吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 2582-2591.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210390
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
城市公交-地铁加权复合网络构建及鲁棒性分析
潘恒彦1( ),张文会2,胡宝雨2,刘尊严2,王永岗1(
),张文会2,胡宝雨2,刘尊严2,王永岗1( ),张枭3
),张枭3
- 1.长安大学 运输工程学院,西安 710064
2.东北林业大学 交通学院,哈尔滨 150040
3.上海市城市建设设计研究总院(集团)有限公司,上海 200125
Construction and robustness analysis of urban weighted subway⁃bus composite network
Heng-yan PAN1( ),Wen-hui ZHANG2,Bao-yu HU2,Zun-yan LIU2,Yong-gang WANG1(
),Wen-hui ZHANG2,Bao-yu HU2,Zun-yan LIU2,Yong-gang WANG1( ),Xiao ZHANG3
),Xiao ZHANG3
- 1.College of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Traffic and Transportation,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,China
3.Shanghai Urban Construction Design & Research Institute(Group) Co. ,Ltd. ,Shanghai 200125,China
摘要:
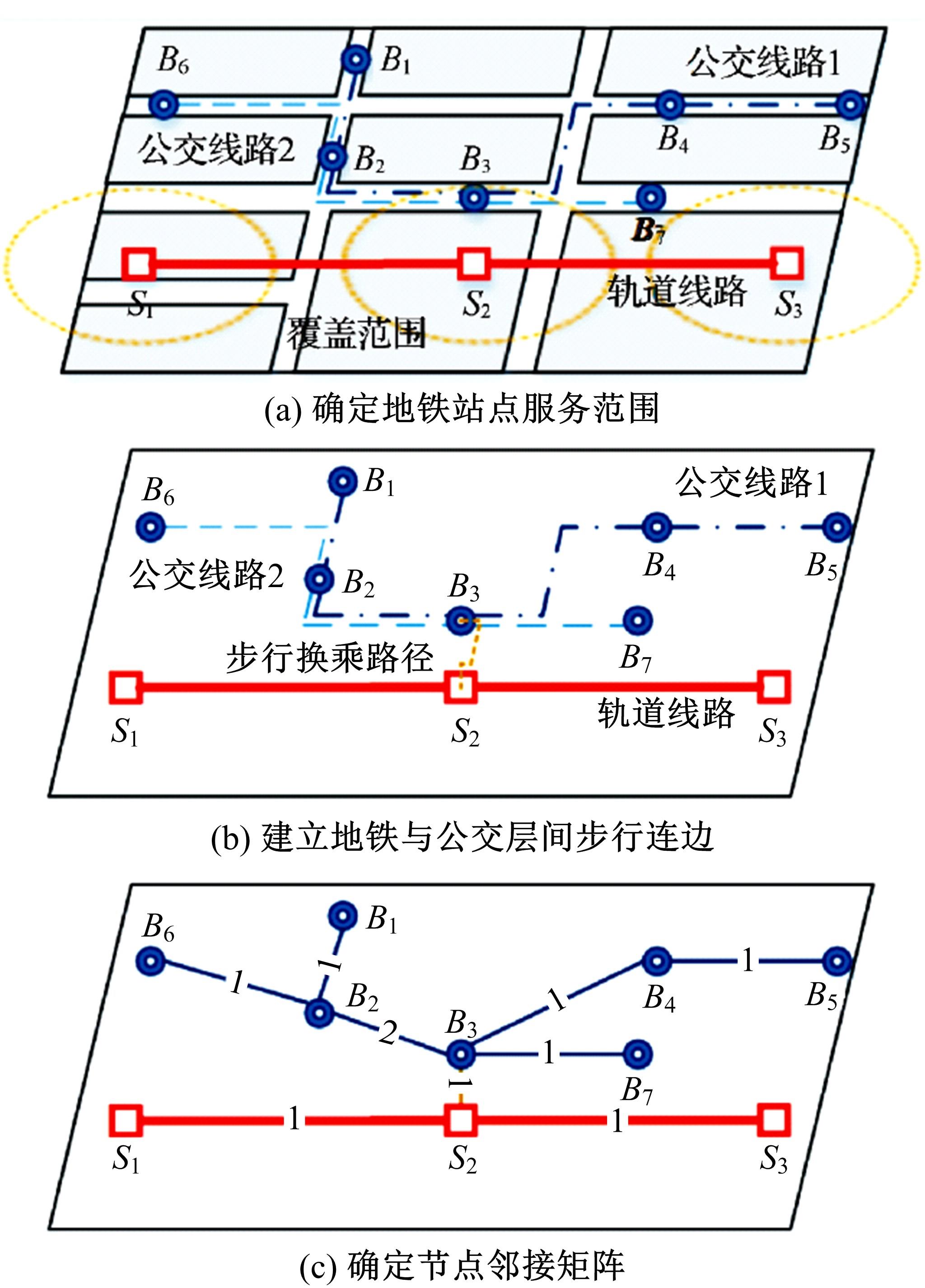
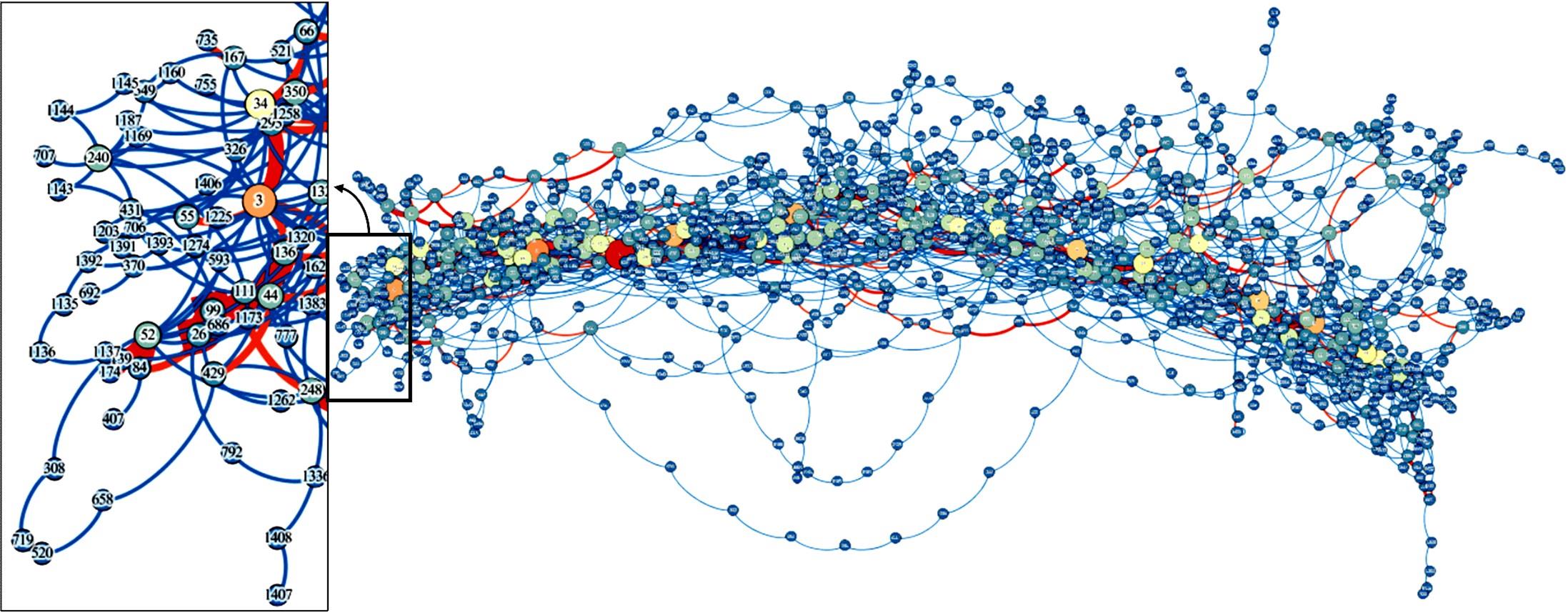
