吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (1): 197-209.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221145
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于分子动力学的生物质透层油稳定性
- 东南大学 交通学院,南京 211189
Molecular dynamics‒based stability of biomass prime coat oil
Shuang SHI( ),Lan-qin LIN,Tao MA(
),Lan-qin LIN,Tao MA( ),Lin-hao GU,Yan-ning ZHANG
),Lin-hao GU,Yan-ning ZHANG
- College of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
摘要:
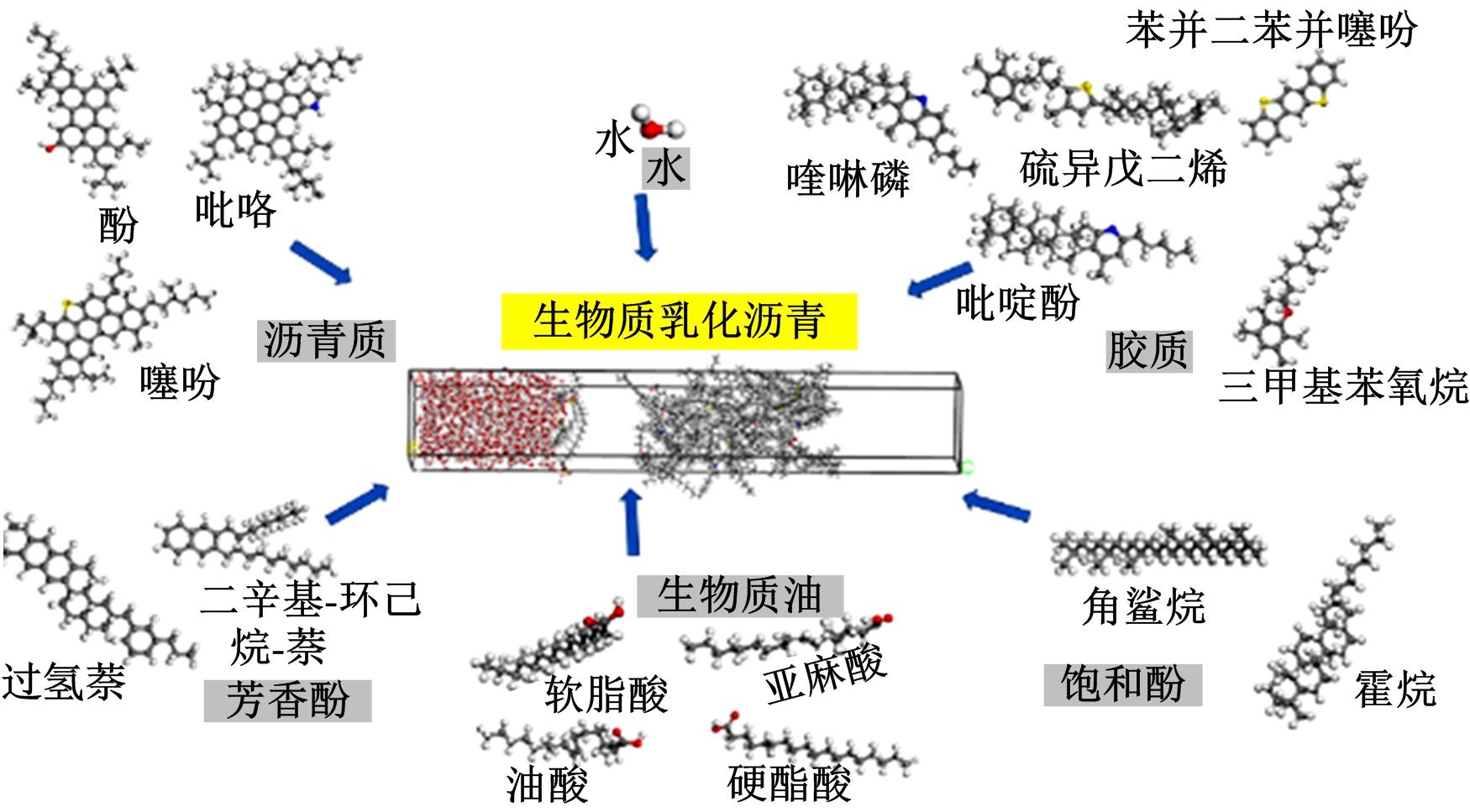
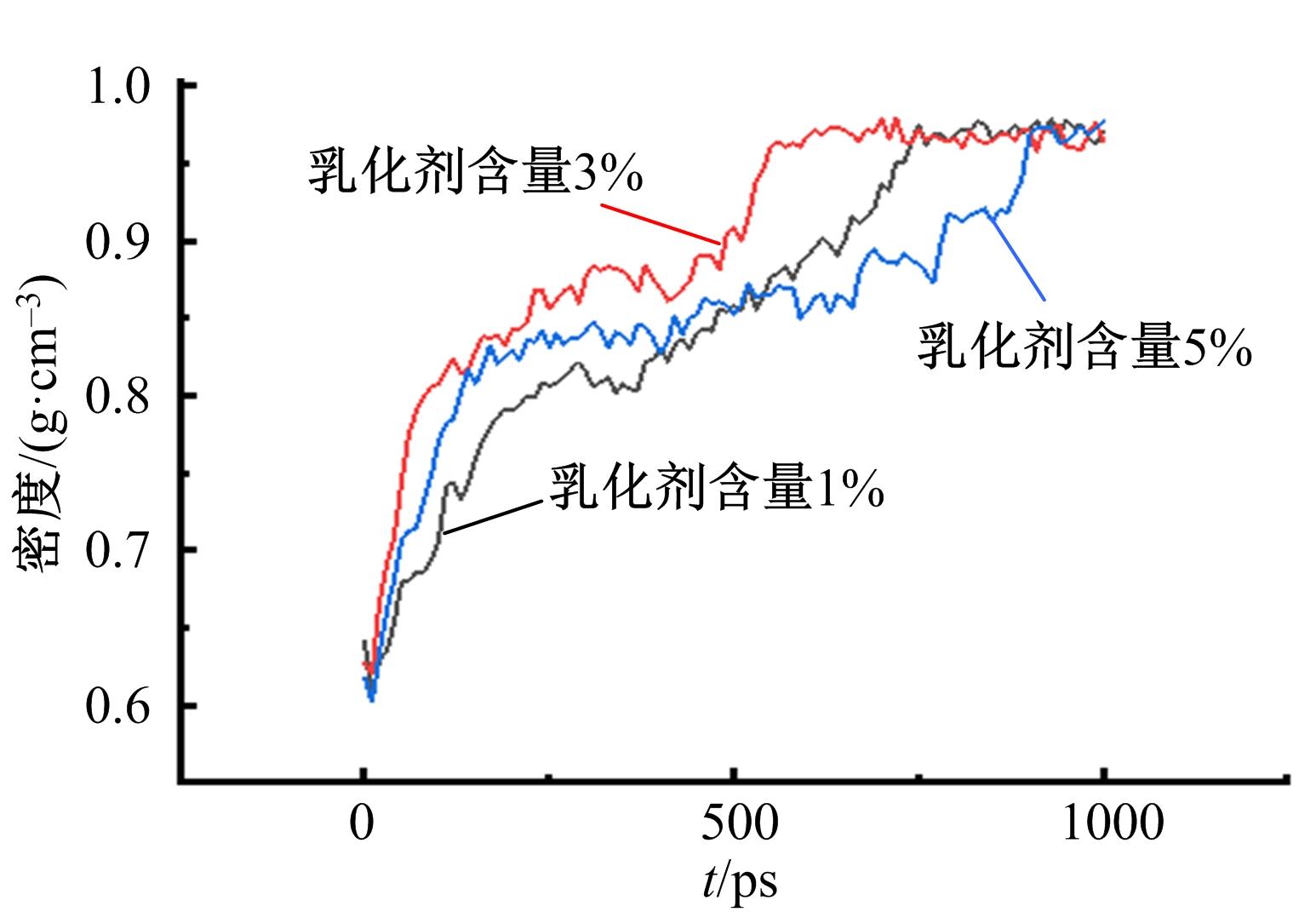
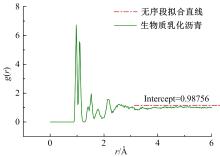
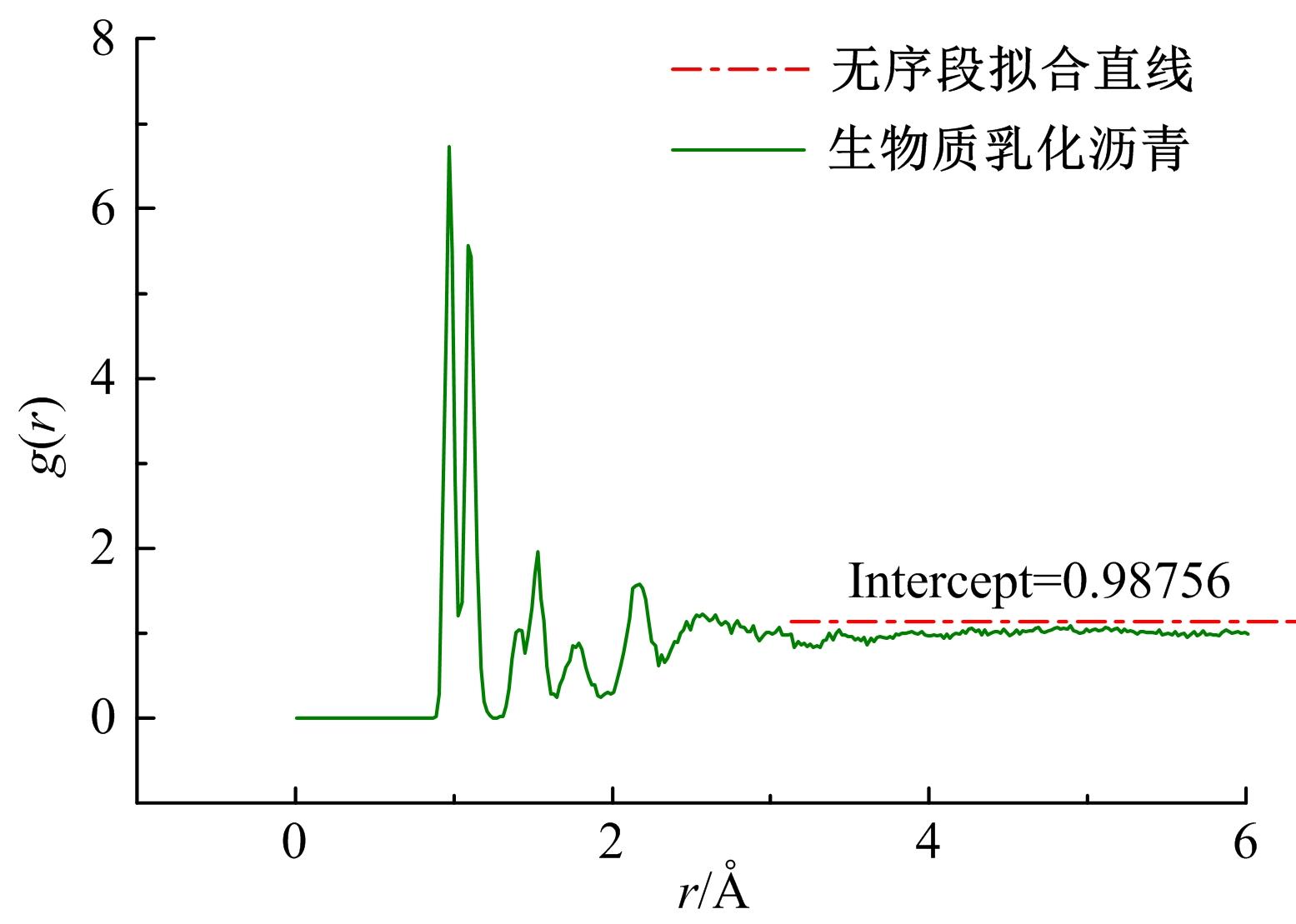
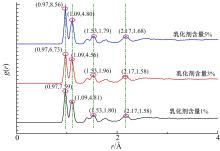
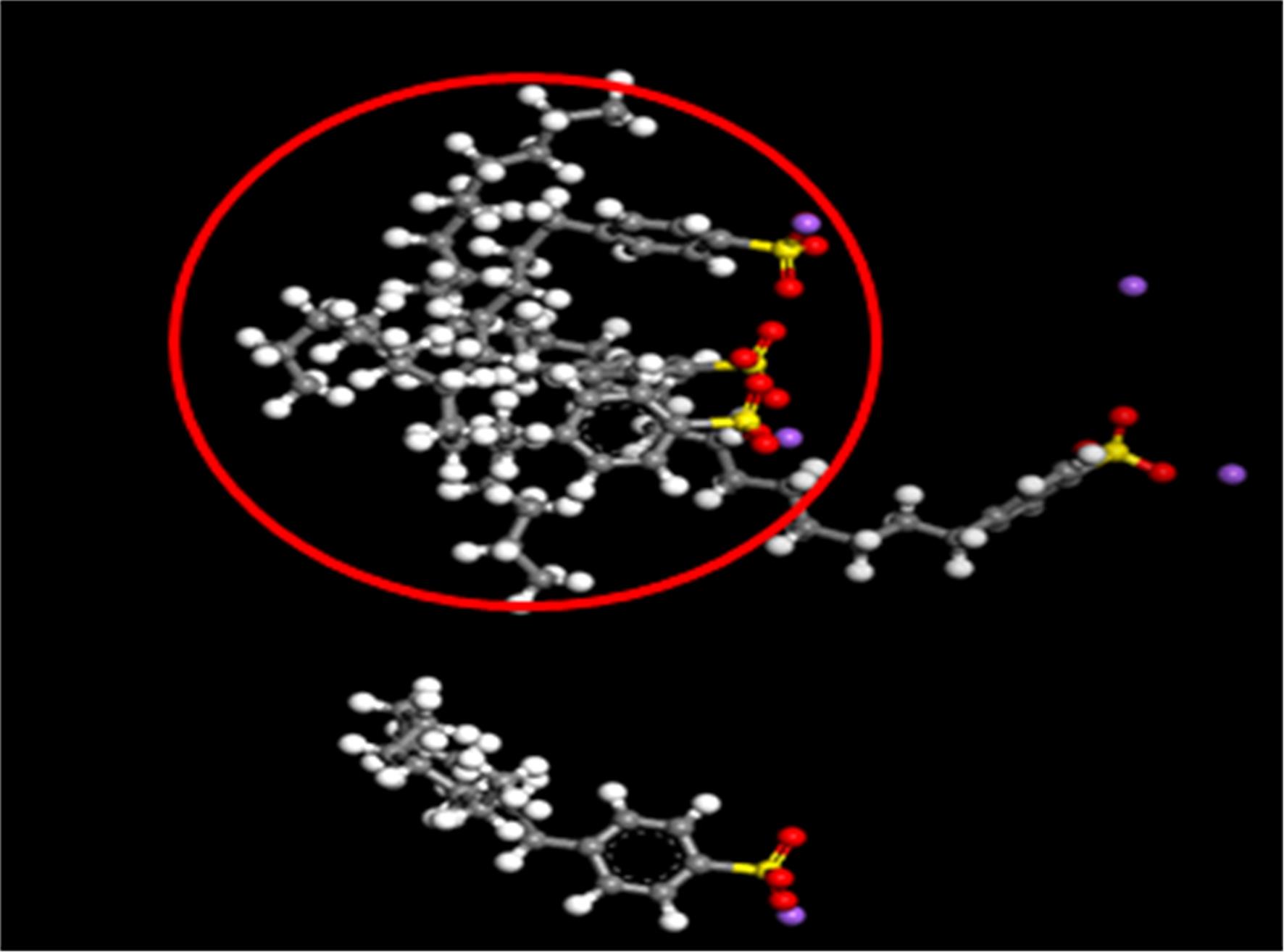
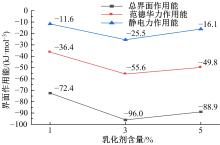
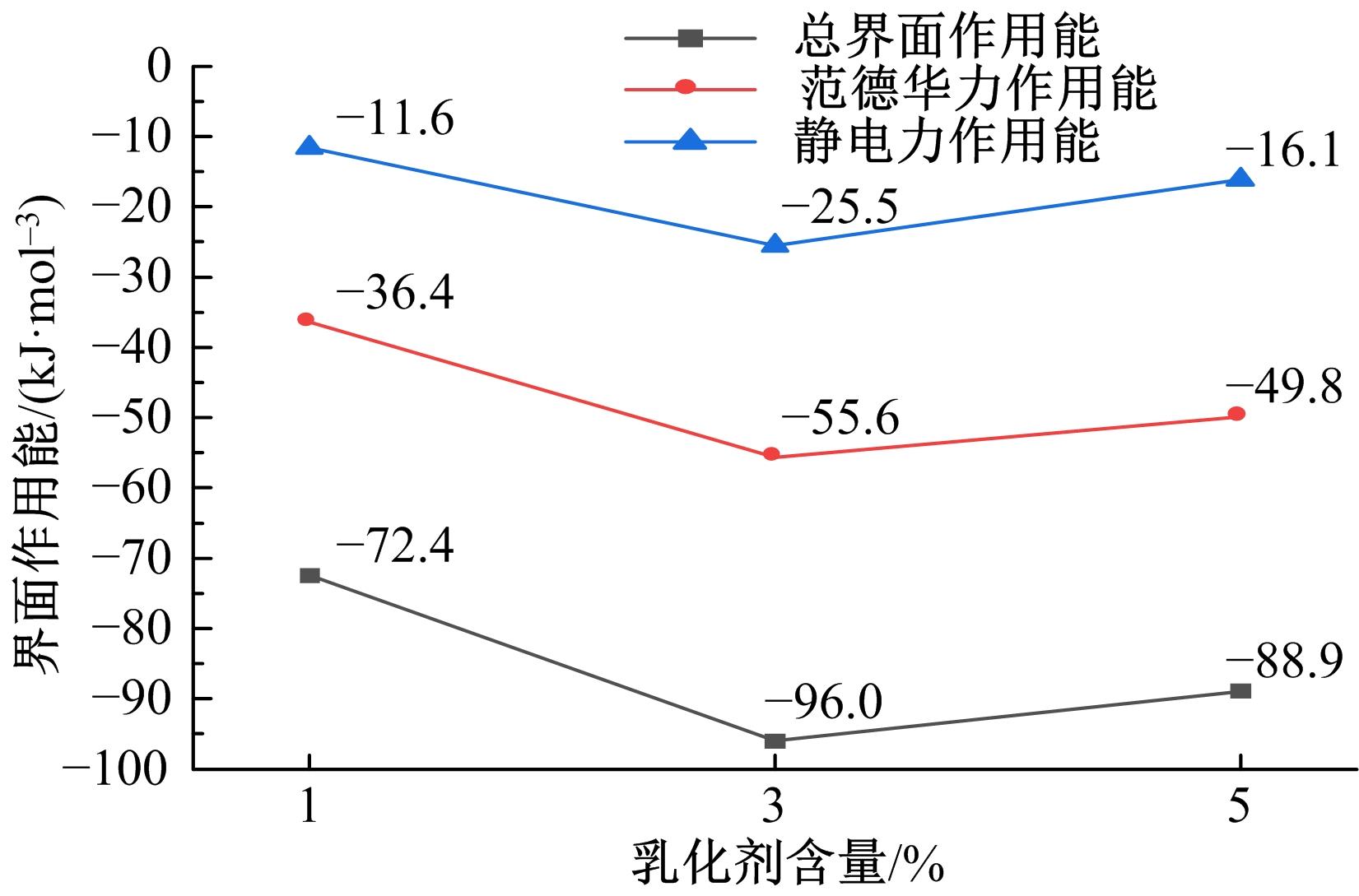
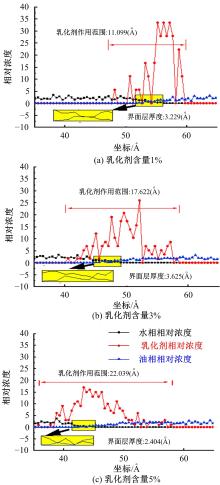
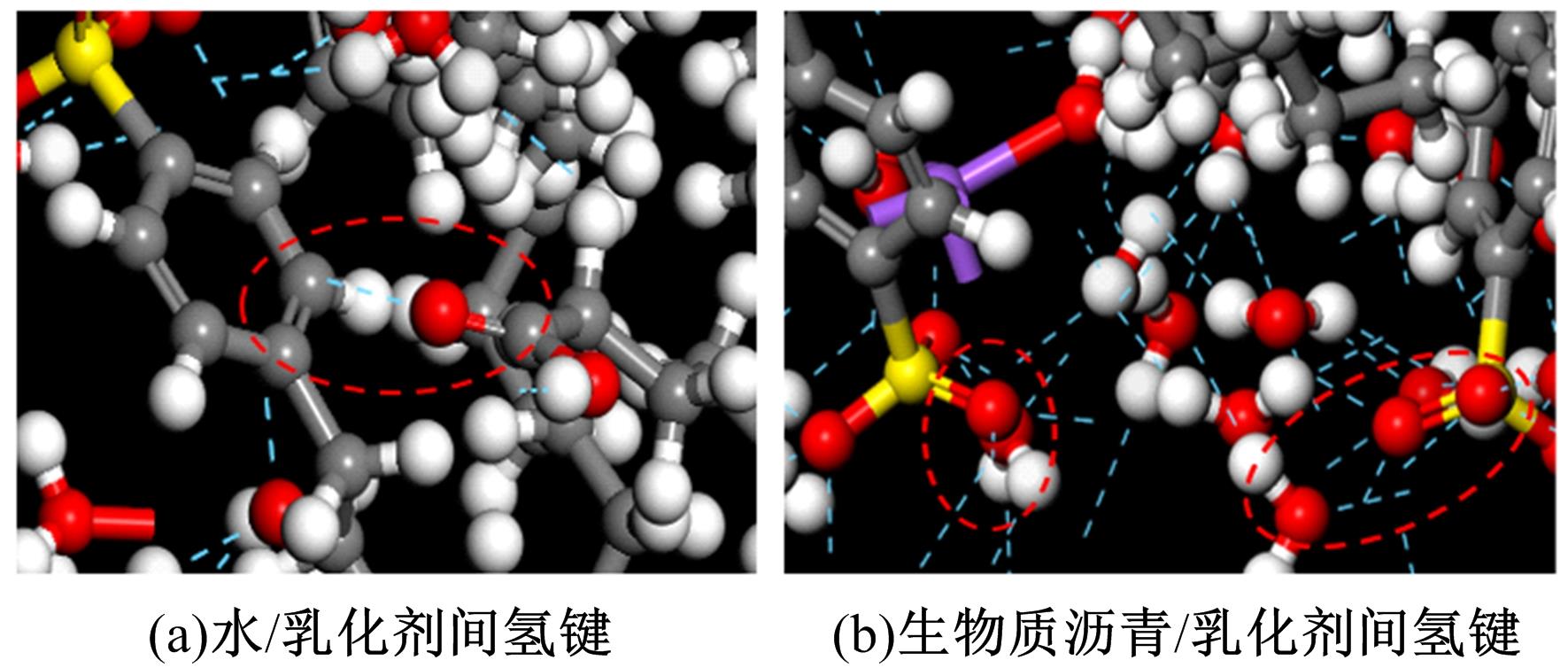
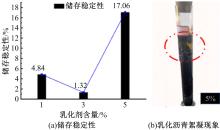
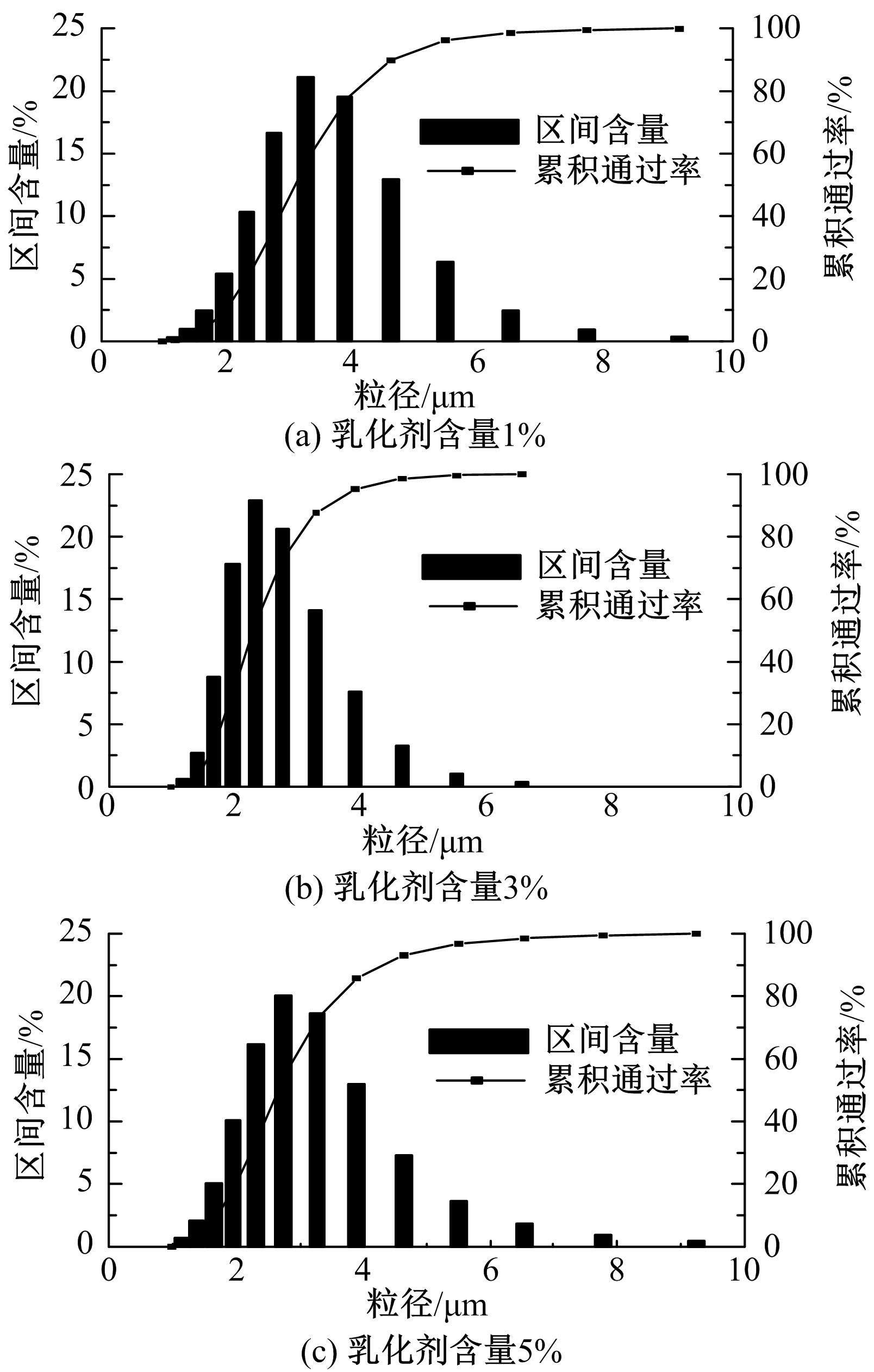
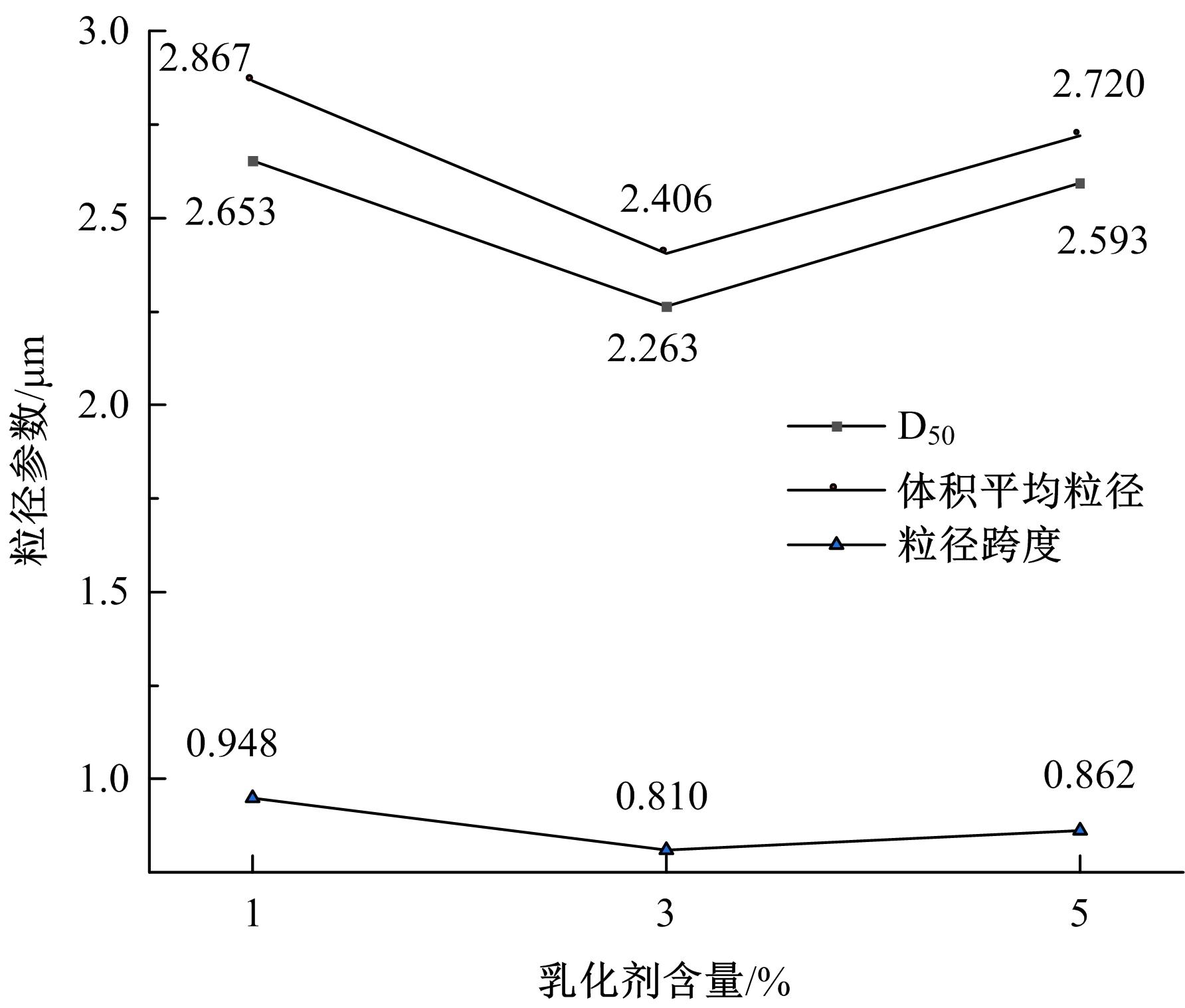
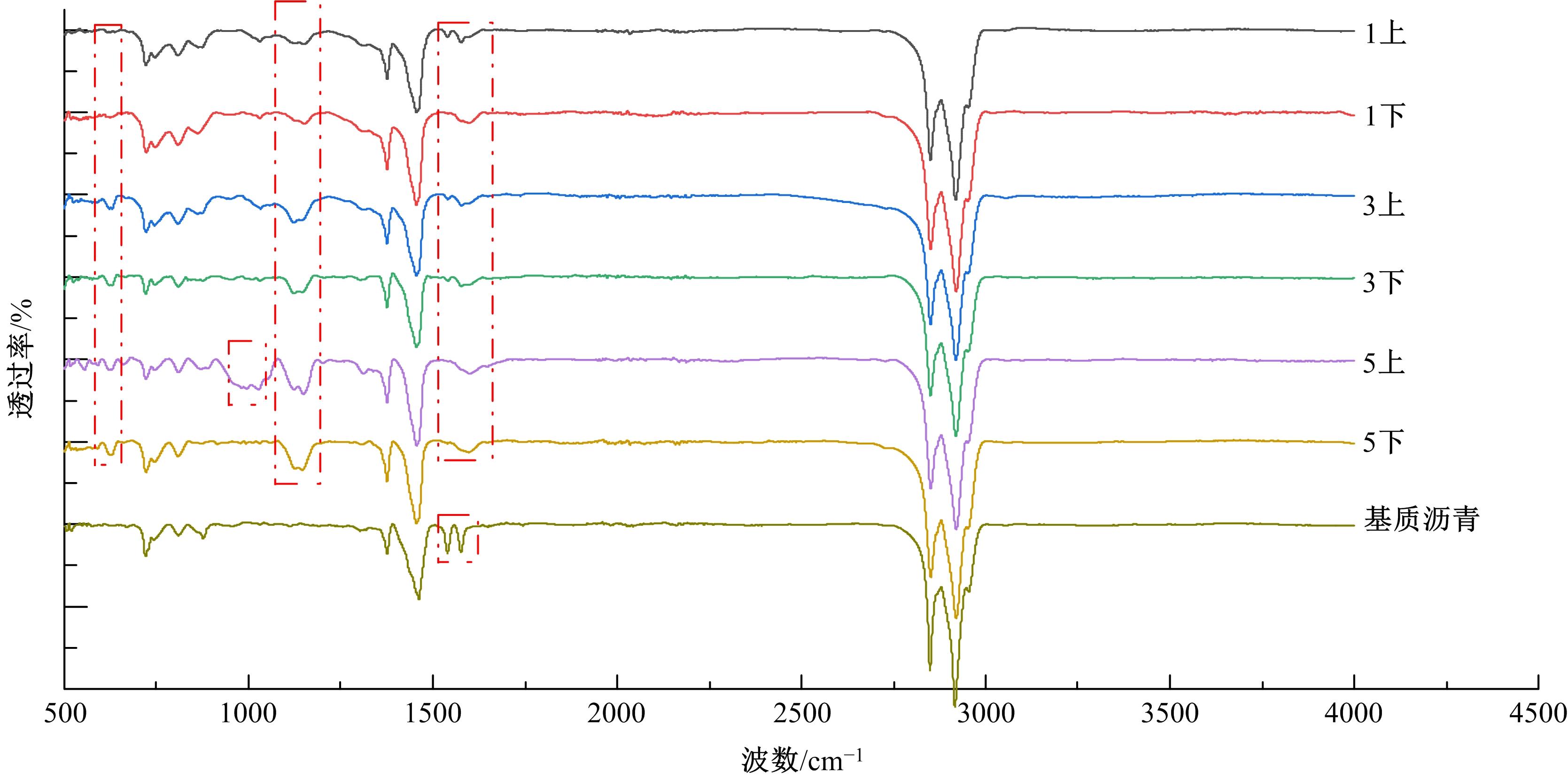
为探究乳化剂掺量对生物质乳化沥青稳定性的影响机理,通过采用Material studio分子动力学模拟及宏微观试验对所制备的1%、3%和5%三种阴离子乳化剂掺量生物质乳化沥青稳定性展开分析。研究结果表明,适量的乳化剂可以降低油水界面间界面张力,扩大两相间的过渡区域,从而阻碍微粒间聚结,降低沉降速度保证乳化稳定性,随着乳化剂增多,会出现团块现象进而导致稳定性下降,由结果可知,3%阴离子乳化剂掺量生物质乳化沥青稳定性最好。
中图分类号:
- A414
| 1 | 屈鑫, 丁鹤洋,王超, 等. 基于分子动力学模拟技术的生物质油改性沥青微观性能研究[J]. 材料导报, 2022(19):1-11. |
| Qu Xin, Ding He-yang, Wang Chao, et al. Research on micro properties of bio-oil modified asphalt based on molecular dynamics simulation technique[J]. Materials Reports, 2022(19): 1-11. | |
| 2 | 李宁利, 朱壮壮, 栗培龙. 生物质油替代路用石油沥青的适用性研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2022, 40(4): 448-454. |
