, Wang Bei, Zeng Yong-song. Influence of adverse weather and road environment on traffic signal timing scheme[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2014, 31(7): 135-142, 158. | |
| 18 | Noble Douglas E. Guidelines for determining traffic signal change and clearance intervals[J]. ITE Journal-Institute of Transportation Engineers,2020, 90(3): 28-31. |
| 19 | Martin P, Perrin J, Hansen B. Inclement weather signal Timings[R]. Salt Lake City, UT: University of Utah,2000. |
| 20 | 刘春晓. 冰雪条件下信号交叉口通行能力研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通学院, 2014. |
| Liu Chun-xiao. Capacity of signalized intersections under snow and ice conditions[D]. Harbin: College of Transportation,Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014. | |
| 21 | Gholami Ali, Andalibian Rasool, Zong Tian. Estimating intersection turning volumes from actuated traffic signal information[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering(English Edition), 2016, 3(6): 507-519. |
| [1] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [2] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [3] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [4] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [5] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [6] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [7] | 盖松雪,曾小清,岳晓园,袁子豪. 基于用户-系统双层优化算法的车位引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [8] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [9] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [10] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [11] | 尹超英,邵春福,黄兆国,王晓全,王晟由. 基于梯度提升决策树的多尺度建成环境对小汽车拥有的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| [12] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [13] | 贾彦峰,曲大义,林璐,姚荣涵,马晓龙. 基于运行轨迹的网联混合车流速度协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2051-2060. |
| [14] | 薛锋,何传磊,黄倩,罗建. 多式轨道交通网络的耦合协调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| [15] | 姚荣涵,祁文彦,郑刘杰,曲大义. 基于车道选择及行车轨迹的左转导向线设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1651-1663. |
|
||