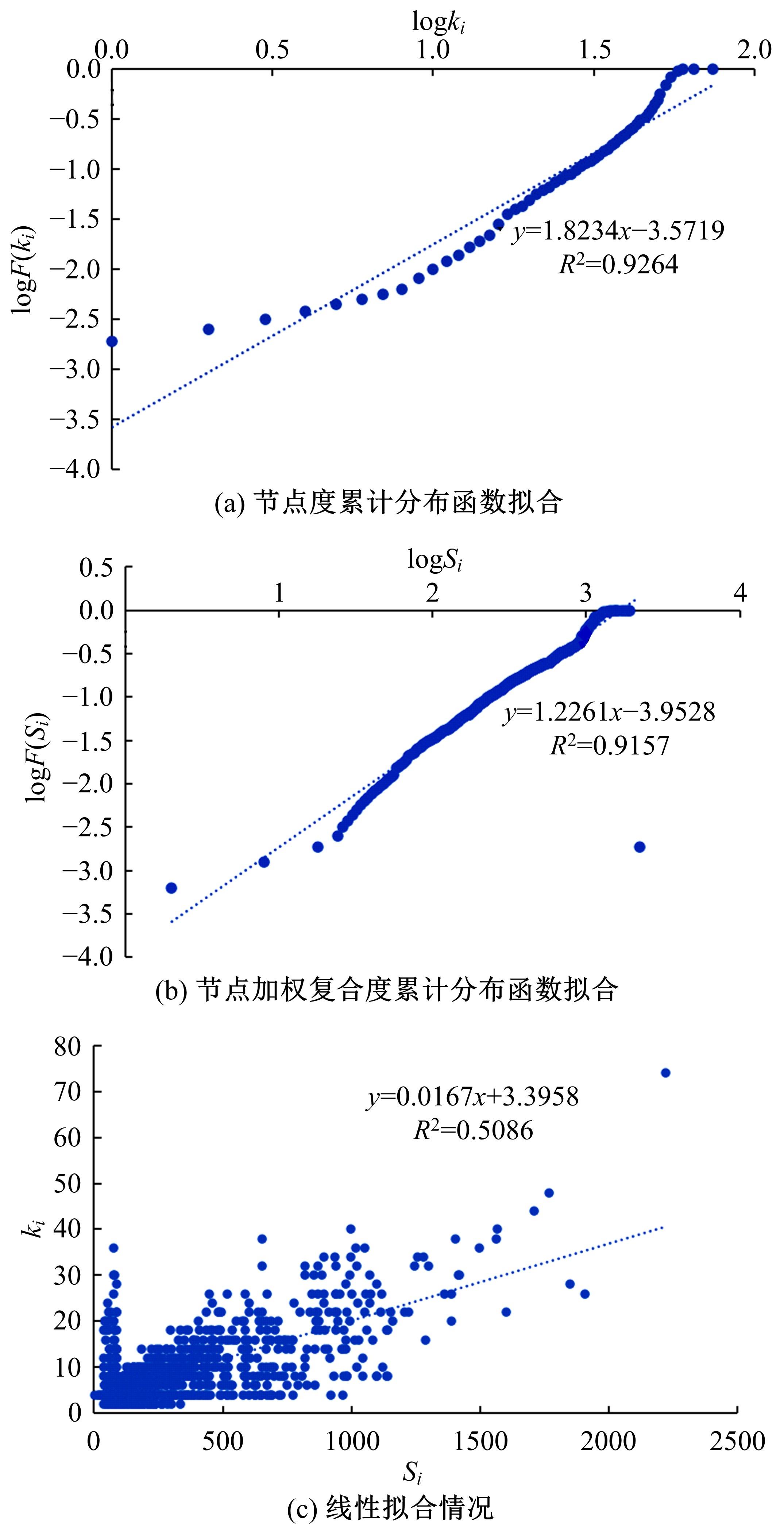
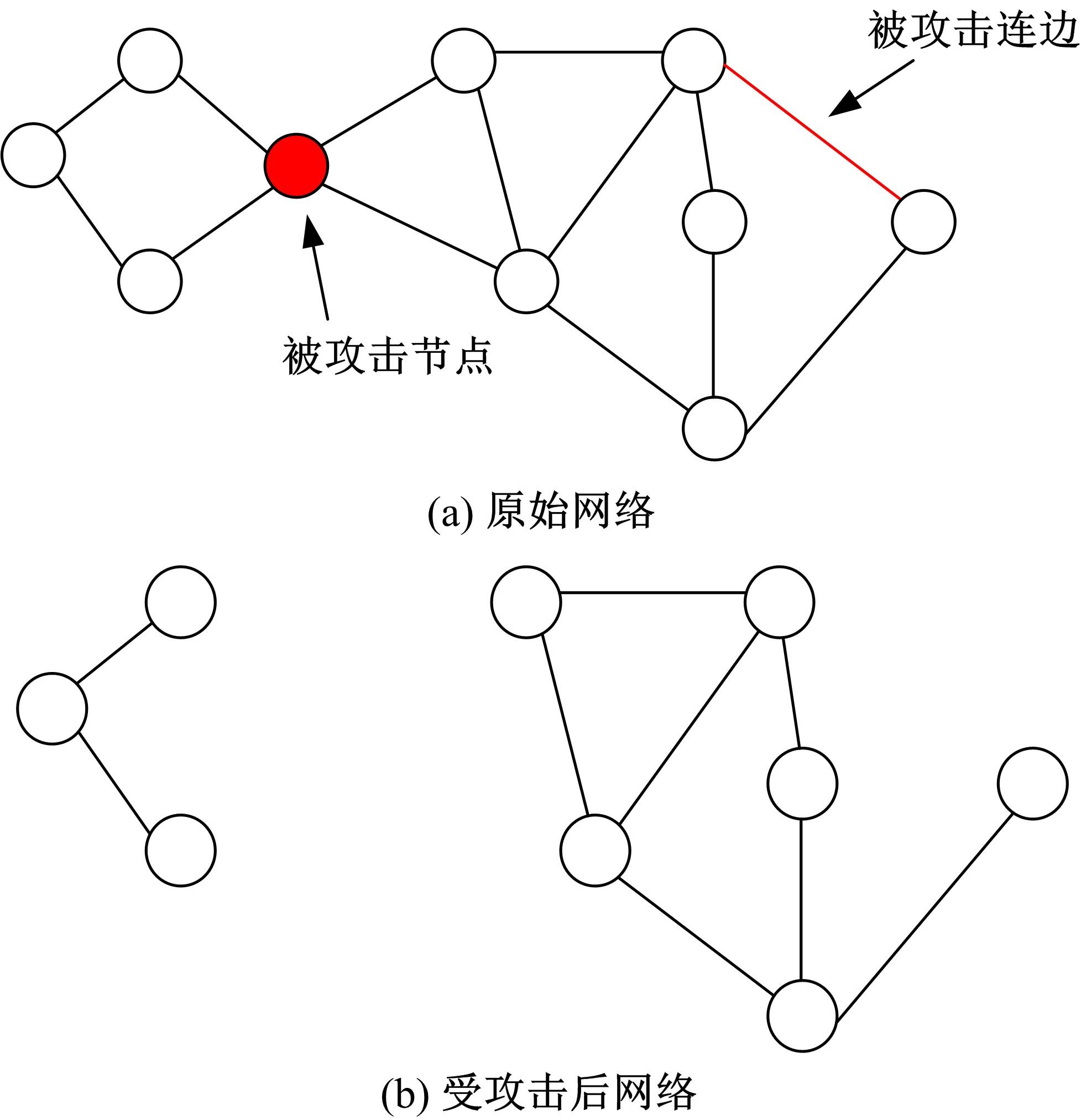
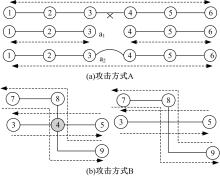
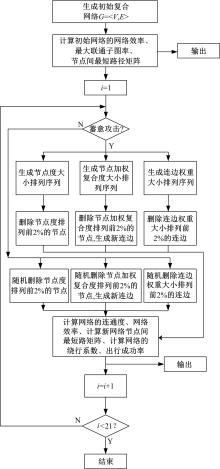
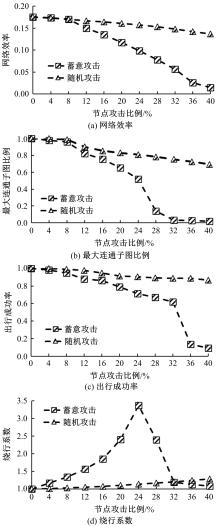
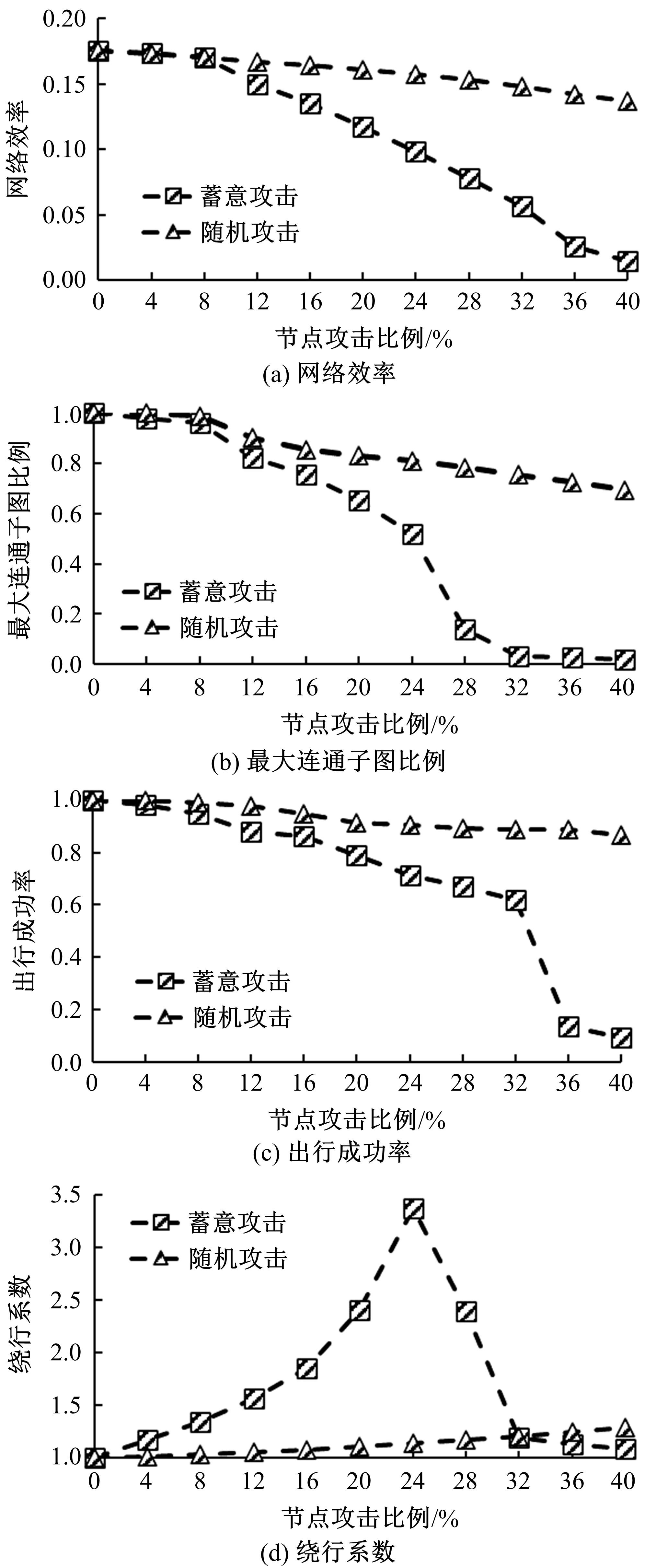
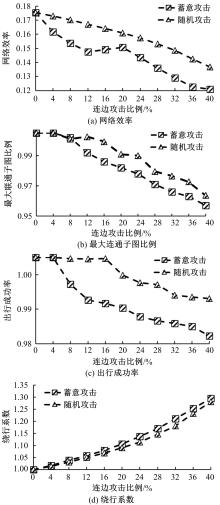
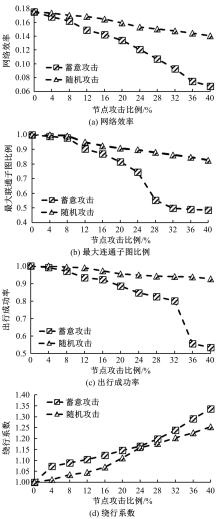
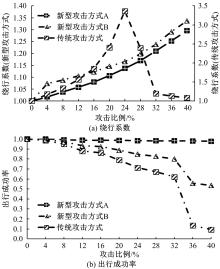
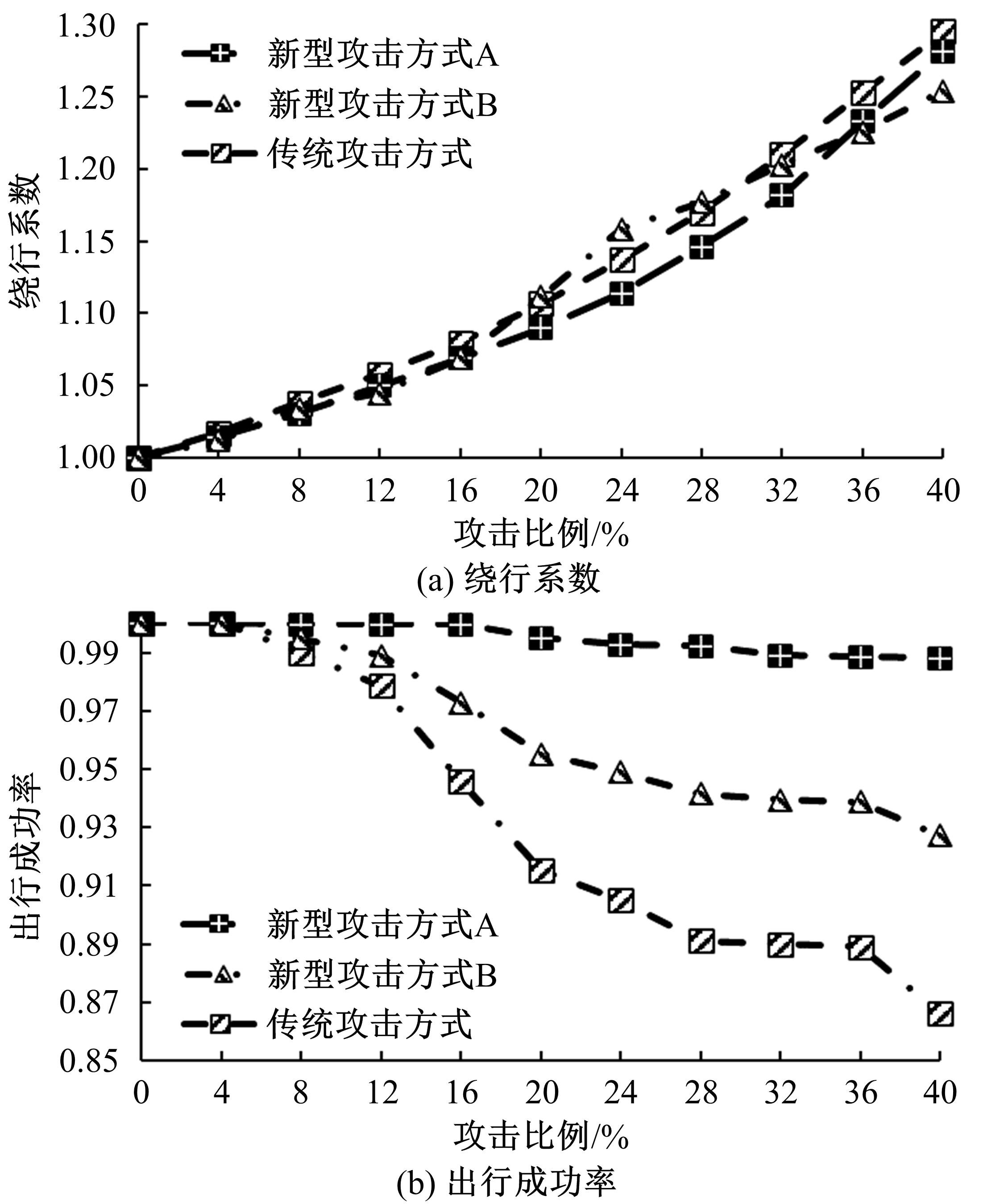
基于复杂网络理论,本文将地铁、公交实际运营特性考虑其中,构建了加权复合网络,提出“出行成功率”与“绕行系数”两个鲁棒性评价新指标,以及更贴近于实际的2种新型攻击方式A与B。通过仿真实验,统计在蓄意攻击、随机攻击2类攻击策略的3种攻击模型下,加权复合网络评价指标(网络效率、最大连通子图率、绕行系数以及出行成功率)的变化情况,分析复合加权网络分别在蓄意攻击与随机攻击下,对上述3种攻击模型的鲁棒特性。结果表明:受到蓄意攻击时,绕行可达方面,复合网络对新型攻击方式A与B的鲁棒性能高于传统攻击方式;出行成功率方面,复合网络对新型攻击方式A的鲁棒性高于对传统攻击方式与新型方式B的鲁棒性。随机攻击下,绕行系数方面,复合网络对3种攻击模式呈现出的鲁棒性交替变化;出行成功率方面,对3者的鲁棒性为:新型攻击方式A>新型攻击方式B>传统攻击方式。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Pang J Z F, Bin O N, Ng K M, et al.Efficiency and robustness of different bus network designs[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 2015, 26(3): 1550024. |