| Li Ning-li, Zhu Zhuang-zhuang, Li Pei-long. Study on applicability of biomass oil to replace asphalt for road use[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2022, 40(4): 448-454. | |
| 3 | 白爱明, 周新星. 生物质油再生沥青的自愈合性能研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 37(8): 29-33. |
| Bai Ai-ming, Zhou Xin-xing. Self-healing properties of bio-oil regenerated asphalt[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2018,37(8): 29-33. | |
| 4 | 张金喜, 张晗. 餐饮废油生物沥青路用性能的试验研究[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2018,44(6): 904-909. |
| Zhang Jin-xi, Zhang Han. Laboratory evaluation of waste cooking oil-based bio-oil modified asphalt binder[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2018, 44(6): 904-909. | |
| 5 | Shi K, Fu Z, Song R, et al. Waste chicken fat oil as a bio-oil regenerator to restore the performance of aged asphalt: rheological properties and regeneration mechanism[J]. Road Materials and Pavement Design,2021: 1-25. |
| 6 | Girimath S, Singh D. Effects of bio-oil on performance characteristics of base and recycled asphalt pavement binders[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 227: 116684. |
| 7 | 罗磊. 沥青与矿料界面相互作用的分子动力学模拟研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学交通学院, 2021. |
| Luo Lei. Molecular dynamics simulation of asphalt-aggregate interfacial interaction[D]. Xi'an: School of Transportation, Chang'an University, 2021. | |
| 8 | 范维玉, 赵品晖, 康剑翘, 等. 分子模拟技术在乳化沥青研究中的应用[J]. 中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 38(6):179-185. |
