吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 2203-2212.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20220394
• • 上一篇
适用于质子交换膜燃料电池系统的高阶滑模观测器
- 1.西南交通大学 机械工程学院,成都 610036
2.中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司,天津 300300
High⁃order sliding mode observer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell system
Cheng LI1,2( ),Hao JING1,Guang-di HU1,Xiao-dong LIU1,Biao FENG1
),Hao JING1,Guang-di HU1,Xiao-dong LIU1,Biao FENG1
- 1.School of Mechanical Engineering,Southwest Jiaotong University,Chengdu 610036,China
2.China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co. ,Ltd. ,Tianjin 300300,China
摘要:
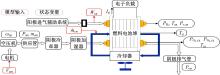
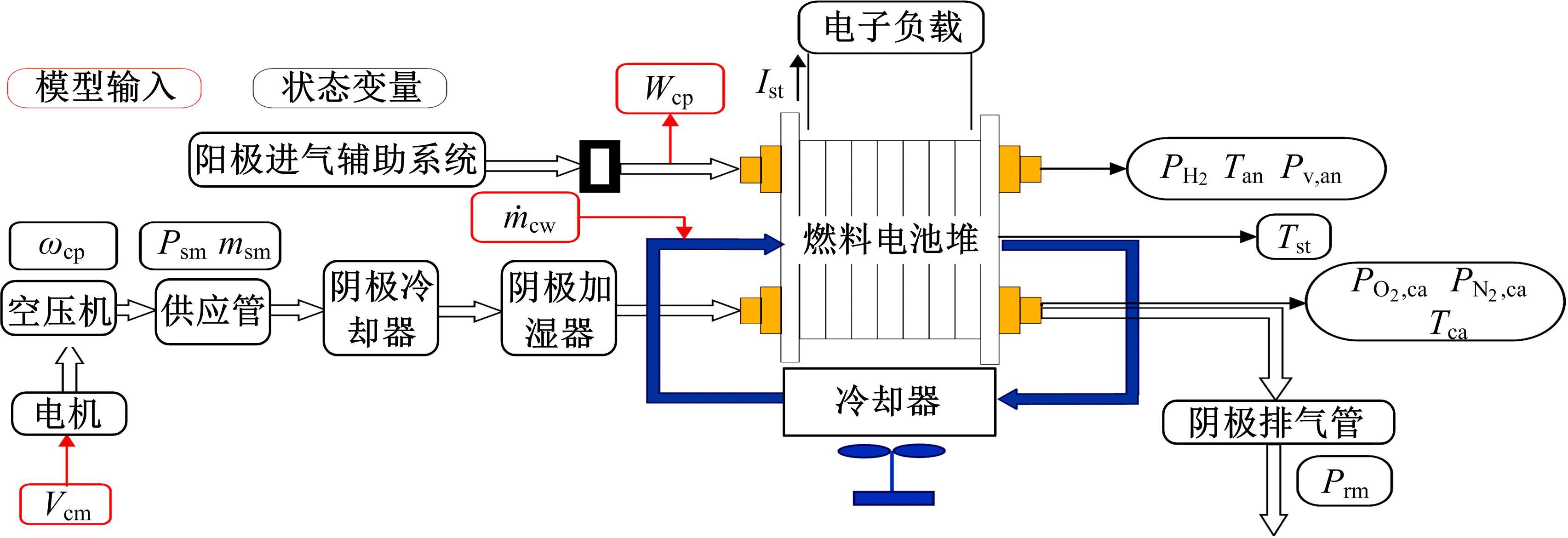
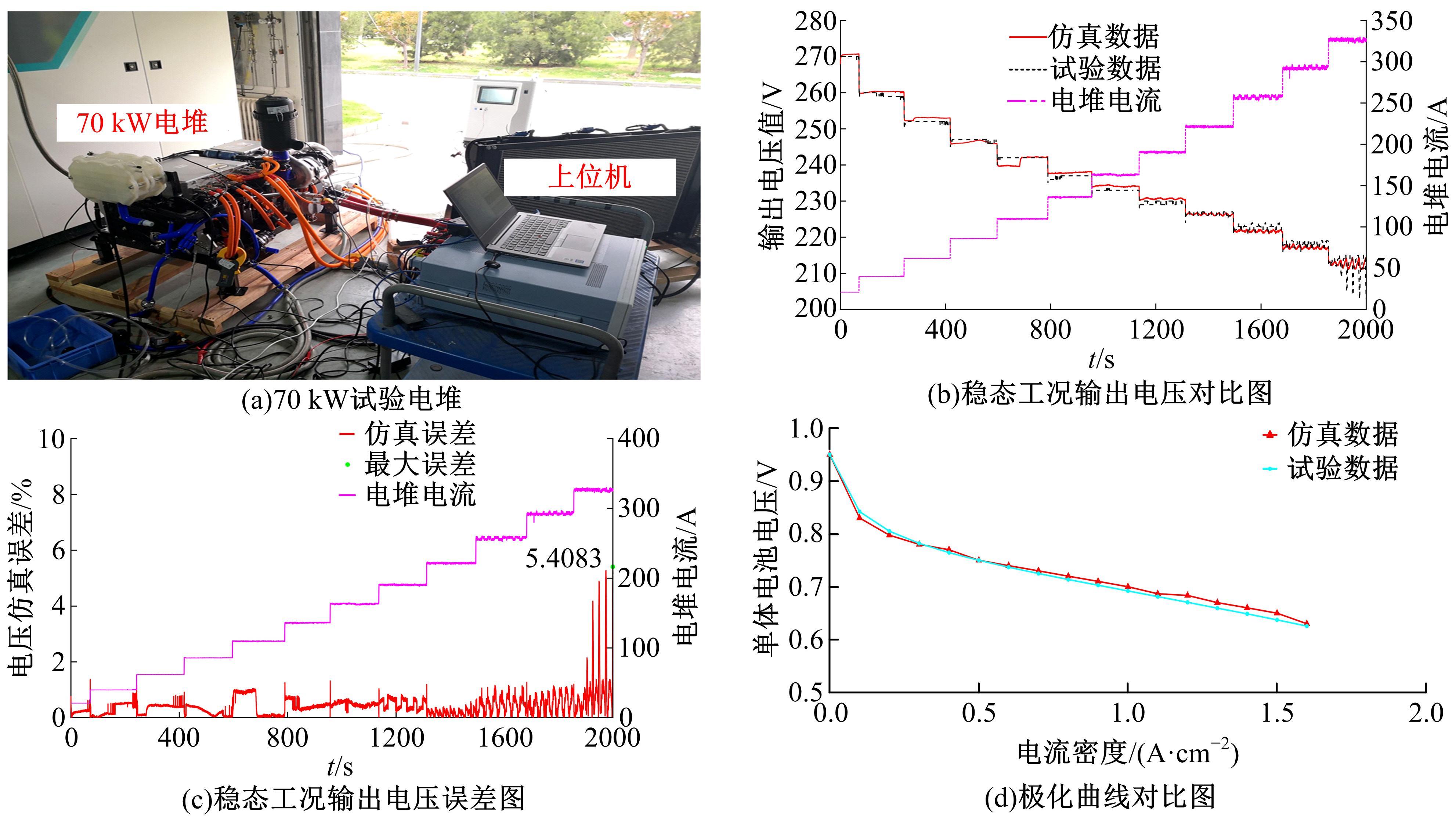
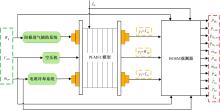
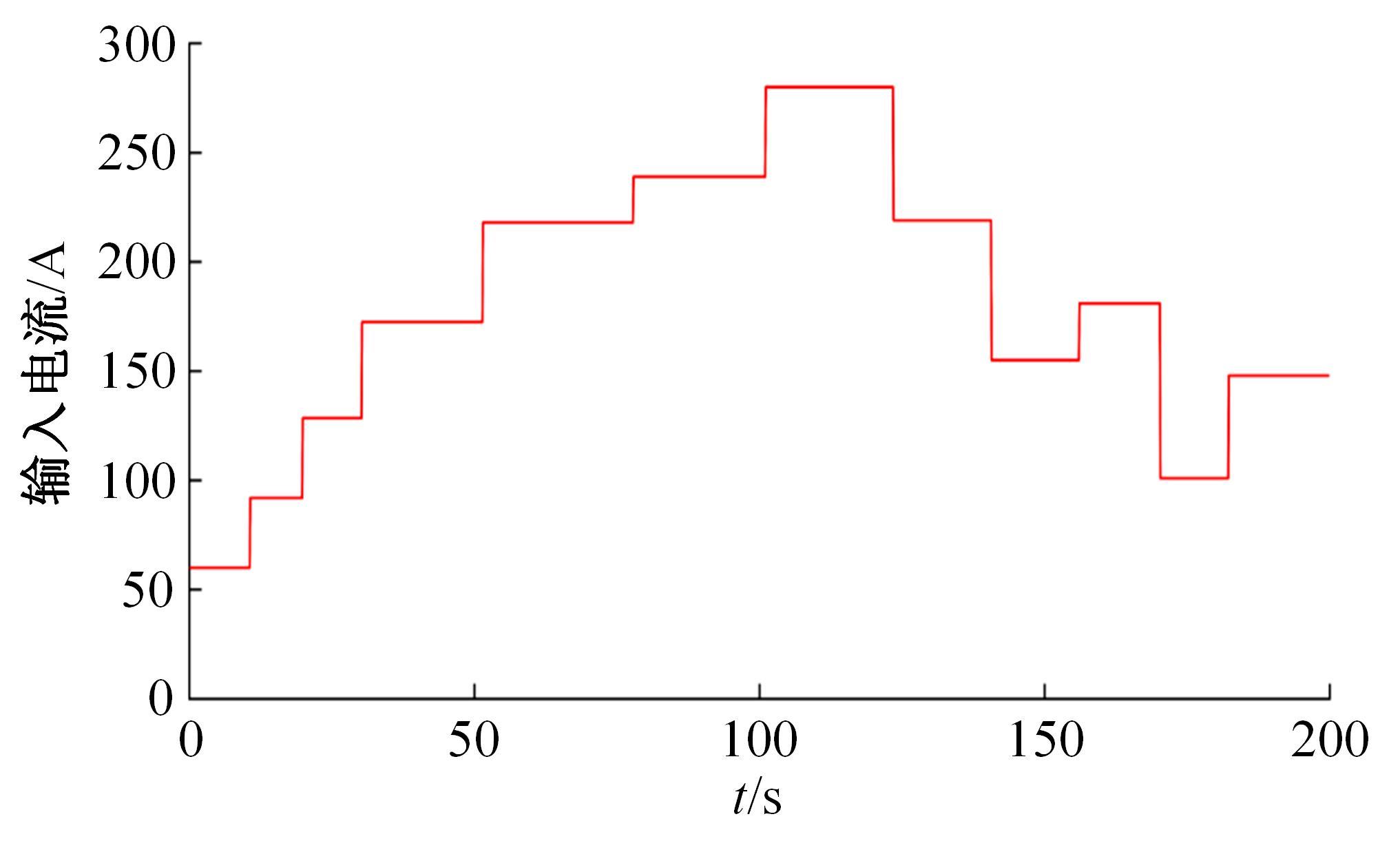
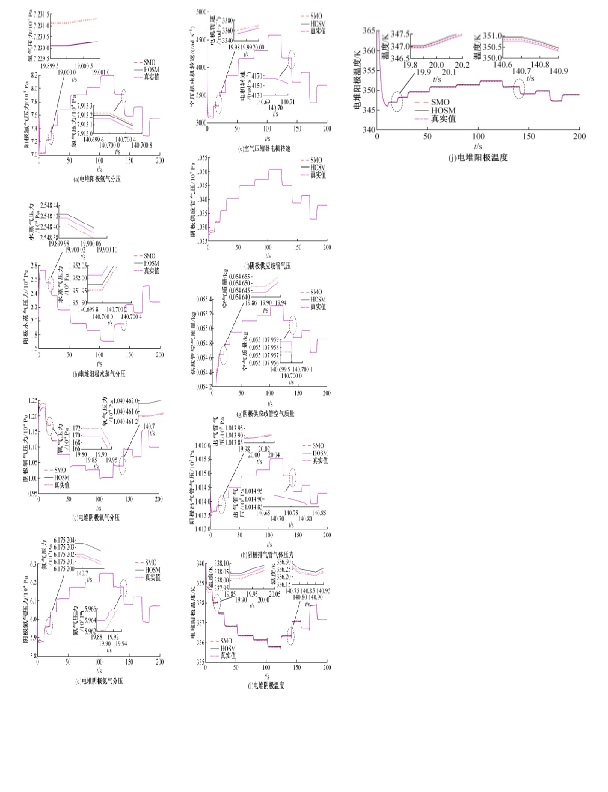
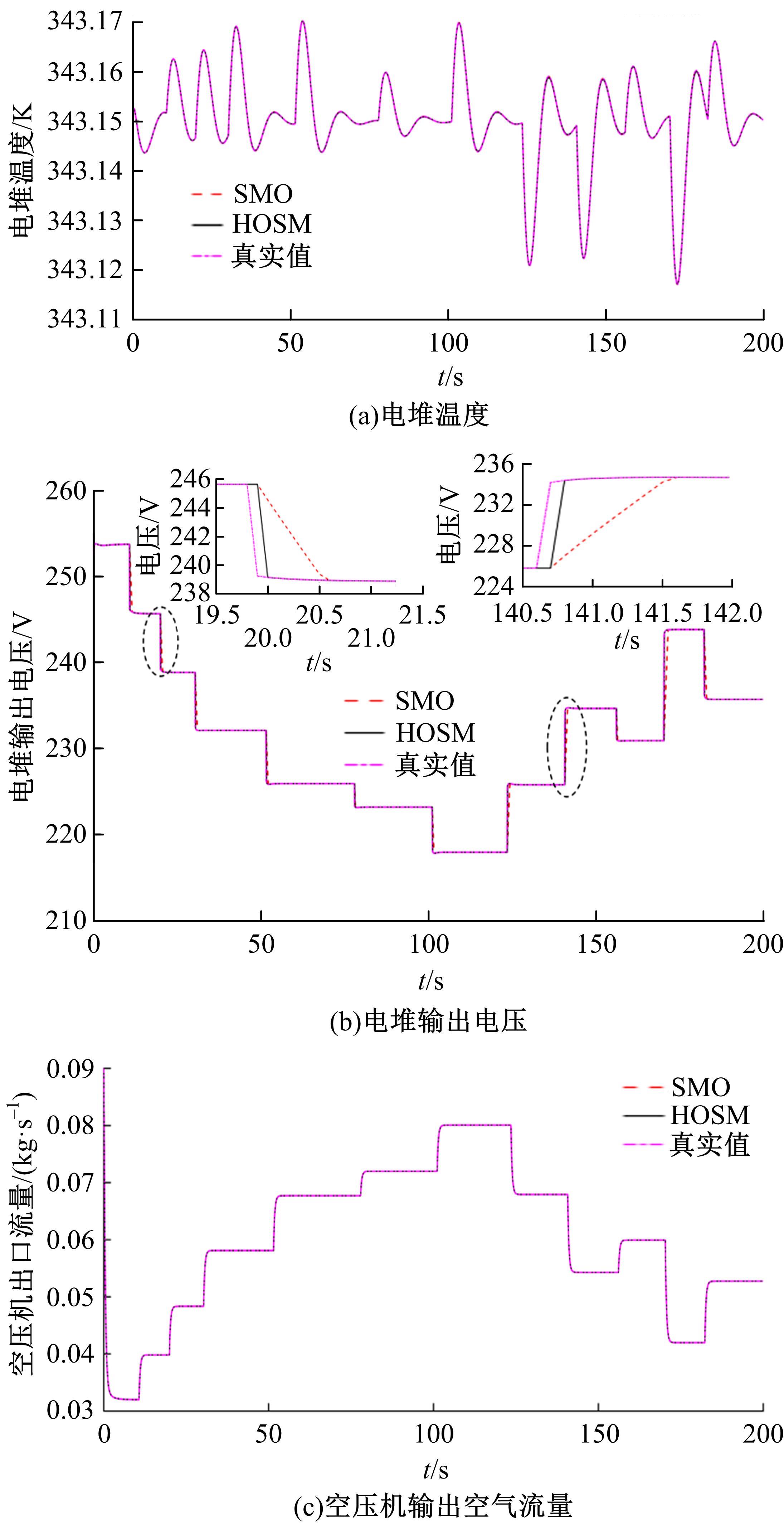
针对质子交换膜燃料电池(PEMFC)系统内部状态变量难以通过传感器直接测量,导致不能对PEMFC系统进行故障诊断和设计基于模型的控制器的问题,设计了高阶滑模(HOSM)观测器。首先,搭建了适用于观测的11阶阳极死端PEMFC系统模型。然后,在该模型的基础上,通过HOSM算法对传感器测量值(电堆电压、空压机出口流量以及电堆温度)与估计值之间的误差进行调节,设计了HOSM观测器。最后,将本文HOSM观测器性能与传统滑模观测器性能进行了仿真实验对比。通过对比观测效果图以及平方误差积分可知:本文观测器能够准确地观测各状态量,并且观测性能更优。
中图分类号:
- TM911.4
| 1 | 张鉴,华青松,郑莉莉, 等.质子交换膜燃料电池建模综述[J]. 电源技术, 2019, 43(6): 1051-1053, 1082. |
