吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 1144-1152.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220623
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
仿生凹坑型吸盘设计与试验
丛茜1,2( ),徐金1,3,史孝杰1,3,金敬福1,3,陈廷坤1,3(
),徐金1,3,史孝杰1,3,金敬福1,3,陈廷坤1,3( )
)
- 1.吉林大学 生物与农业工程学院,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 汽车仿真与控制国家重点实验室,长春 130022
3.吉林大学 工程仿生教育部重点实验室,长春 130022
Bionic pit design and experiment of the sucker
Qian CONG1,2( ),Jin XU1,3,Xiao-jie SHI1,3,Jing-fu JIN1,3,Ting-kun CHEN1,3(
),Jin XU1,3,Xiao-jie SHI1,3,Jing-fu JIN1,3,Ting-kun CHEN1,3( )
)
- 1.College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.State Key Laboratory of Automotive Simulation and Control,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
3.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
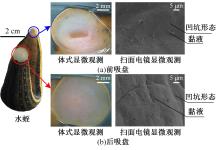
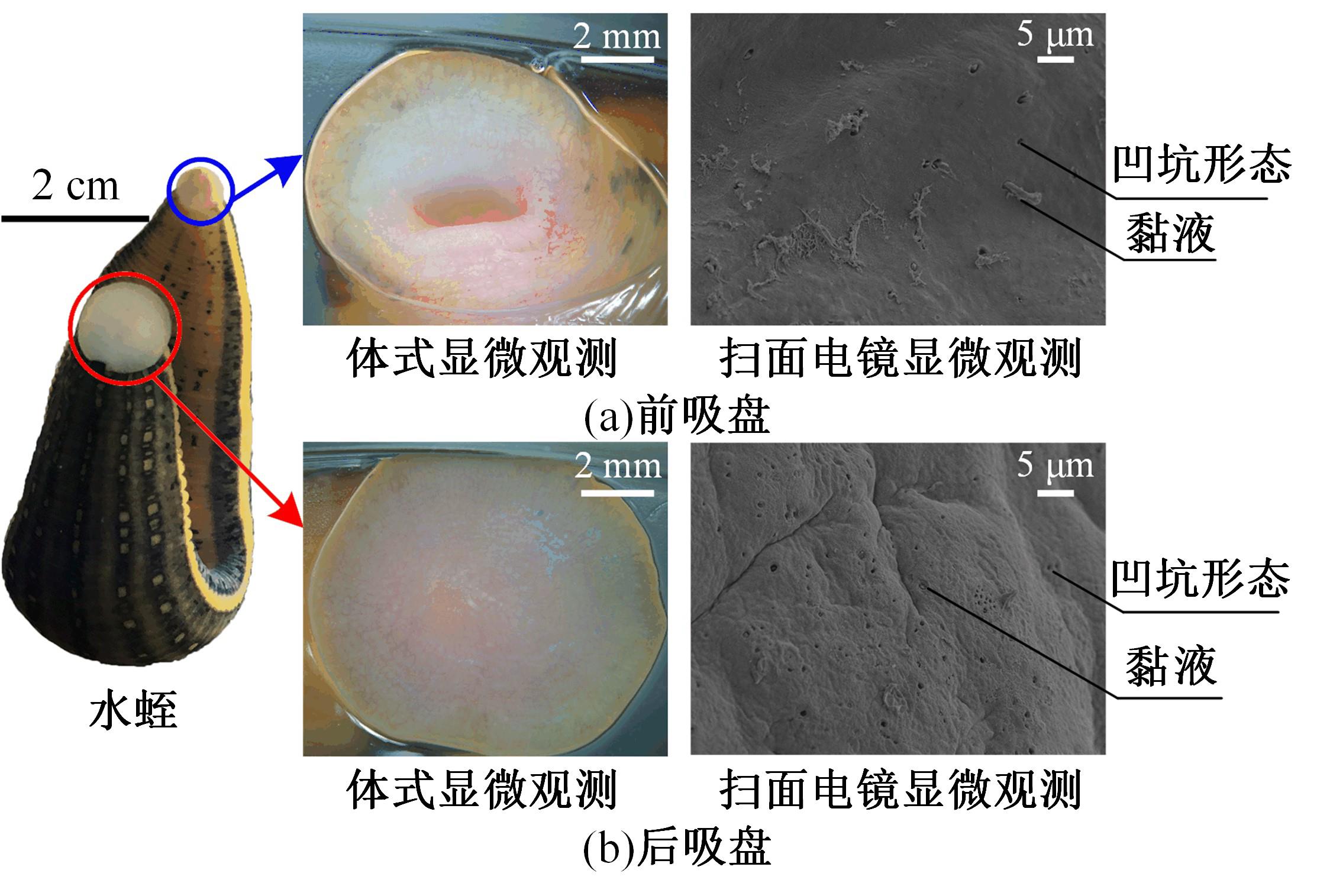
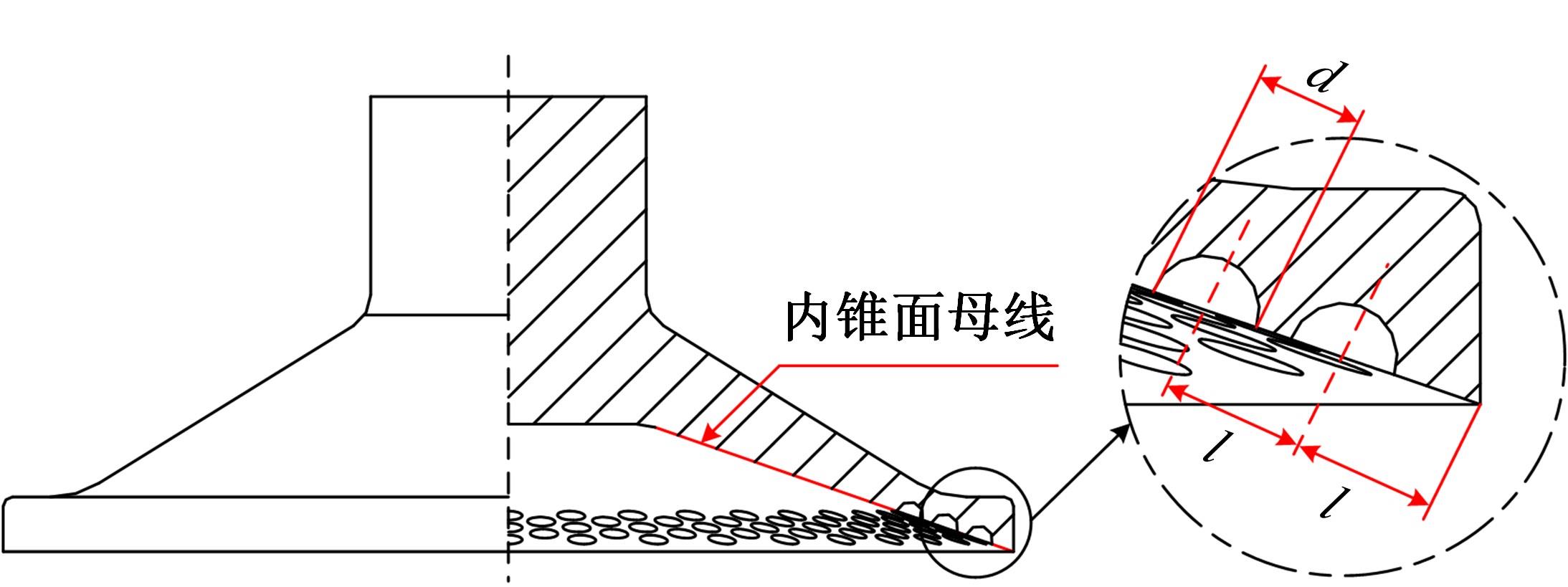
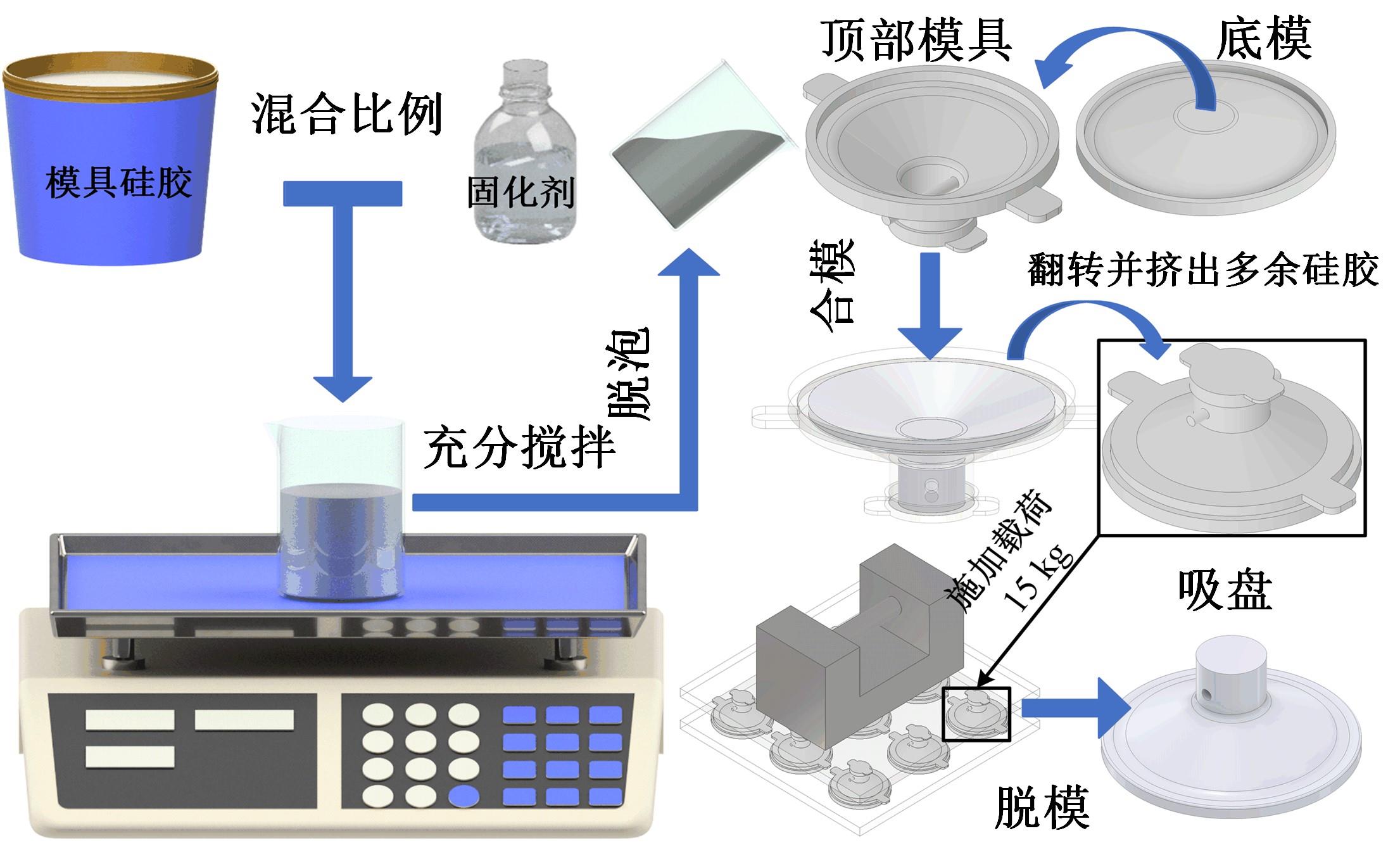
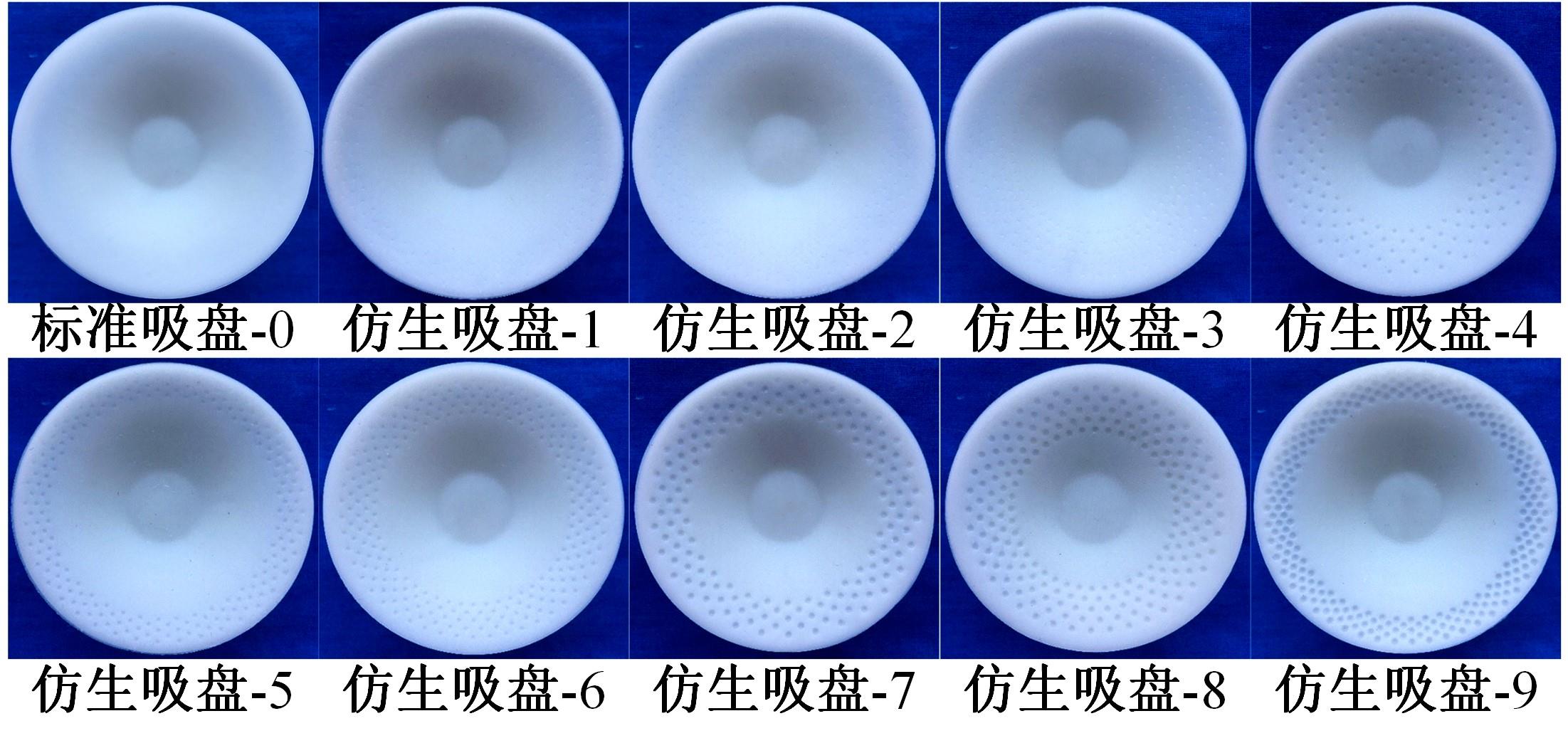
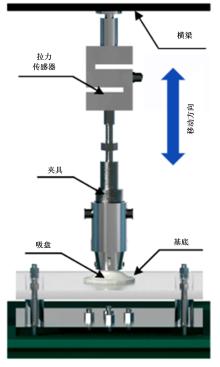
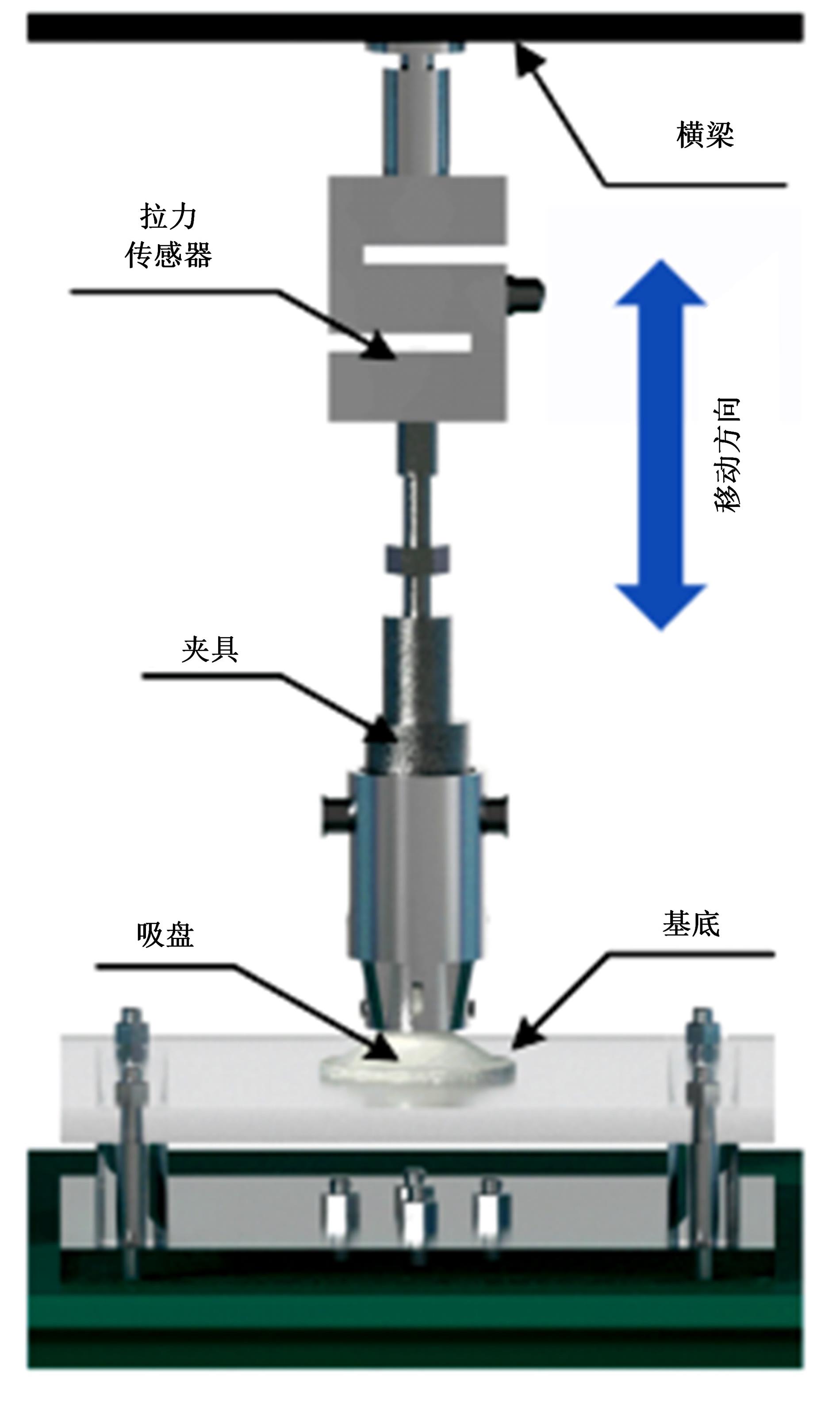
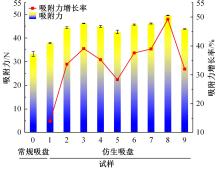
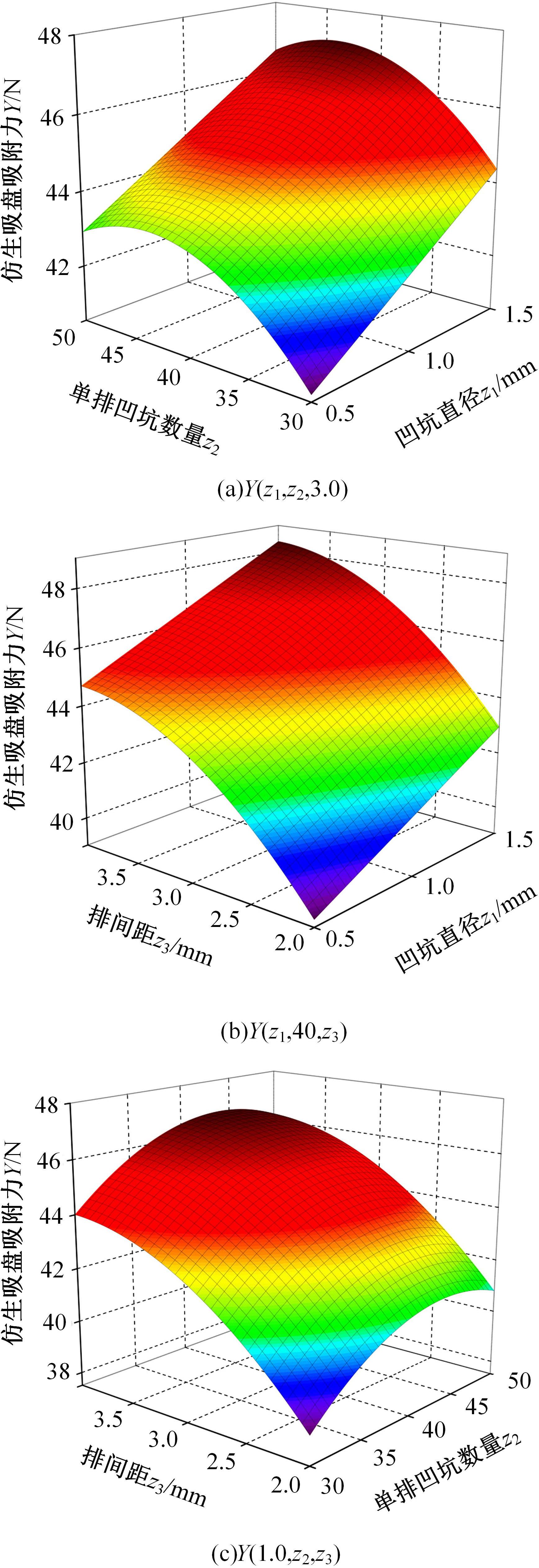
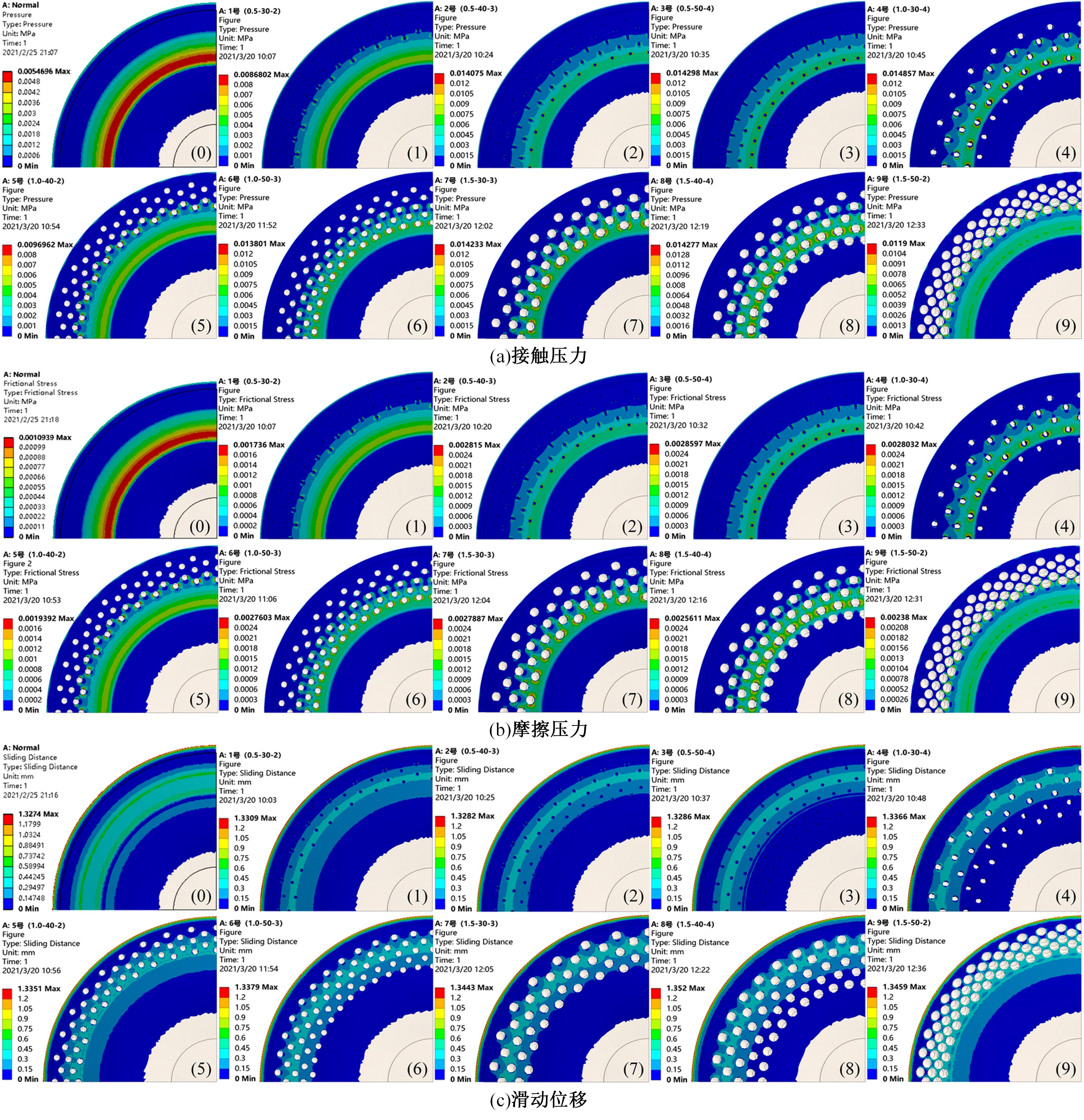
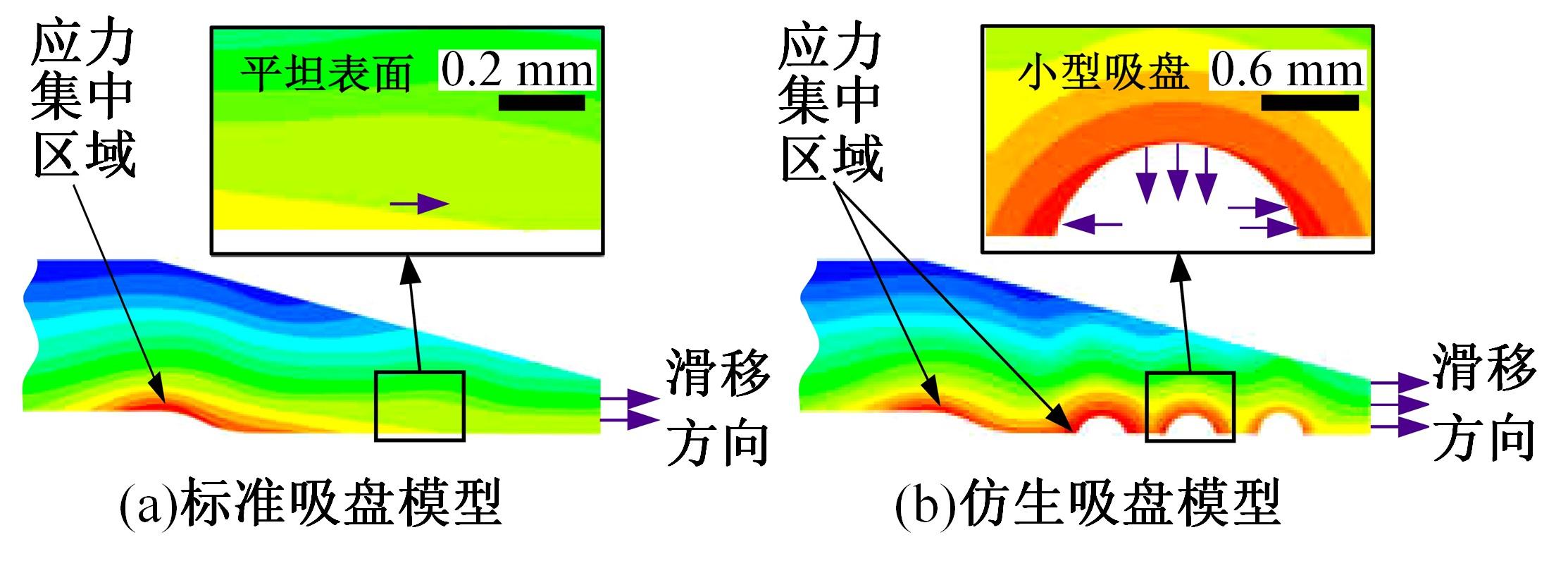