| Fan Wei-yu, Zhao Pin-hui, Kang Jian-qiao, et al. Application of molecular simulation technology to emulsified asphalt study[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 38(6):179-185. | |
| 9 | 何亮, 李冠男, 郑雨丰, 等. 沥青体系的分子动力学研究进展及展望[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(19): 19083-19093. |
| He Liang, Li Guan-nan, Zheng Yu-feng, et al. Research progress and prospect of molecular dynamics of asphalt systems[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(19): 19083-19093. | |
| 10 | 罗万力. 基于分子动力学模拟的阴离子沥青乳化剂界面活性研究[D]. 重庆:重庆交通大学交通运输学院, 2020. |
| Luo Wan-li. Study on interfacial activity of anionic asphalt emulsifier based on molecular dynamics simulation[D]. Chongqing: College of Traffic and Transportation, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 11 | Yu X, Wang J, Si J, et al. Research on compatibility mechanism of biobased cold-mixed epoxy asphalt binder[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 250:118868. |
| 12 | Yu C, Hu K, Yang Q, et al. Analysis of the storage stability property of carbon nanotube/recycled polyethylene-modified asphalt using molecular dynamics simulations[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(10): 1658. |
| 13 | Li D D, Greenfield M L. Chemical compositions of improved model asphalt systems for molecular simulations[J]. Fuel,2014, 115: 347-356. |
| 14 | Wang Xu. Study of cohesion and adhesion properties of asphalt concrete with molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2016, 112: 161-169. |
| 15 | Fardin, Rajesh. Molecular simulations of asphalt rheology: application of time–temperature superposition principle[J]. Journal of Rheology, 2018, 62(4): 941-954. |