| Zhang Jian, Hua Qing-song, Zheng Li-li, et al. A review of proton exchange membrane fuel cell modeling[J]. Power Technology, 2019, 43(6): 1051-1053, 1082. | |
| 2 | 文泽军, 闵凌云, 谢翌, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池建模与控制的综述[J]. 电源技术, 2018, 42(11): 1757-1760. |
| Wen Ze-jun, Min Ling-yun, Xie Yi, et al. A review on modeling and control of proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Power Technology, 2018, 42(11): 1757-1760. | |
| 3 | Deng H, Li Q, Liu Z, et al. Low frequency current ripple mitigation of two stage three-phase PEMFC generation systems[J]. Journal of Power Electronics, 2016, 16(6): 2243-2257. |
| 4 | 王哲, 谢怡, 臧鹏飞, 等. 基于极小值原理的燃料电池客车能量管理策略[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(1): 36-43. |
| Wang Zhe, Xie Yi, Zang Peng-fei, et al. Energy management strategy for fuel cell buses based on the principle of minimal value[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 36-43. | |
| 5 | 李飞, 赵冬冬, 皇甫宜耿, 等. 适用于PEMFC系统状态估计的鲁棒非线性观测器[J]. 电源学报, 2019, 17(2): 19-25. |
| Li Fei, Zhao Dong-dong, Huangfu Yi-geng, et al. Robust nonlinear observer for state estimation of PEMFC systems[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 17(2): 19-25. | |
