吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1070-1077.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210782
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
交通需求估计下的检测器布局和手机数据扩样推断
- 1.江苏大学 汽车与交通工程学院, 江苏 镇江 212013
2.南京林业大学 汽车与交通工程学院, 南京 210037
3.公安部道路交通安全研究中心, 北京 100062
Sensor deployment strategy and expansion inference of mobile phone data for traffic demand estimation
Chao SUN1( ),Hao-wei YIN1,Wen-yun TANG2,Zhao-ming CHU3
),Hao-wei YIN1,Wen-yun TANG2,Zhao-ming CHU3
- 1.School of Automotive and Traffic Engineering,Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang 212013,China
2.College of Automobile and Traffic Engineering,Nanjing Forestry University,Nanjing 210037,China
3.Research Institute for Road Safety of MPS,Beijing 100062,China
摘要:
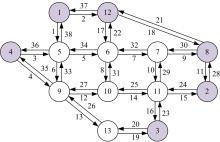
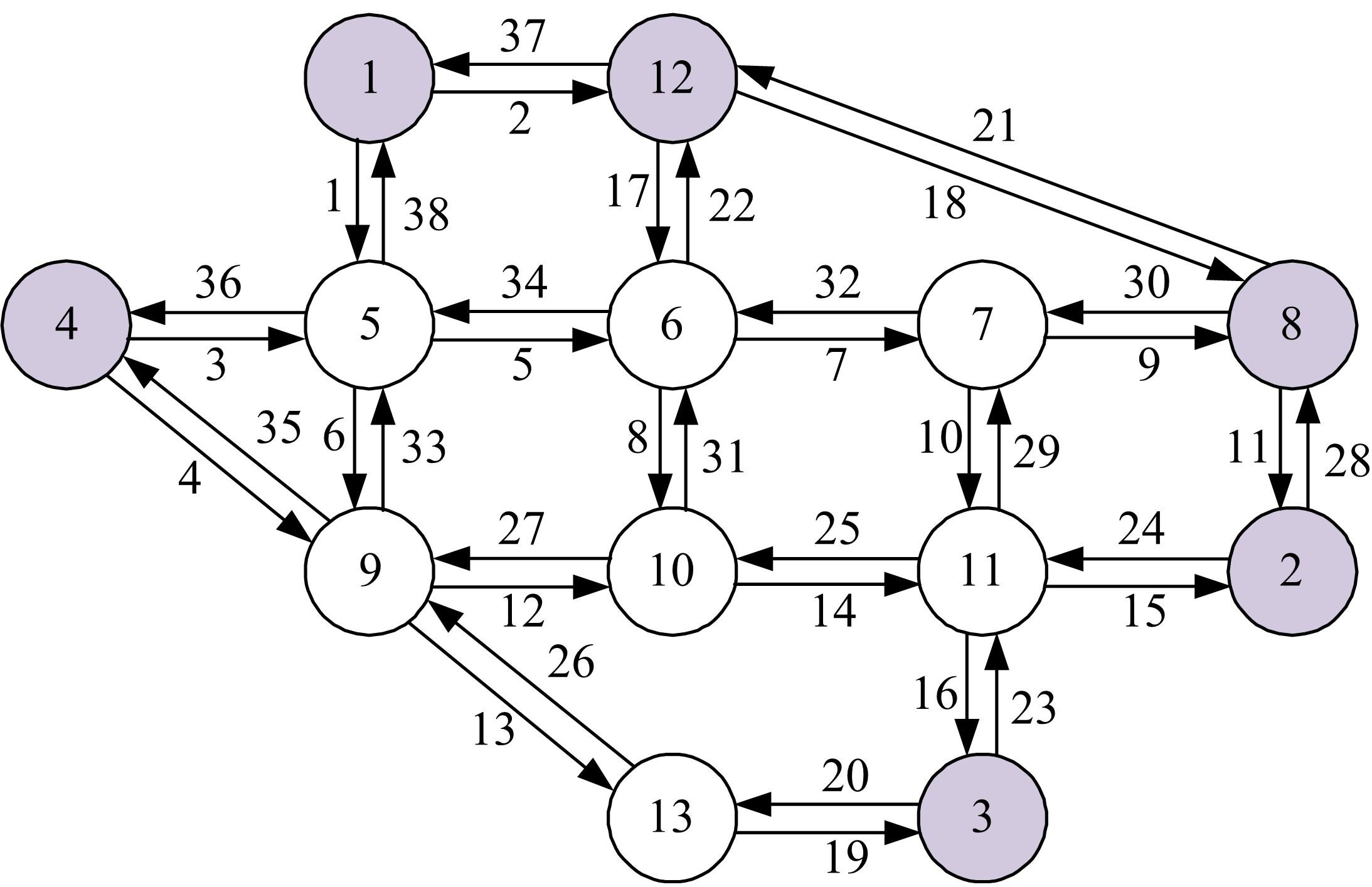
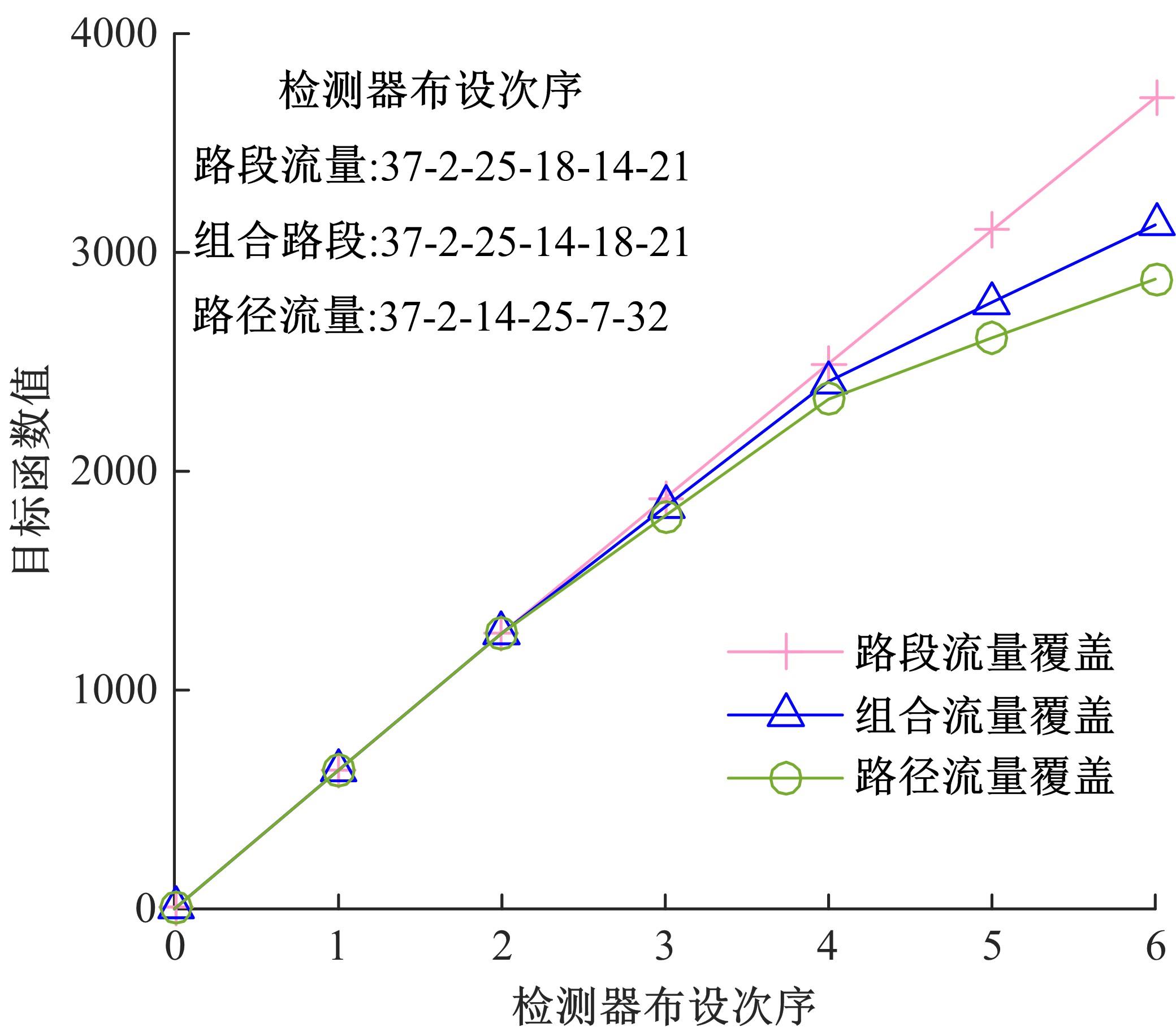
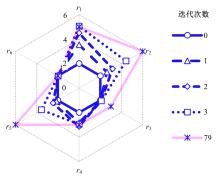
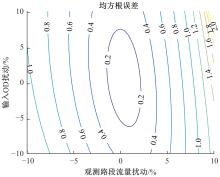
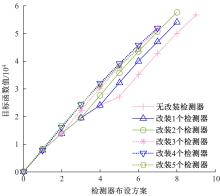