为了提高吸盘的吸附性能,基于水蛭吸盘表面存在的凹坑形态,运用仿生学原理,在常规吸盘表面设计凹坑形态,使吸盘工作表面存在多个小型吸盘,提高吸盘的吸附性能。运用部分正交多项式回归分析,探究凹坑形态的直径、单排凹坑数量及排间距对吸盘吸附力的影响。试验表明,不同凹坑的形态参数对吸盘吸附力具有不同的影响效果,当凹坑直径为1.5 mm、单排凹坑的数量为40个及排间距为4 mm时,仿生吸盘在基底表面的吸附力为49.54 N,相对于标准吸盘在基底表面的吸附力提高49.21%。建立设计因素与评价指标间的数学回归模型,确定对吸盘吸附力影响的显著性主次顺序为排间距、凹坑直径、单排凹坑数量。仿真分析表明,工作表面存在的凹坑形态改变了吸附时吸盘表面接触压力及摩擦应力的分布,并且仿生吸盘工作表面的摩擦应力和接触压力均大于标准吸盘,增大了仿生吸盘在基底表面的吸附力。
中图分类号:
- TB17
| 1 | 苑进, 李扬, 刘雪美, 等. 禽蛋自动捡拾系统结构设计及机械手运动规划[J]. 农业工程学报, 2016, 32(8): 48-55. |
| Yuan Jin, Li Yang, Liu Xue-mei, et al. Structure design of egg auto-picking system and manipulator motion planning[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(8): 48-55. | |
| 2 | 黄超, 刘衍聪, 伊鹏. 蛋胚成活性分拣机器人真空吸盘装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(16): 276-282. |
| Huang Chao, Liu Yan-cong, Yi Peng. Design and test of vacuum suction device for egg embryo activity sorting robot[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(16): 276-282. | |
| 3 | 常旭, 杨东超, 孙可平, 等. 水平井爬行器中电永磁吸盘的设计与优化[J]. 中国机械工程, 2019, 30(4): 399-405. |
| Chang Xu, Yang Dong-chao, Sun Ke-ping, et al. Design and optimization of electropermanent magnet suckers in horizontal well tractors[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 30(4): 399-405. | |