| 2 | Derrible S, Kennedy C. The complexity and robustness of metro network[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Application, 2010, 389(17): 3678-3691. |
| 3 | Yang Y H, Liu Y X, Zhou M X, et al. Robustness assessment of urban rail transit based on complex network theory: a case study of the beijing subway[J]. Safety Science, 2015, 79: 149-162. |
| 4 | Latora V, Marchiori M. Is the boston subway a small-world network[J]. Physical A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2002, 314(1-4): 109-113. |
| 5 | Angeloudis P, Fisk D. Large subway systems as complex networks[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2006, 367(4): 553-558. |
| 6 | 陈峰, 胡映月, 李小红, 等. 城市轨道交通有权网络相继故障可靠性研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2016, 16(2): 139-145. |
| Chen Feng, Hu Ying-yue, Li Xiao-hong, et al. Cascading failures in weighted network of urban rail transit[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2016, 16(2): 139-145. | |
| 7 | 甘俊杰, 聂规划, 徐迪. 武汉市地铁网络复杂特性与鲁棒性研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2018, 25(6): 120-126. |
| Jun-jie Gang, Nie Gui-hua, Xu Di. Complex characteristics and robustness of wuhan metro network[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2018, 25(6): 120-126. | |
| 8 | 蔡鉴明, 邓薇. 长沙地铁网络复杂特性与级联失效鲁棒性分析[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2019, 16(6): 1587-1596. |
| Cai Jian-ming, Deng Wei. Complex characteristics of Changsha metro network and robustness analysis of cascading failures[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2019, 16(6): 1587-1596. | |
| 9 | 杜斐, 黄宏伟, 张东明, 等. 上海轨道交通网络的复杂网络特性及鲁棒性研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 49(5): 701-707. |