| 16 | 陈华鑫, 贺孟霜, 纪鑫和, 等. 沥青性能与沥青组分的灰色关联分析[J]. 长安大学学报: 自然科学版,2014, 34(3): 1-6. |
| Chen Hua-xin, He Meng-shuang, Ji Xin-he, et al. Gray correlation analysis of asphalt performance and four fractions[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 34(3): 1-6. | |
| 17 | 殷开梁. 分子动力学模拟的若干基础应用和理论[D].杭州: 浙江大学理学院,2006. |
| Yin Kai-liang. Some basic applications and theories of molecular dynamics simulation[D]. Hangzhou: School of Science, Zhejiang University, 2006. | |
| 18 | 丁勇杰. 基于分子模拟技术的沥青化学结构特征研究[D].重庆:重庆交通大学材料科学与工程学院, 2013. |
| Ding Yong-jie. Study on chemical structure characteristics of asphalt based on molecular simulation technology[D]. Chongqing: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2013. | |
| 19 | 李根泽. 基于分子模拟技术的路用沥青感温性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学交通学院, 2019. |
| Li Gen-ze. Study on temperature sensitivity of road asphalt based on molecular simulation technology[D].Changchun: College of Transportation, Jilin University, 2019. | |
| 20 | 康家祥. 非离子型环氧树脂乳化剂的制备及其性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学理学院, 2021. |
| Kang Jia-xiang. Study on the preparation and proper‐ties of non-ionic epoxy resin emulsifiers[D]. Hang‐zhou: College of Science, Zhejiang Sci-tech University, 2021. | |
| 21 | 李媛媛, 桑世林, 王凯杰, 等. 非离子型水性环氧树脂乳化剂的制备与性能研究[J]. 涂料工业, 2021, 51(9): 25-32. |
| Li Yuan-yuan, Sang Shi-lin, Wang Kai-jie, et al. Preparation and properties of nonionic waterborne epoxy resin emulsifier[J]. Paint & Coatings Industry, 2021, 51(9): 25-32. | |