| 4 | Choi M K, Park O K, Choi C, et al. Cephalopod-inspired miniaturized suction cups for smart medical skin[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2016, 5(1): 80-87. |
| 5 | 毕玉超, 高勇, 丛鑫, 等. ABB拆垛机器人辅助吸盘装置的设计[J]. 烟草科技, 2019, 52(5): 105-108. |
| Bi Yu-chao, Gao Yong, Cong Xin, et al. Design of auxiliary sucker device for ABB unstacking robot[J]. Tobacco Science & Technology, 2019, 52(5): 105-108. | |
| 6 | 秦红斌, 张吉鑫, 陈国良. 一种新型真空吸盘装置[J].真空科学与技术学报, 2017, 37(1): 12-16. |
| Qin Hong-bin, Zhang Ji-xin, Chen Guo-liang. Design optimization of vacuum sucker for high precision flexible assembly fixture of autoglass[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2017, 37(1): 12-16. | |
| 7 | 赵军友, 张亚宁, 毕晓东, 等. 喷砂除锈爬壁机器人磁吸附结构优化设计及整机性能试验[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 44(4): 94-99. |
| Zhao Jun-you, Zhang Ya-ning, Bi Xiao-dong, et al. Optimum design of magnetic adsorption structure and machine performance test for sand blasting and rust-removing wall-climbing robot[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2020, 44(4): 94-99. | |
| 8 | 刘汉邦, 李新荣, 刘立东. 服装面料自动抓取转移方法的研究进展[J]. 纺织学报, 2021, 42(1): 190-196. |
| Liu Han-bang, Li Xin-rong, Liu Li-dong. Research progress of automatic grabbing and transfer methods for garment fabrics[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2021, 42(1): 190-196. | |