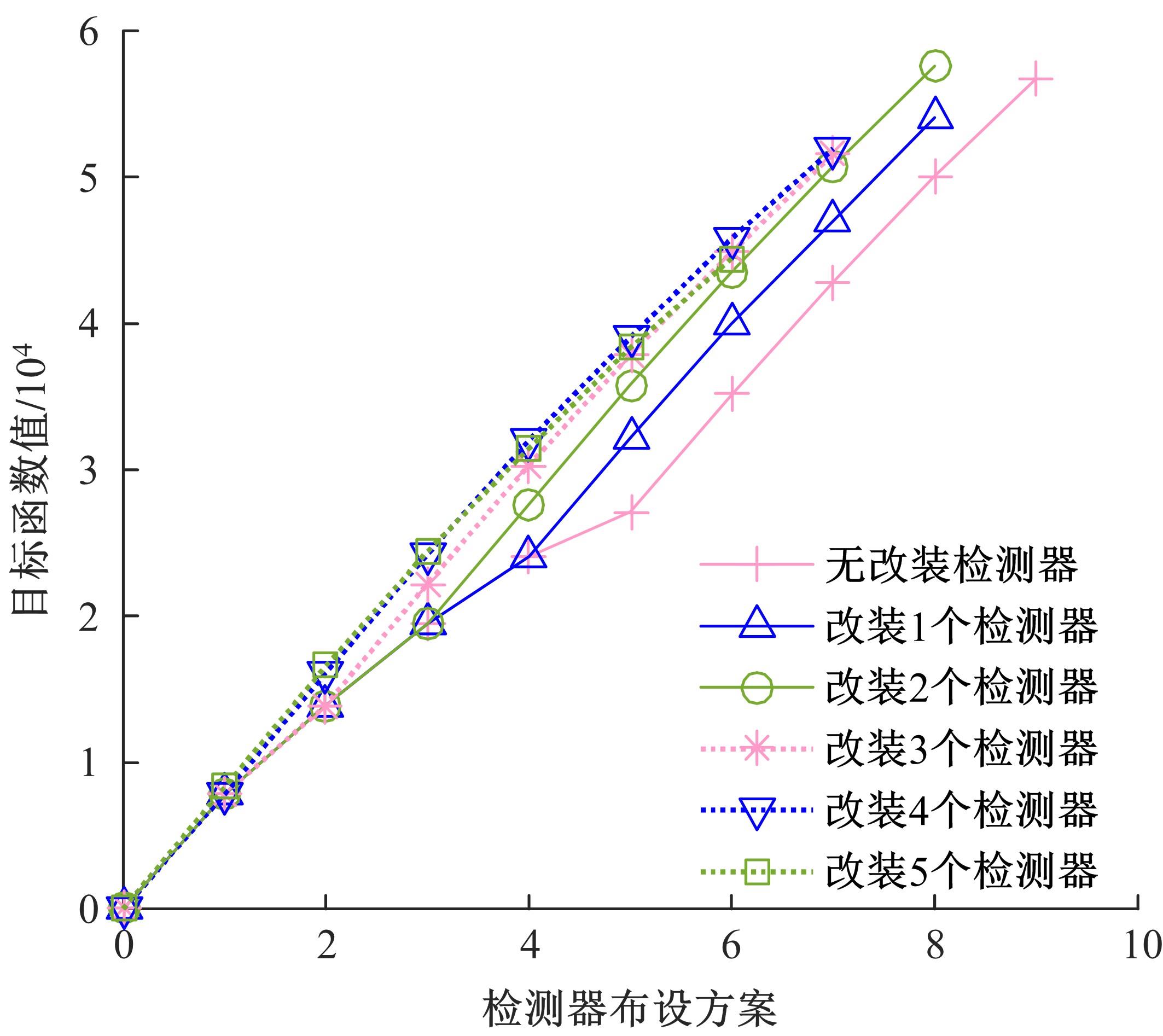
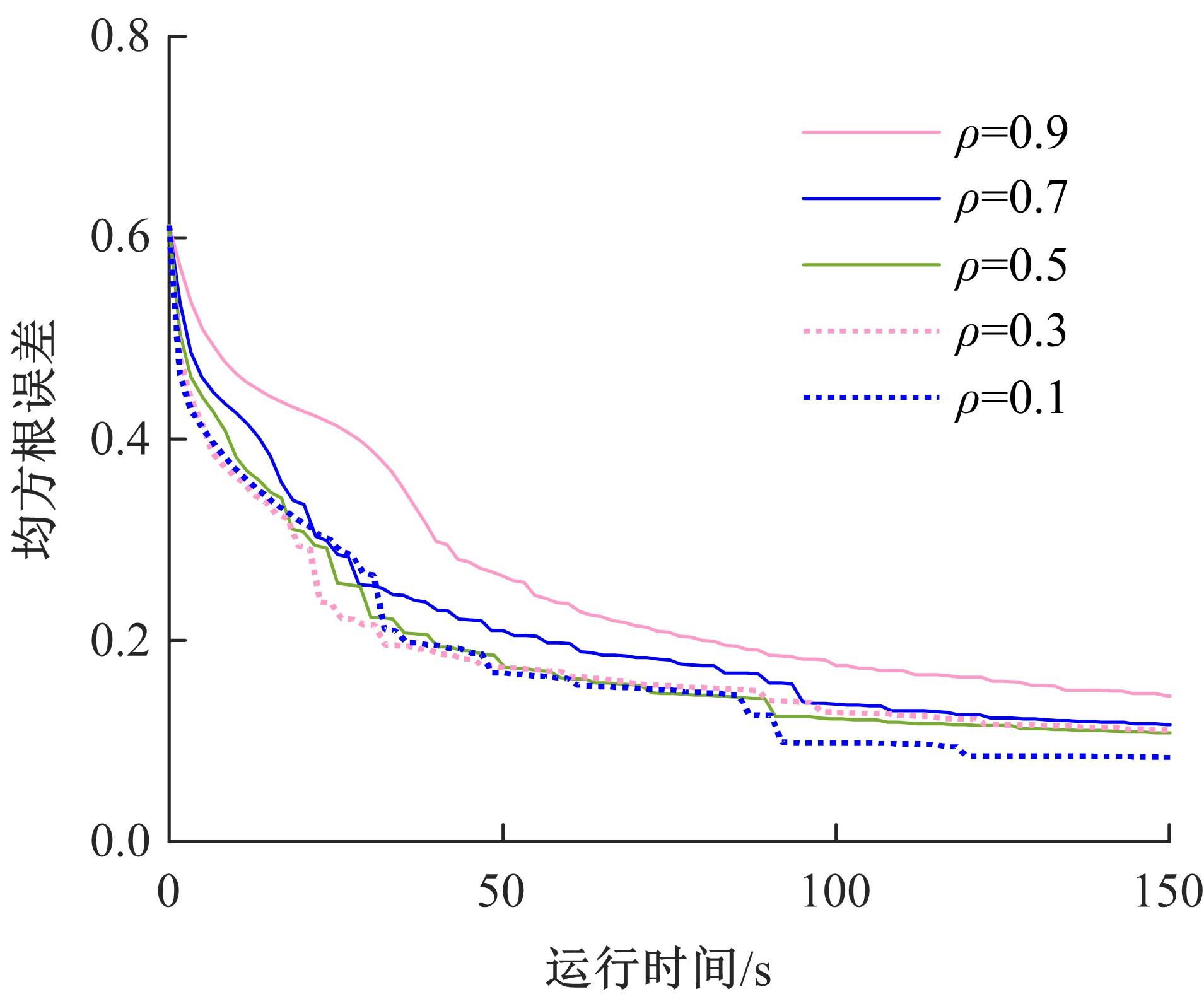
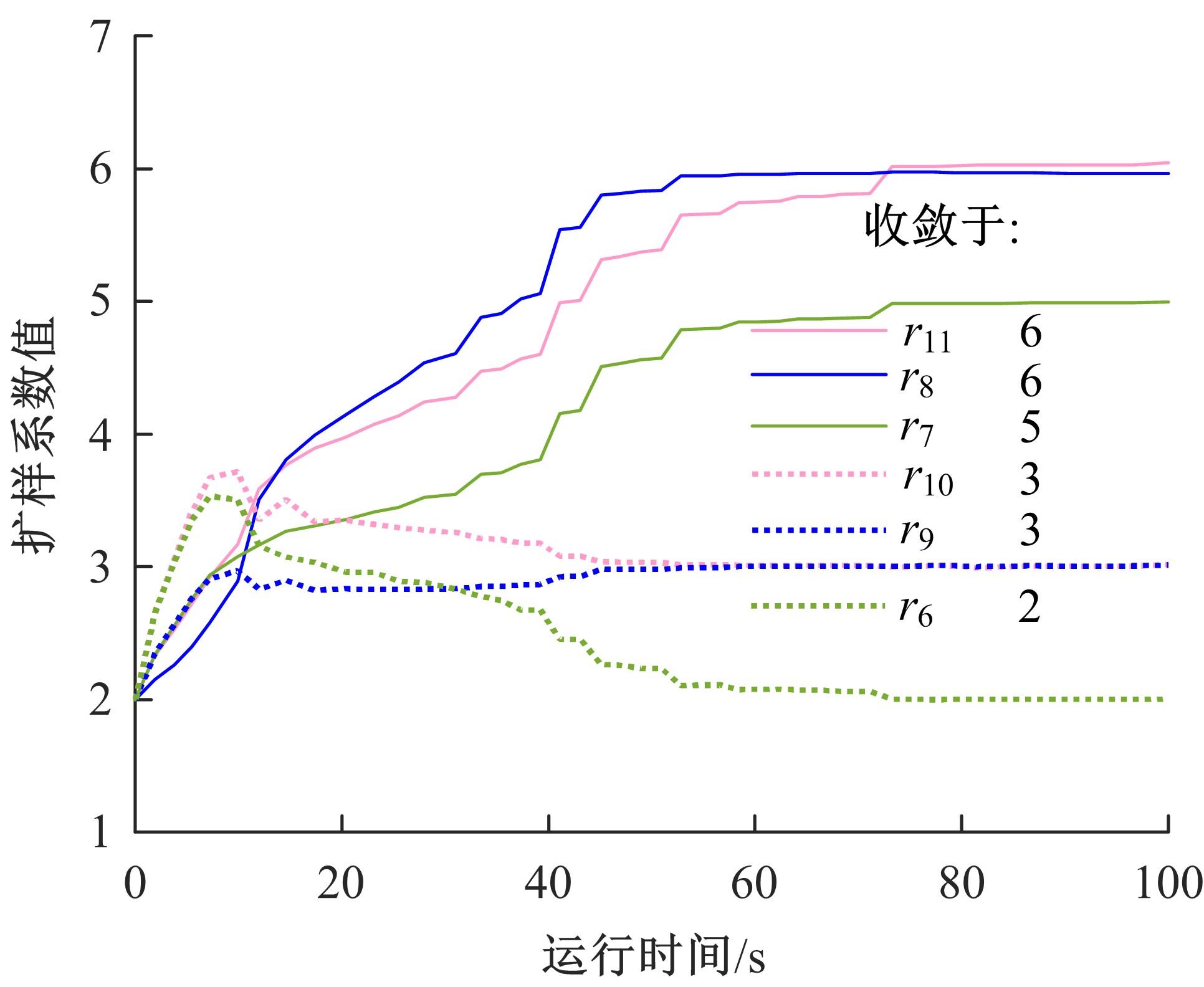
基于出行样本数据估计的城市交通起讫点(OD)需求需要进一步扩张到全体出行者数量上,运用数学规划理论研究了检测器布局策略和扩样系数推断方法。考虑路段和路径覆盖信息最大原则,提出检测器布局模型以确定最优的检测器布设数量和位置。根据布设检测器上的观测路段流量,建立扩样系数推断双层规划模型,其中上层目标函数最小化观测流量与待估流量之间的偏差,约束为扩样系数、OD需求和路段流量之间的解析关系,下层采用随机用户均衡分配获取OD-路段关联比例。设计了逐次动态识别检测器和迭代算法分别求解检测器布局与扩样系数推断模型。通过算例表明,整合的检测器布局与扩样系数推断模型估计的扩样系数精度为0.01,建立的检测器布局模型可以用来确定改装检测器的最优策略,设计的算法均可以快速收敛于均衡解。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Chen X, Peng L, Zhang M, et al. A public traffic demand forecast method based on computational experiments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 18(4): 984-995. |
| 2 | 李军, 郑培庆. 基于IC卡数据的公交通勤熵变模型的构建与应用[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2020, 20(1): 234-240. |
| Li Jun, Zheng Pei-qing. Construction and application of transit commuting entropy change model based on smart card data[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2020, 20(1): 234-240. | |