| 22 | 李仙. 氯磺化聚乙烯改性丙烯酸酯水乳液及其相关分子动力学模拟[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学材料科学与工程学院, 2020. |
| Li Xian. Chlorosulfonated rubber modified acrylate water emulsion and its related molecular simulation[D]. Nanjing: School of Materials Science and Engineering, Nanjing Forestry University, 2020. | |
| 23 | 苏曼曼, 张洪亮, 张永平, 等. SBS与沥青相容性及力学性能的分子动力学模拟[J]. 长安大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 37(3): 24-32. |
| Su Man-man, Zhang Hong-liang, Zhang Yong-ping, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of compatibility and mechanical properties of sbs and asphalt[J]. Journal of Chang'an University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 37(3): 24-32. | |
| 24 | 王岚, 张乐, 刘旸. 基于分子动力学的胶粉改性沥青中胶粉与沥青相容性研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2018, 21(4): 689-694. |
| Wang Lan, Zhang Le, Liu Yang. Compatibility of rubber powder and asphalt in rubber powder modified asphalt by molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2018, 21(4): 689-694. | |
| 25 | Xu Tao, Li Chi-xuan, Fan Su-ying. Method for evaluating compatibility between sbs modifier and asphalt matrix using molecular dynamics models[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2021, 33(8): 4021207. |
| 26 | 孔祥军. 长链烷基咪唑啉界面活性的构效关系研究[D]. 青岛:中国石油大学(华东)化学工程与环境学院, 2016. |
| Kong Xiang-jun. Study on structure-activity relationship of interfacial activity of long chain alkyl imidazoline[D]. Qingdao: College of Chemical Engineering and Environment), China University of Petroleum (East China), 2016. | |