| 6 | Yuan H, Dai H F, Wei X Z, et al. Model-based observers for internal states estimation and control of proton exchange membrane fuel cell system: a review[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 468: No. 228376. |
| 7 | Pukrushpan J T, Stefanopoulou A G, Peng H. Control of fuel cell breathing[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2004, 24(2): 30-46. |
| 8 | Wang Y X, Chen Q, Ou K, et al. Time delay thermal control of a compact proton exchange membrane fuel cell against disturbances and noisy measurements[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 244: No. 114444. |
| 9 | 葛乐, 吉佩丝, 杨忠, 等. 基于扩张状态观测器的PEMFC电堆温度控制[J].电源技术, 2016, 40(5): 1020-1022, 1032. |
| Ge Le, Ji Pei-si, Yang Zhong, et al. Temperature control of PEMFC power stack based on expansion state observer[J]. Power Technology, 2016, 40(5): 1020-1022, 1032. | |
| 10 | Rakhtala S M, Noei A R, Ghaderi R, et al. Control of oxygen excess ratio in a PEM fuel cell system using high-order sliding-mode controller and observer[J]. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering & Computer Sciences, 2015, 23(1): 255-278. |
| 11 | Pilloni A, Pisano A, Usai E. Observer-based air excess ratio control of a PEM fuel cell system via high-order sliding mode[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(8): 5236-5246. |