| 3 | 朱才华, 孙晓黎, 李岩. 站点分类下的城市公共自行车交通需求预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(2): 531-540. |
| Zhu Cai-hua, Sun Xiao-li, Li Yan. Forecast of urban public bicycle traffic demand by station classification[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 531-540. | |
| 4 | 孙超, 宋茂灿, 陈志超, 等. 观测路径出行时间下随机网络交通需求估计[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(3): 206-215. |
| Sun Chao, Song Mao-can, Chen Zhi-chao, et al. Traffic demand estimation with observed path travel time in stochastic network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(3): 206-215. | |
| 5 | Wen T, Gardner L, Dixit V, et al. Two methods to calibrate the total travel demand and variability for a regional traffic network[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2018, 33(4): 282-299. |
| 6 | Sun C, Chang Y, Shi Y, et al. Subnetwork origin-destination matrix estimation under travel demand constraints[J]. Networks and Spatial Economics, 2019, 19(4): 1123-1142. |
| 7 | Sun W, Schmöcker J D, Fukuda K. Estimating the route-level passenger demand profile from bus dwell times[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 130: No.103273. |
| 8 | Caceres N, Wideberg J P, Benitez F G. Deriving origin-destination data from a mobile phone network[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2007, 1(1): 15-26. |
| 9 | Wang Z B, Wang S C, Lian H T. A route-planning method for long-distance commuter express bus service based on OD estimation from mobile phone location data: the case of the Changping Corridor in Beijing[J]. Public Transport, 2021, 13(1): 101-125. |
| 10 | Rokib S A, Karim M A, Qiu T Z, et al. Origin-destination trip estimation from anonymous cell phone and foursquare data[C]∥Transportation Research Board 94th Annual Meeting, Washington DC, USA, 2015: 1-18. |
| 11 | Ge Q, Fukuda D. Updating origin-destination matrices with aggregated data of GPS traces[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 69: 291-312. |
| 12 | Demissie M G, Antunes F, Bento C, et al. Inferring origin-destination flows using mobile phone data: a case study of Senegal[C]∥The 13th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2016: 1-6. |