| Du Fei, Huang Hong-wei, Zhang Dong-ming, et al. Analysis of characteristics of complex network and robustness in shanghai metro network[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2016, 49(5): 701-707. | |
| 10 | 强添纲, 赵明明, 裴玉龙. 城市多模式交通网络的复杂网络特性与鲁棒性研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2019, 37(1): 65-71. |
| Qiang Tian-gang, Zhao Ming-ming, Pei Yu-long. An analysis of characteristics of complex network and robustness in harbin multi-mode traffic network[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2019, 37(1): 65-71. | |
| 11 | 罗艺, 钱大琳. 公交-地铁复合网络构建及网络特性分析[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2015, 15(5): 39-44. |
| Luo Yi, Qian Da-lin. Construction of subway and bus transport networks and analysis of the network topology characteristics[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2015, 15(5): 39-44. | |
| 12 | 鲍登, 高超, 张自力. 基于复杂网络的公交-地铁复合网络鲁棒性分析[J]. 西南师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 42(5): 22-27. |
| Bao Deng, Gao Chao, Zhang Zi-li. Analysis of robustness of bus and subway interdependent network based on the complex network theory[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 42(5): 22-27. | |
| 13 | Wang L J, Zheng S Y, Wang Y G, et al. Identification of critical nodes in multimodal transportation network[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2021, 580: 126170. |
| 14 | 薛锋, 何传磊, 黄倩, 等. 多式轨道交通网络的耦合协调度[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. |
| Xue Feng, He Chuan-lei, Huang Qian, et al. Coordination degree of multimodal rail transit network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(6): 2040-2050. | |
| 15 | 鞠艳妮, 李宗平, 陈宇帆, 等. 区域轨道交通系统节点重要度及故障恢复研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2021, 31(2): 112-119. |
| Ju Yan-ni, Li Zong-ping, Chen Yu-fan, et al.Study on node importance and failure recovery of regional rail transit system[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2021, 31(2): 112-119. | |