| 27 | Rivera J L, McCabe C, Cummings P T. Molecular simulations of liquid-liquid interfacial properties: Watern-alkane and water-methanoln-alkane systems[J]. Physical Review E, 2003, 67(1): 011603. |
| 28 | 于立军. 阴离子表面活性剂在油水界面吸附行为的实验和理论研究[D]. 青岛:中国石油大学(华东)材料科学与工程学院, 2011. |
| Yu Li-jun. Experimental and theoretical study on adsorption behavior of anionic surfactants at oil-water interface[D]. Qingdao: School of Materials Science and Engineering, China University of Petroleum (East China), 2011. | |
| 29 | 李登辉, 李丽洁, 兰贯超, 等. SBS增韧石蜡/增塑剂共混相容性的分子动力学模拟[J]. 含能材料, 2018, 26(3): 223-229. |
| Li Deng-hui, Li Li-jie, Lan Guan-chao, et al. Molecular dynamics simulation of sbs toughened paraffin/plasticizer blend compatibility[J]. Energetic Materials, 2018, 26(3): 223-229. | |
| 30 | 武建民, 杜本发, 李洪珍. 基于乳化沥青颗粒平均粒径的透层油性能评价方法[J]. 公路, 2016, 61(7): 265-269. |
| Wu Jian-min, Du Ben-chao, Li Hong-zhen. Performance evaluation method of permeable oil based on average particle size of emulsified asphalt[J]. Highway, 2016, 61(7): 265-269. | |
| 31 | 何丽红, 温仙仙, 侯艺桐, 等. 阴离子乳化沥青粒径大小及分布影响因素分析[J]. 重庆交通大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 40(6): 99-104. |
| He Li-hong, Wen Xian-xian, Hou Yi-tong, et al. Influence factors of particle size and distribution of anionic emulsified asphalt[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 40(6): 99-104. | |
| 32 | 陶翔. 新型季铵盐沥青乳化剂的合成与性能研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学化学与化工学院, 2015. |
| Tao Xiang. Synthesis and properties of novel quaternary ammonium salt asphalt emulsifier[D]. Jinan: Shandong: School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Shandong University, 2015. | |