| 9 | Guo T T, Liu X Y, He T F, et al. Synchro-drive-based underwater climbing adsorption robot[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(3): 6250-6257. |
| 10 | 彭宪宇, 马传栋, 纪佳馨,等. 海洋生物水下粘附机理及仿生研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2020, 40(6): 816-830. |
| Peng Xian-yu, Ma Chuan-dong, Ji Jia-xin, et al. Underwater adhesion mechanisms and biomimetic study of marine life[J]. Tribology, 2020, 40(6): 816-830. | |
| 11 | Roderick W R T, Cutkosky M R, Lentink D. Bird-inspired dynamic grasping and perching in arboreal environments[J]. Science Robotics, 2021, 6(61): 7562. |
| 12 | 张子啸, 余才林. 真空技术在5G产业链的应用[J].真空科学与技术学报, 2020, 40(12): 1115-1118. |
| Zhang Zi-xiao, Yu Cai-lin. The applications of vacuum technology in the 5G technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2020, 40(12): 1115-1118. | |
| 13 | 熙鹏. 鲍鱼腹足吸附性研究及仿生吸盘设计与试验[D]. 长春: 吉林大学生物与农业工程学院, 2020. |
| Xi Peng. Study on the adsorption of abalone abdominal foot and the design and experiment of bionic sucker [D]. Changchun: College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering,Jilin University, 2020. | |