| 16 | 牟能冶, 康秋萍, 贾程方. 突发事件影响下的城市快递网络脆弱性评估[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2020, 30(12): 125-132. |
| Mu Neng-ye, Kang Qiu-ping, Jia Cheng-fang. Vulnerability assessment of urban express networks under influence of emergencies[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2020, 30(12): 125-132. | |
| 17 | 林鹏飞, 翁剑成, 付宇, 等. 基于刷卡数据的轨道交通加权网络结构特征[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(3): 956-962. |
| Lin Peng-fei, Weng Jian-cheng, Fu Yu, et al. Structure characteristics of rail transit weighted network based on smart card data[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3): 956-962. | |
| 18 | .城市综合交通体系规划标准 [S]. |
| [1] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [2] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [3] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [4] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [5] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [6] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [7] | 盖松雪,曾小清,岳晓园,袁子豪. 基于用户-系统双层优化算法的车位引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [8] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [9] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [10] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [11] | 尹超英,邵春福,黄兆国,王晓全,王晟由. 基于梯度提升决策树的多尺度建成环境对小汽车拥有的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| [12] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [13] | 汪怡然,陈景旭,王岳平,霍锦彪,刘志远. 考虑服务公平性的定制公交动态响应方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2574-2581. |
| [14] | 吴静娴,申华鹏,韩印,杨敏. 考虑城市建成环境非线性作用的通勤时间模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2568-2573. |
| [15] | 林赐云,谢天承,覃蔚,郭旭,李正浩,郑臻. 冰雪天气下交叉口信号配时优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2316-2324. |
|
||