| 33 | Liu Hou. Influence of storage conditions on the stability of asphalt emulsion[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology,2017, 35(12): 1217-1223. |
| 34 | Kiihnl L, Braham A F. Developing a particle size specification for asphalt emulsion[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 293: 123414. |
| 35 | 张虎. 乳化沥青颗粒粒径分布对沥青性能的影响[J]. 交通世界, 2016(19): 110-111. |
| Zhang Hu. Influence of emulsified asphalt particle size distribution on asphalt properties[J]. Transportation World, 2016(19): 110-111. | |
| 36 | 韦万峰, 郭鹏, 唐伯明. 再生沥青混合料新-旧沥青扩散混合效率研究综述[J]. 材料导报, 2017, 31(11): 109-114. |
| Wei Wan-feng, Guo Peng, Tang Bo-ming. Review of the research on diffusion efficiency of virgin-aged asphalt in recycled asphalt mixture[J]. Materials Reports, 2017, 31(11): 109-114. | |
| 37 | 全秀洁. 亲水基团对十二烷基阴离子乳化沥青稳定性及破乳过程的影响[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学交通运输学院, 2021. |
| Quan Xiu-jie. Effect of hydrophilic groups on stability and demulsification of dodecyl anionic emulsified asphalt[D]. Chongqing: College of Traffic and Transportation, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2021. | |
| 38 | 周艺, 李泉, 童瑶, 等. 再生剂对SBS改性沥青宏观性能与微观结构的影响[J]. 公路, 2022(6): 302-309. |
| Zhou Yi, Li Quan, Tong Yao, et al. Effect of regenerant on macroproperties and microstructure of sbs modified asphalt[J]. Highway, 2022(6): 302-309. | |
| 39 | 陈江,李响,韩路, 等. 废胎胶粉对沥青的改性机理研究[J]. 山西建筑, 2021, 47(1): 110-111, 196. |
| Chen Jiang, Li Xiang, Han Lu, et al. Study on modification mechanism of asphalt by waste tire rubber powder[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2021, 47(1): 110-111, 196. |
