吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2839-2844.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210404
基于博弈论的城市道路变道切入行为模型
- 1.东北林业大学 交通学院,哈尔滨 150040
2.吉林建筑科技学院 计算机科学与工程学院,长春 130114
Cut⁃in behavior model based on game theoretic approach on urban roads
Guo-zhu CHENG1( ),Qiu-yue SUN1,Yue-bo LIU2(
),Qiu-yue SUN1,Yue-bo LIU2( ),Ji-long CHEN1
),Ji-long CHEN1
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,China
2.School of Computer Science and Engineering,Jilin University of Architecture and Technology,Changchun 130114,China
摘要:
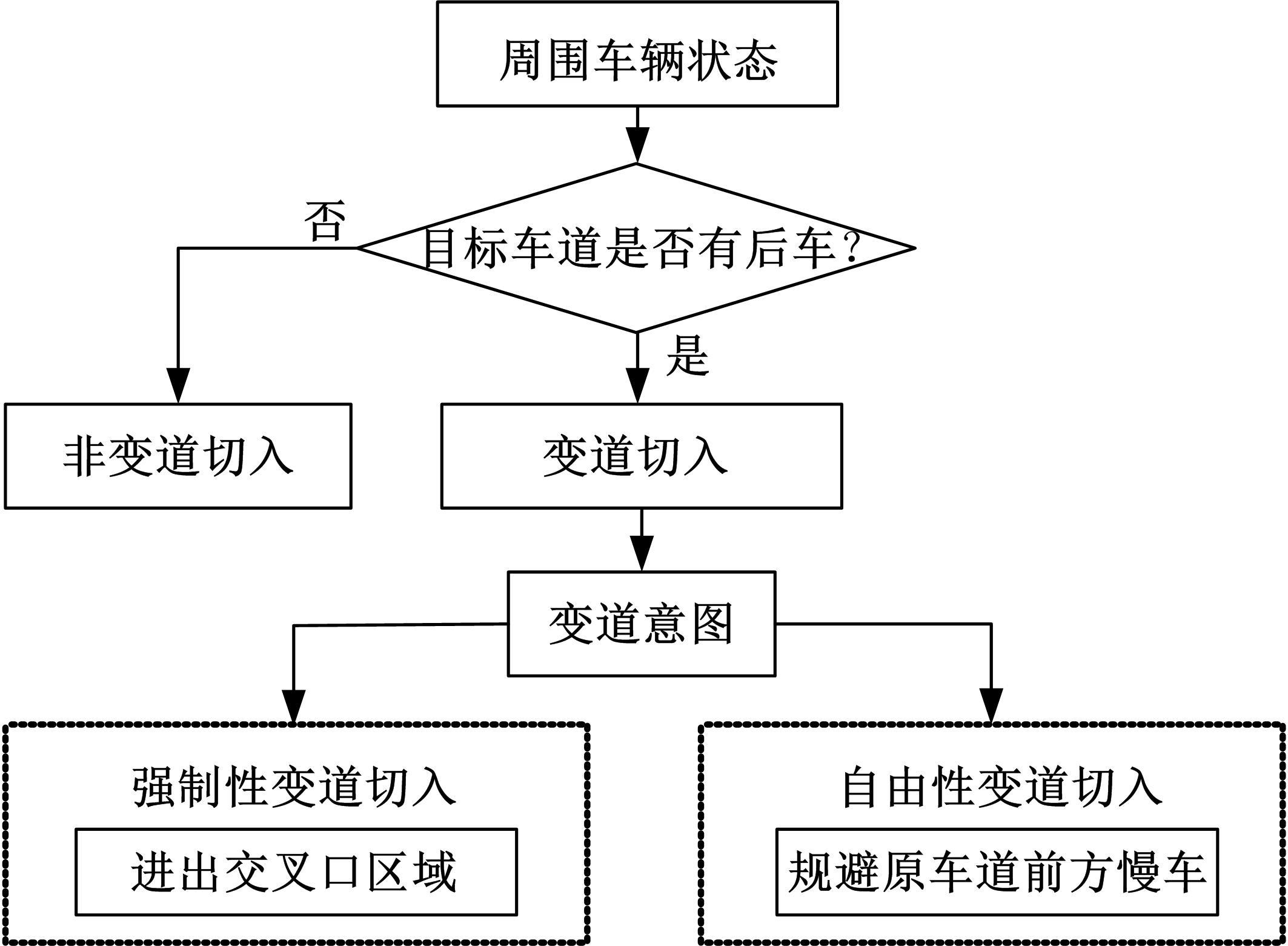
为解决城市道路变道切入行为带来的交通安全和道路拥堵问题,研究了变道切入行为在城市道路中的决策模型。在考虑安全收益、速度收益和变道收益的基础上,量化博弈双方的收益,并结合驾驶人变道意图给出变道切入行为中变道车和目标车道后车的收益函数,构建非合作博弈模型并求纳什均衡解;对模型中的收益参数进行标定,使用NGSIM数据进行模型校对。研究结果表明:模型对于城市道路变道车和邻后车的决策行为具有良好的拟合度,强制性变道切入行为中变道车和邻后车决策行为变量的RMSE分别为0.1385和0.4361,自由性变道切入行为中RMSE分别为0.2278和0.1748;在博弈行为中,安全收益比换道收益对变道车驾驶人的决策影响更大,其中自由性变道切入行为中更加明显;而速度收益始终比安全收益对邻后车驾驶人的决策影响更大,收益权重为0.9和0.1。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 王雪松,杨敏明. 基于自然驾驶数据的变道切入行为分析[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版,2018, 46(8): 1057-1063. |
| Wang Xue-song, Yang Min-ming. Cut-in behavior analyses based on naturalistic driving data[J]. Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science), 2018, 46(8):1057-1063. | |
| 2 | Talebpour A, Mahmassani H S. Influence of connected and autonomous vehicles on traffic flow stability and throughput[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 71: 143-163. |
| 3 | Ali Y, Zheng Z, Haque M M. Connectivity's impact on mandatory lane-changing behaviour: Evidences from a driving simulator study[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 93: 292-309. |
| 4 | Talebpour A, Mahmassani H S, Hamdar S H. Modeling lane-changing behavior in a connected environment: a game theory approach[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 59: 216-232. |
| 5 | Liu H X, Xin W P, Adams Z M, et al. A game theoretical approach for modeling merging and yielding behavior at freeway on-ramp section[C]∥Transportation and Traffic Theory, London, England,2007:196-211. |
| 6 | Wang M, Hoogendoorn S P, Daamen W, et al. Game theoretic approach for predictive lane-changing and car-following control[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2015, 58: 73-92. |
| 7 | Kang K, Rakha H A. Game theoretical approach to model decision making for merging maneuvers at freeway on-ramps[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2017, 2623(1): 19-28. |
| 8 | Ali Y, Zheng Z, Haque M M, et al. A game theory-based approach for modelling mandatory lane-changing behaviour in a connected environment[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 106: 220-242. |
| 9 | Lin D, Li L, Jabari S E. Pay to change lanes: a cooperative lane-changing strategy for connected/automated driving[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 105: 550-564. |