| 14 | Wang Y P, Yang X B, Chen Y F, et al. A biorobotic adhesive disc for underwater hitchhiking inspired by the remora suckerfish[J]. Science Robotics, 2017, 2(10):No.eaan8072. |
| 15 | Ditsche P, Summers A. Learning from Northern clingfish (Gobiesox maeandricus): bioinspired suction cups attach to rough surfaces[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 2019, 374(1784): No.20190204. |
| 16 | Greco G, Bosia F, Tramacere F, et al. The role of hairs in the adhesion of octopus suckers: a hierarchical peeling approach[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2020, 15(3): No.035006. |
| 17 | Li J, Zhang Y, Liu S, et al. Insights into adhesion of abalone: a mechanical approach [J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2018, 77: 331-336. |
| 18 | Kampowski T, Eberhard L, Gallenmuller F,et al. Functional morphology of suction discs and attachment performance of the Mediterranean medicinal leech(Hirudoverbana Carena)[J]. Journal of The Royal Society: Interface, 2016, 13(117): No.20160096. |
| 19 | 陈玉鹏. 仿生湿态粘附微纳界面的构筑与研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019. |
| Chen Yu-peng. Construction and research of bio-inspired wet adhesive surfaces with micro/nanostructures[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019. | |
| 20 | Qiao S T, Wang L, Jeong H Y, et al. Suction effects in cratered surfaces[J]. Journal of the Royal Society: Interface, 2017, 14: 20170377. |
| 21 | Wang L, Kyoung-Ho H, Qiao S T, et al. Suction effects of crater arrays[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2019, 30: No.100496. |
| 22 | Wang L, Qiao S T, Lu N S. Effects of surface tension on the suction forces generated by miniature craters[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2017, 15: 130-138. |
| 23 | Hou J P, Wright E, Bonser R H C, et al. Development of biomimetic squid-inspired suckers[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2012, 9: 484-493. |
| 24 | Baik S, Kim J, Lee H J, et al. Highly adaptable and biocompatible octopus-like adhesive patches with meniscus-controlled unfoldable 3D microtips for underwater surface and hairy skin[J]. Advanced Science, 2018, 5: No.1800100. |
| 25 | 任露泉. 试验设计及其优化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,2009: 39-59. |
| 26 | 陈龙, 云忠, 蒋毅. 基于鱼吸附原理的仿生吸盘设计与性能分析[J]. 北京化工大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 45(6): 100-105. |
| Chen Long, Yun Zhong, Jiang Yi. Design and adsorption performance analysis of a bio-inspired suction cup based on the adsorption principle employed by remoras(sukerfish)[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology(Natural Science), 2018, 45(6): 100-105. | |