| [1] | 王艳敏,张伟琦,段广鑫,葛杨. 电子节气门的连续非奇异终端滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2127-2135. |
| [2] | 杨柳,王创业,王梦言,程阳. 设置自动驾驶小客车专用车道的六车道高速公路交通流特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2043-2052. |
| [3] | 周正峰,于晓涛,陶雅乐,郑茂,颜川奇. 基于灰色关联分析的树脂与弹性体高黏沥青高温性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2078-2088. |
| [4] | 马涛,马源,黄晓明. 基于多元非线性回归的智能压实关键参数最优解[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2067-2077. |
| [5] | 魏海斌,韩栓业,毕海鹏,刘琼辉,马子鹏. 智能感知道路主动除冰雪系统及实验技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1411-1417. |
| [6] | 汪少华,储堃,施德华,殷春芳,李春. 基于有限时间扩张状态观测的HEV鲁棒复合协调控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1272-1281. |
| [7] | 郑睢宁,何锐,路天宇,徐紫祎,陈华鑫. RET/胶粉复合改性沥青制备及其混合料性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1381-1389. |
| [8] | 关博文,邸文锦,王发平,吴佳育,张硕文,贾治勋. 干湿循环与交变荷载作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1112-1121. |
| [9] | 杨帆,李琛琛,李盛,刘海伦. 温缩作用下双层连续配筋混凝土路面配筋率设计参数对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1122-1132. |
| [10] | 何德峰,周丹,罗捷. 跟随式车辆队列高效协同弦稳定预测控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 726-734. |
| [11] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [12] | 魏海斌,马子鹏,毕海鹏,刘汉涛,韩栓业. 基于力学响应分析方法的导电橡胶复合路面铺装技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 531-537. |
| [13] | 彭勇,章秀芳,郭泽宇,陆学元,李彦伟. 离散元法分析集料接触特性对沥青混合料剪切疲劳寿命的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 178-187. |
| [14] | 孙雅珍,郑直,黄伟明,王金昌. 基于状态空间法的含裂缝水泥路面结构分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 188-196. |
| [15] | 时成林,王勇,吴春利,宋文祝. 路堤挡土墙主动土压力计算方法修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1394-1403. |
|
||