| 10 | Nakata M, Yamauchi A, Tanimoto J, et al. Dilemma game structure hidden in traffic flow at a bottleneck due to a 2 into 1 lane junction[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2010, 389(23): 5353-5361. |
| 11 | Hidas P. Modelling vehicle interactions in microscopic simulation of merging and weaving[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2005, 13(1): 37-62. |
| 12 | Arbis D, Dixit V V. Game theoretic model for lane changing: incorporating conflict risks[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2019, 125: 158-164. |
| 13 | Montanino M, Punzo V. Making NGSIM data usable for studies on traffic flow theory[J]. Transportation Research Record: Journal of the Transportation Research Board, 2013, 2390(1): 99-111. |
| 14 | 蔺湘然. 基于NGSIM数据的车道级车辆换道策略研究[J]. 综合运输,2019, 41(4): 120-126. |
| Lin Xiang-ran. Lane-level vehicle lane change strategy based on NGSIM data[J]. China Transportation Review,2019, 41(4): 120-126. | |
| 15 | 曾小华,宋美洁,宋大凤,等. 基于车联网信息的公交客车行驶工况数据处理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| Zeng Xiao-hua, Song Mei-jie, Song Da-feng, et al. Data processing method of bus driving condition based on internet of vehicles information[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(5): 1692-1699. |
| [1] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [2] | 马敏,胡大伟,舒兰,马壮林. 城市轨道交通网络韧性评估及恢复策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 396-404. |
| [3] | 方松,马健霄,李根,沈玲宏,徐楚博. 城市快速路右侧车道移动作业区行车风险分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1786-1791. |
| [4] | 宋现敏,杨舒天,刘明鑫,李志慧. 站点间公交行程时间波动特性及预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1792-1799. |
| [5] | 张玮,张树培,罗崇恩,张生,王国林. 智能汽车紧急工况避撞轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1515-1523. |
| [6] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [7] | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,陈润超. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| [8] | 徐洪峰,陈虹瑾,张栋,陆千惠,安娜,耿现彩. 面向网联汽车环境的单点全感应式信号配时技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1324-1336. |
| [9] | 盖松雪,曾小清,岳晓园,袁子豪. 基于用户-系统双层优化算法的车位引导模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1344-1352. |
| [10] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [11] | 冯天军,孙学路,黄家盛,田秀娟,宋现敏. 基于三种过街方式的两相位信号交叉口延误[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 550-556. |
| [12] | 李兴华,冯飞宇,成诚,王洧,唐鹏程. 网约拼车服务选择偏好分析及建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 578-584. |
| [13] | 尹超英,邵春福,黄兆国,王晓全,王晟由. 基于梯度提升决策树的多尺度建成环境对小汽车拥有的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 572-577. |
| [14] | 贾洪飞,邵子函,杨丽丽. 终点不确定条件下网约车合乘匹配模型及算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 564-571. |
| [15] | 马洁,黄家骏,田俊,董杨慧. 地铁车站换乘通道内乘客疏散的目标决策行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2600-2606. |
|