| 12 | 邓惠文, 李奇, 崔幼龙, 等. 基于多边界层的RNO质子交换膜燃料电池发电系统状态估计研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2019, 39(5): 1532-1543. |
| Deng Hui-wen, Li Qi, Cui You-long, et al. Study on state estimation of RNO proton exchange membrane fuel cell power generation system based on multiple boundary layers[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2019, 39(5): 1532-1543. | |
| 13 | Piffard M, Gerard M, Da Fonseca R, et al. Sliding mode observer for proton exchange membrane fuel cell: automotive application[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 388: 71-77. |
| 14 | Liu J X, Lin W Y, Alsaadi F, et al. Nonlinear observer design for PEM fuel cell power systems via second order sliding mode technique[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 168: 145-151. |
| 15 | Sankar K, Jana A K. Nonlinear multivariable sliding mode control of a reversible PEM fuel cell integrated system[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2018, 171: 541-565. |
| 16 | Sankar K, Jana A K. Nonlinear control of a PEM fuel cell integrated system with water electrolyzer[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2021, 171: 150-167. |
| 17 | 洪凌. 车用燃料电池发电系统氢气回路控制[D].杭州:浙江大学控制科学与工程学院,2017. |
| Hong Ling. Hydrogen circuit control for automotive fuel cell power generation system[D]. Hangzhou: School of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, 2017. | |
| 18 | Li D Z, Li C, Gao Z Q, et al. On active disturbance rejection in temperature regulation of the proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 283: 452-463. |
| 19 | Zhao X Q, Li Y K, Liu Z X, et al. Thermal management system modeling of a water-cooled proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(7): 3048-3056. |
| 20 | Kunusch C, Puleston P F, Mayosky M A, et al. Control-oriented modeling and experimental validation of a PEMFC generation system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2011, 26(3): 851-861. |
| 21 | Wang Y, Li H, Feng H, et al. Simulation study on the PEMFC oxygen starvation based on the coupling algorithm of model predictive control and PID[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 249: No. 114851. |
| [1] | 王克勇,鲍大同,周苏. 基于数据驱动的车用燃料电池故障在线自适应诊断算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2107-2118. |
| [2] | 曹起铭,闵海涛,孙维毅,于远彬,蒋俊宇. 质子交换膜燃料电池低温启动水热平衡特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2139-2146. |
| [3] | 杨子荣,李岩,冀雪峰,刘芳,郝冬. 质子交换膜燃料电池运行工况参数敏感性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1971-1981. |