| 27 | Sandoval J A, Jadhav S, Quan H C, et al. Reversible adhesion to rough surfaces both in and out of water, inspired by the clingfish suction disc[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2019, 14(6): No.66016. |
| 28 | Zhang Y, Liu Y B, Sui X, et al. A mechatronics-embedded pneumatic soft modular robot powered via single air tube[J]. Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(11): No. 2260. |
| 29 | 张宇. 软体模块化机器人变形分析与协调运动控制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学机电工程学院, 2020. |
| Zhang Yu. Research on deformation analysis and coordinated locomotion control for soft modular robots [D]. Harbin: School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. |
| [1] | 杨欣,王阳,宋家锋,朱勇,黄彬兵,许述财. 基于虾螯结构的仿生夹层板设计及数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 842-851. |
| [2] | 张永忠,马云海. 具有高效吸能特性的新型仿蜂窝多级薄壁结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 259-267. |
| [3] | 朱光强,李天宇,周福君,王文明. 鲜食玉米仿生摘穗装置设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1231-1244. |
| [4] | 刘镇宁,江柯,赵韬韬,樊文选,卢国龙. 大功率质子交换膜燃料电池测试系统的开发及试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2025-2033. |
| [5] | 黄晗,闫庆昊,向枳昕,杨鑫涛,陈金宝,许述财. 基于虾螯的仿生多胞薄壁管耐撞性分析及优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 716-724. |
| [6] | 邹猛,郭子琦,陈朕,曹洪涛,朱建中,徐丽涵. 模拟月尘与典型金属材料摩擦磨损特性试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2307-2315. |
| [7] | 朱光强,李天宇,周福君. 鲜食玉米仿生摘穗柔性夹持输送装置设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2486-2500. |
| [8] | 左建林,刘恩渤,贾政斌,徐圣昊,肖建林. 基于内侧半月板结构设计的仿生假体有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2319-2324. |
| [9] | 陈奕颖,金敬福,丛茜,陈廷坤,任露泉. 不同冰点介质对冰黏附强度的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1926-1932. |
| [10] | 于征磊,陈立新,徐泽洲,信仁龙,马龙,金敬福,张志辉,江山. 基于增材制造的仿生防护结构力学及回复特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1540-1547. |
| [11] | 于征磊,信仁龙,陈立新,朱奕凝,张志辉,曹青,金敬福,赵杰亮. 仿蜂窝防护结构的承载特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1140-1145. |
| [12] | 王康,姚猛,李立犇,李建桥,邓湘金,邹猛,薛龙. 基于月面表取采样触月压痕的月壤力学状态分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1146-1152. |
| [13] | 钱志辉,吴思杰,王强,周新艳,吴佳南,任雷,任露泉. 仿生张拉机械腿及其抗冲击性能仿真分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 758-764. |
| [14] | 刘春宝,陈山石,盛闯,钱志辉,任露泉,任雷. 蜘蛛生物液压驱动原理及其功能仿生探索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 375-381. |
| [15] | 翁小辉,孙友宏,张书军,谢军,常志勇. 基于仿生鼻腔优化的油气检测方法与实验新技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 382-388. |
|
||