| 13 | Wang J, Wang D H, Song X M, et al. Dynamic OD expansion method based on mobile phone location[C]∥Fourth International Conference on Intelligent Computation Technology and Automation, Shenzhen, China, 2011: 788-791. |
| 14 | Xu X D, Lo H K, Chen A, et al. Robust network sensor location for complete link flow observability under uncertainty[J]. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2016, 88: 1-20. |
| 15 | Liang Y Y, Wu Z Z, Hu J. Road side unit location optimization for optimum link flow determination[J]. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 2020, 35(1): 61-79. |
| 16 | Sun X, Bai Z X, Lin K, et al. Optimization model of traffic sensor layout considering traffic big data[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020(19): 1-11. |
| 17 | Xie C C, Shao M H. Optimal time interval for investigating prior information in network sensor location problem[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2021, 2675(3): 238-248. |
| [1] | 贾洪飞,徐英俊,杨丽丽,王楠. 商品车多式联运联盟成员选择及利益分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1060-1069. |
| [2] | 肖雪,李克平,彭博,昌满玮. 基于决策-规划迭代框架的智驾车换道行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 746-757. |
| [3] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [4] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [5] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [6] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [7] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [8] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [9] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [10] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [11] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [12] | 盖松雪,曾小清,岳晓园,袁子豪. 基于用户-系统双层优化算法的车位引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [13] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [14] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [15] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
|
||