| [4] | 隗海林,王泽钊,张家祯,刘洋. 基于Avl-Cruise的燃料电池汽车传动比及能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [5] | 肖阳,王洁,刘孟军,杨发庆,张天瑶,兰巍. 质子交换膜燃料电池气体扩散层的力学改进模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2147-2155. |
| [6] | 刘岩,丁天威,王宇鹏,都京,赵洪辉. 基于自适应控制的燃料电池发动机热管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2168-2174. |
| [7] | 张佩,王志伟,杜常清,颜伏伍,卢炽华. 车用质子交换膜燃料电池空气系统过氧比控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [8] | 高金武,王义琳,刘华洋,王艺达. 基于滑模观测器的质子交换膜燃料电池阴极进气系统解耦控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2156-2167. |
| [9] | 陈凤祥,张俊宇,裴冯来,侯明涛,李其朋,李培庆,王洋洋,张卫东. 质子交换膜燃料电池氢气供应系统的建模及匹配设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1982-1995. |
| [10] | 刘镇宁,江柯,赵韬韬,樊文选,卢国龙. 大功率质子交换膜燃料电池测试系统的开发及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2025-2033. |
| [11] | 池训逞,侯中军,魏伟,夏增刚,庄琳琳,郭荣. 基于模型的质子交换膜燃料电池系统阳极气体浓度估计技术综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [12] | 裴尧旺,陈凤祥,胡哲,翟双,裴冯来,张卫东,焦杰然. 基于自适应LQR控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [13] | 张恒,詹志刚,陈奔,隋邦杰,潘牧. 气体扩散层各向异性传输特性的孔尺度模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2055-2062. |
| [14] | 胡广地,景浩,李丞,冯彪,刘晓东. 基于高阶燃料电池模型的多目标滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2182-2191. |
| [15] | 陈凤祥,伍琪,李元松,莫天德,李煜,黄李平,苏建红,张卫东. 2.5吨燃料电池混合动力叉车匹配、仿真及优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2044-2054. |
|
||